Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Scaling the Graft Length and Graft Density of Irradiation-Grafted Copolymers
- First Published: 05 November 2018

Front Cover: In article 1800311, Sandor Balog and co-workers give experimental evidence—obtained via small-angle scattering—demonstrating that the graft length and the graft density of radiation grafted copolymers may be scaled, and consequently, the dimensions and density of the phase-segregated domains may be designed at wish in the future.
Masthead
Full Papers
Scaling the Graft Length and Graft Density of Irradiation-Grafted Copolymers
- First Published: 30 September 2018
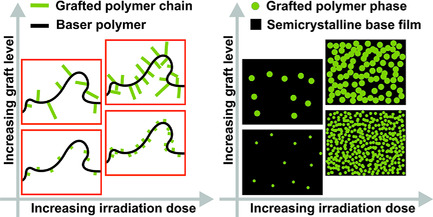
Irradiation-induced graft copolymerization is often used to combine the functionality of immiscible polymers; however, controlling the graft length and the graft density has been considered infeasible. This paper demonstrates that by tuning the irradiation dose and the graft level, the graft density and graft length—and consequently, the dimensions and density of the phase-segregated domains—can be scaled.
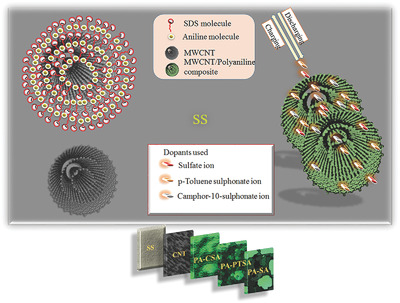
Effect of Different Electrolytes on the Supercapacitor Behavior of Single and Multilayered Electrode Materials Based on Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/Polyaniline Composite
- First Published: 04 October 2018
Exploration of the Direct Arylation Polymerization Method for the Practical Application of Conjugated Materials: Synthetic Scale-Up, Solar Cell Performance, and Cost Analyses
- First Published: 03 October 2018
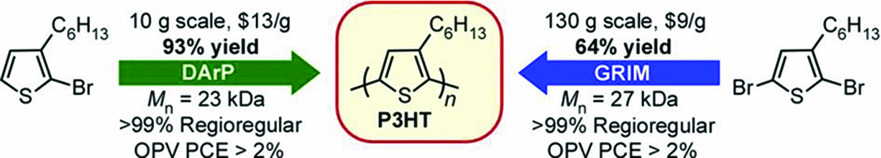
The scalability of direct arylation polymerization (DArP) batch reactions for preparing poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) is investigated. DArP polymers are compared to those resulting from P3HT prepared via Grignard metathesis (GRIM) on a large scale. DArP and GRIM polymers show comparable device performance in organic solar cells and the costs per gram for the polymers resulting from each synthetic method are comparable.
Study of the Foaming Kinetics in Epoxidized Natural Rubber Foams Crosslinked by Electron Beam Irradiation
- First Published: 08 October 2018
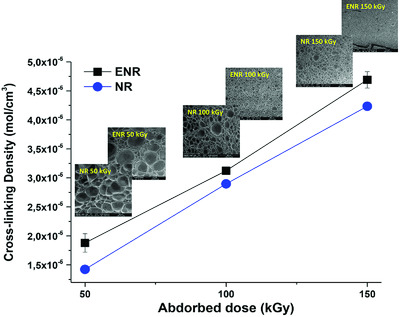
Cellular materials based on natural rubber and epoxidized natural rubber are studied in this work. The influence of the presence of epoxy groups and the level of absorbed dose are analyzed. The foams produced with epoxidized natural rubber present higher crosslinking density, more homogenous cellular structures, and lower cell sizes than the foams produced with natural rubber.
Oriented Polar Crystals in Poly(Vinylidene Fluoride) Produced by Simultaneously Applying Pressure and Flow
- First Published: 04 October 2018
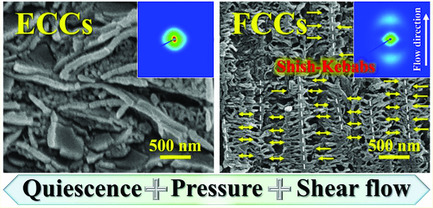
Oriented polar crystals in poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) are of significance in developing flexible piezoelectric devices. Here, using a pressuring and shearing device, oriented polar crystals in the form of shish-kebab superstructure is for the first time fabricated via crystallizing PVDF under flow (30 s–1) and pressure (200 MPa). These results provide new opportunities to fabricate high-performance piezoelectric devices.
Tuning the Thermal Properties of Azopolymers Synthesized by Post-Functionalization of Poly(propargyl Methacrylate) with Azobenzene Azides: Influence on the Generation of Linear and Circular Birefringences
- First Published: 08 October 2018
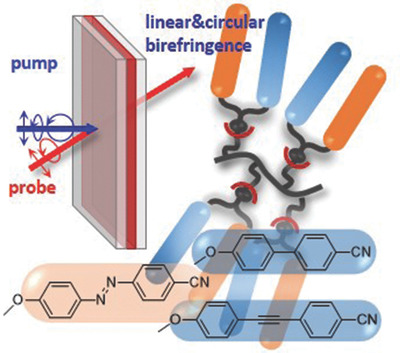
A flexible approach to bifunctional polymers combining promesogenic and photoresponsive moieties in the same repeating units is described using click chemistry tools. By tuning the linking groups of the bifunctional moieties to the polymethacrylic chain, the liquid crystallinity and the photoinduction of simultaneous linear and circular birefringence is controlled.
Tailoring Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Cationically UV-Cured Systems by a Rational Design of Vinyl Ether Ester Oligomers using Enzyme Catalysis
- First Published: 04 October 2018
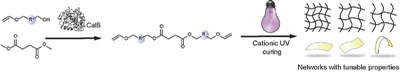
This work presents an efficient and benign enzymatic synthesis of vinyl ether ester oligomers for solvent-free resin applications. The synthesis is complete in less than 1 h and the oligomers are thereafter crosslinked during 2 min with UV-initiated cationic polymerization, which yielded transparent free-standing films that have a wide range of T gs from −10 to 100 °C depending on composition.