Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Association between genetic variants of transmembrane transporters and susceptibility to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: Current understanding and existing evidence
- Pages: 115-129
- First Published: 14 November 2023

The majority of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with anthracycline pharmacogenomics were identified in the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) and solute carrier (SLC) transporters, generating increasing interest in the pharmacogenetic implications of their genetic variations for anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC). The asterisk (*) highlights the extensively studied genetic variant associated with anthracycline transport. Specifically, the SLC28A3 rs7853758 variant has been employed in clinical practice to predict the risk of developing AIC.
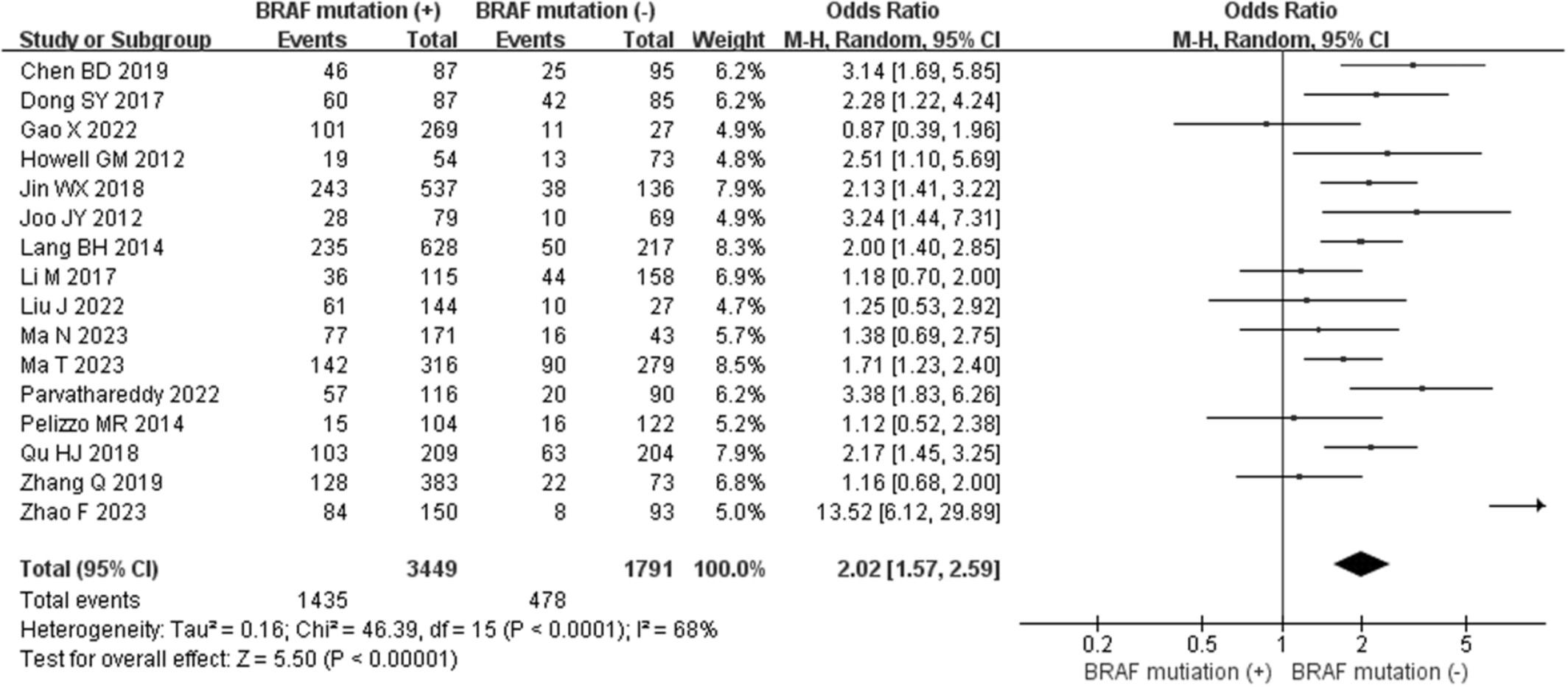
Gene mutations as predictors of central lymph mode metastasis in cN0 PTC: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 130-139
- First Published: 20 November 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
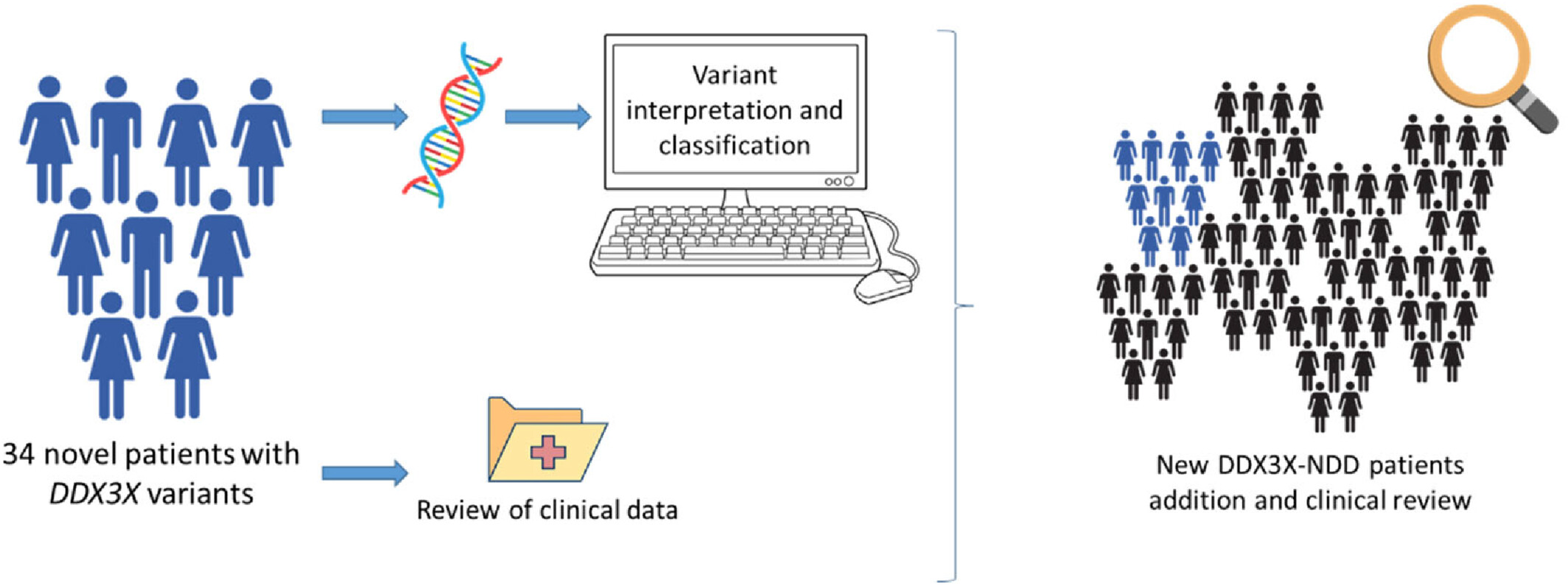
Genetic and phenotypic findings in 34 novel Spanish patients with DDX3X neurodevelopmental disorder
- Pages: 140-149
- First Published: 30 October 2023
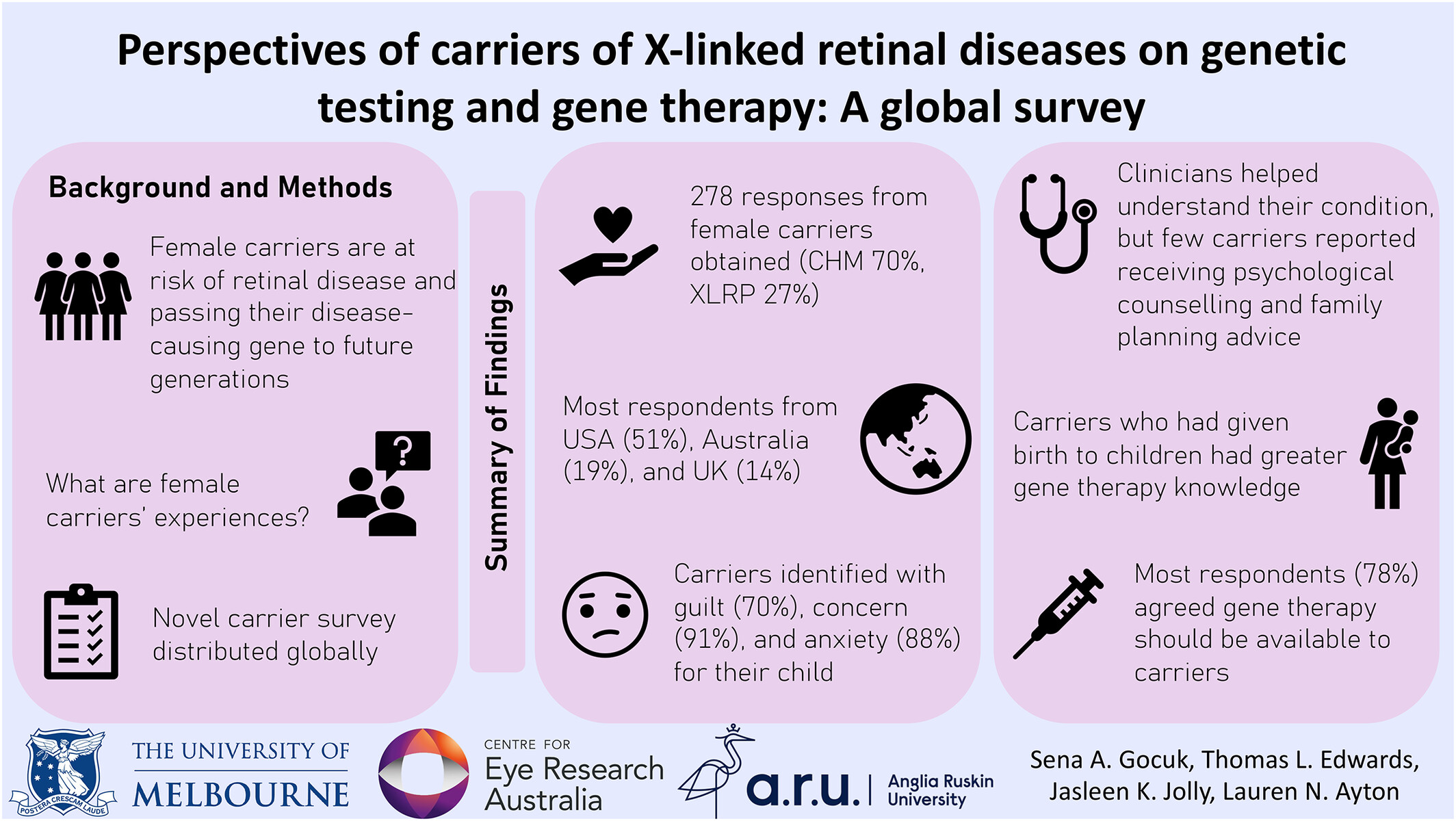
Perspectives of carriers of X-linked retinal diseases on genetic testing and gene therapy: A global survey
- Pages: 150-158
- First Published: 20 October 2023
