Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Research Article
Adjunct cultures of autochthonous Lactobacillus strains to diversify and improve cheese maturation
- First Published: 11 June 2024
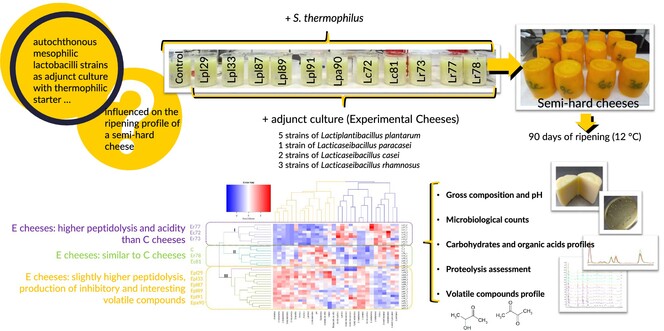
Eleven autochthonous Lactobacillus strains were employed to produce experimental semihard cheeses. One group was characterised by its consumption of citric acid and the production of diverse desirable volatile compounds, another group by its acidification and peptidolytic activity, while two strains exhibited no discernible impact on the cheese maturation process.
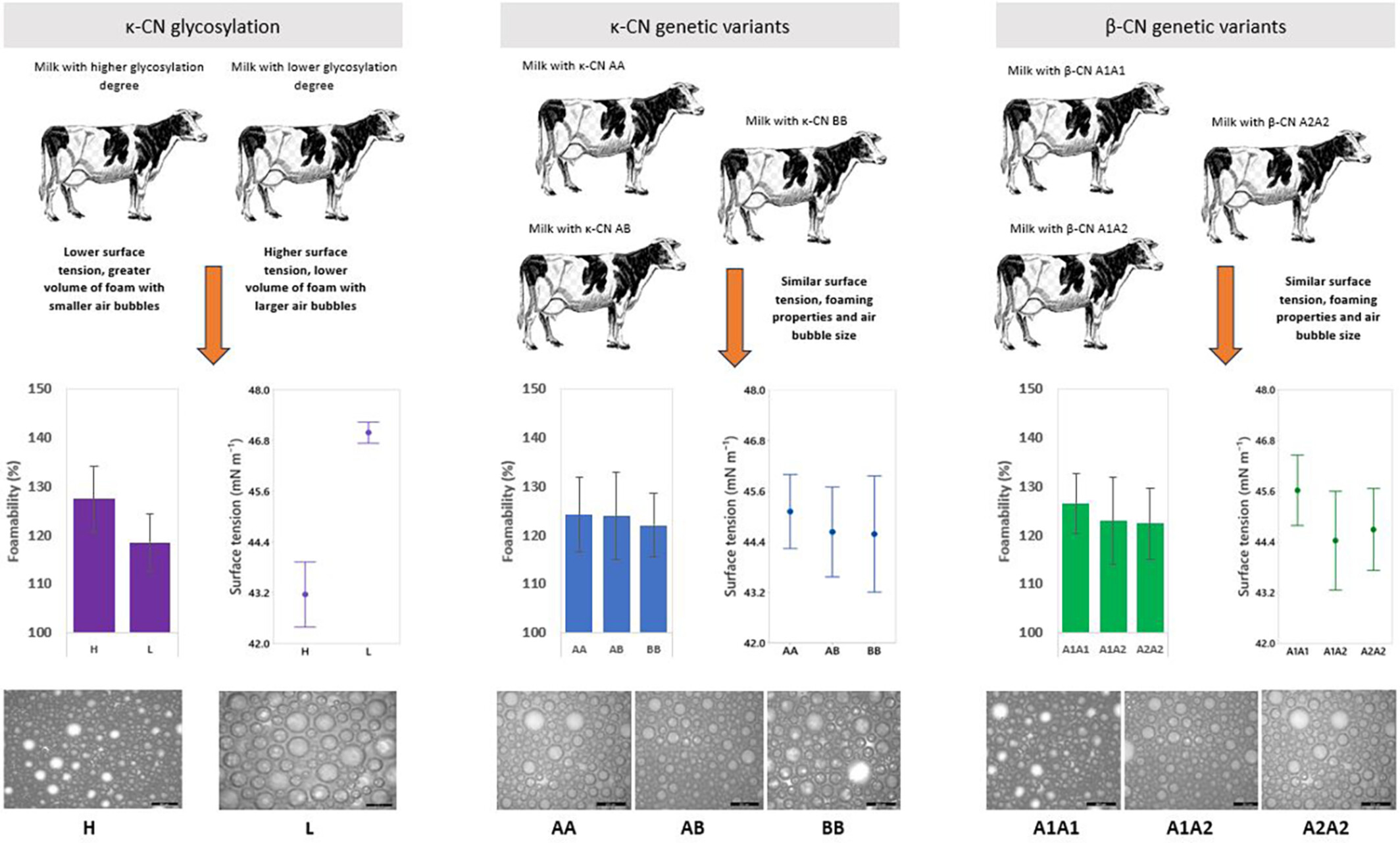
Effect of casein genetic variants and glycosylation on bovine milk foaming properties
- First Published: 11 June 2024
Antihypertensive effects of the Limosilactobacillus reuteri Z09 and Lactobacillus helveticus Z11 fermented milk in spontaneously hypertensive rats
- First Published: 18 June 2024
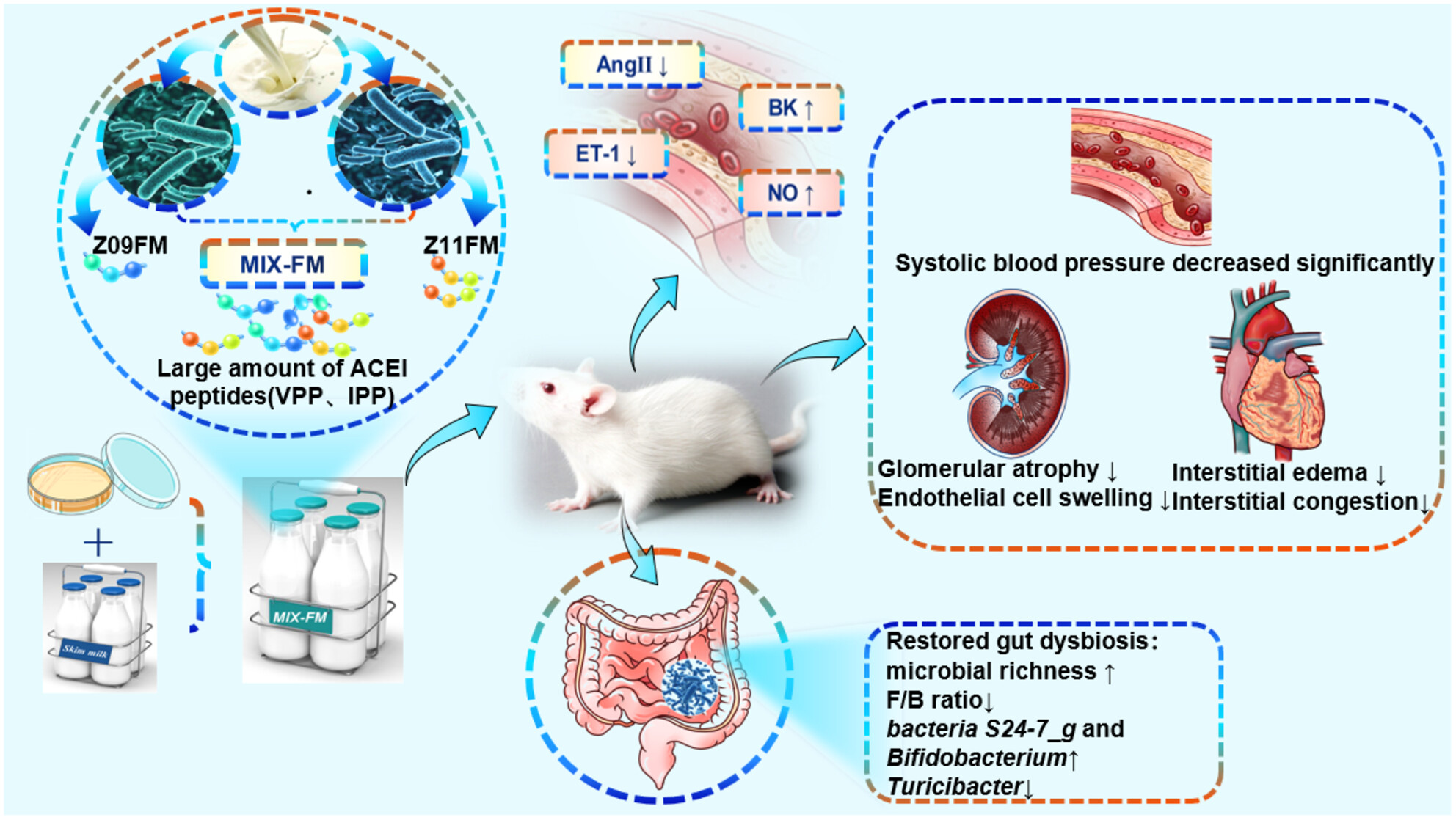
The Limosilactobacillus reuteri ZJUIDS09 and Lactobacillus helveticus ZJUIDS11 mixed (1:1) fermented milk has the strongest hypotensive effect than single-strain fermented milk in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mixed fermented milks can better regulate serum biochemical indicators and alleviate intestinal flora dysbiosis than single-strain fermented milks.
Monoglyceride-based oleogel and oleofoam as the fat substitute in fat-reduced ice creams: The relation between partial coalescence degree and quality characteristics
- First Published: 07 July 2024
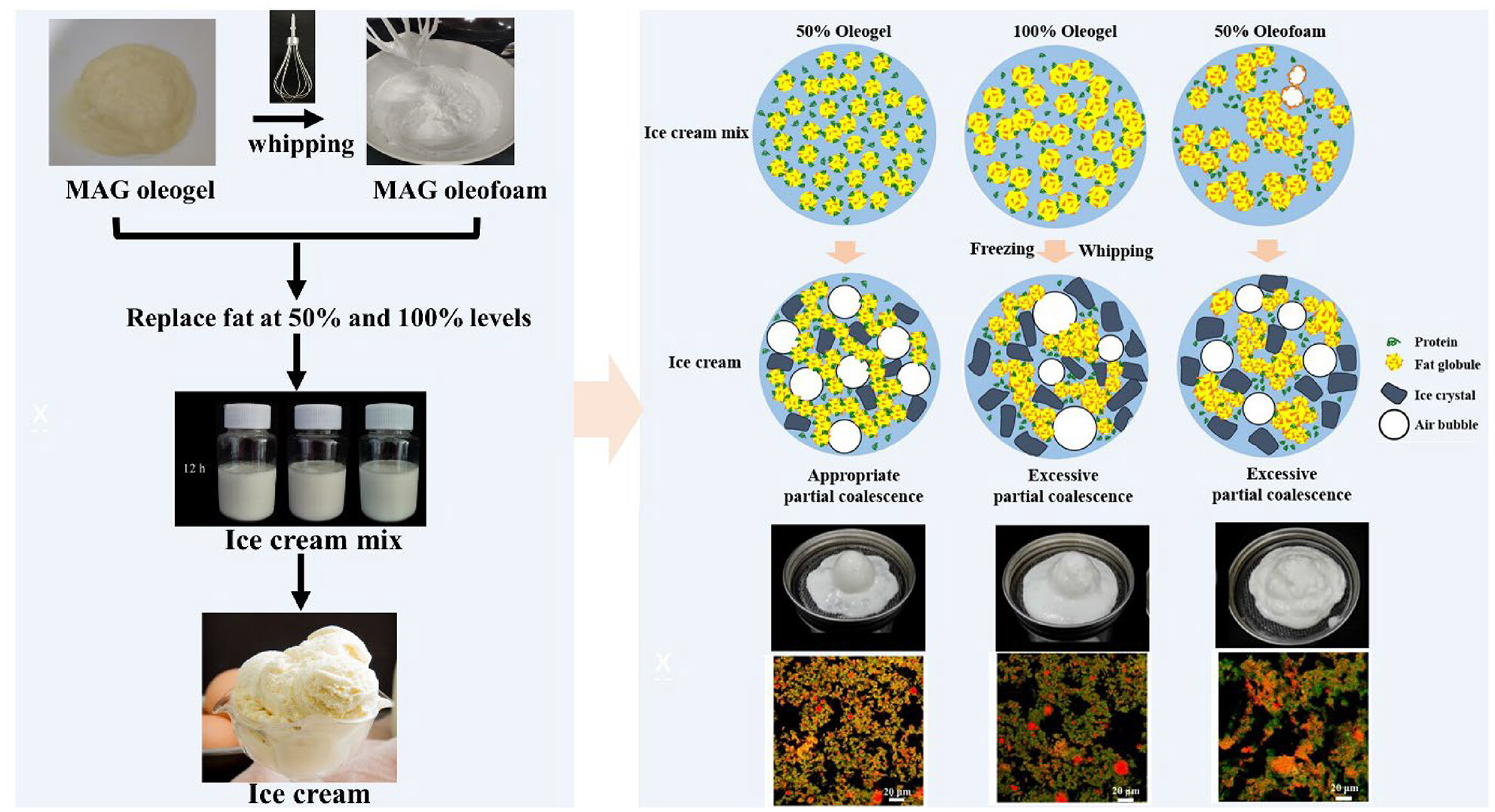
Novel oleocolloids, monoglyceride (MAG)-based oleogel and oleofoam, were used to produce fat-reduced ice creams as fat replacers. The performance of fat-reduced ice cream was closely related to the fat destabilisation degree, and ice cream with 50% oleogel substitution possessed ideal quality characteristics.
Review
The unregulated plant-based ‘milk’ industry: A threat to nutrition, health and safety?
- First Published: 09 July 2024
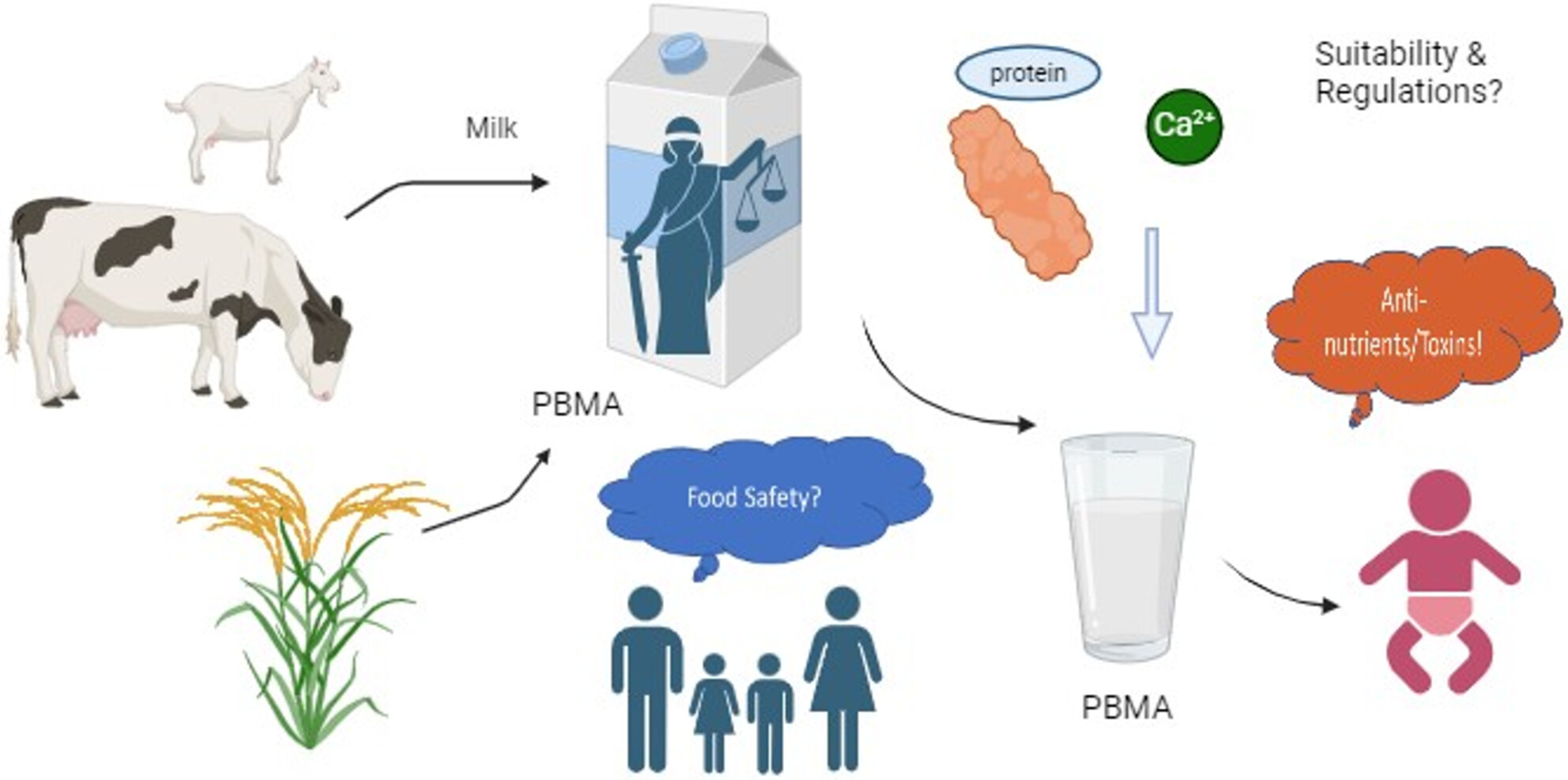
The review paper discusses the suitability of plant-based milk alternatives to feed young children/infants, need of regulatory requirements and nutritional variability from milk along with the emphasis on developing distinct regulations and standards to assure safety, health and wellness of consumers.
