Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 12/2017
- First Published: 13 December 2017

Front Cover: The reactive plasticization of polylactide with acrylated poly(ethylene glycol) (acrylPEG) forms grafted inclusions inside the matrix. The inclusions exhibit a core-shell structure, where the core consisted of less dense poly(acrylPEG) than the shell. Upon drawing, the inclusions are stretched, and submicron cracks form between inclusions. This is reported by Berit Brüster, Camilo Amozoqueño, Patrick Grysan, Inma Peral, Benjamin Watts, Jean-Marie Raquez, Philippe Dubois, and Frédéric Addiego, article number 1700326.
Masthead
Contents
Communications
Electrothermal Actuator on Graphene Bilayer Film
- First Published: 17 October 2017
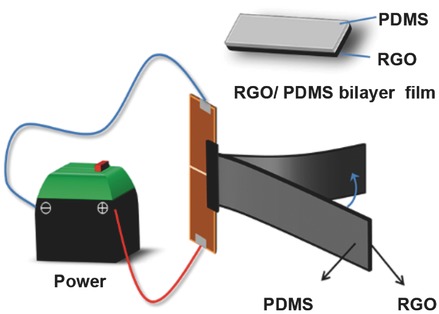
Electric current generated Joule heating on a graphene bilayer film subsequently results in the expansion and bending of the bilayer film, which achieves electrical-to-mechanical energy transition of a smart actuator. Various actuation modes are demonstrated by the bilayer structure design and the electric current controlling.
Key Production Parameters to Obtain Transparent Nanocellular PMMA
- First Published: 17 October 2017

Transparent nanocellular polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) is produced for the first time. The key parameters needed for its production are low saturation temperatures (−32 °C) combined with high saturation pressures (6–20 MPa). The materials obtained by using this method present high homogeneous cellular structure, with cell nucleation densities higher than 1016 nuclei cm−3 and cell sizes clearly below 50 nm.
Inkjet Printing Based Layer-by-Layer Assembly Capable of Composite Patterning of Multilayered Nanofilms
- First Published: 10 November 2017
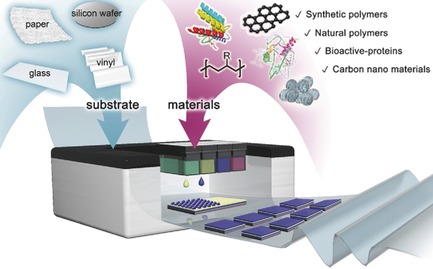
Multilayered nanofilms with various functional materials (synthetic and natural polymer, protein, and graphene) are fabricated by integrating layer-by-layer assembly and inkjet printing. Thickness, roughness, combinations, structures, and shapes of the nanofilms are desirably controllable. In addition, the printed nanofilms are deposited on several substrates ranging from silicon wafer to paper.
Gel Electrolytes of Covalent Network Polybenzimidazole and Phosphoric Acid by Direct Casting
- First Published: 13 November 2017
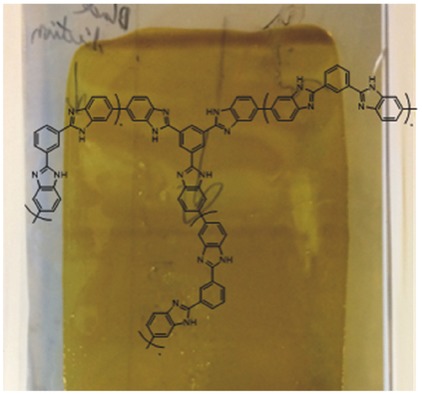
Covalent network polybenzimidazole membranes are obtained via a novel sequential direct casting procedure. Free-standing and mechanically robust gel electrolytes are obtained with phosphoric acid contents of up to 95 wt%. It supports high proton conductivity at temperatures well above 100 °C as ultimately manifested by low internal resistance in fuel cells operating at 180 °C.
Full Papers
Resolving Inclusion Structure and Deformation Mechanisms in Polylactide Plasticized by Reactive Extrusion
- First Published: 14 November 2017
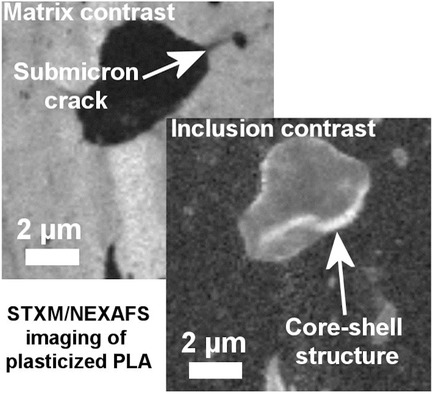
The reactive plasticization of polylactide with acrylated poly(ethylene glycol) (acrylPEG) forms grafted inclusions inside the matrix. The inclusions exhibit a core–shell structure, where the core consisted of less dense poly(acrylPEG) than the shell. Upon drawing, the inclusions are stretched, while their density decreases at the shell and core regions. At the same time, sub-micrometer cracks form between inclusions.