Rigorous evaluation of genetic and epigenetic effects on clinical laboratory measurements using Japanese monozygotic twins
- Pages: 159-172
- First Published: 29 October 2023
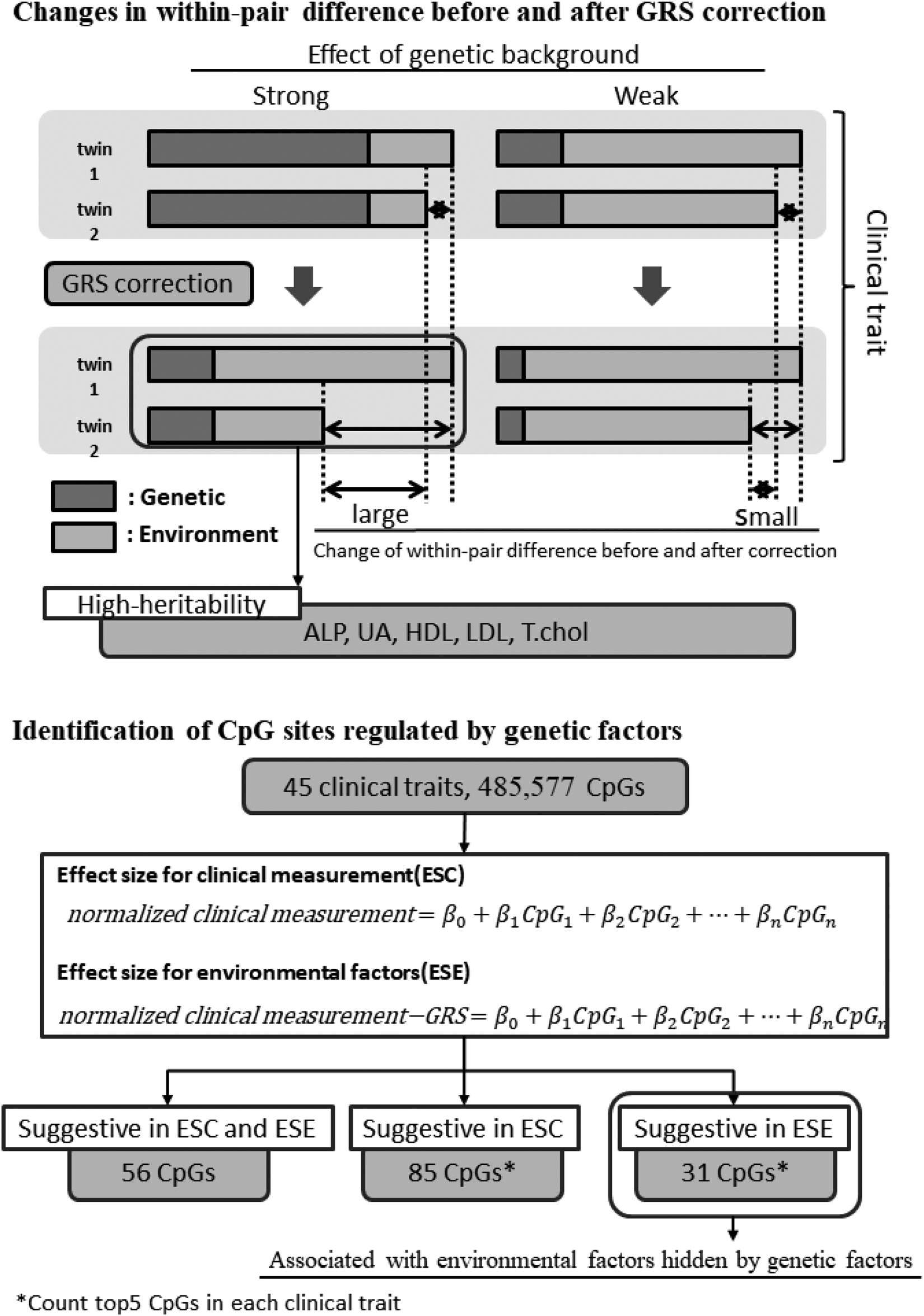
Monozygotic twin samples showed that five clinical measurements were strongly genetically affected. CpG sites are classified into three groups: regulated only by environmental factors, by environmental factors masked by genetic factors, and only by genetic factors. Our method has the potential to identify trait-related methylation sites.
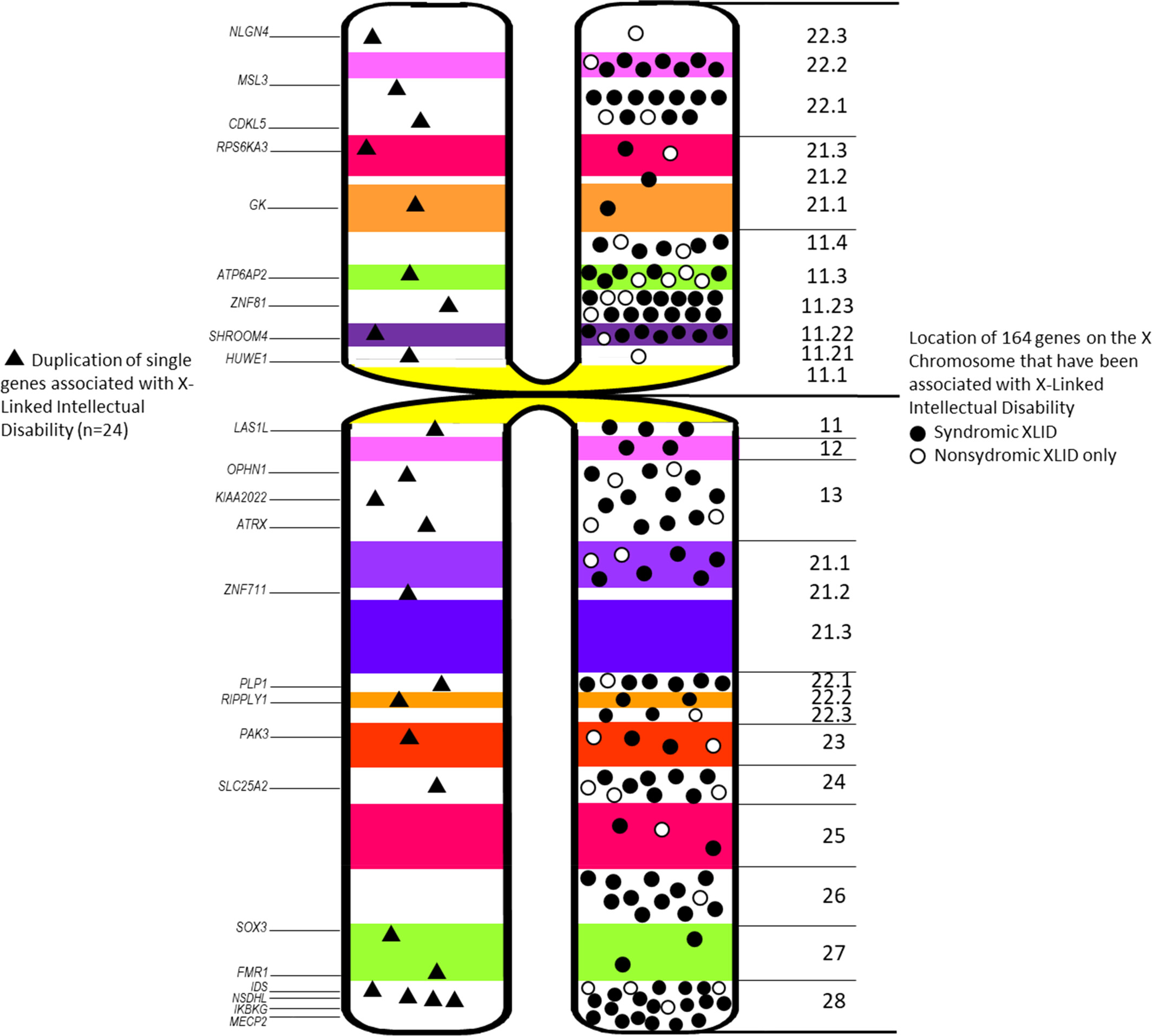
Clinical findings in individuals with duplication of genes associated with X-linked intellectual disability
- Pages: 173-184
- First Published: 29 October 2023
SHORT REPORTS