Research Article
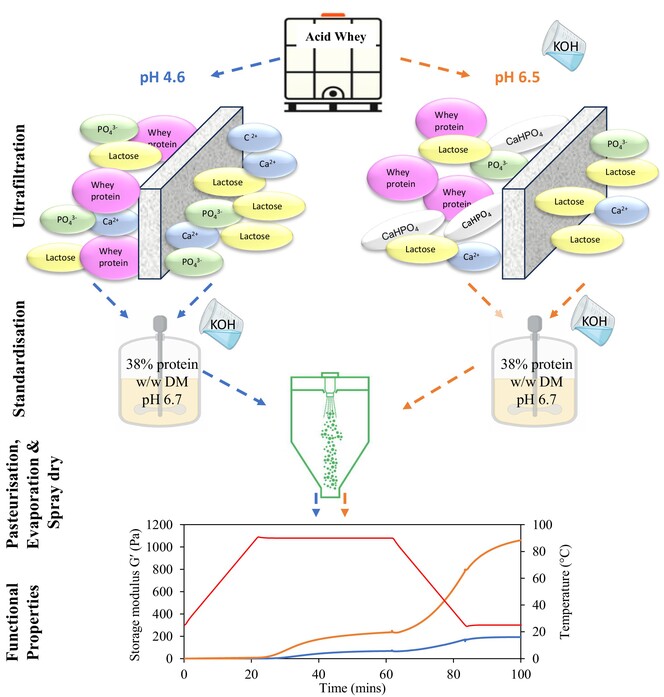
Effect of ultrafiltration of acid whey at pH 4.6 or 6.5 on whey concentrate composition and resultant powder properties
- First Published: 11 August 2024
Review
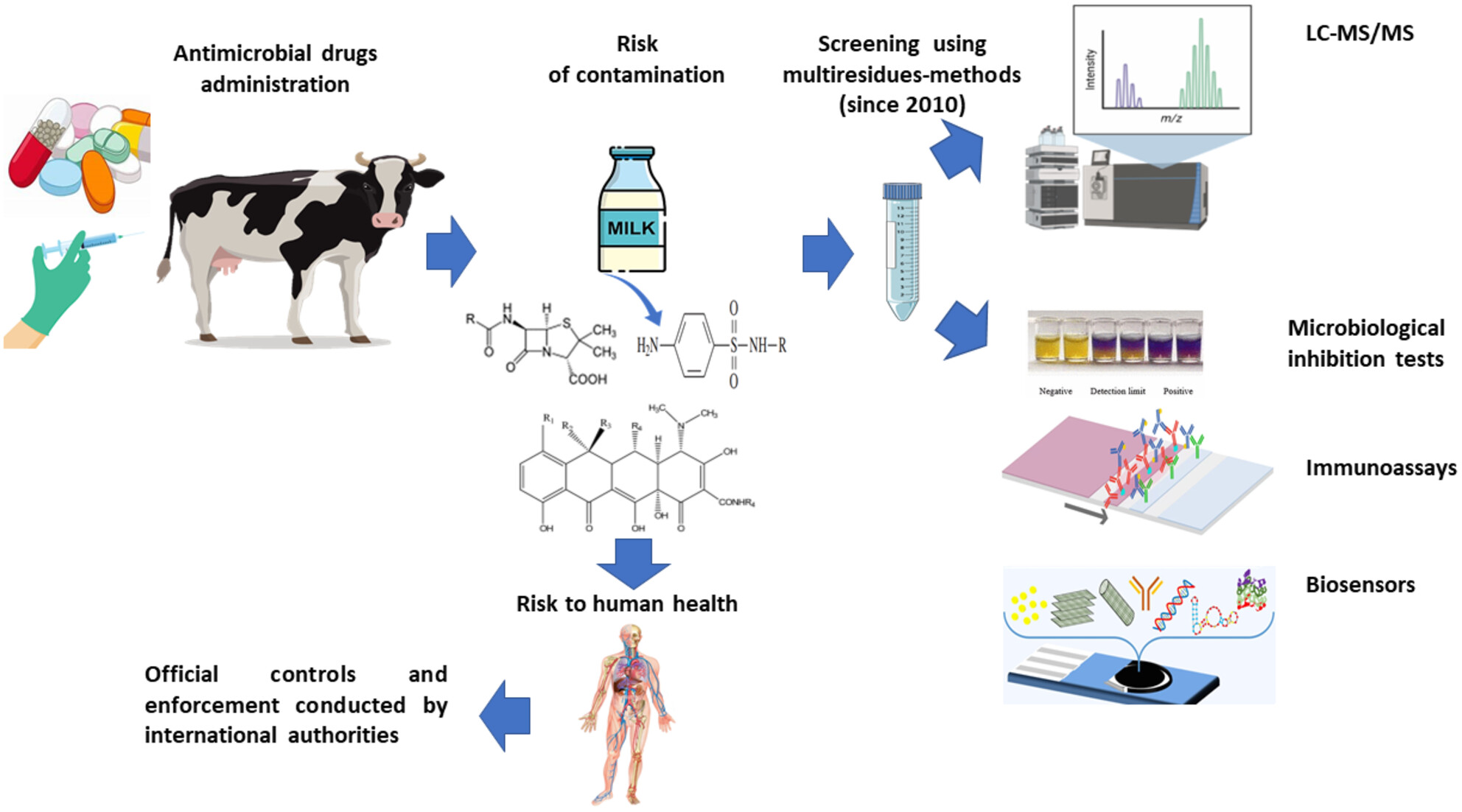
Screening methods for antibiotic residue detection in milk: Recent advances, challenges, and regulations
- First Published: 24 September 2024
Research Article
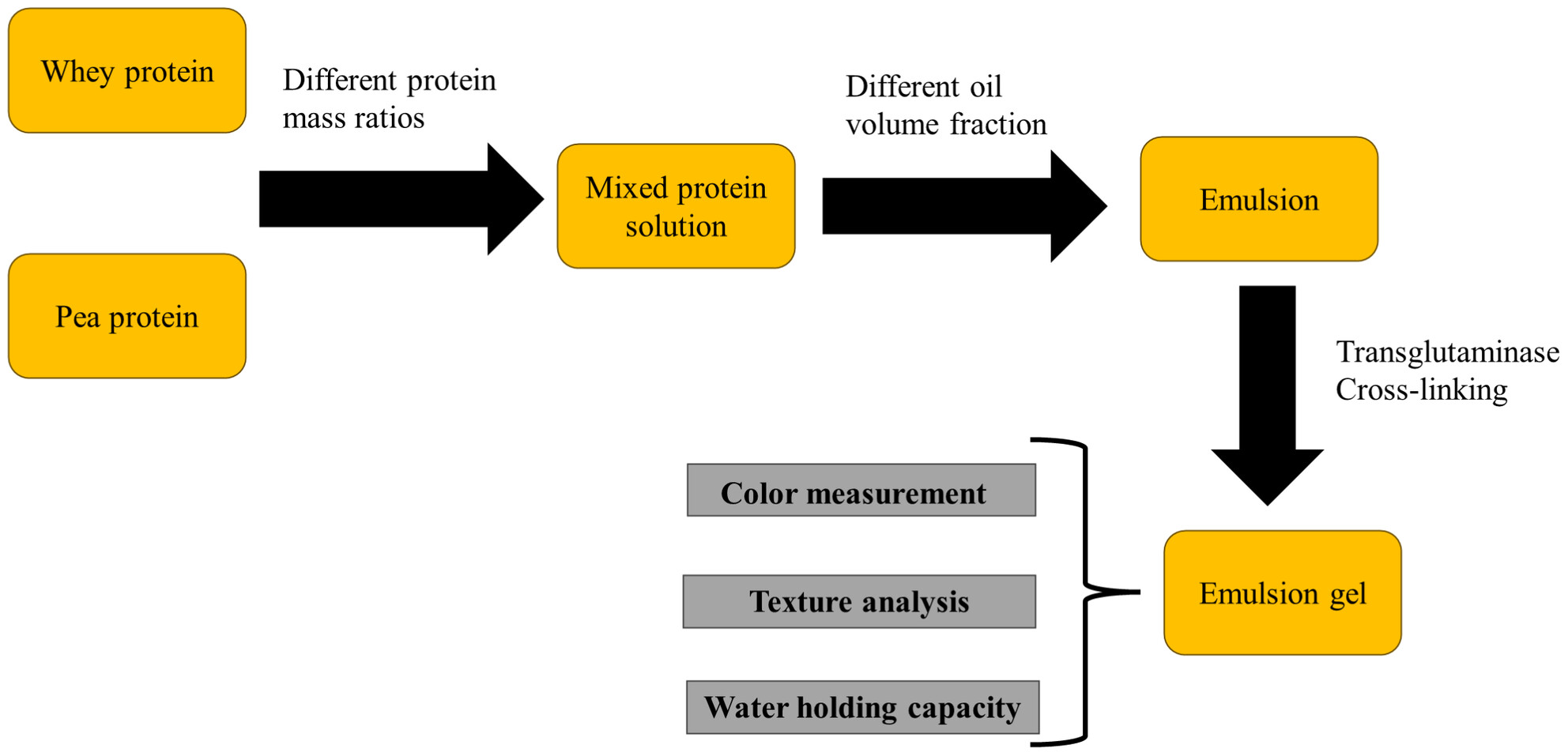
Fabrication and characterisation of whey–pea protein-based emulsion gels induced by transglutaminase cross-linking
- First Published: 25 September 2024
Control of Pseudomonas fluorescens in milk by a novel bacteriophage YZU_PF006
- First Published: 02 October 2024
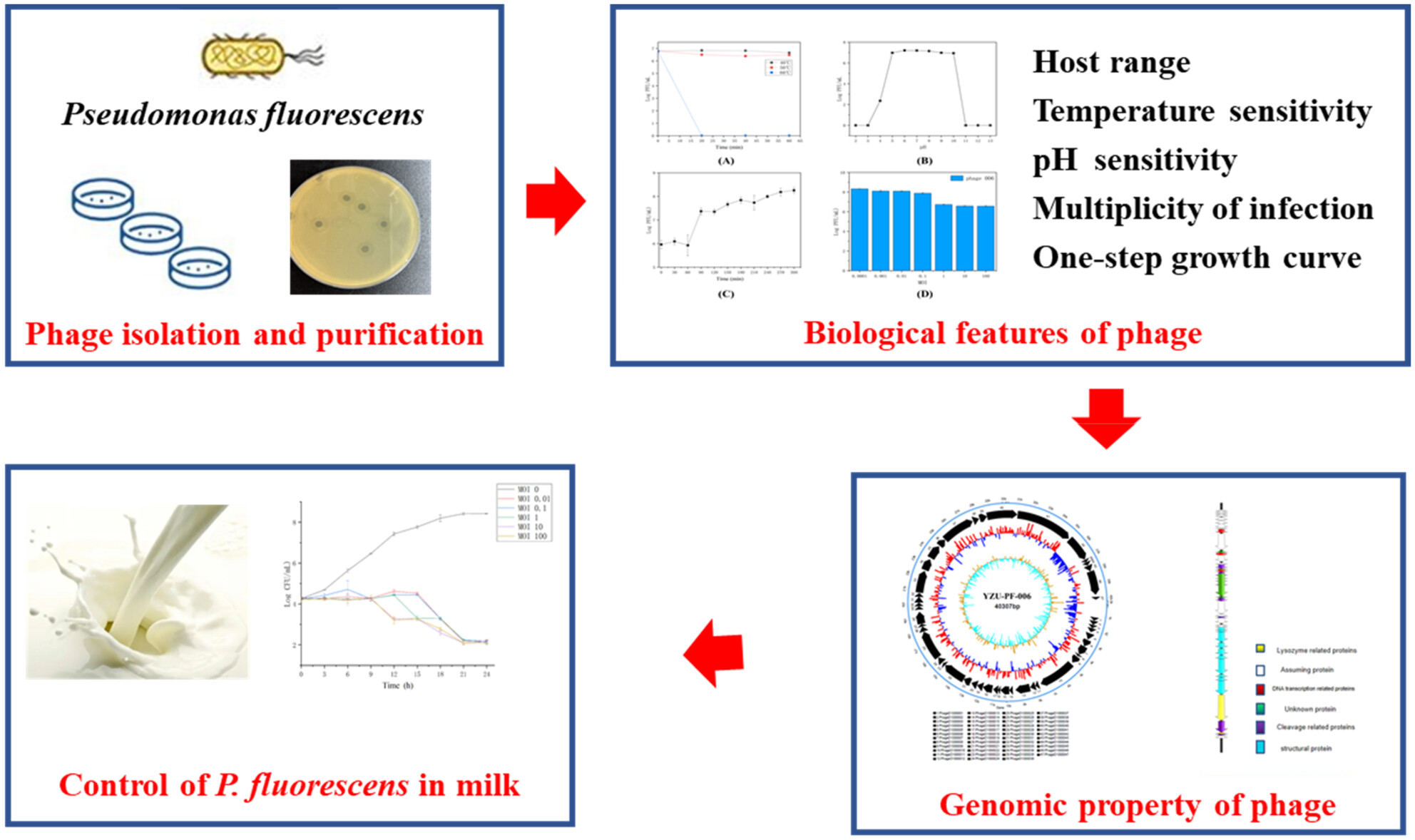
In this work, a cold-active and highly lytic phage YZU-PF-006 against Pseudomonas fluorescens was isolated from sewage sampled in Yangzhou, and its morphological feature was obtained by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The main biological features, including host range, optimal multiplicity of infection (MOI), pH and thermal stability, and one-step growth curve, were determined. Genomic property of phage YZU-PF-006 was identified by genome sequencing. Moreover, phage YZU-PF-006 was also utilised to control P. fluorescens contamination in milk.
