Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
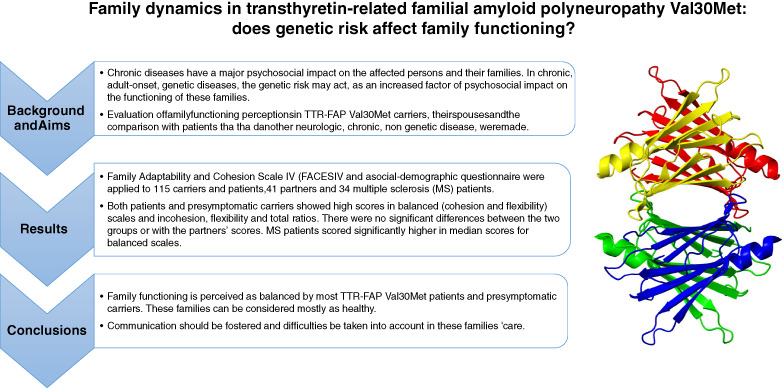
Family dynamics in transthyretin-related familial amyloid polyneuropathy Val30Met: Does genetic risk affect family functioning?
- Pages: 401-408
- First Published: 18 July 2018
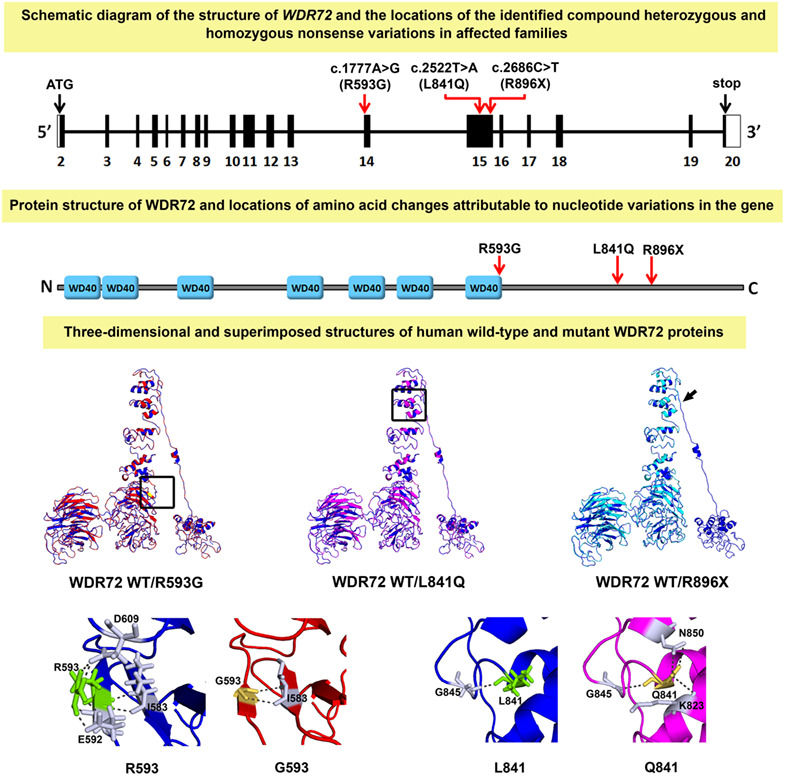
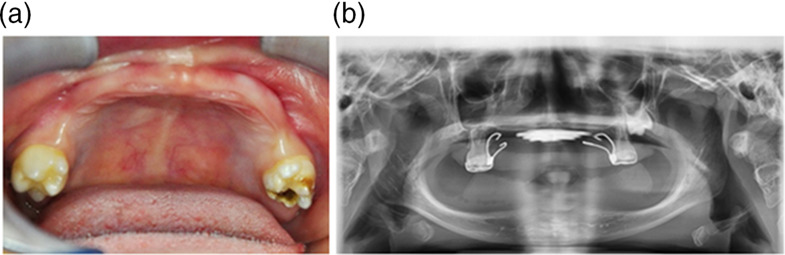
Distal renal tubular acidosis caused by tryptophan-aspartate repeat domain 72 (WDR72) mutations
- Pages: 409-418
- First Published: 20 July 2018
