Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Caenorhabditis elegans mounts a p38 MAPK pathway-mediated defence to Cutibacterium acnes infection
- First Published: 15 June 2020
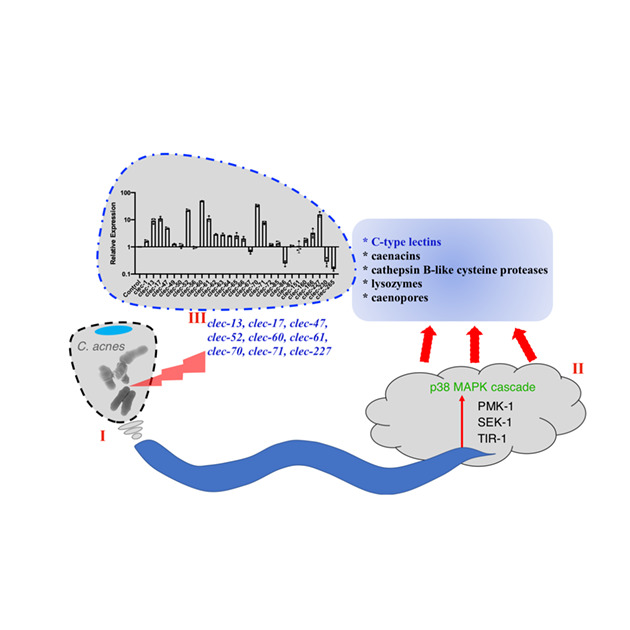
The opportunistic pathogen Cutibacterium acnes could be lethal to model animal Caenorhabditis elegans both on solid agar and liquid media. C. elegans mounted a defense through PMK-1/SEK-1/TIR-1 kinase cascade. C. acnes induced the expression of several APPs. Especially, nine putatively secretory C-type lectins (clec-13, clec-17, clec-47, clec-52, clec-60, clec-61, clec-70, clec-71, and clec-227) were upregulated during infection, which are p38 MAPK pathway-dependent in C. elegans. C. elegans serves as a valuable model to study C. acnes infection-related agents in the host.
Evolution and function of bacterial RCC1 repeat effectors
- First Published: 27 July 2020
Targeting E. coli invasion of the blood–brain barrier for investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic development of E. coli meningitis
- First Published: 24 May 2020
A critical role for CARD9 in pneumocystis pneumonia host defence
- First Published: 16 June 2020
The heterotrimeric G-protein beta subunit Gpb1 controls hyphal growth under low oxygen conditions through the protein kinase A pathway and is essential for virulence in the fungus Mucor circinelloides
- First Published: 19 June 2020
Rickettsial pathogen uses arthropod tryptophan pathway metabolites to evade reactive oxygen species in tick cells
- First Published: 19 June 2020
Protective effect of fungal extracellular vesicles against murine candidiasis
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Three proline rotamases involved in calcium homeostasis play differential roles in stress tolerance, virulence and calcineurin regulation of Beauveria bassiana
- First Published: 29 June 2020
EGFR/FAK and c-Src signalling pathways mediate the internalisation of Staphylococcus aureus by osteoblasts
- First Published: 25 June 2020