Examination of the impact of using lactose or permeate for protein standardisation of skimmed milk on viscosity characteristics during evaporation
- First Published: 02 October 2024
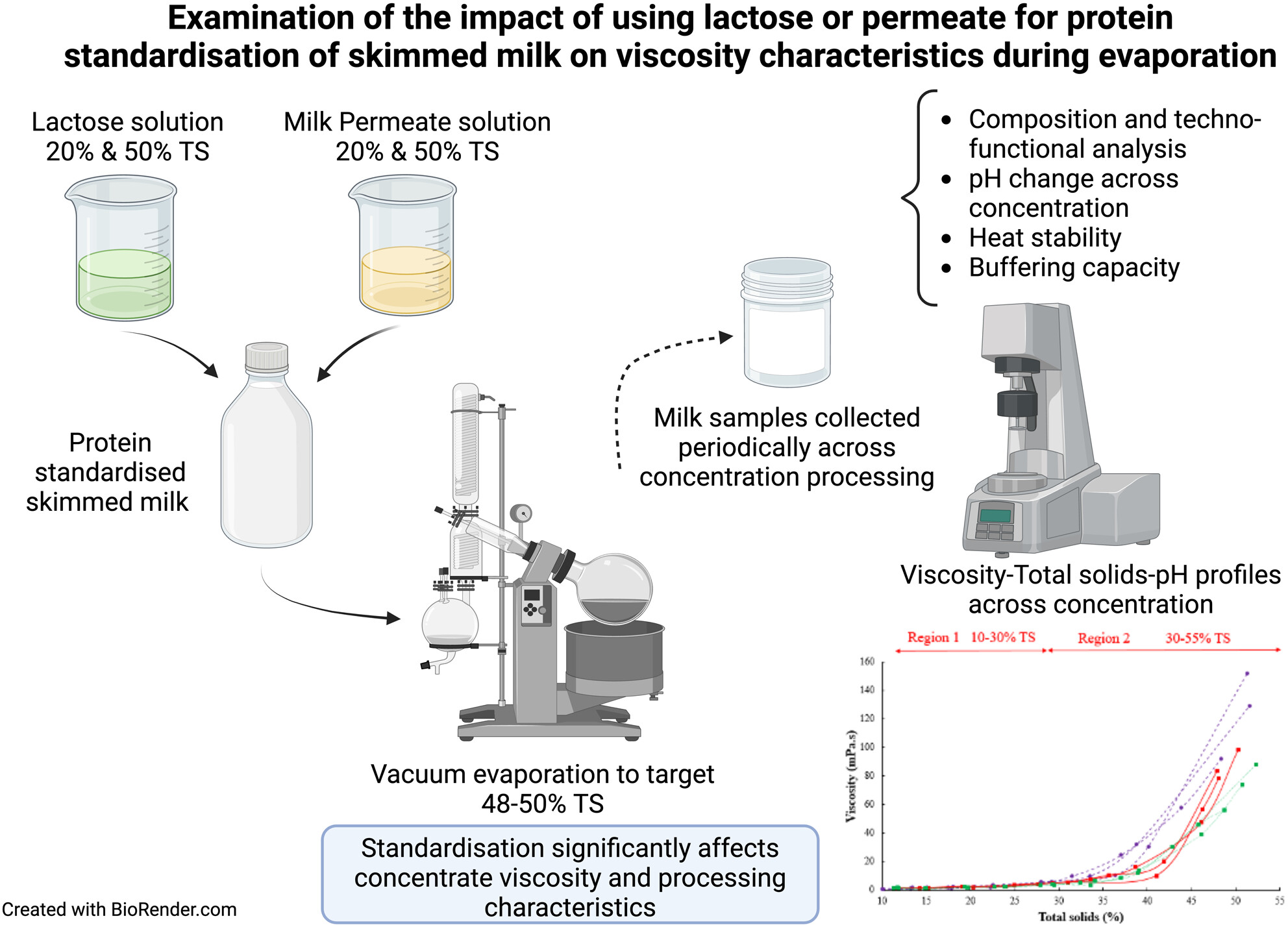
Protein content and standardisation greatly affect the rate of viscosity development and final viscosity at similar total solids, during the concentration of skim milk. Use of standardisation will have an impact on what level of solids is achievable to avoid the risk of processing issues arising from high viscosity (e.g. poor heat transfer, fouling and blockages). Figure created with BioRender.com.
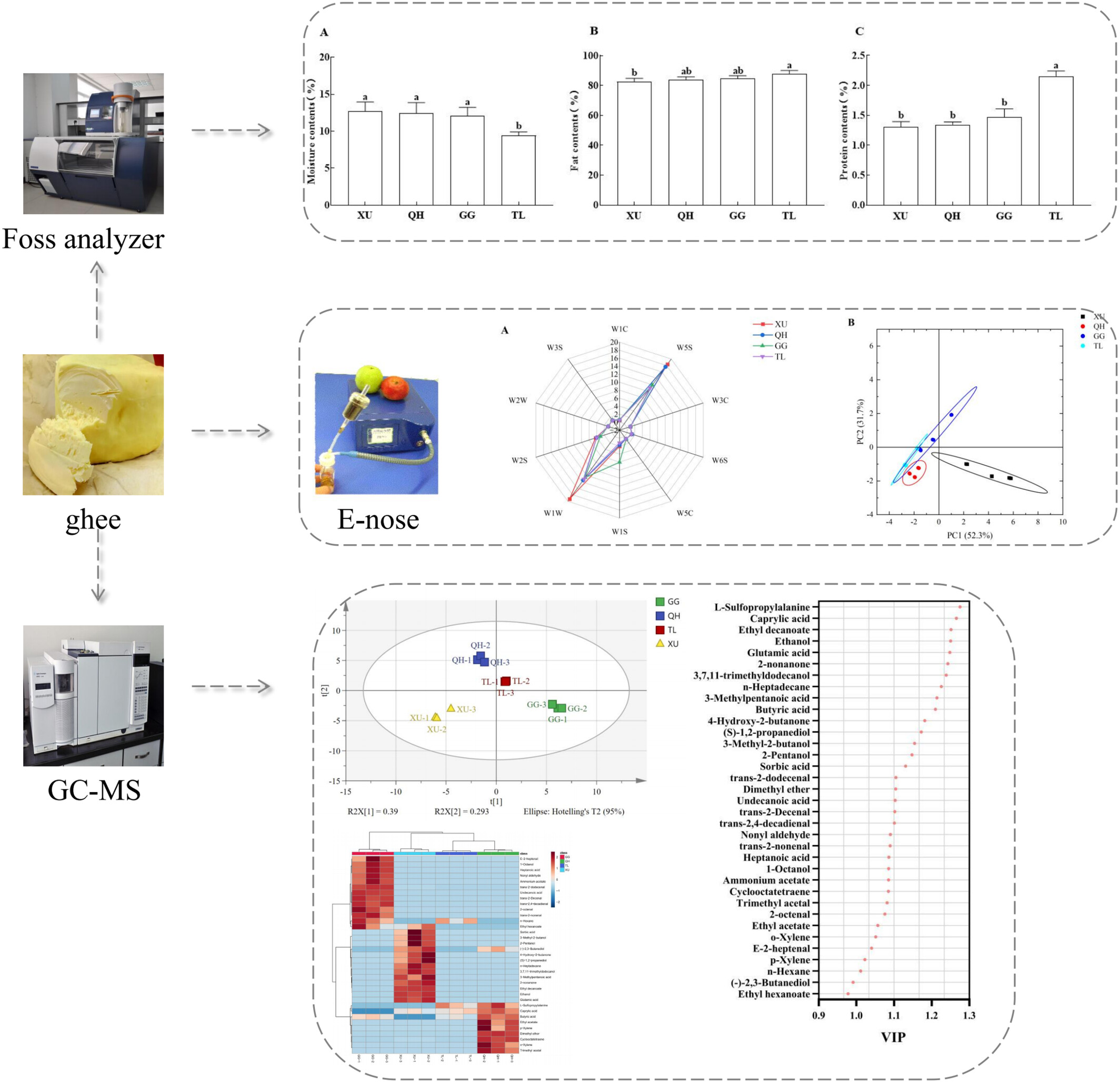
Comparison of flavour of ghee from different pastoral areas based on electronic nose and GC–MS
- First Published: 02 October 2024
Review
Genetic variation in bovine milk proteins: Implications for functional and nutritional properties
- First Published: 19 October 2024
Research Article
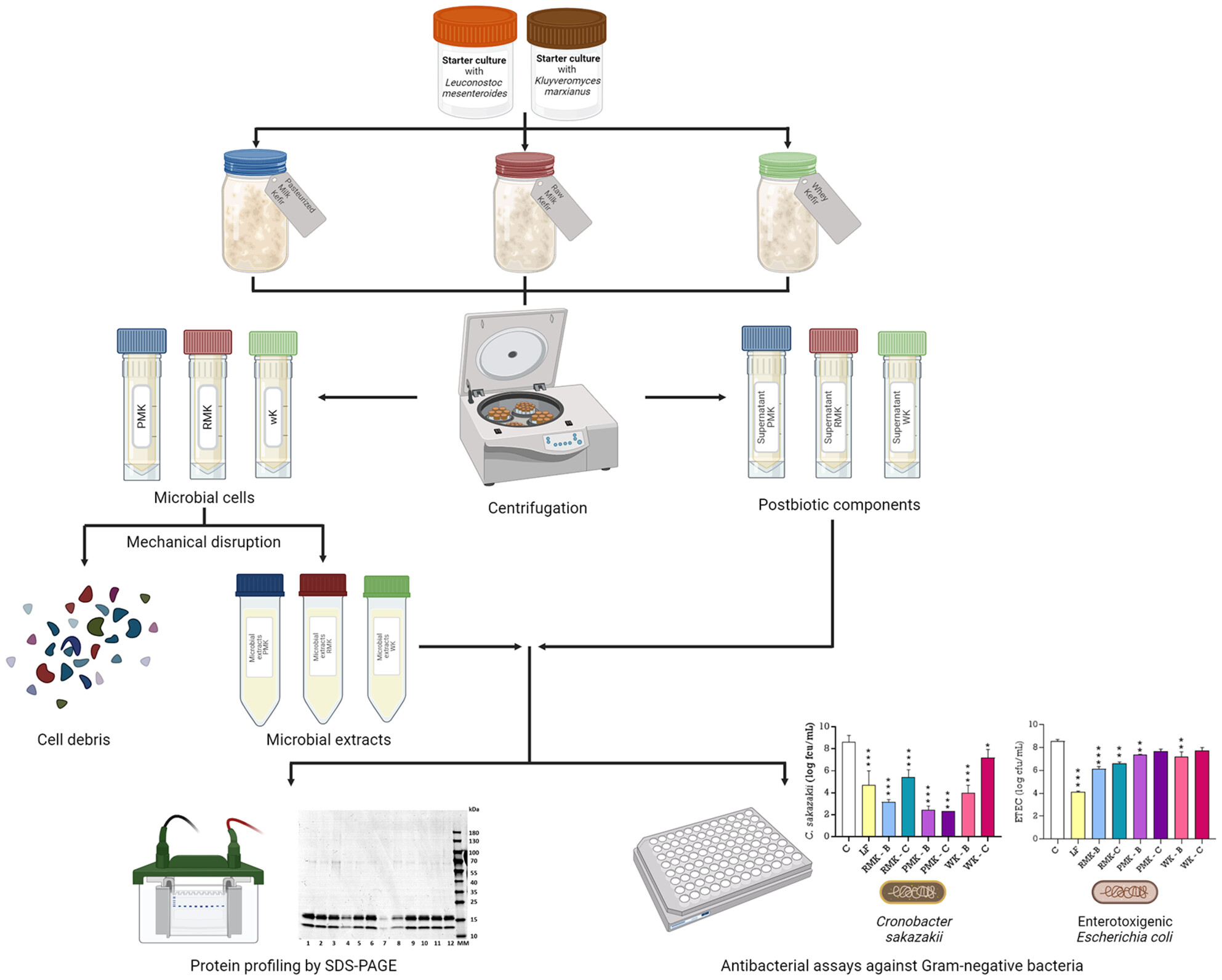
Antibacterial activity and antioxidant capacity of dairy kefir beverages
- First Published: 27 October 2024
Review
Adaptive and predictive approaches to mitigate the impact of milk seasonality on composition, processing technologies and quality of milk powders
- First Published: 30 October 2024
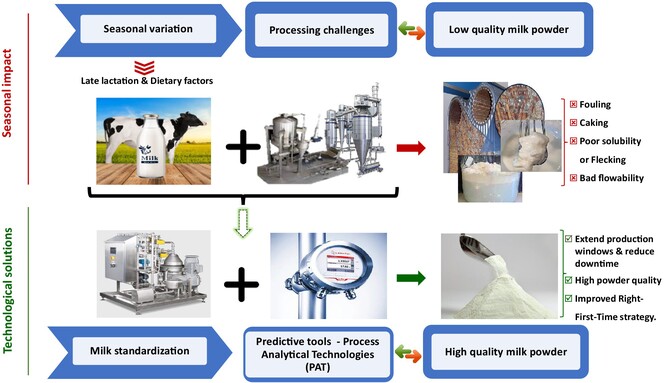
This review presents recent technological advancements and predictive tools for mitigating or correcting these effects on milk powder production. Against the backdrop of seasonal milk fluctuations, this review aims to uncover the factors that influence physicochemical changes and the resulting functional changes in milk powder, adaptive process tools used to mitigate these issues and the technological solutions and challenges associated with mitigating the main problem in the processing of powdered milk.
Research Article
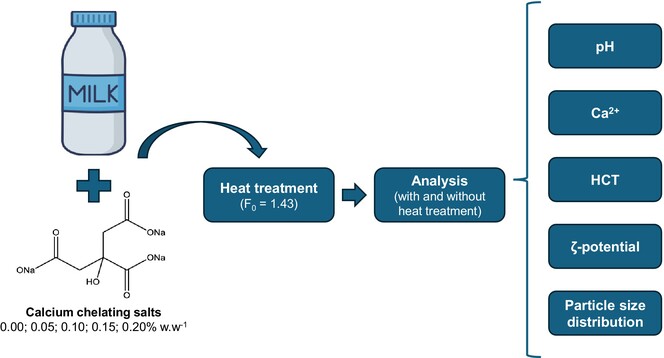
Influence of different calcium-chelating salts on the colloidal structure of skimmed milk under simulated heat treatment conditions
- First Published: 30 October 2024
Review
Microbial dysbiosis in the gut–mammary axis as a mechanism for mastitis in dairy cows
- First Published: 30 October 2024
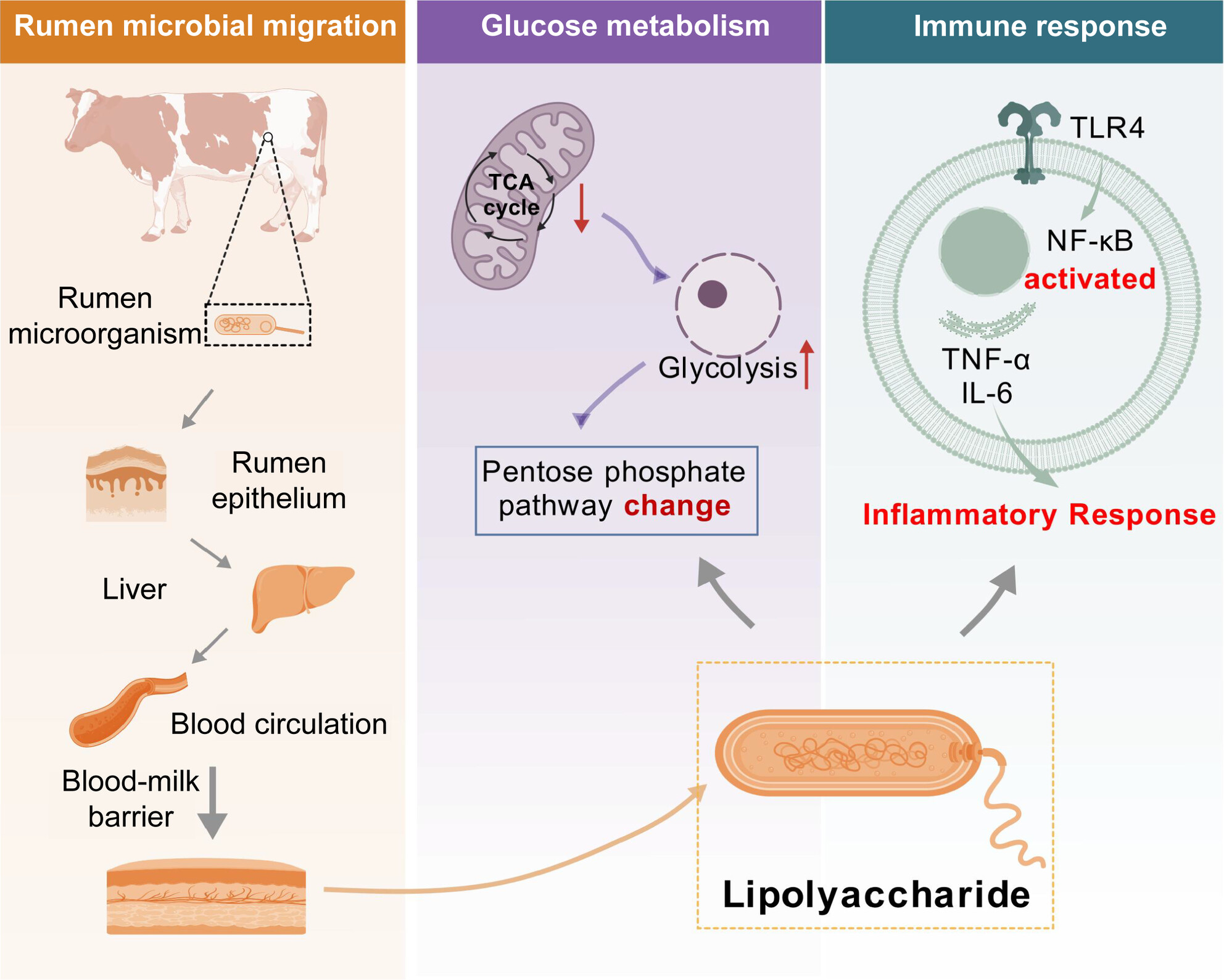
Rumen dysbiosis can cause mastitis through the rumen–mammary axis. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the bloodstream and cross the blood–milk barrier to reach mammary tissue. Mastitis leads to changes in glucose metabolism, including impaired TCA cycle, increased glycolysis and altered pentose phosphate pathway. Additionally, mastitis activates immune cells by binding to TLR4, triggering the production of immune factors and initiating an immune response.