Carboxylated Lignin as an Effective Cohardener for Enhancing Strength and Toughness of Epoxy
- First Published: 12 October 2017
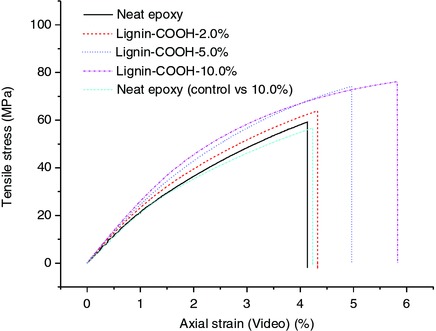
Cured epoxy incorporated with carboxylic acid–modified kraft lignin as a cohardener at moderate loading contents exhibits simultaneous enhancement of tensile modulus, flexural modulus, tensile strength, and toughness, which can promote the utilization of this sustainable biomass as an alternative feedstock in practical thermosetting applications in terms of substituting petrochemical product.
Relaxation Dynamics and Strain Persistency of Azobenzene-Functionalized Polymers and Actuators
- First Published: 23 October 2017
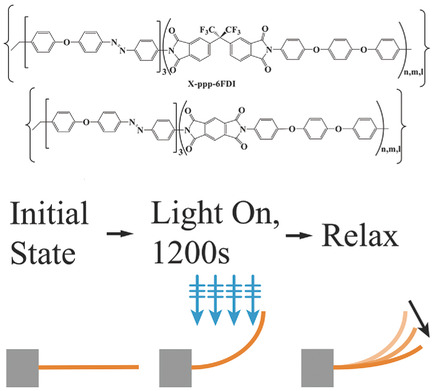
Understanding the relaxation dynamics and strain persistency in photomechanical polymers is crucial to the development of these materials for functional devices. The relaxation of five azobenzene functionalized polyimides after irradiation with blue light is studied. A finite element model coupling chromophore population dynamics to material strain is used to clarify the material behavior and to explore a bistable actuator concept.
Preparation of Hollow Fiber Membranes by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation along with Hydrogen Gas Formation Using a Single Orifice Spinneret
- First Published: 23 October 2017
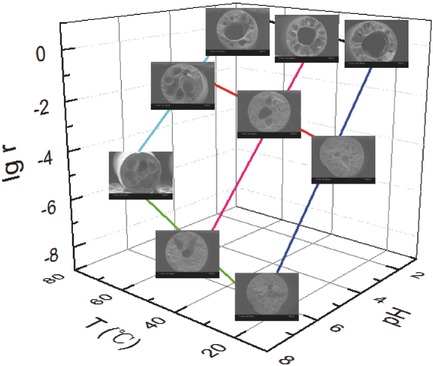
A direct spinning method is reported for fabricating hollow fiber membranes through feeding a polymer solution containing gas producing agent with a single orifice spinneret. Effects of concentration of polysulfone dope, temperature, and pH of coagulant bath on structure and performance of the hollow fiber membranes (HFMs) are investigated. The prepared HFMs show promising application for dyes separation.
Effect of Draw Ratio on Physical, Release, and Antibacterial Properties of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Loaded with Lysozyme
- First Published: 14 November 2017
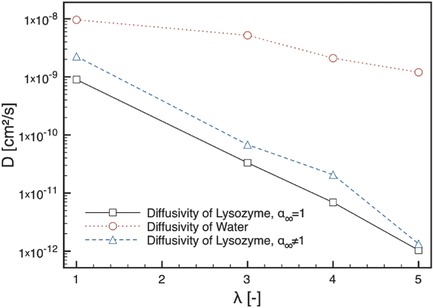
Poly(ε-caprolactone) and lysozyme are submitted to draw processing at different draw ratios. The release of lysozyme is studied and found dependent on the draw ratio. The relationship between release rate and antimicrobial activity is also investigated. The macromolecular chain orientation is demonstrated to be an interesting and easy tool for the achievement of desired controlled release systems.