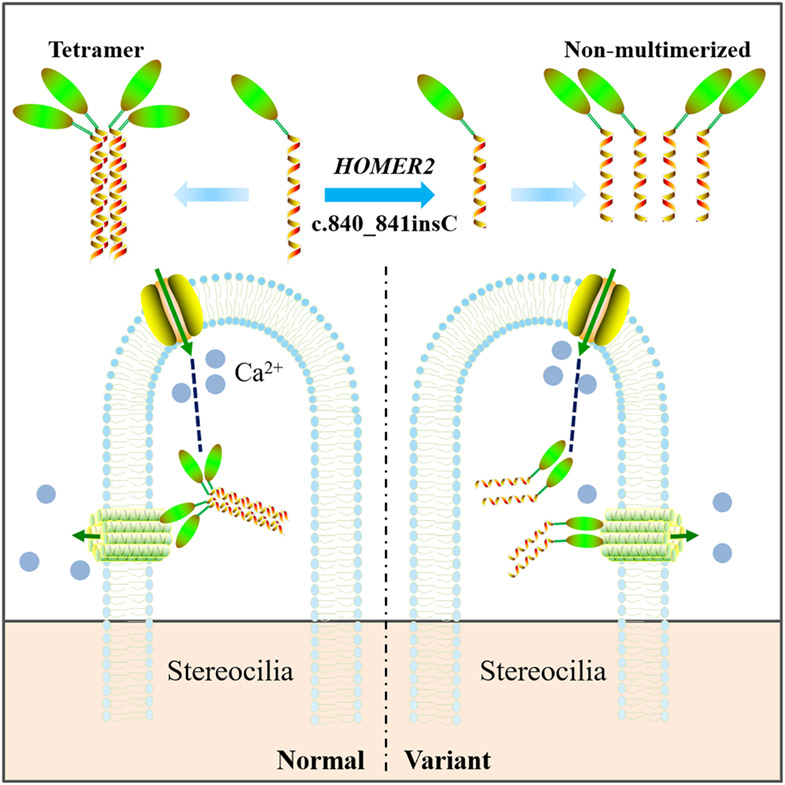
Whole exome sequencing identified a second pathogenic variant in HOMER2 for autosomal dominant non-syndromic deafness
- Pages: 419-428
- First Published: 26 July 2018
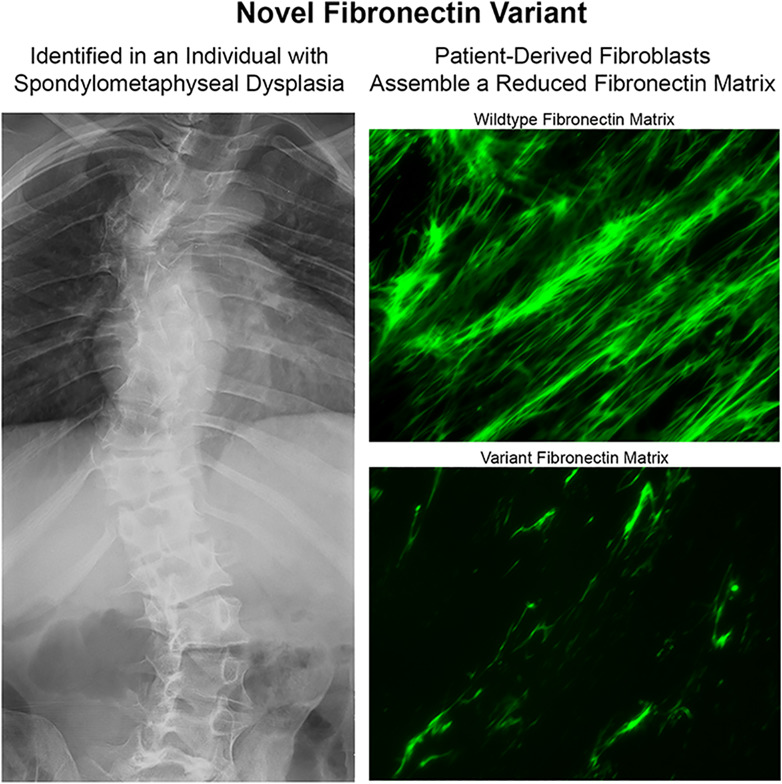
Mechanistic insights into the cellular effects of a novel FN1 variant associated with a spondylometaphyseal dysplasia
- Pages: 429-437
- First Published: 26 July 2018
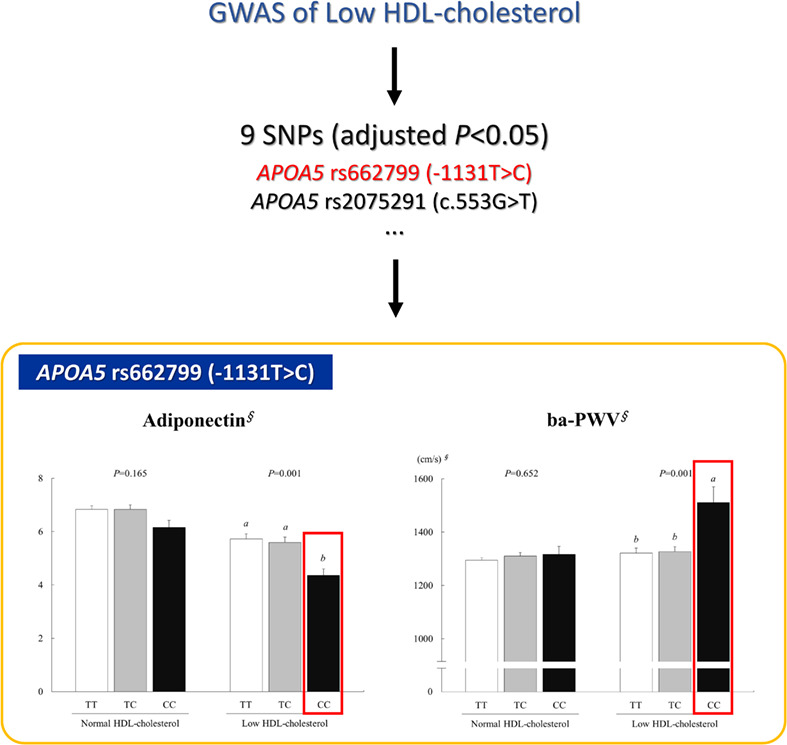
