Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 1/2018
- First Published: 15 January 2018

Front Cover: Electrically actuating and waveguiding amorphous polymer submicron fibers can be used to produce novel opto–electromechanical devices. The fibers are further functionalized by embedding other functional materials. This cover image represents dye-embedded light-emitting amorphous submicron fibers which actuate in response to the polarity of an applied voltage and guide the emitted light in the fibers. This is reported by Yuya Ishii, Taiki Nobeshima, Heisuke Sakai, Keisho Omori, Sei Uemura and Mitsuo Fukuda in article number 1700302.
Inside Front Cover
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 1/2018
- First Published: 15 January 2018

Inside Front Cover: A highly sensitive stretchable strain sensor, which consists of elastic fibrous membrane coated with conducting polymer is introduced. The sensor can detect applied strain by measuring the conductance change caused by the change in the nanocracking structure on the coated conducting polymer. This is reported by Hyungkook Jeon, Seong Kyung Hong, Seong J. Cho and Geunbae Lim in article number 1700389.
Masthead
Editorial
Reviews
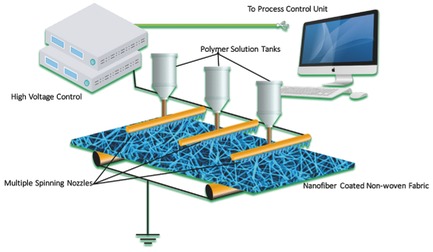
Raising Nanofiber Output: The Progress, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Reasons for the Pursuit
- First Published: 14 November 2017
Communications
Fabrication of a Highly Sensitive Stretchable Strain Sensor Utilizing a Microfibrous Membrane and a Cracking Structure on Conducting Polymer
- First Published: 04 December 2017
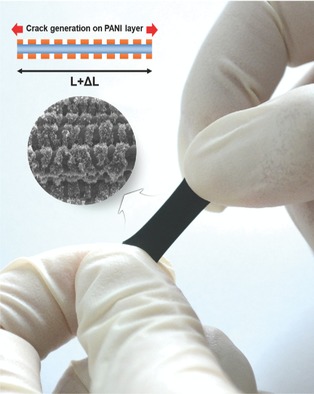
A highly sensitive stretchable strain sensor is introduced, which consists of elastic fibrous membrane coated with conducting polymer. The sensor can detect applied strain by measuring the conductance change caused by the change in the nanocracking structure on the coated conducting polymer. Furthermore, by aligning microfibers, the sensitivity of the sensor is dramatically enhanced (more than 40-fold higher).
Hierarchical Polymer Blend Fibers of High Structural Regularity Prepared by Facile Solvent Vapor Annealing Treatment
- First Published: 11 December 2017

By carefully understanding the phase separation and crystallization behavior of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)-based blends, one can tune the spatial distribution of the PCL phase, the growth of PCL crystalline regions, and therefore the amount and the sensitivity of amorphous PCL chains in response to solvent vapor annealing treatment. This will allow the easy and reliable production of hierarchically structured polymer materials with high regularity.
Full Papers
Amorphous Electrically Actuating Submicron Fiber Waveguides
- First Published: 21 September 2017
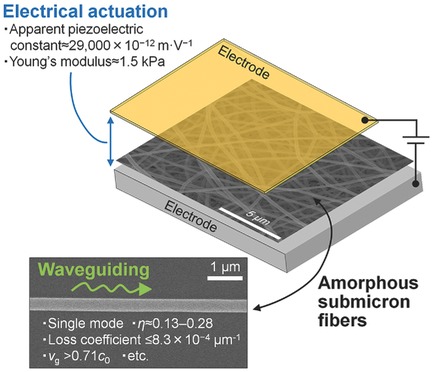
The properties of novel electrically actuating and waveguiding amorphous polymer submicron fibers are investigated in detail. These fibers guide light at subwavelength diameters with a group velocity greater than 0.71c0. The fiber mat also demonstrates electrical actuation with a high apparent piezoelectric constant of ≈29 000 × 10−12 m V−1. Extremely small and functional waveguides can be used to produce novel opto-electromechanical devices.