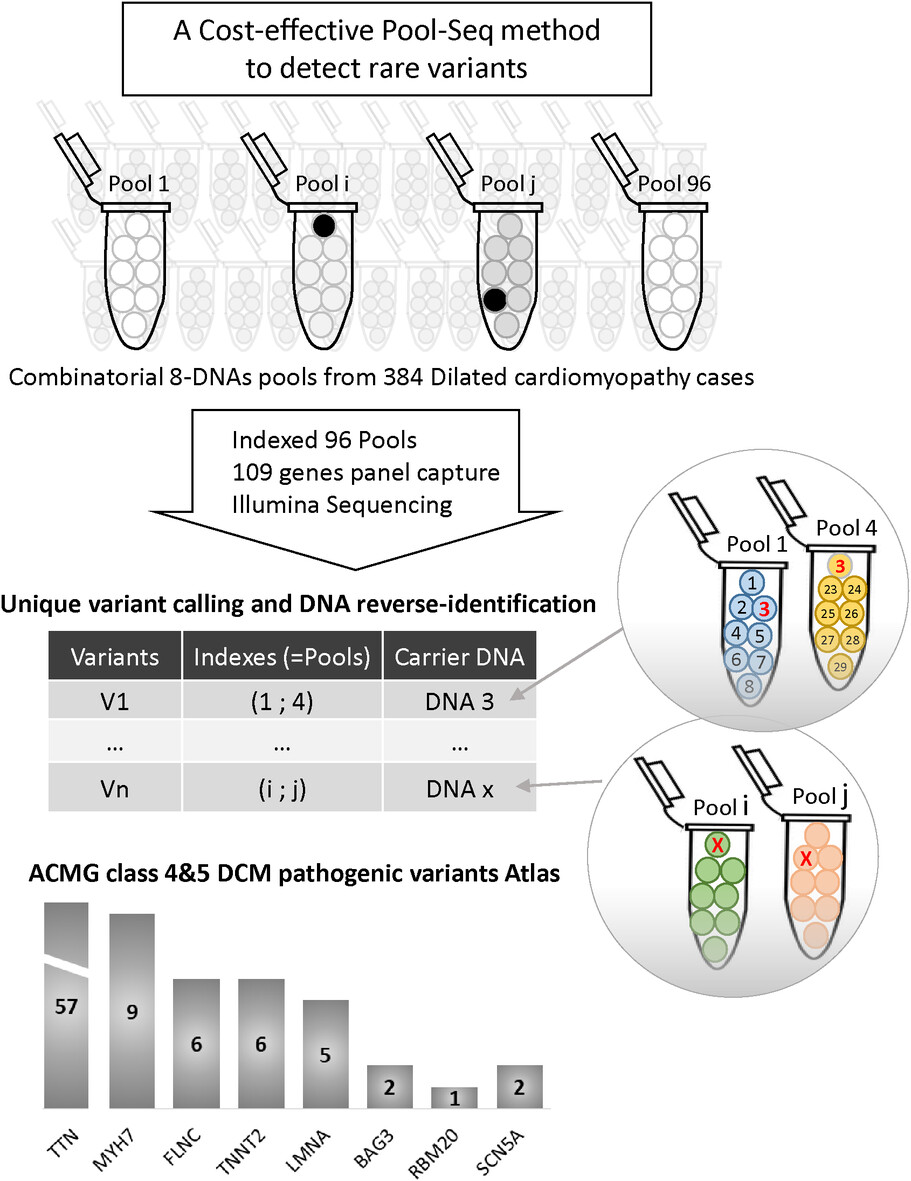
DNA-pools targeted-sequencing as a robust cost-effective method to detect rare variants: Application to dilated cardiomyopathy genetic diagnosis
- Pages: 185-189
- First Published: 30 October 2023
A novel non-recurrent CNV deletion involving TBX4 and leaving TBX2 intact causes congenital alveolar dysplasia
- Pages: 190-195
- First Published: 11 October 2023
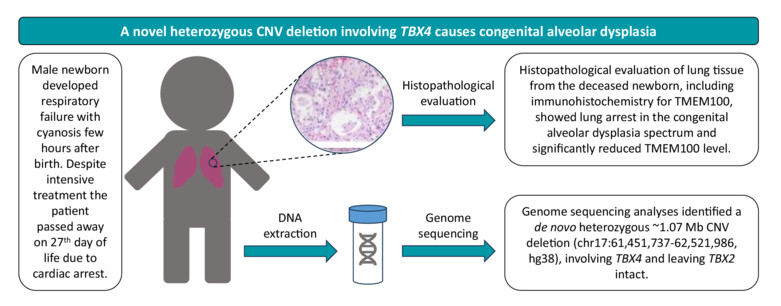
We describe a male neonate who died at 27 days of life from acute respiratory distress caused by lung growth arrest along the spectrum of congenital alveolar dysplasia confirmed by histopathological assessment. Trio-based genome sequencing revealed in the proband a de novo heterozygous ~1.07 Mb CNV deletion at 17q23.2, encompassing TBX4.
