Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Theory Simul. 7-8/2009
- First Published: 21 October 2009

Cover: The effect of solvent molecular size on the self-assembly of amphiphilic diblock copolymers in selective solvent is studied by using the real-space self-consistent field theory. The self-assembled morphology changes from circle-like micelle to line-like micelle, then to loop-like micelle by decreasing the solvent molecular size. Further details can be found in the article by W. Li and W. Jiang* on page 434.
Contents
Frontispiece
Special Article Series - Essay
Modeling for Polymer Design
- Pages: 384-386
- First Published: 21 October 2009
The special article series ‘Modeling for Polymer Design’ demonstrates the close relation between synthesis and modeling, i.e., between advanced synthetic polymer chemistry and a physical understanding of the underpinning reaction kinetics. Both areas must be viewed as one unit if synthetic processes are to be optimized with regard to the chosen reaction conditions as well as the addition and design of controlling agents and/or catalysts.
Frontispiece
Special Article Series - Feature Article
Quantum-Chemical Modeling of Free-Radical Polymerization
- Pages: 388-400
- First Published: 21 October 2009
Computational chemistry is rapidly establishing itself as a reliable and useful tool for studying the mechanism and kinetics of radical polymerization. This review outlines the current ‘best-practice’ methodology for obtaining chemically accurate calculations, examines its scope and limitations, and highlights some of its leading applications.
Frontispiece
Special Article Series - Full Paper
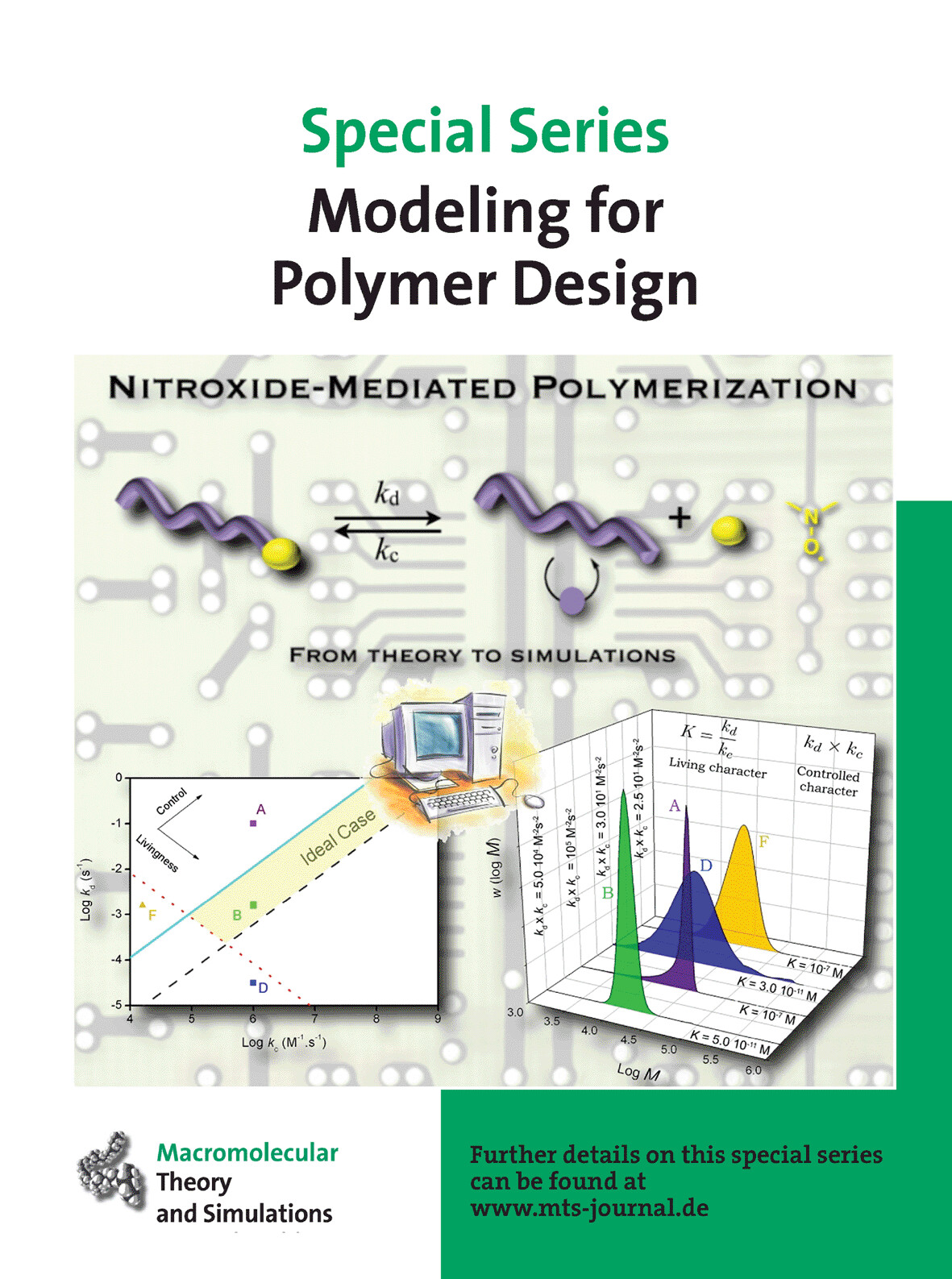
Kinetic Modeling of Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerization: Conditions for Living and Controlled Polymerization
- Pages: 402-419
- First Published: 21 October 2009
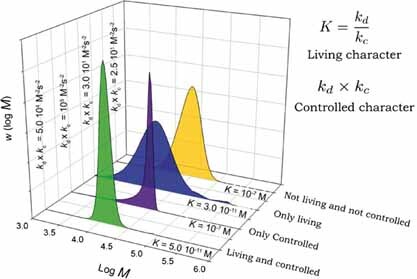