Research Article
Effect of processing conditions on rheology, texture, and microstructure of paneer
- First Published: 06 November 2024
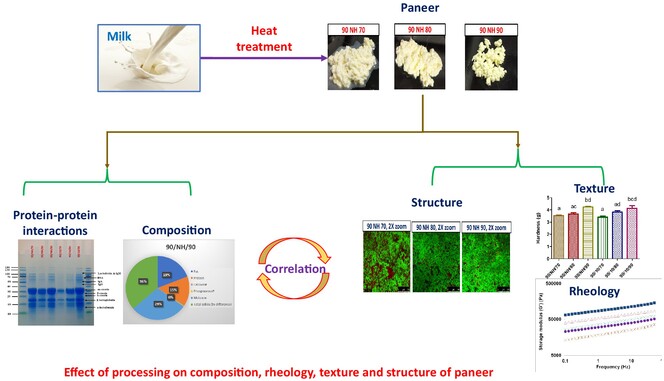
Coagulation at 90°C significantly affected the proximate composition, and processing characteristics of paneer. Increasing the coagulation temperature (70–90°C) enhanced interactions between whey and casein proteins. The highest values of G′, G″, and consistency coefficient were obtained following coagulation at 90°C. Coagulation temperature had a direct impact on the density of paneer protein matrices.
Impact of temperature and concentration on flow behaviour of reconstituted lactose and protein-rich dairy powders
- First Published: 06 November 2024
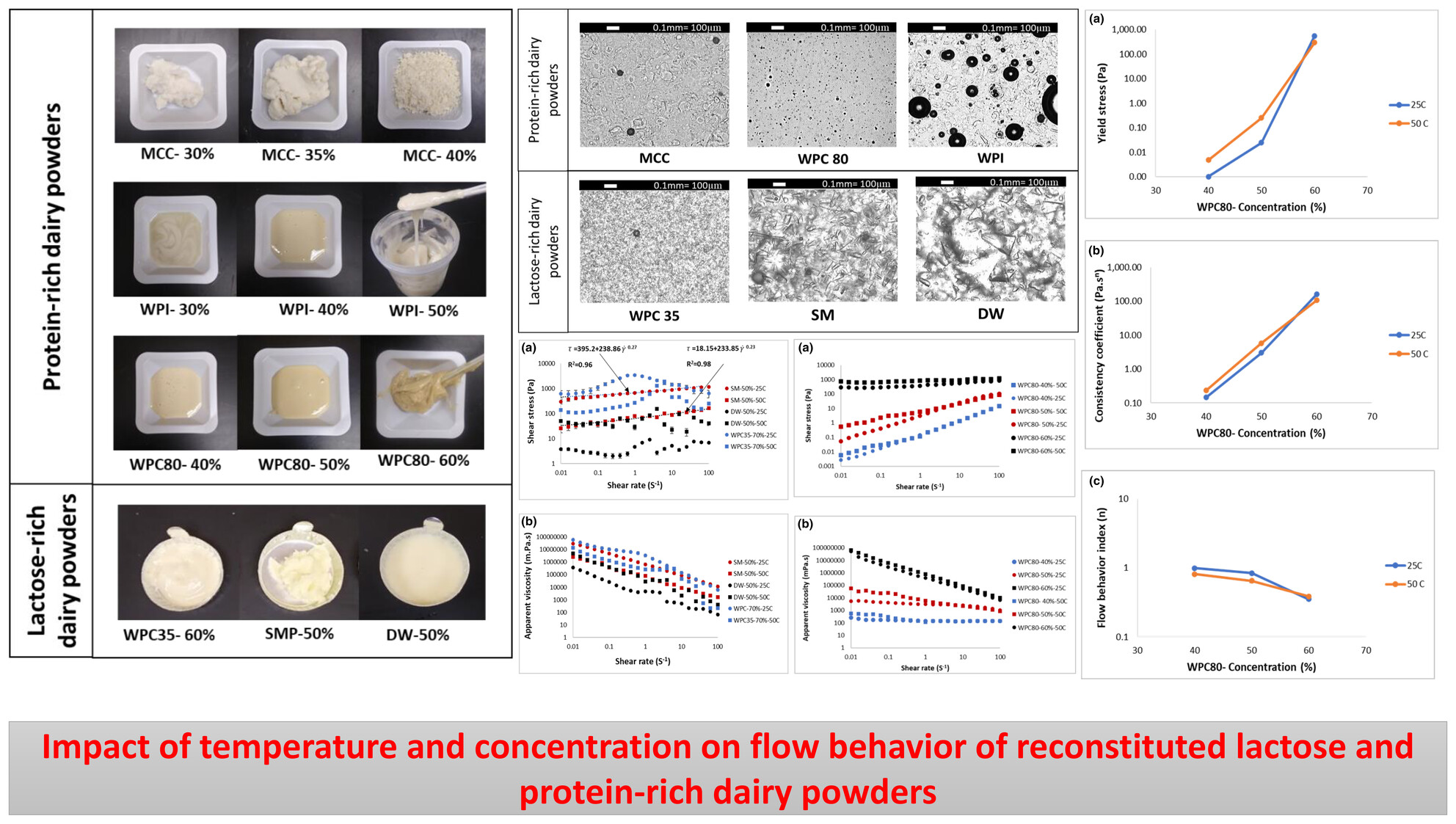
It is important to study the rheological properties of dairy products to know the limits of the maximum usable concentration in different dairy manufacturing processes, such as ultrafiltration, evaporation, atomisation of liquid droplets during the drying process. This study provides useful insights into the dairy industry for designing products, processes and equipment for lactose-rich and protein-rich product streams.
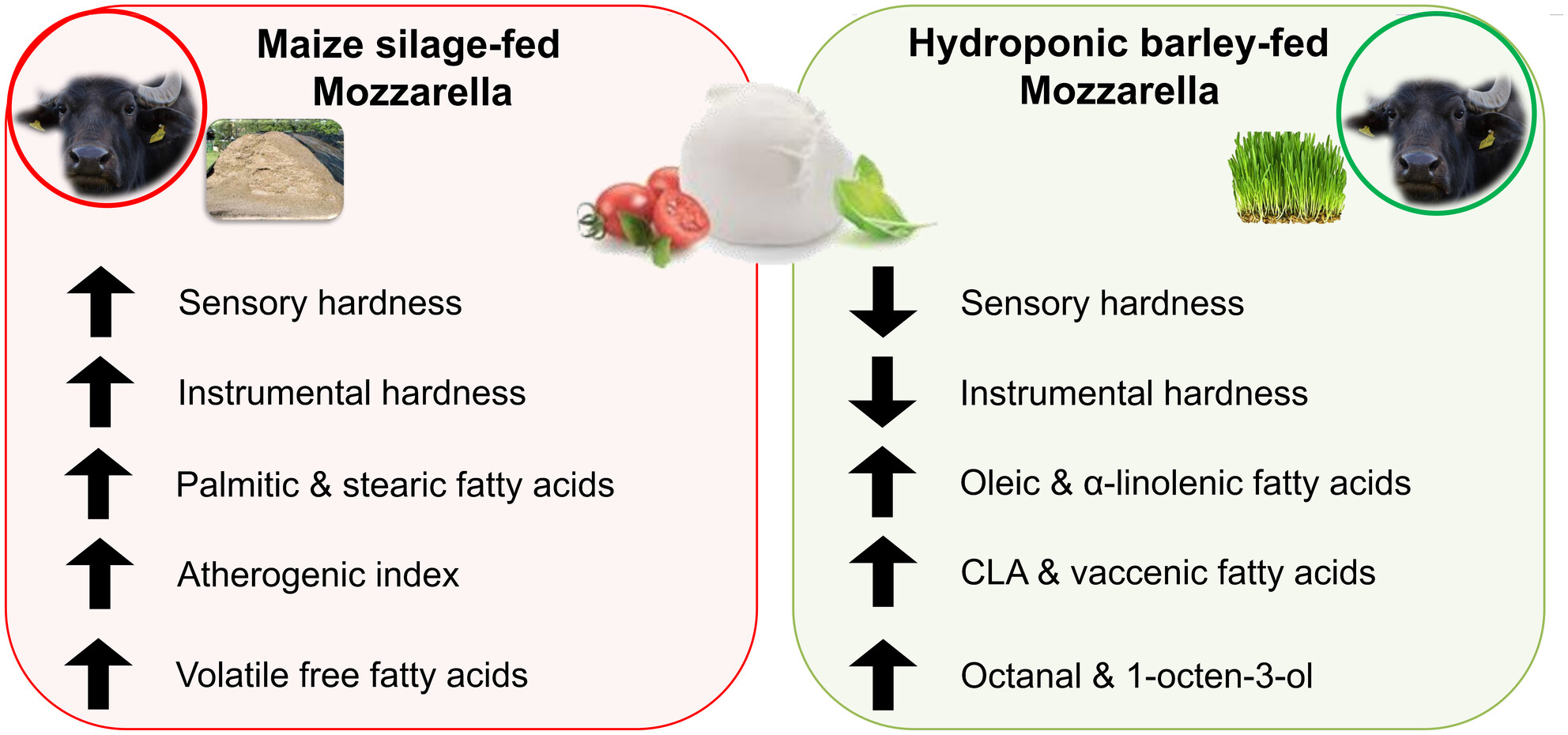
Can hydroponic forage affect the chemical and sensory properties of PDO buffalo Mozzarella cheese?
- First Published: 11 November 2024
Bovine milk as a source of nitro-conjugated linoleic acid
- First Published: 11 November 2024
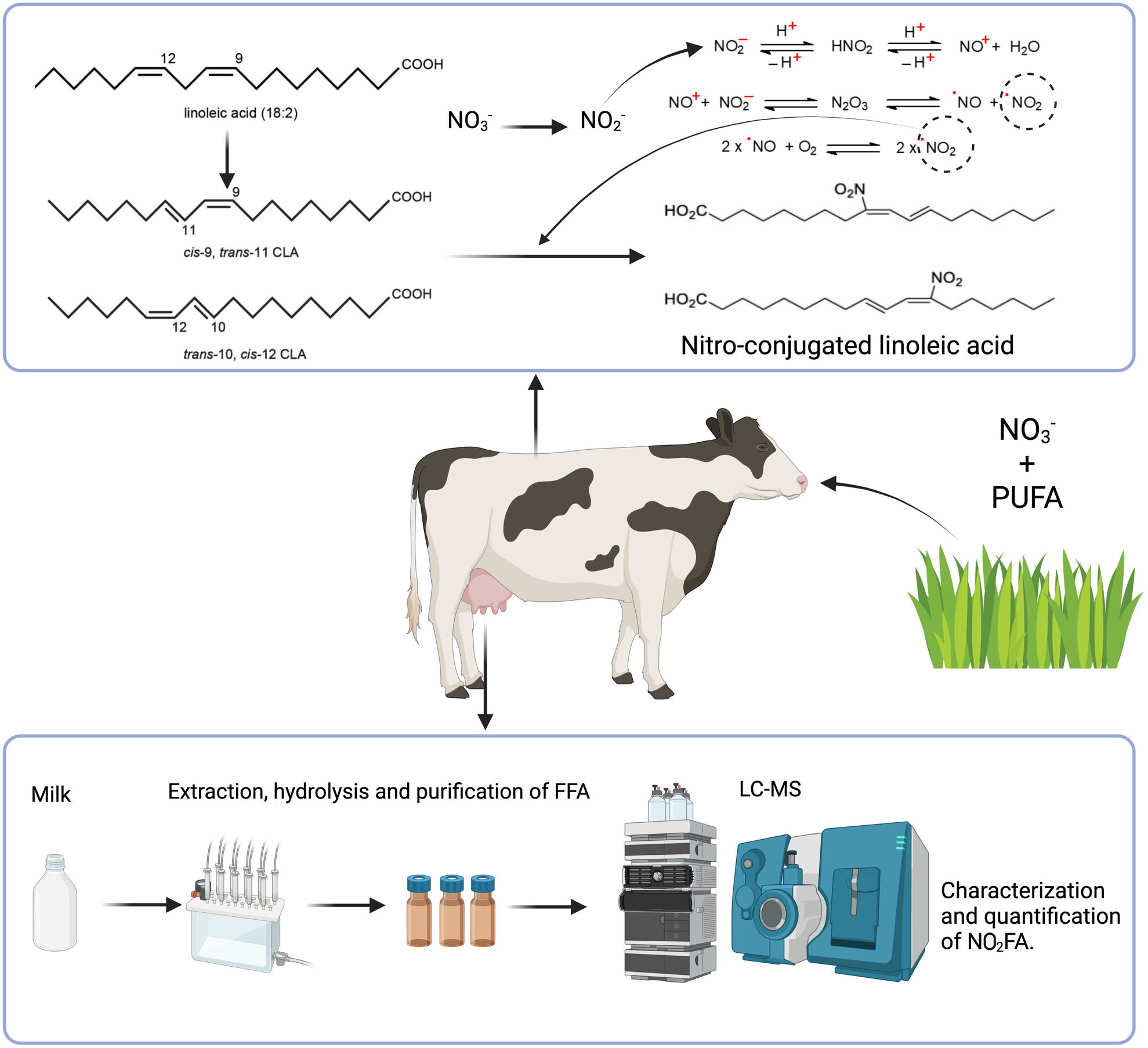
This study investigates the presence of nitrated fatty acids (NO2-FAs) in bovine milk. NO2-conjugated linoleic acid (NO2-cLA) was detected at micromolar concentrations, accounting for 2.7% of total cLA. Variations in NO2-cLA levels were noted across different Holstein strains and lactation stages. The study confirmed the electrophilic nature of NO2-cLA present in bovine milk, likely formed through cLA nitration in the digestive tract. These findings suggest significant biological implications of NO2-cLA in milk, necessary further research into its health benefits.