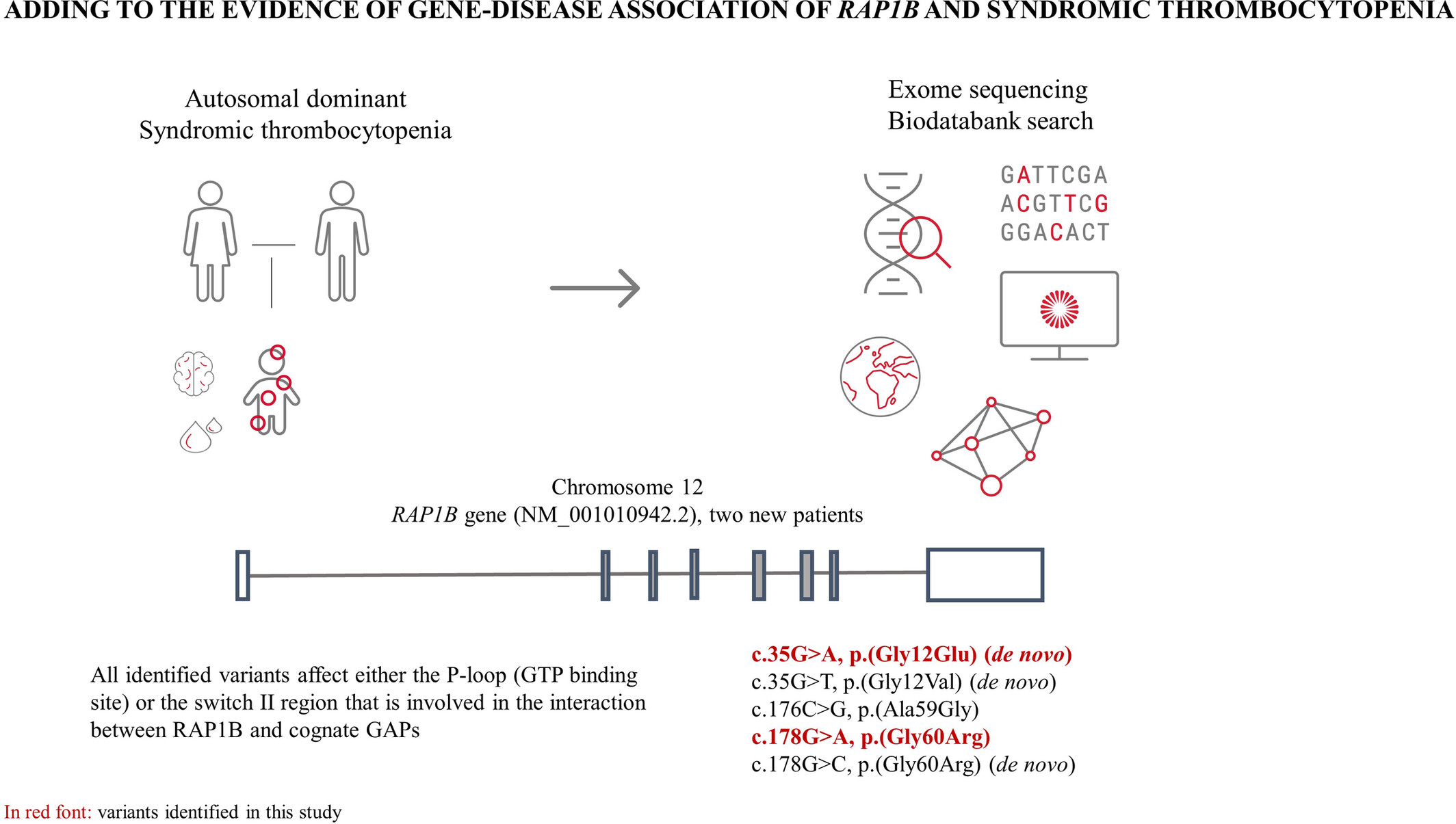
Adding to the evidence of gene-disease association of RAP1B and syndromic thrombocytopenia
- Pages: 196-201
- First Published: 18 October 2023
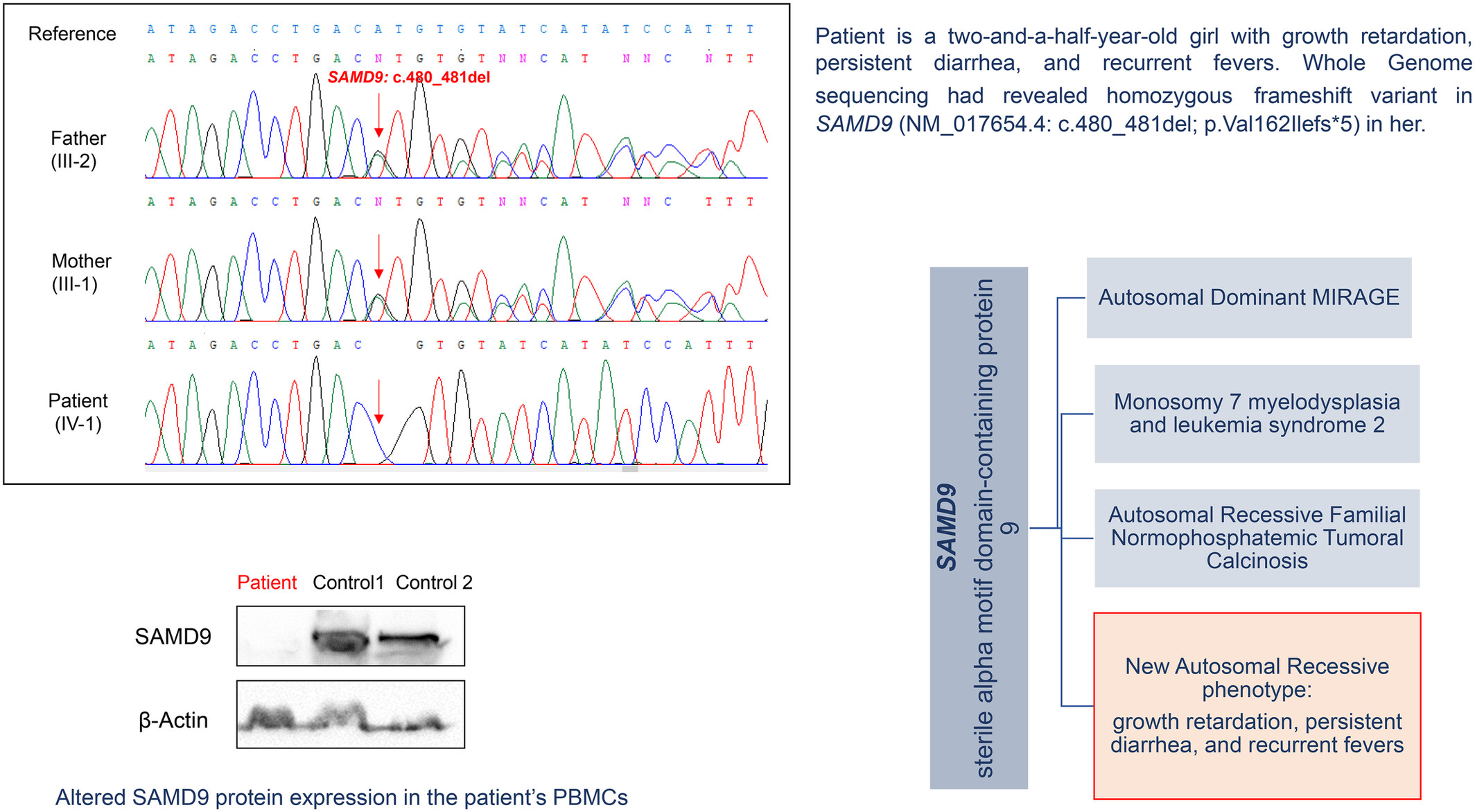
A homozygous frameshift variant expands the clinical spectrum of SAMD9 gene defects
- Pages: 202-208
- First Published: 13 October 2023
The third case of Marbach-Rustad progeroid syndrome caused by a de novo LEMD2 variant