Initiated-Chemical Vapor Deposition of Polymer Thin Films: Unexpected Two-Regime Growth
- First Published: 11 October 2017
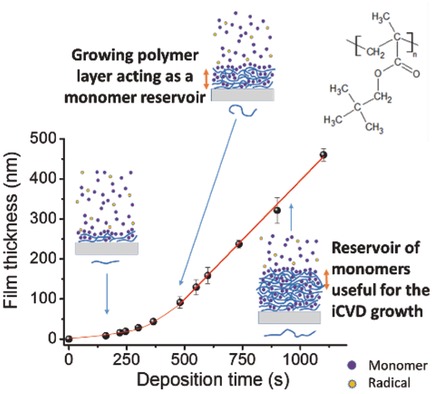
The initiated chemical vapor deposition of poly(meth)acrylate-based thin films follows surprisingly a two-regime growth. This paper provides an explanation based on a combination of an experimental study of the polymer thin films properties as a function of deposition time and film thickness and a simple model taking into account the local increase of the concentration of monomers available for the polymerization.
Influence of the Hydrophobic–Hydrophilic Nature of Biomedical Polymers and Nanocomposites on In Vitro Biological Development
- First Published: 10 November 2017
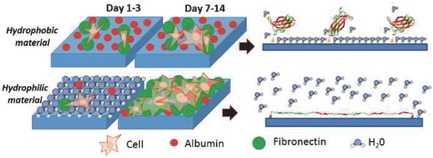
Studying the biological development and compatibility, this original research shows, as at the initial stage, the cell proliferation is greater on hydrophobic materials (poly(ε-caprolactone)-poly(lactic acid)), but over longer stage, cell proliferation is greater on hydrophilic materials (poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-ethyl methacrylate). This effect is improved with the creation of composites using hydroxyapatite and halloysite nanotubes.
Mechanical and Rheological Behavior of Hybrid Cross-Linked Polyacrylamide/Cationic Micelle Hydrogels
- First Published: 10 November 2017
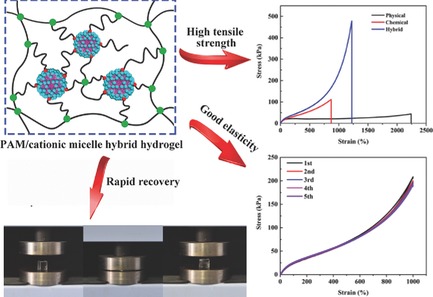
A hybrid cross-linked polyacrylamide/cationic micelle hydrogel is fabricated by in situ free radical polymerization, and cationic micelles act as physical cross-linking points in the chemically cross-linked polyacrylamide. The introduction of cationic micelles can consummate effectively the network structure, contributing to the excellent mechanical properties of the hybrid hydrogels. This provides a different view for the design of high elastic and tough hydrogels.
Semicrystalline Shape-Memory Elastomers: Effects of Molecular Weight, Architecture, and Thermomechanical Path
- First Published: 14 November 2017
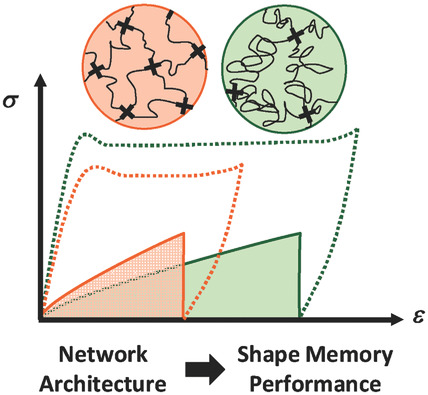
The effect of architecture and molecular weight on shape-memory performance is examined for a series of poly(caprolactone) networks prepared using thiol–ene click chemistry. A sample's thermomechanical history, especially cold drawing, is shown to have a significant impact on shape-memory fixity and the amount of recoverable elastic energy.
Surface Modification of Carbon Fibers by Free Radical Graft-Polymerization of 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate for High Mechanical Strength Fiber–Matrix Composites
- First Published: 12 October 2017
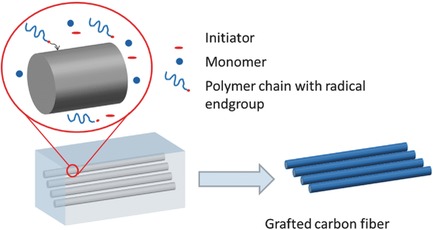
Free radical graft polymerization of vinylic monomers to carbon fibers is described. Grafting with hydroxyethyl methacrylate allows for the introduction of polar groups suitable for the reaction with an epoxy-based resin. The corresponding composites show improved mechanical properties compared to composites prepared from carbon fibers equipped with standard sizing: tensile strength increases by 10%, interlaminar shear strength improves by 20%.