Influence of fat globules structure on the physicochemical properties and digestive characteristics in dairy products: A study on liquid cow milk, semi-liquid yoghurt and semi-solid cheese
- First Published: 10 December 2024
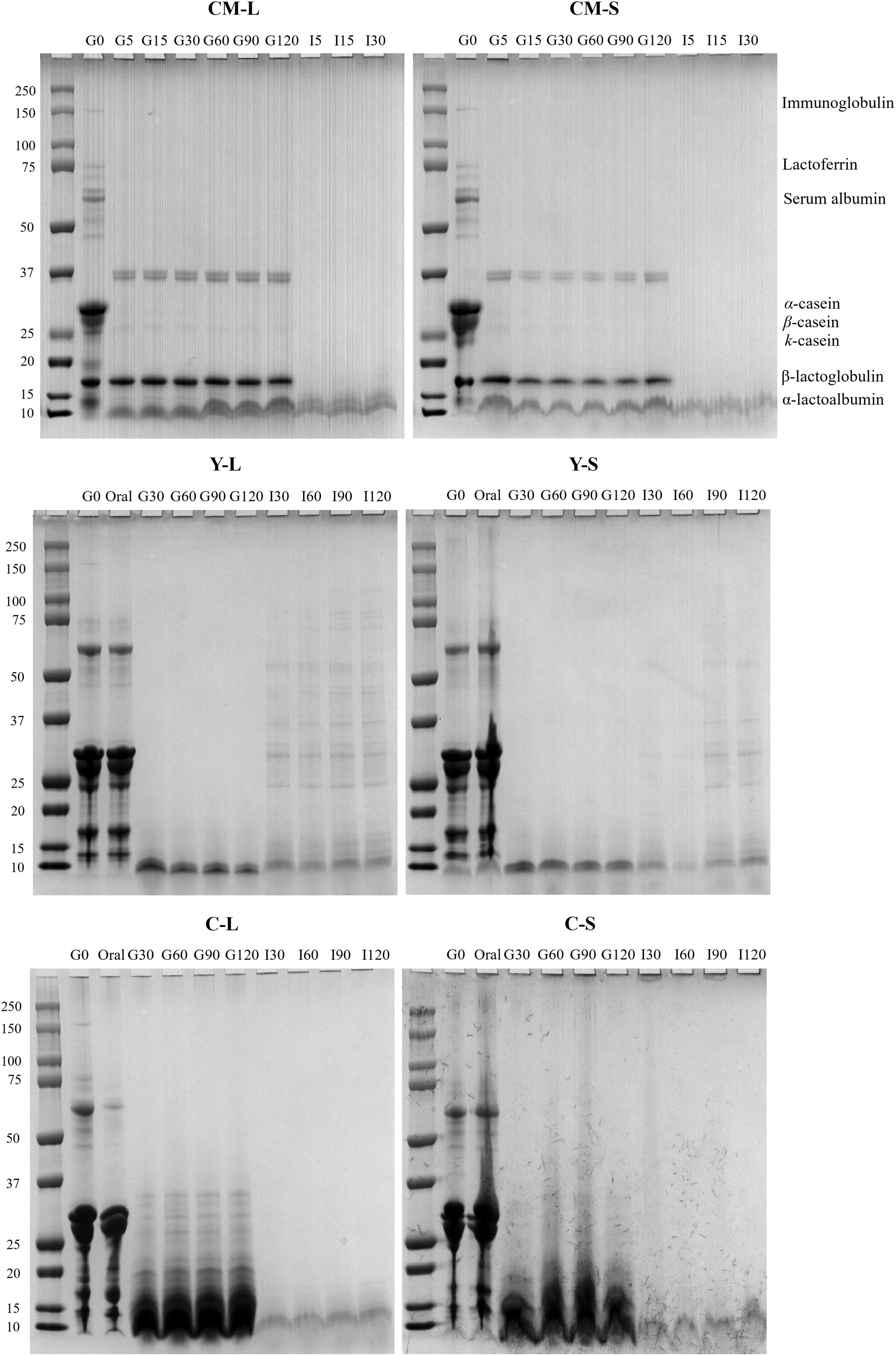
The physicochemical properties and digestive behaviours in dairy matrices, including liquid cow milk, semi-liquid yoghurt and semi-solid cheese with different fat globules by homogeniation were identified. The interaction between proteins and lipids during digestion was found to help design the fat structure with different food matrices in the future.
Short Communication
Analysis of nutritional profiles in colostrum and mature milk of giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca) based on proteomics
- First Published: 10 December 2024
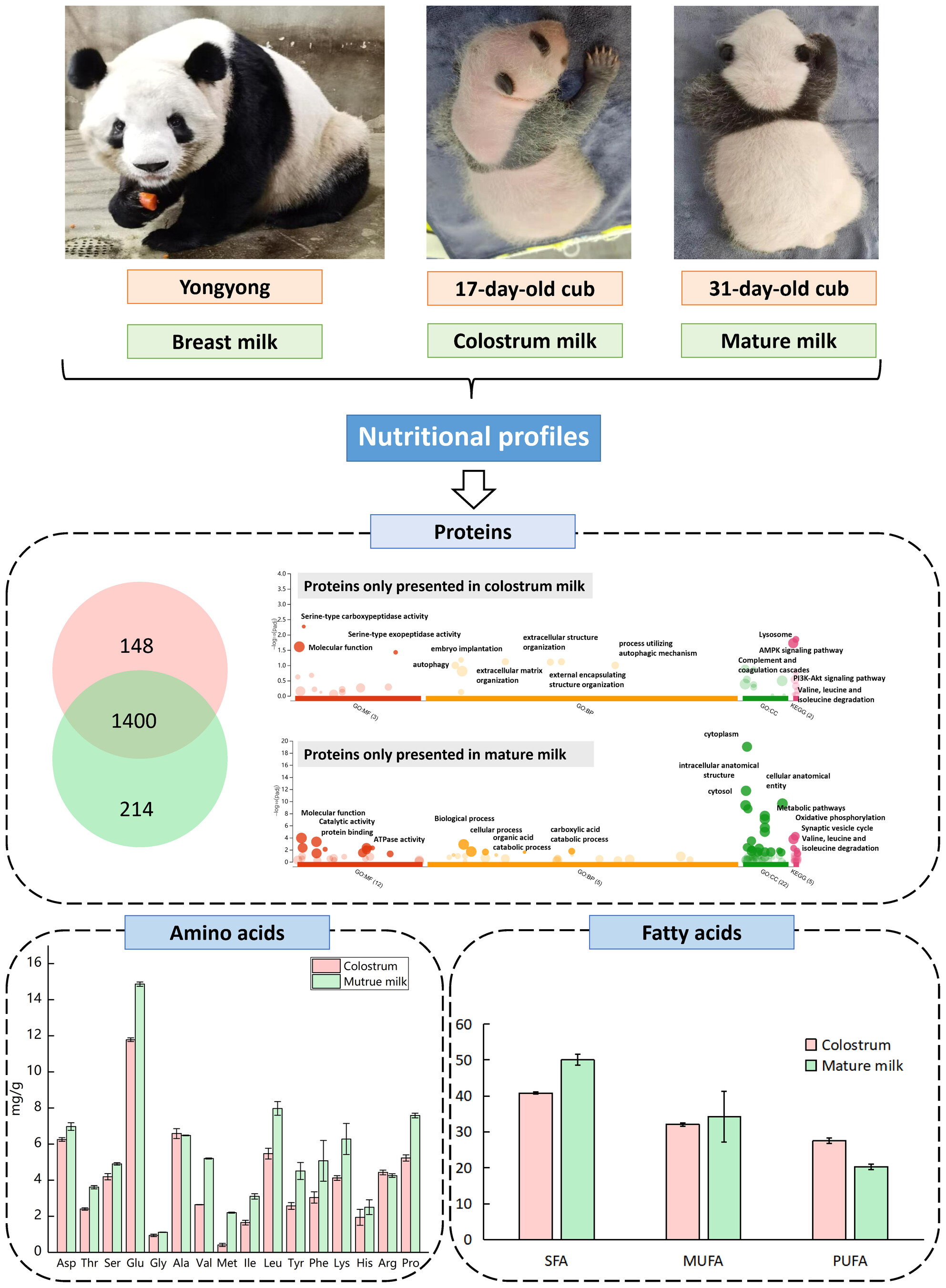
The colostrum was rich in immunoreactive proteins, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial proteins, while the mature milk contained proteins involved in ribosome, fatty acid degradation and amino acid metabolism. The content of most amino acids in mature milk was significantly higher than colostrum, and the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids in colostrum was higher than in mature milk.
Research Article
Effects of different heat treatments on the bioactive components, bactericidal and antioxidative capacity of bovine milk
- First Published: 10 December 2024
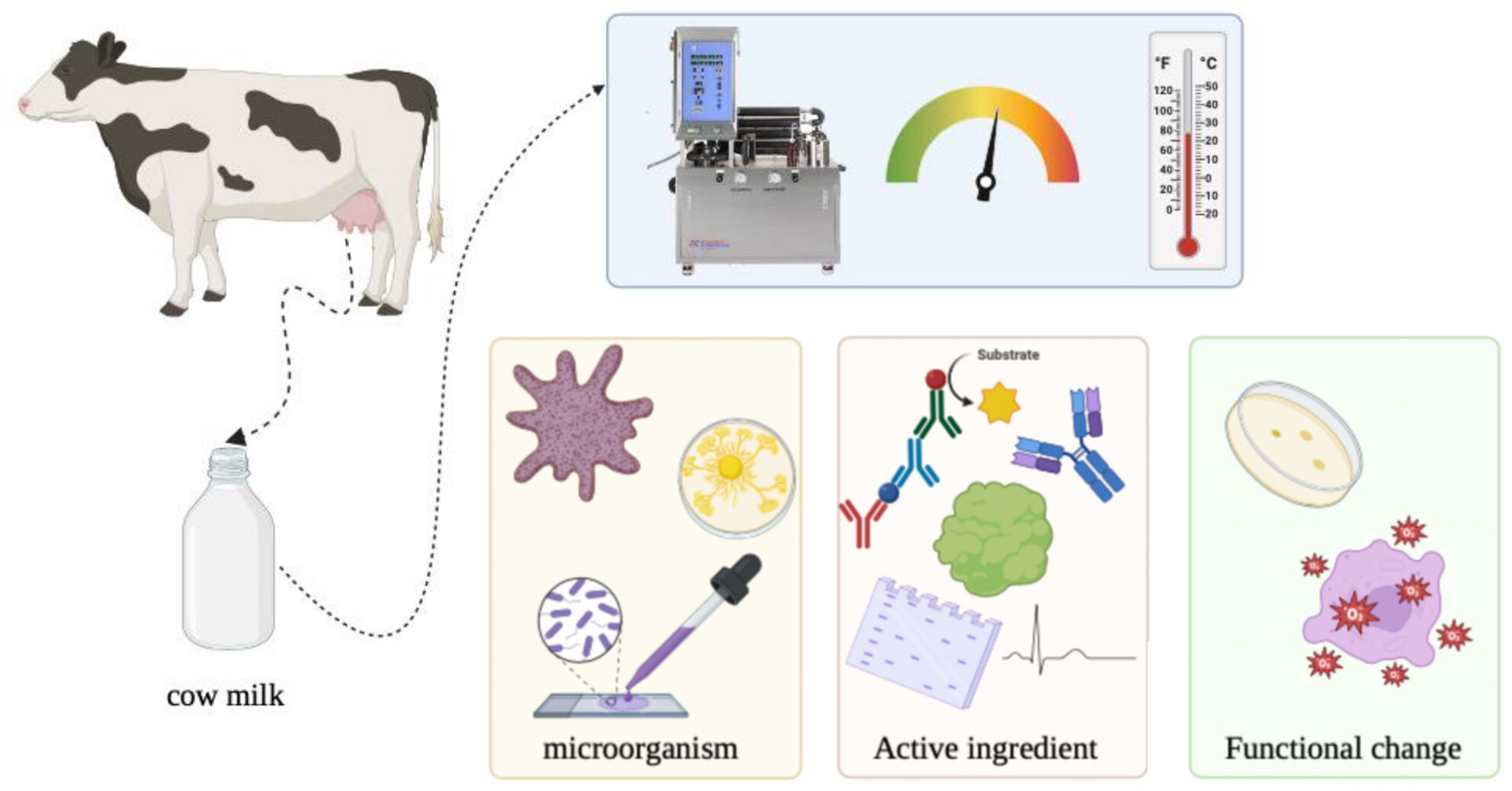
A wide range of heating temperatures was applied to treat raw milk in this study. When the heating temperature is increased from 72°C to 100°C, the number of microorganisms is significantly reduced and the content of bioactive ingredients such as lactoferrin and vitamins gradually decreases, resulting in a compromised antioxidant and antibacterial capacity of milk. However, only a slight lactose glycation occurred to whey proteins in the whole heating temperatures.