Apolipoprotein A5 gene variants are associated with decreased adiponectin levels and increased arterial stiffness in subjects with low high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol levels
- Pages: 438-444
- First Published: 22 August 2018
SHORT REPORTS
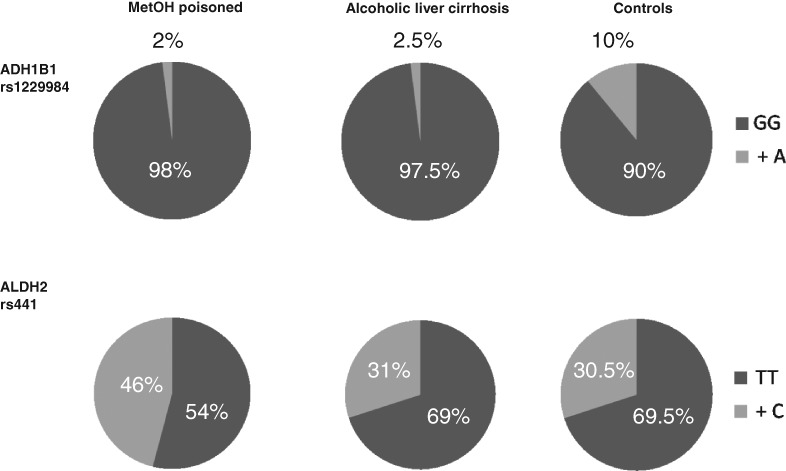
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 polymorphism affects the outcome of methanol poisoning in exposed humans
- Pages: 445-449
- First Published: 02 July 2018
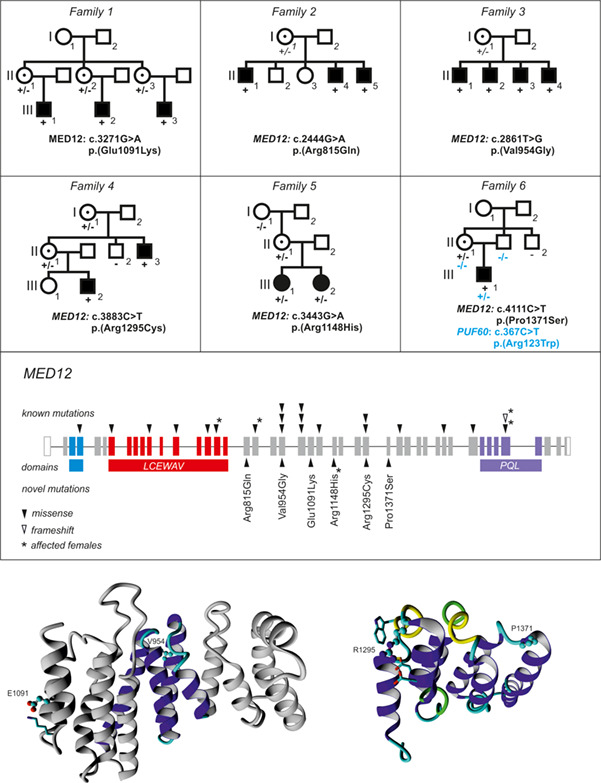