- Pages: 209-213
- First Published: 23 October 2023
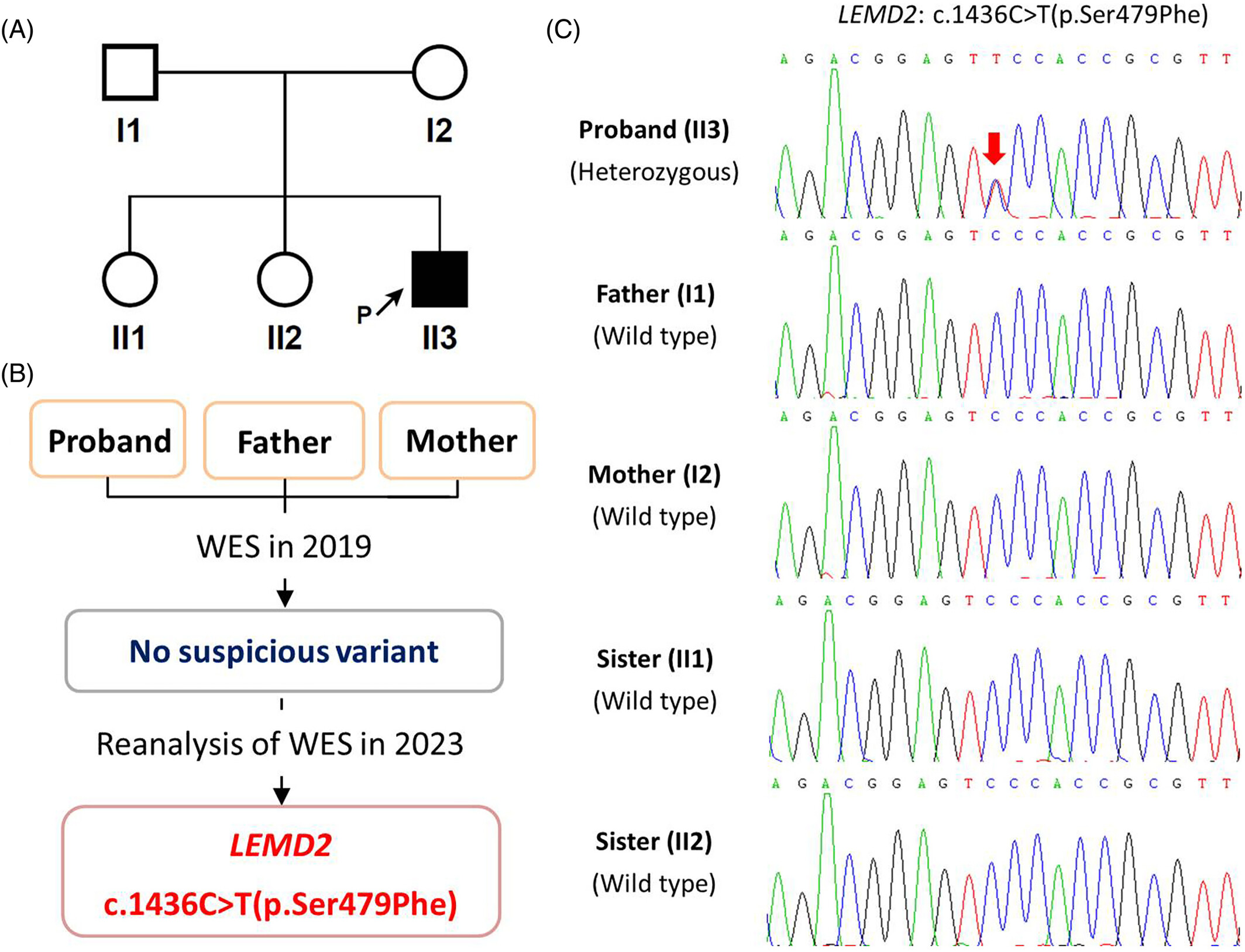
The third case of Marbach-Rustad progeroid syndrome. (A) The family pedigree. (B) Whole exome sequencing (WES) in 2019 did not find a suspicious variant, whereas reanalysis in 2023 revealed LEMD2 c.1436C>T(p.Ser479Phe) variant as the cause. (C) Sanger sequencing confirmed the de novo LEMD2 c.1436C>T(p.Ser479Phe) heterozygous variant in the proband.