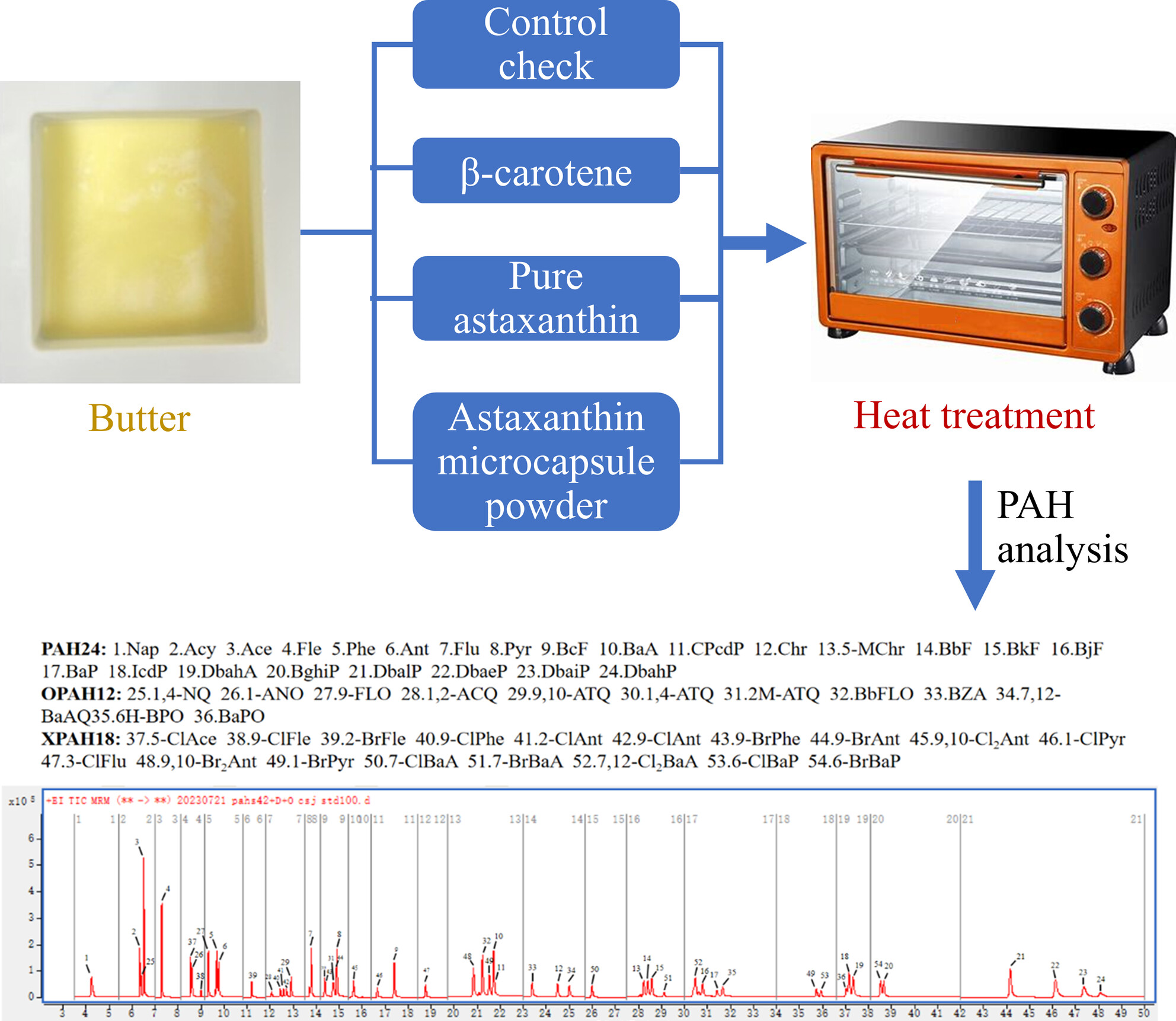
Beta-carotene and astaxanthin inhibit the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and oxygenated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in butter during heat treatment
- First Published: 10 December 2024
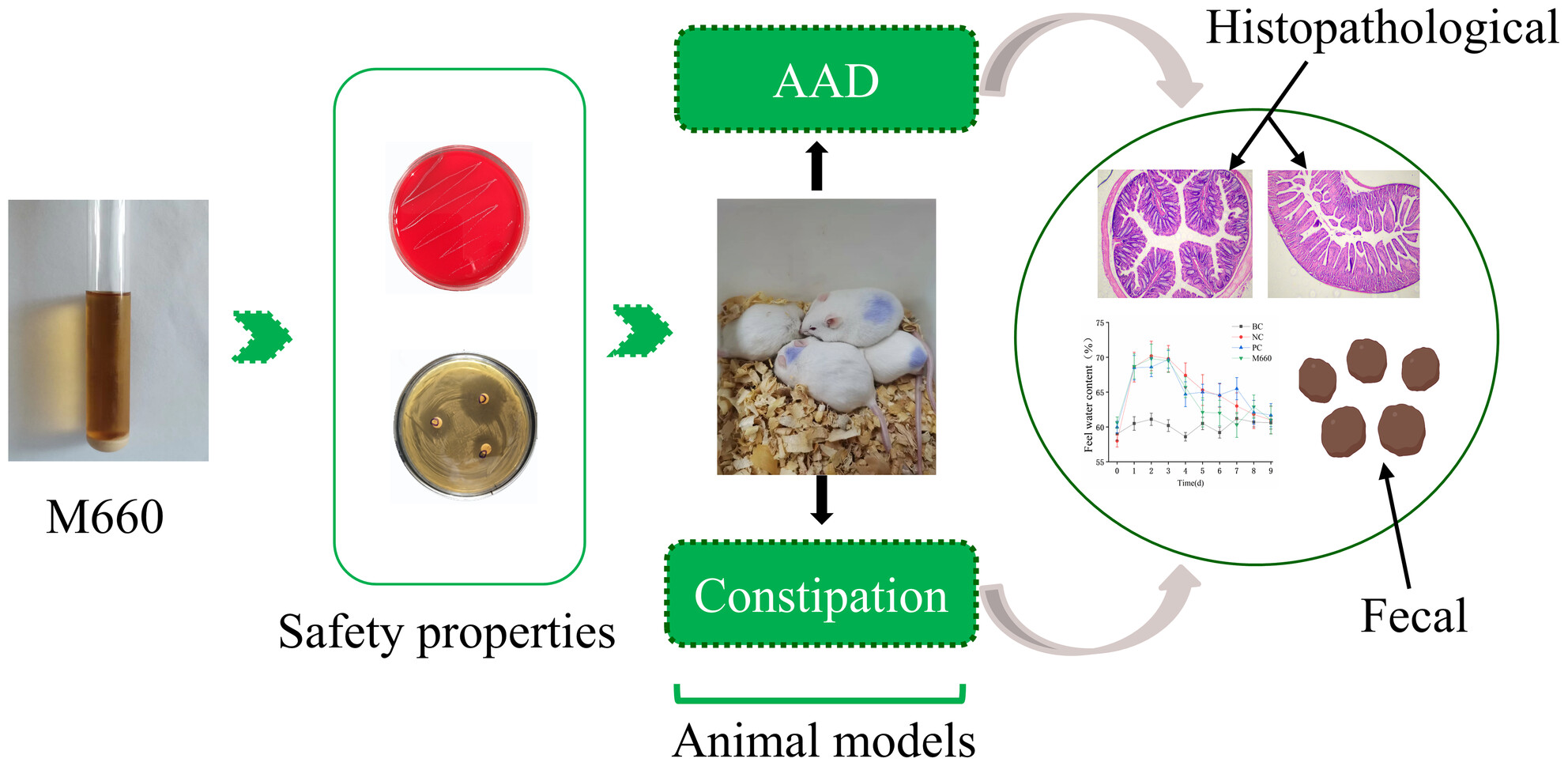
Probiotic effects of human milk-derived Lactiplantibacillus plantarum M660 on mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhoea and constipation
- First Published: 10 December 2024
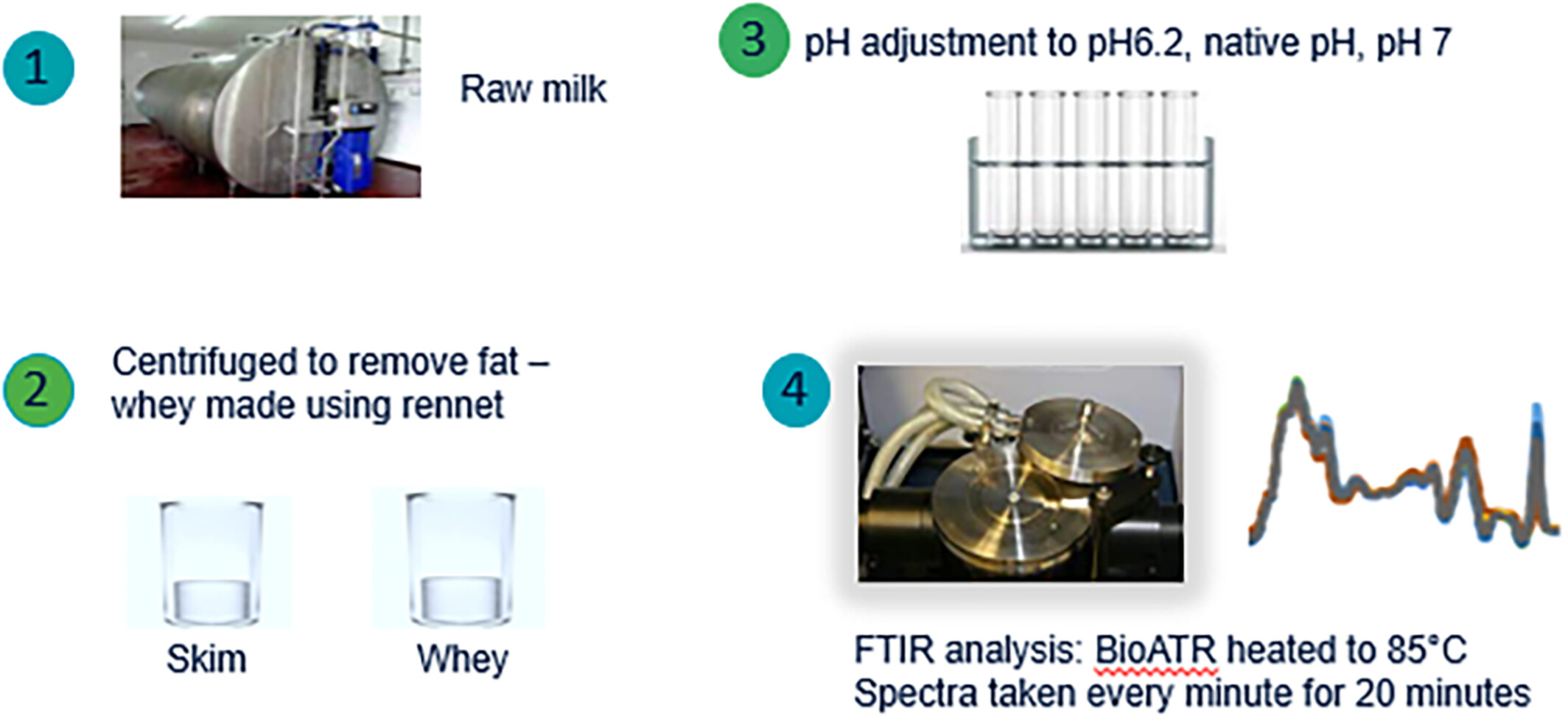
Real-time measurement of heat stability of skim milk using attenuated total reflectance (ATR)-FTIR spectroscopy
- First Published: 18 December 2024
Changes in flavour and aroma compounds of ultra-high-temperature processed and aseptic-filled milk caused by storage conditions (temperature and duration)
- First Published: 06 February 2025
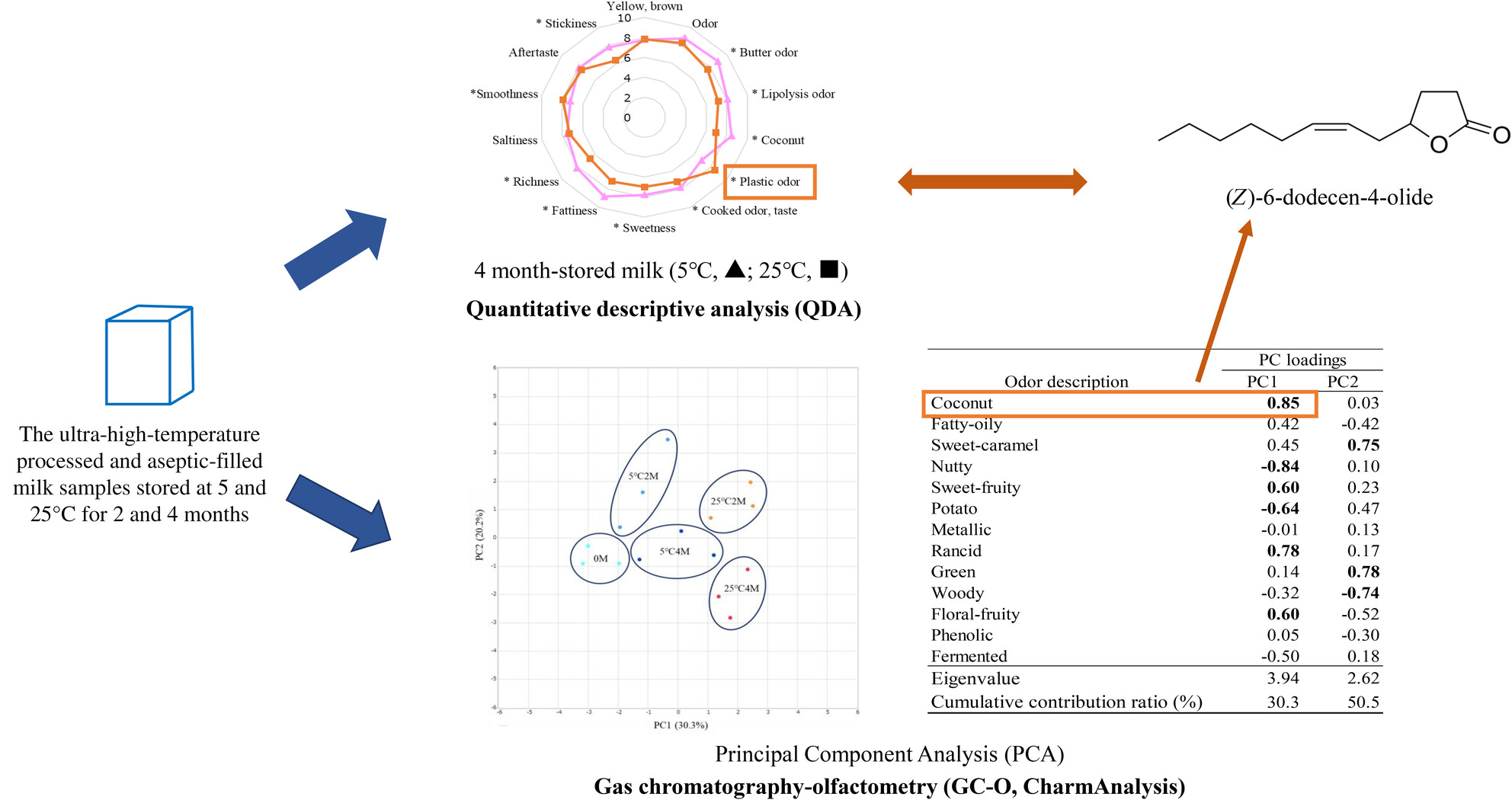
The changes during a 4-month storage period at 5 or 25°C were investigated for sensory characteristics, volatiles and odorants of LL milk. The increase in sensory score of “plastic odour” was a specific change associated with the 25°C stored milk, and (Z)-6-dodecen-4-olide with “coconut” odour was related to the change.