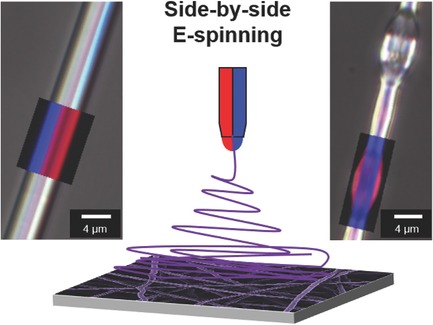
Tailoring the Morphology of Responsive Bioinspired Bicomponent Fibers
- First Published: 25 July 2017
Ionic Liquid Approach Toward Manufacture and Full Recycling of All-Cellulose Composites
- First Published: 06 September 2017
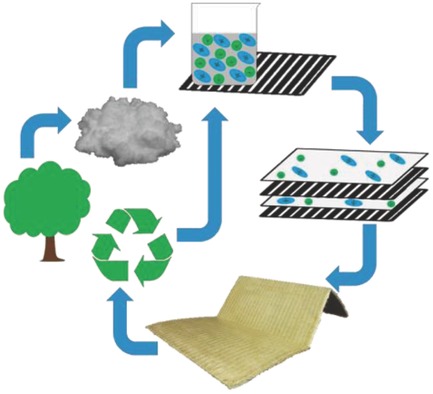
The manufacture of all-cellulose composites (ACCs) reinforced with high-strength rayon fibers is reported. Solutions of cellulose in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium acetate are used as matrix precursors. Full recycling of these ACCs is successfully demonstrated in several cycles by using the recycled material for subsequent matrix preparation without any significant loss in mechanic performance.
Tough and Enzyme-Degradable Hydrogels
- First Published: 24 July 2017
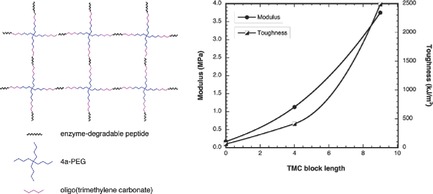
This paper describes a means of creating an enzyme-degradable hydrogel with mechanical properties approximating those of soft connective tissues such as the articular cartilage and meniscus. These properties are achieved through Michael-type addition crosslinking of a bis-cysteine peptide with a terminally acrylated 4-arm-poly(ethylene glycol) (4a-PEG)-block-oligo(trimethylene carbonate).
High-Impact Polyamide Composites with Linear Ethylene–Norbornene Anhydride Copolymers from Insertion Polymerization
- First Published: 23 August 2017
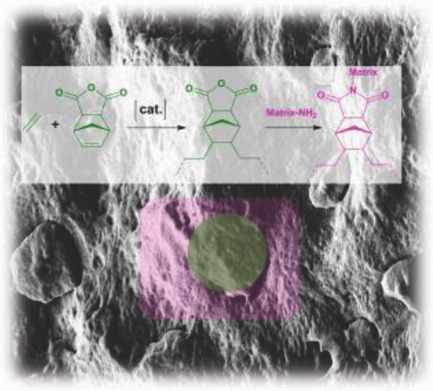
Norbornene-anhydride-functionalized linear polyethylenes from catalytic insertion copolymerization under mild conditions provide a high impact resistance to nylon-6,6 that compares favorably to existing impact modifiers, at ambient and low temperatures. Morphologies of the blends underline a strong binding between the microphases.
House of Cards Nanostructuring of Graphene Oxide and Montmorillonite Clay for Oil–Water Separation
- First Published: 28 September 2017
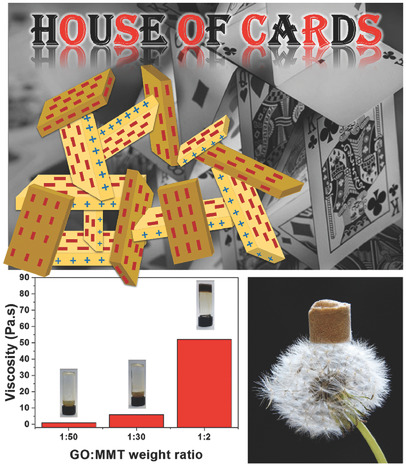
A house-of-cards structure is proposed for two different 2D nanomaterials (graphene oxide and montmorillonite) interacting electrostatically. Such behavior is manifested by a dramatic change in viscosity leading to the formation of a hydrogel, which is later used as a precursor for the fabrication of aerogels. The materials are promising for oil–spill cleanup and oil–water separation.