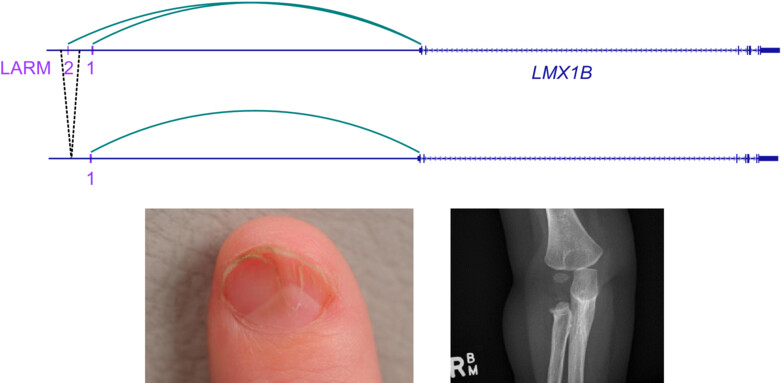
De novo enhancer deletion of LMX1B produces a mild nail-patella clinical phenotype
- Pages: 214-219
- First Published: 29 October 2023
A splice donor variant of GAS8 induces structural disorganization of the axoneme in sperm flagella and leads to nonsyndromic male infertility
- Pages: 220-225
- First Published: 11 November 2023
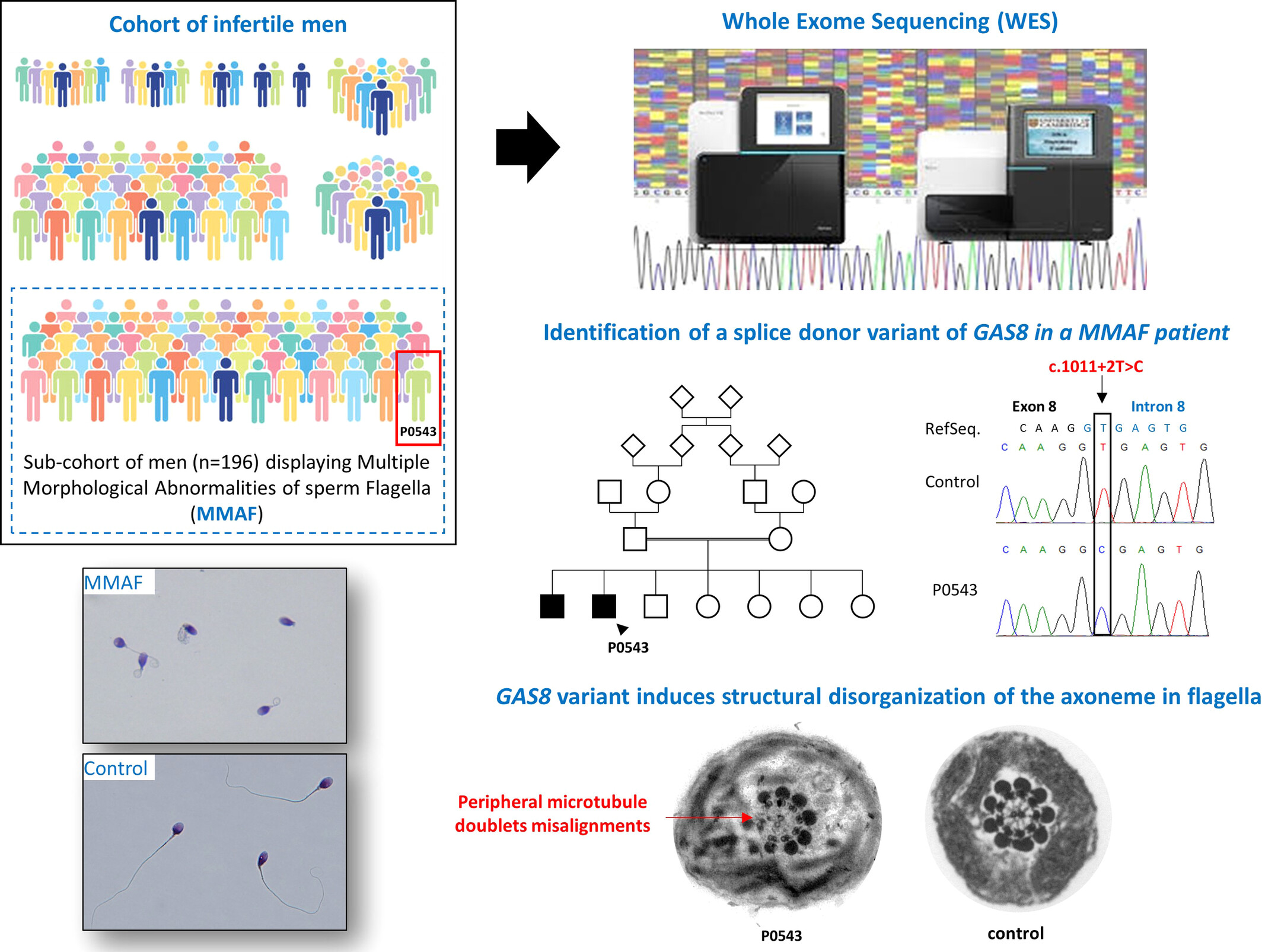
From a large cohort of infertile men, we focused on a subcohort of 196 men displaying asthenozoospermia due to multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella (MMAF). Whole exome sequencing (WES) data analysis allowed the identification of rare homozygous splicing variant in GAS8, disrupting the nexin-dynein regulatory complex (N-DRC) and inducing a severe disorganisation of the axoneme in sperm flagella.