Review
Incorporation of dietary phenolic compounds into dairy products: Interactions and beneficial effects
- First Published: 18 December 2024
Conference Proceedings
The Dairy Academy 2024 – A ‘European Excellence in Dairy Learning’ (AEDIL Dairy CoVE) event
- First Published: 19 December 2024
Invited Mini Review
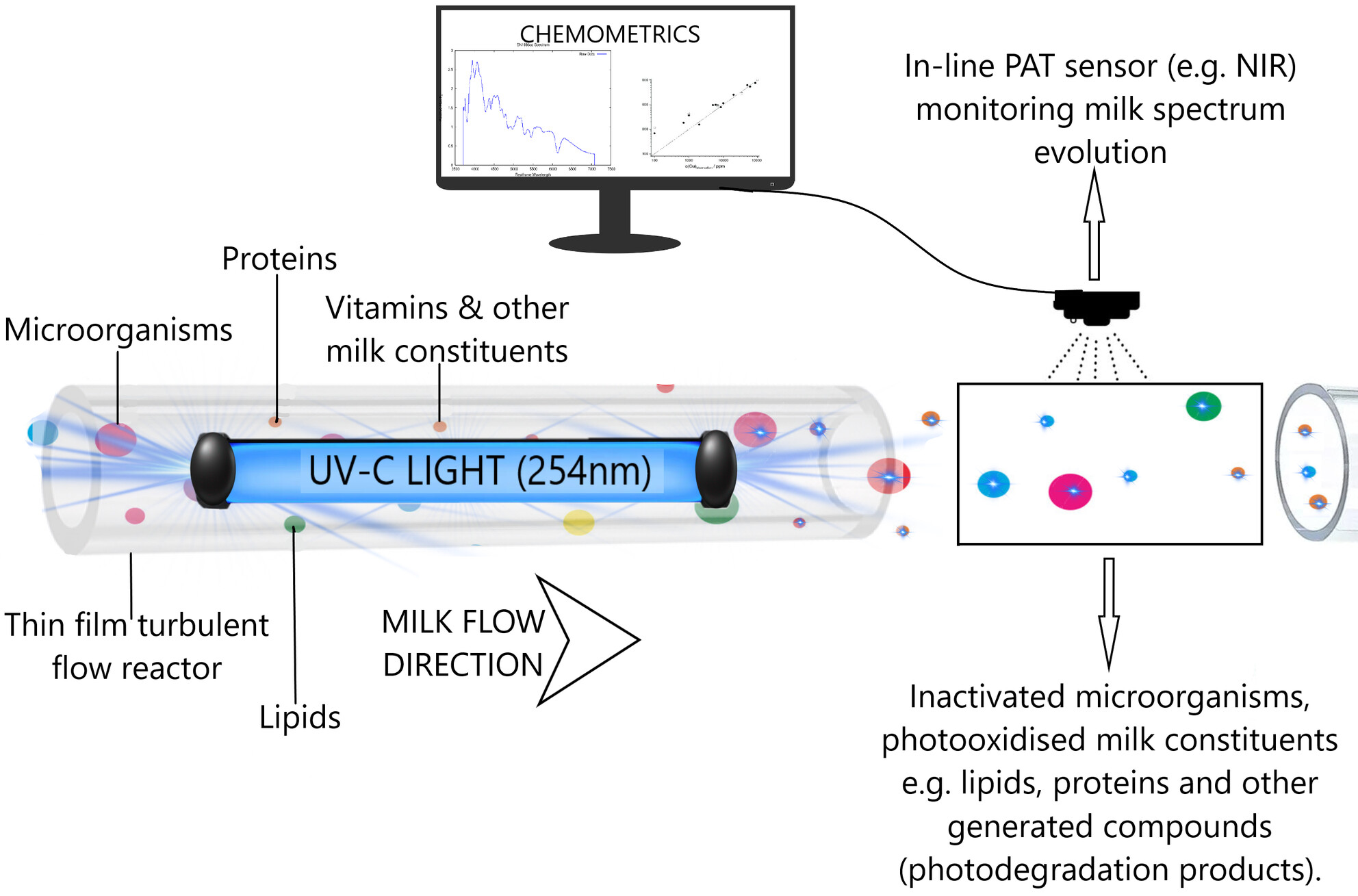
Challenges in developing a Process Analytical Technology (PAT)-based verification of UV-C treatment of milk
- First Published: 14 January 2025
Research Article
Recovery of milk fat from waste ice cream through ethanol-induced emulsion destabilisation
- First Published: 07 January 2025
Obituary
Obituary: Professor Patrick Fanahan (P. F.) Fox (1937–2024)
- First Published: 22 January 2025
Research Article
Effect of pH variation on physicochemical and morphological properties of Micellar Casein Concentrate and its utilisation for nanoencapsulation of curcumin
- First Published: 21 February 2025
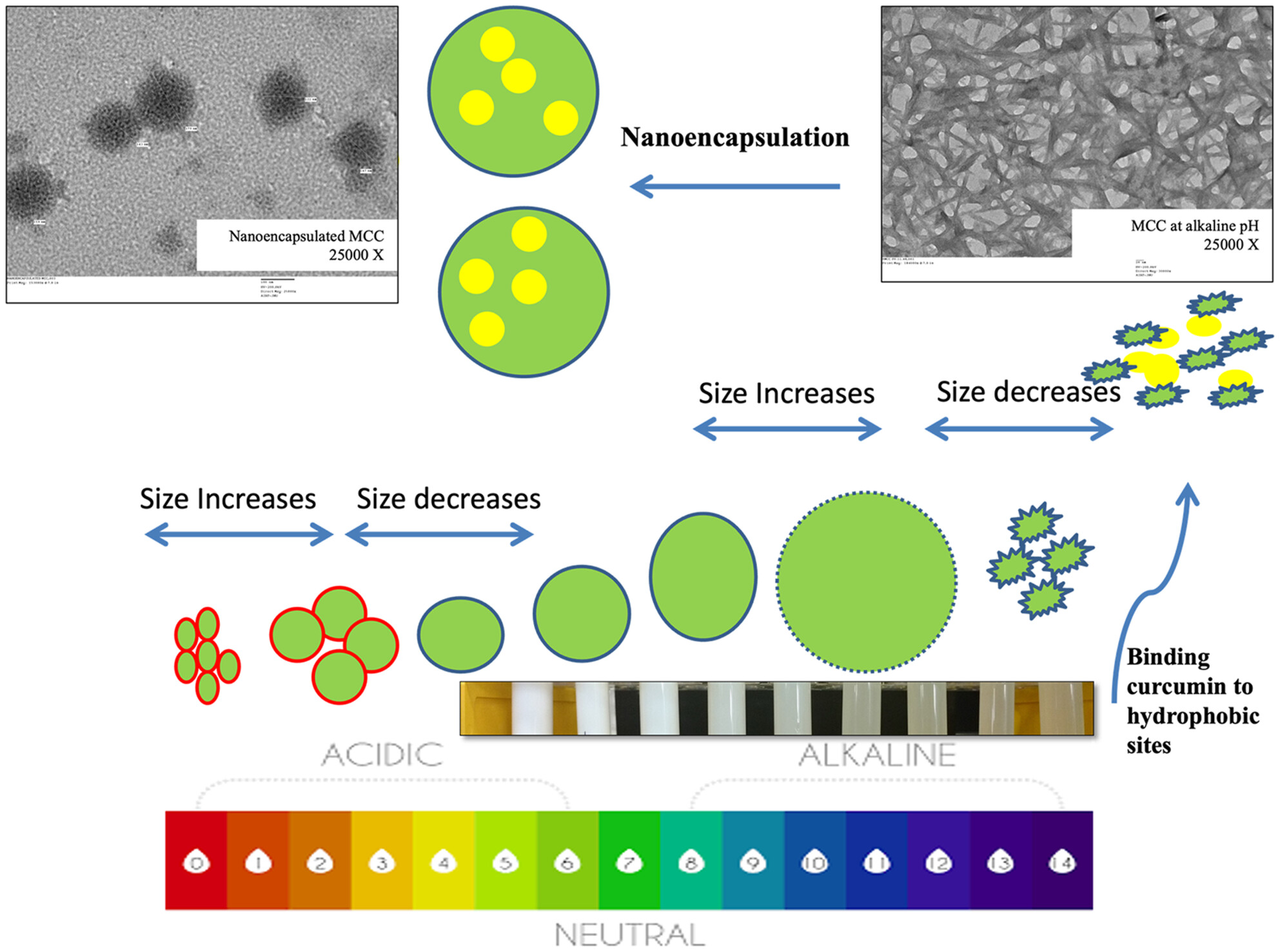
In the present investigation, the micellar casein concentrate in vitro digestion model showed a 98.12 ± 1.49% release of curcumin after 120 min of intestinal phase and only 6.12 ± 0.24% at end of gastric phase. This ensured increased bioavailability of curcumin, without getting degraded and promotes its wider applicability in development of functional foods.
A study of Candida albicans from raw bovine milk: Phenotypic and molecular characterisation, evaluation of the thermotolerance and the effects on pH
- First Published: 16 February 2025
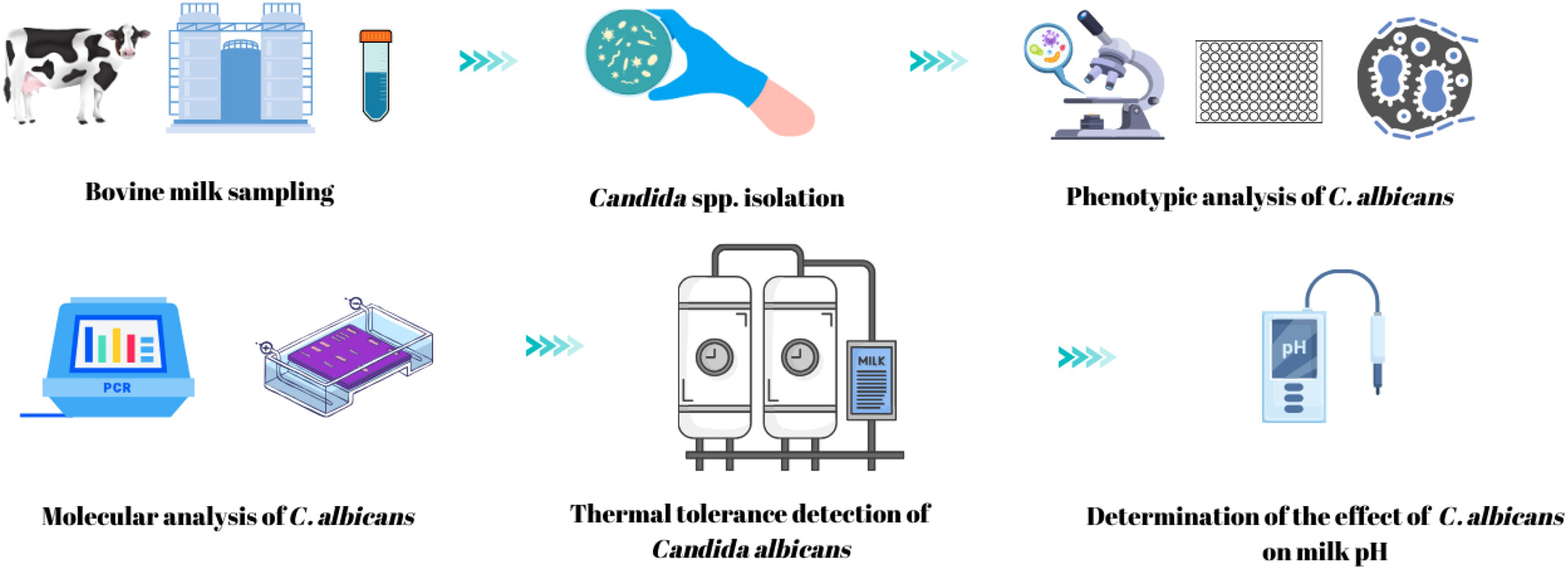
Candida albicans was the most abundant Candida species examined in raw bovine milk. C. albicans isolated from milk exhibited significant virulence, antifungal resistance, and biofilm producing properties. The heat treatment at 63°C for 30 min was the most effective method in reducing the microbial load of C. albicans in milk.
Editorial
Research Article
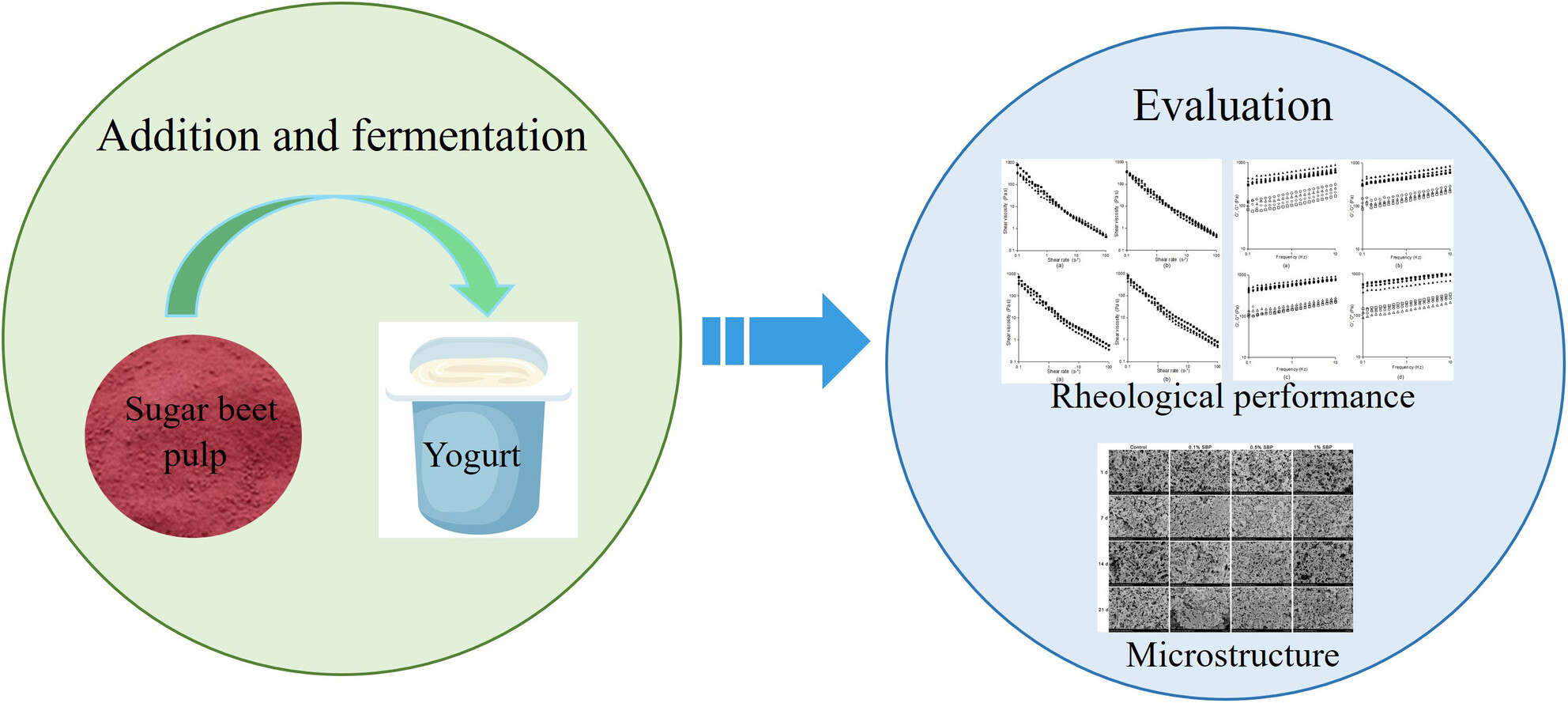
Effects of sugar beet pulp on the microstructure, rheological and textural properties of set yogurt
- First Published: 17 February 2025
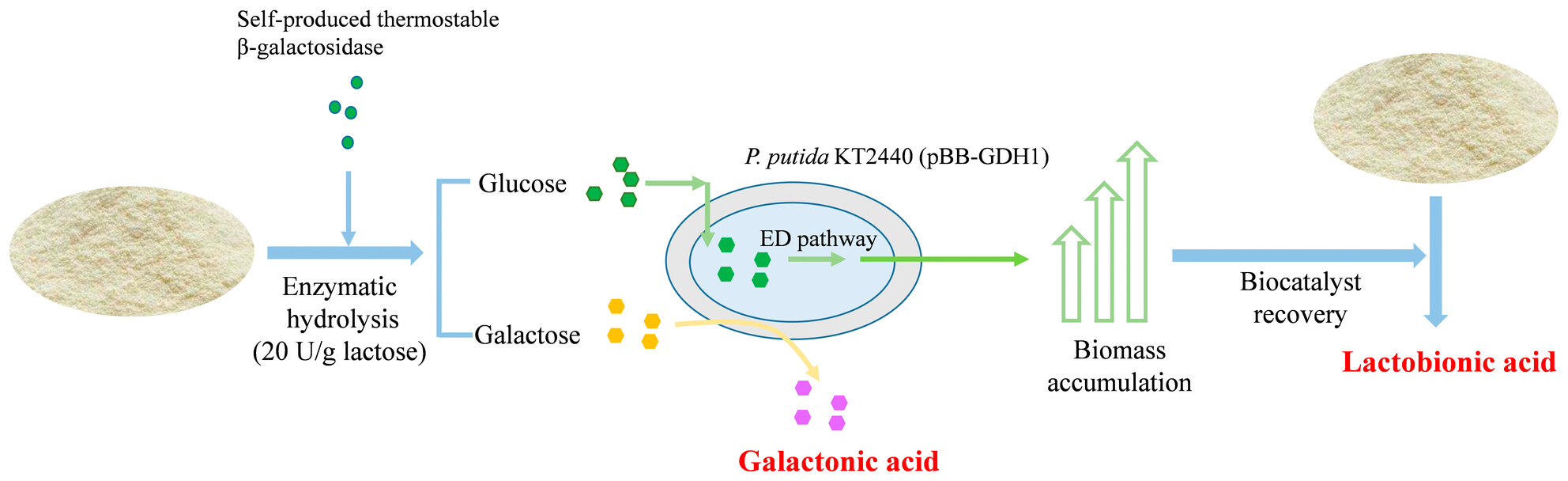
Co-production of galactonic acid and lactobionic acid from cheese whey using recyclable engineered Pseudomonas putida
- First Published: 22 February 2025
Physiological characteristics of Bacillus strains originated from dairy products and their impacts on rheological properties of pasteurised yoghurt
- First Published: 26 February 2025
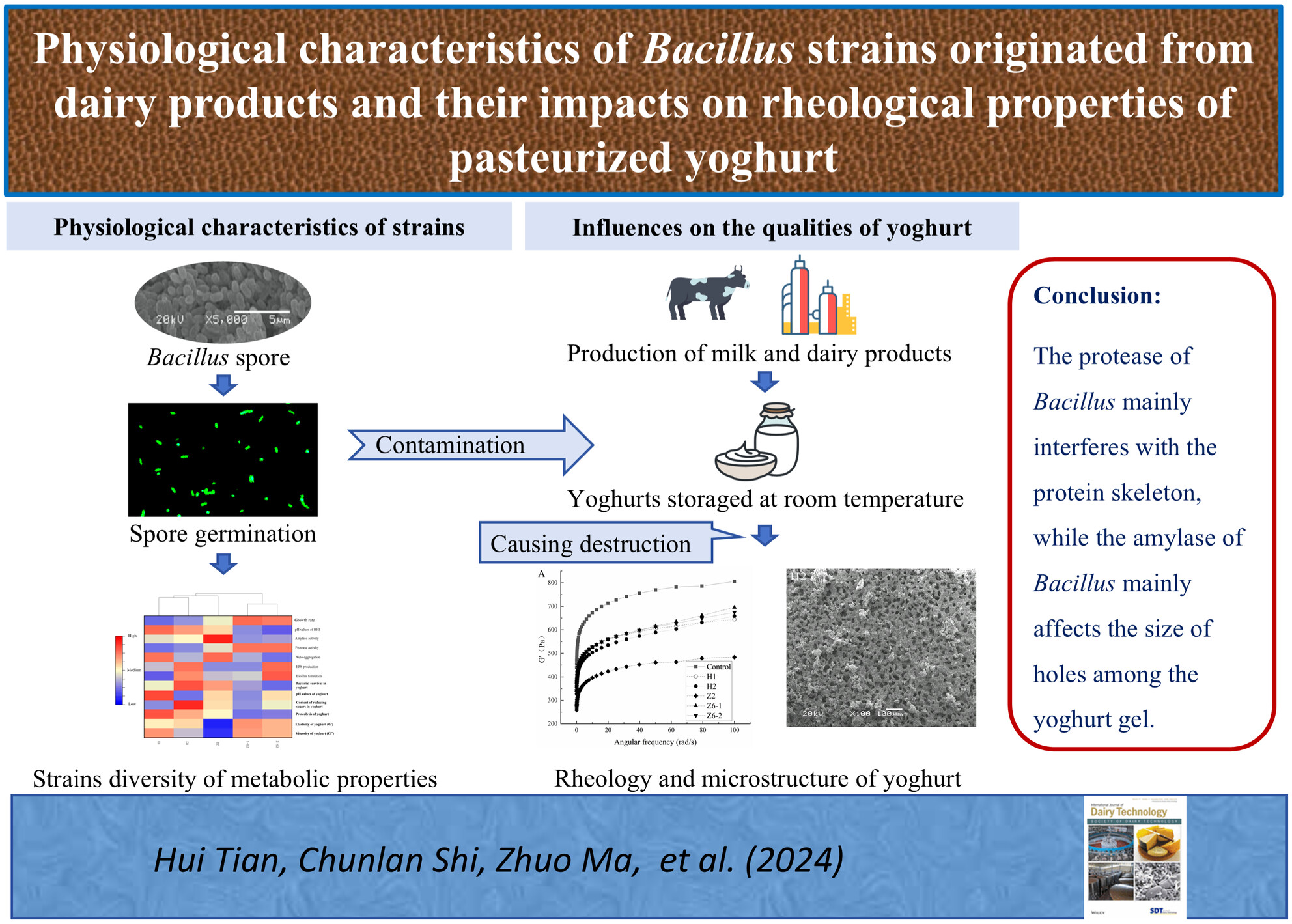