The influence of various rate coefficients on both the kinetics and the controlled character of the reaction as well as the livingness of polymers obtained by nitroxide-mediated polymerization (NMP) are studied using the program package PREDICI. These simulations result in very interesting guidelines, which can help predict, prior to any experiment, the optimum experimental conditions needed for specific properties, such as living fraction values.
Frontispiece
Special Article Series - Full Paper
Optimum Reaction Conditions for the Synthesis of Macromonomers Via the High-Temperature Polymerization of Acrylates
- Pages: 421-433
- First Published: 21 October 2009
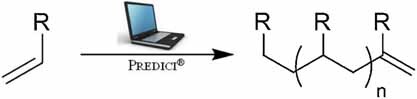
Based on a chain-end differentiated model for high-temperature acrylate polymerization including transfer to polymer reactions, midchain radical propagation, and reversible β-scission of chains, the efficiency of macromonomer formation is evaluated. The model shows good agreement with experimental data and recommendations for choosing optimum conditions for macromonomer synthesis are provided.
Full Papers
Effect of Solvent Molecular Size on the Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymer in Selective Solvent
- Pages: 434-440
- First Published: 21 October 2009
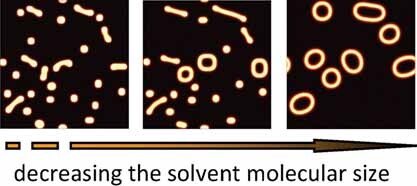
The effect of solvent molecular size on the self-assembly of amphiphilic diblock copolymer in selective solvent is studied by using the real-space self-consistent field theory. The self-assembled morphology changes from circle-like micelle to line-like micelle, then to loop-like micelle by decreasing the solvent molecular size in a wide range of solvent selectivity.
A Molecular Dynamics Study of Two Apposing Polyelectrolyte Brushes with Mono- and Multivalent Counterions
- Pages: 441-452
- First Published: 21 October 2009
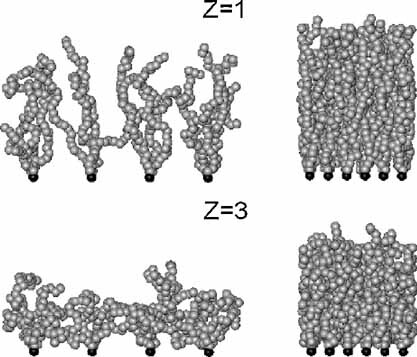
The conformation of polyelectrolyte brushes is remarkably dependent on the counterion valence and the grafting density. A collapsed configuration of polyelectrolyte chains can be observed when trivalent counterions are added to the brush systems and the increase of the grafting density can cause an extended configuration.
On the Phase Nature of Polymer Brush Collapse upon Solvent Deterioration
- Pages: 453-459
- First Published: 21 October 2009