Soybean-Oil-Based Thermosetting Resins with Methacrylated Vanillyl Alcohol as Bio-Based, Low-Viscosity Comonomer
- First Published: 23 October 2017
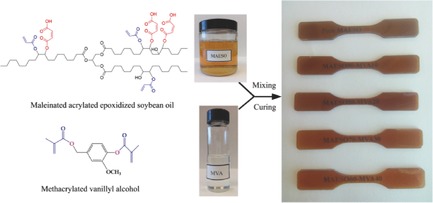
Methacrylated vanillyl alcohol (MVA) monomer shows promising results as a bio-based comonomer to replace styrene for maleinated acrylated epoxidized soybean-oil (MAESO) resins and exhibits advantages in terms of low volatility, sustainability, environmental friendliness, good processability, and improved glass transition temperature. Moreover, both methacrylated vanillyl alcohol and MAESO resin are derived from bio-based renewable resource.
Thermoplastic SEBS Elastomer Nanocomposites Reinforced with Functionalized Graphene Dispersions
- First Published: 08 December 2017
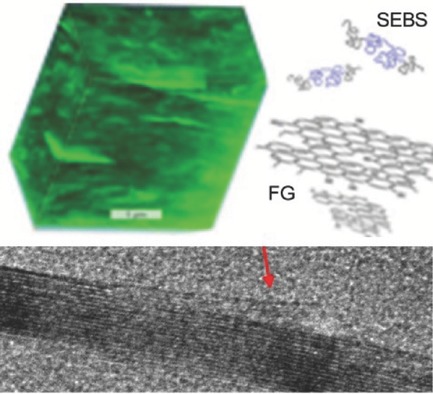
Blending polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene-r-butylene)-b-polystyrene (SEBS) elastomer with functionalized graphene (FG) dispersions in tetrahydrofuran prior to melt processing enables uniform dispersion of single- and few-layer FG, whereas nonfunctionalized graphite yields larger graphene stacks together with micrometer-sized graphite. SEBS/FG composites exhibit superior mechanical properties with higher Shore A hardness, electrical conductivity at a lower percolation threshold, and enhanced gas barrier resistance.
Control of Pore Structure in Polymeric Monoliths Prepared from Colloidal Dispersions
- First Published: 06 December 2017
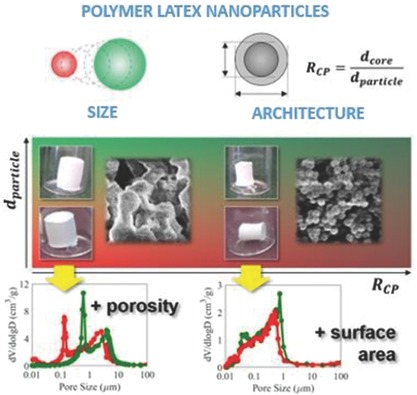
Primary nanoparticle architecture, size, and initial concentration have a high impact on the mechanical stability and morphology of polymeric materials produced from colloidal dispersion via reactive gelation. Appropriately tuning those parameters allows the reliable control on the pore size distribution and the production of highly porous materials.
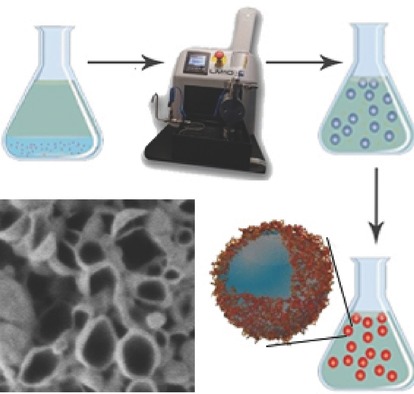
Large-Scale Preparation of Polymer Nanocarriers by High-Pressure Microfluidization
- First Published: 14 December 2017