Impacts of five Bacillus strains (Bacillus licheniformis H1, B. licheniformis H2, B. subtilis Z2, B. cereus Z6-1 and B. cereus Z6-2) originated from dairy products on the quality of pasteurised yoghurt were investigated. Physiological characteristics of the strains as well as the influence of artificial Bacillus contamination on pasteurised yoghurt were examined. Physiological characteristics of the five Bacillus strains were strongly strain-specific. Both B. cereus strains had the highest growth rate and acid production in Brian Heart Infusion broth and the strongest proteolytic ability in skimmed milk. Bacillus subtilis Z2 exhibited the highest amylase activity, and the highest yields of extracellular polysaccharides and biofilm were obtained from B. cereus Z6-2 and B. licheniformis H2. The acidic environment (about pH 4.2–4.4) was not suitable for the growth of Bacilli, as the low survival rate after inoculation and the slow growth during the 60-day incubation at 28°C. Nonetheless, the contamination with Bacilli could still negatively impact the rheological properties of pasteurised yoghurt, due to the protease and amylase activity of the strains. Yoghurt contaminated with B. licheniformis H1 showed strong proteolytic activity, resulting in a gel with relatively low elasticity. Yoghurt containing H2 exhibited a high amylase activity, leading to the formation of many interspersed holes. The Z2 strain had the strongest effect on the rheological properties of yoghurt, resulting in the lowest viscoelasticity. Bacillus cereus Z6-1 and Z6-2 had little effect on the gel structure, causing the yoghurt to have relatively high viscoelasticity. Together, the above findings indicate that protease from Bacillus strains mainly interferes with the thickness of the protein matrix of the yoghurt, while amylase mainly affects the size of holes in the gel. The residual Bacillus strains may adversely affect the rheological properties of pasteurised yoghurt, particularly in products with a long shelf life.
Erratum
Correction to Minimising bubble-related fouling: How to improve performance at lower cost and increased product quality—A theoretical proposal for ultra-high-temperature processing of milk
- First Published: 04 March 2025
Short Communication
Activity of bacteriophage endolysins LP101_021 and PlyP100 against Listeria monocytogenes for Squacquerone soft cheese decontamination
- First Published: 18 March 2025
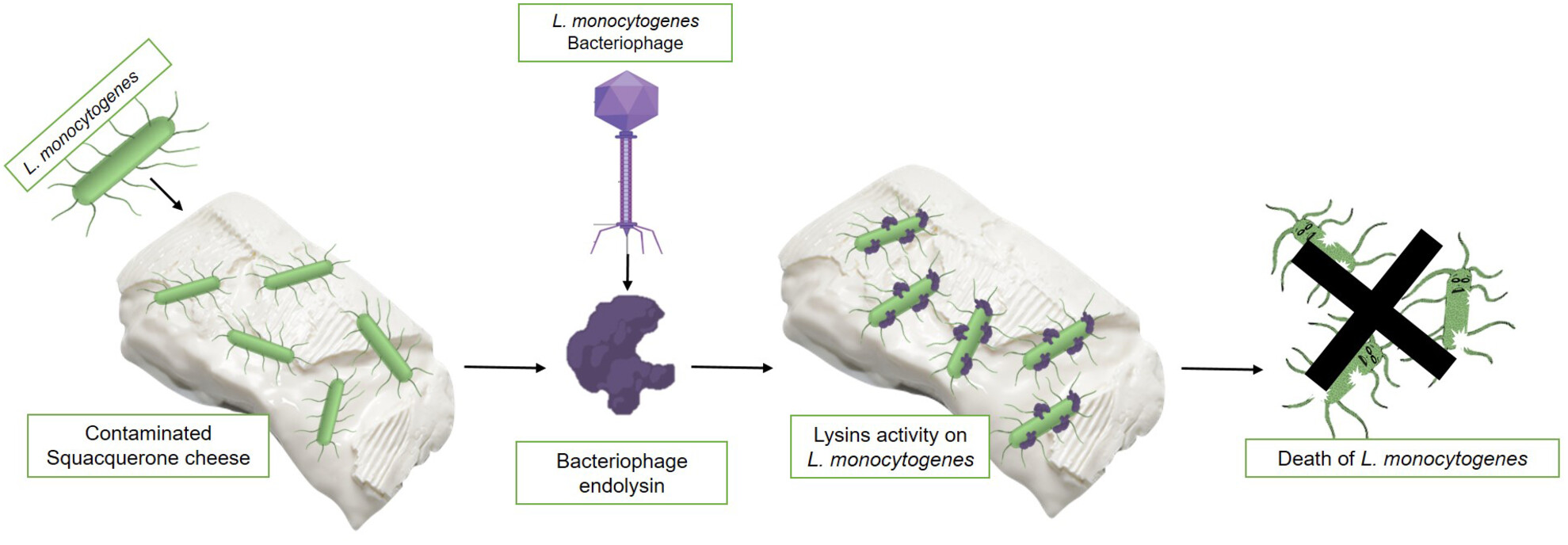
The results of this study contribute valuable insights into the field of food microbiology and biocontrol, supporting the role of endolysins as a targeted, effective means of controlling Listeria monocytogenes in food (cheese), reinforcing their potential as an antimicrobial tool in food processing and preservation, enhancing food safety.
Research Article
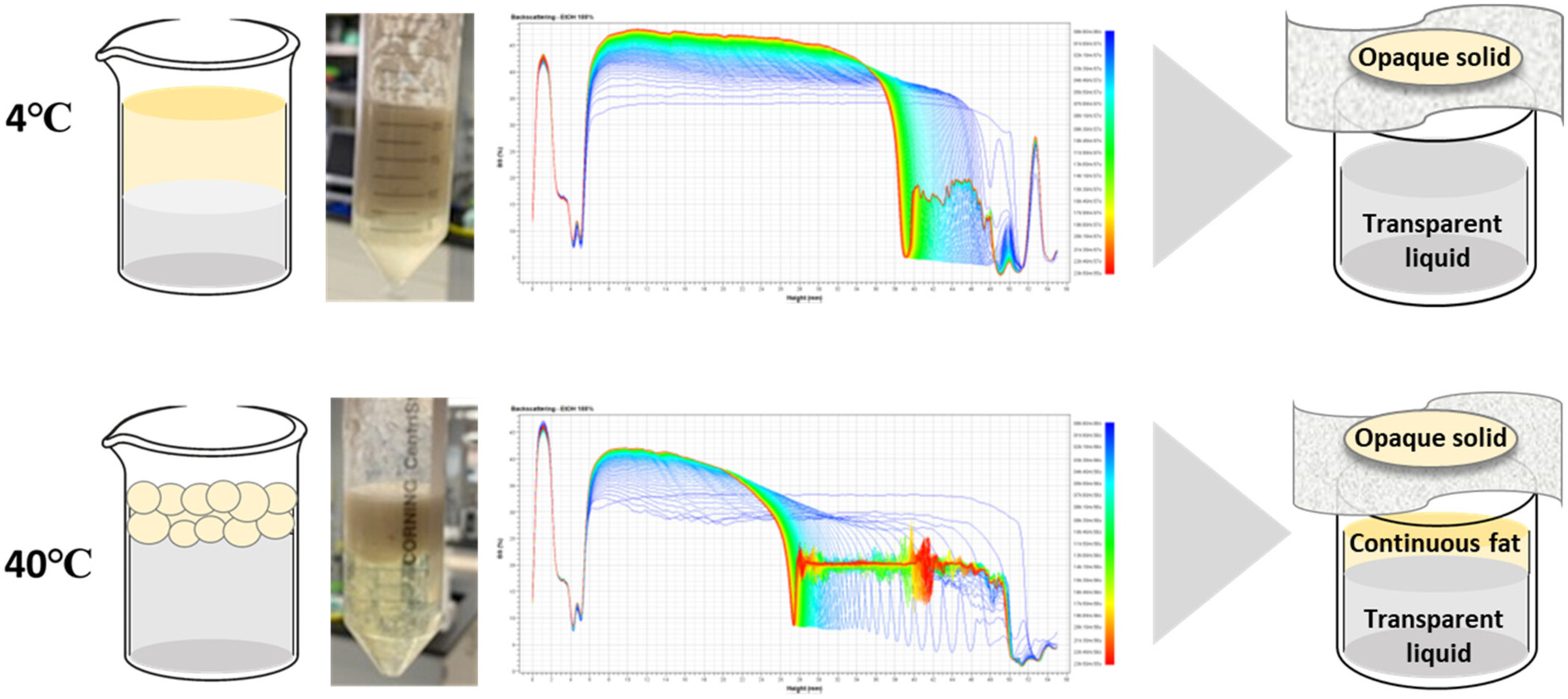
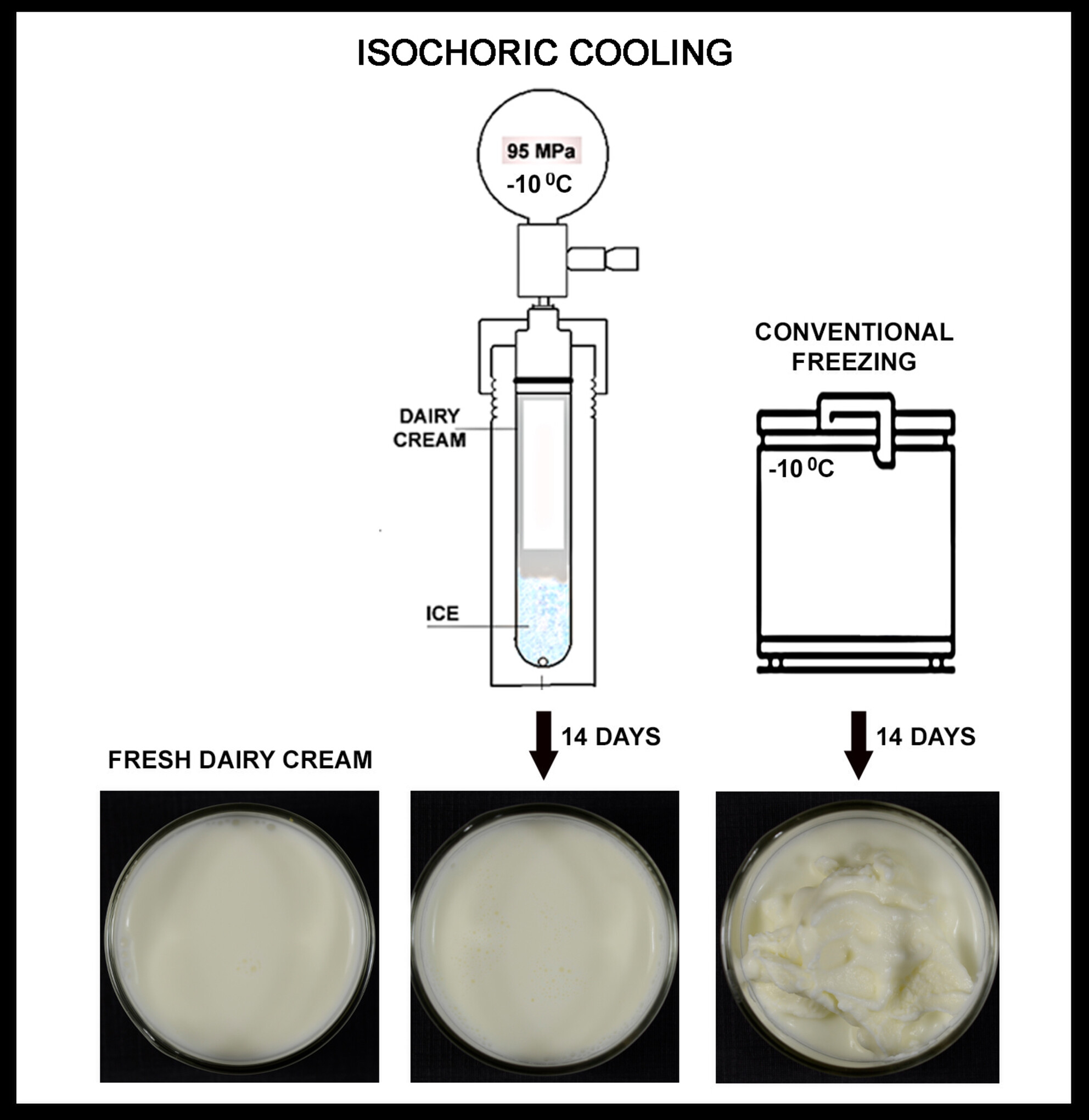
Isochoric cooling process preserves dairy cream at subfreezing temperatures with freeze–thaw stability
- First Published: 13 March 2025
Editorial
Special issue ‘The 10th Conference on China Dairy Science and Technology’
- First Published: 27 March 2025