RESEARCH LETTERS
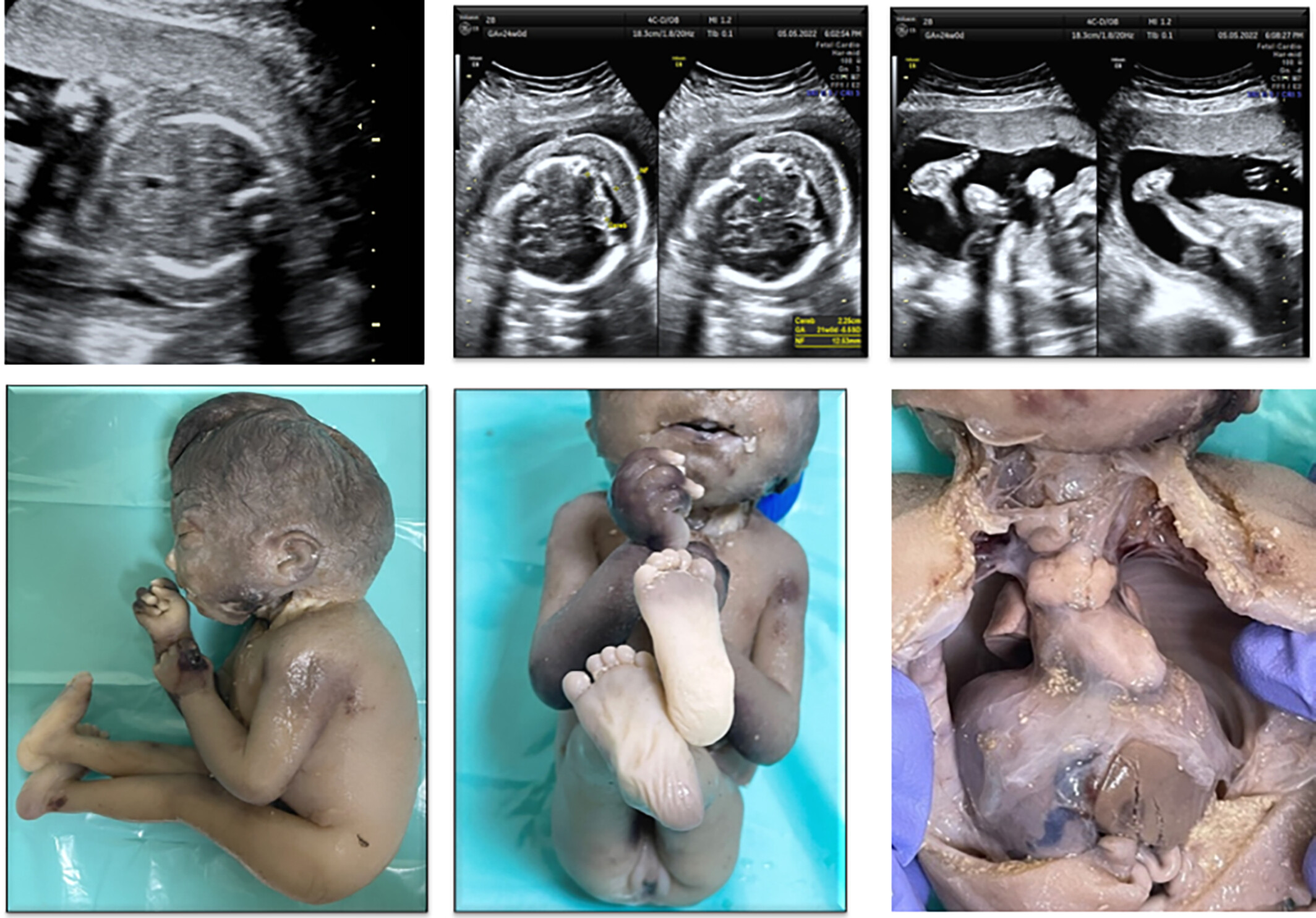
Variants in DOK7 results in fetal akinesia deformation sequence: A case report and review of literature
- Pages: 226-227
- First Published: 17 October 2023
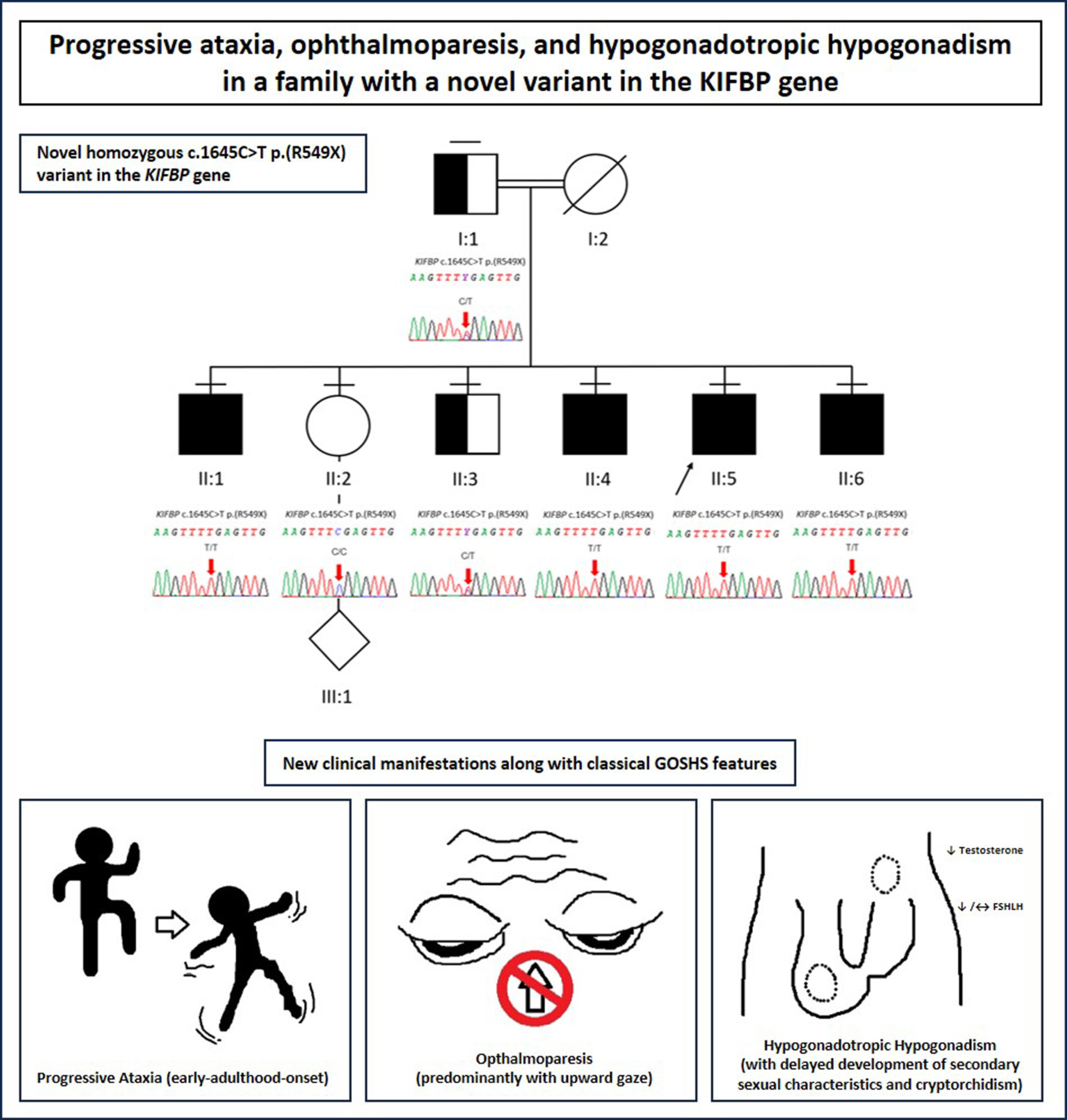
Progressive ataxia, ophthalmoparesis, and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in a family with a novel variant in the KIFBP gene
- Pages: 228-230
- First Published: 30 October 2023