The power of the Mediator complex—Expanding the genetic architecture and phenotypic spectrum of MED12-related disorders
- Pages: 450-456
- First Published: 13 July 2018
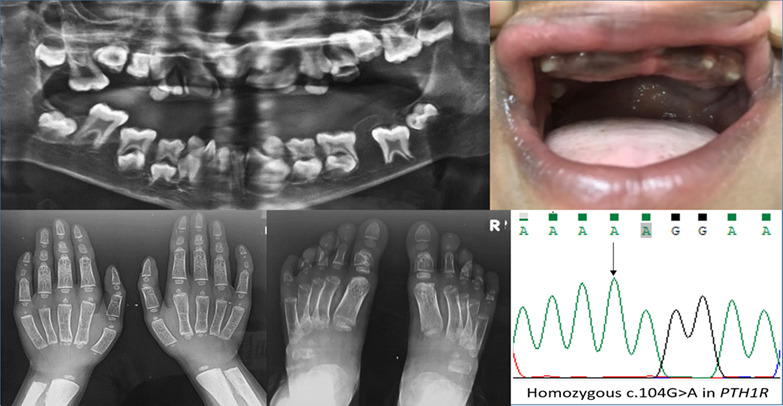
Report of second case and clinical and molecular characterization of Eiken syndrome
- Pages: 457-460
- First Published: 10 July 2018
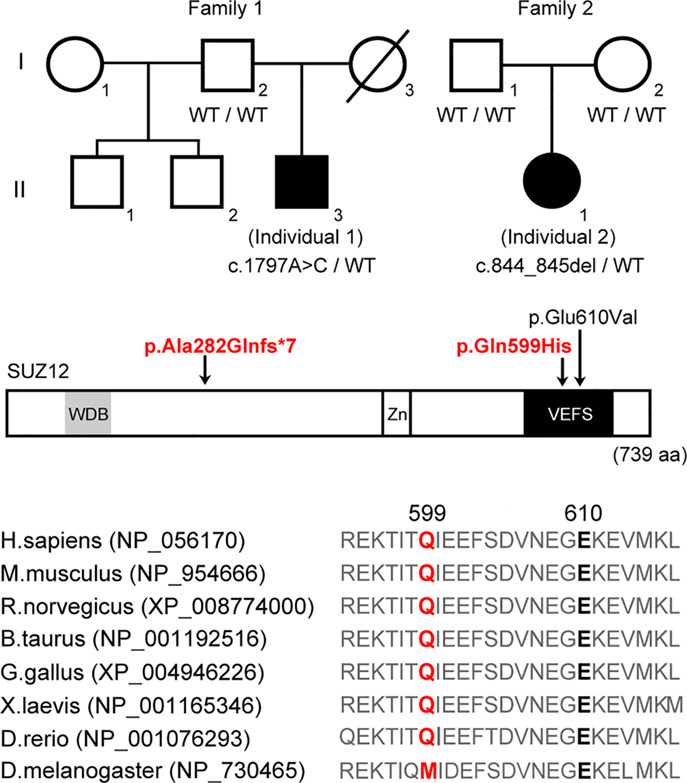
Novel SUZ12 mutations in Weaver-like syndrome
- Pages: 461-466
- First Published: 18 July 2018
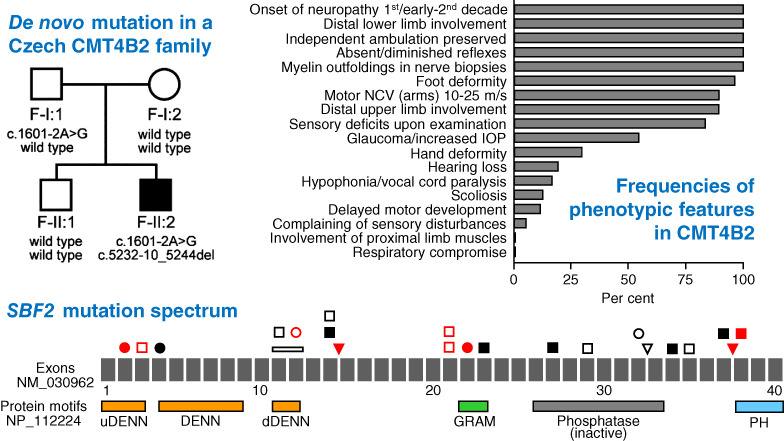
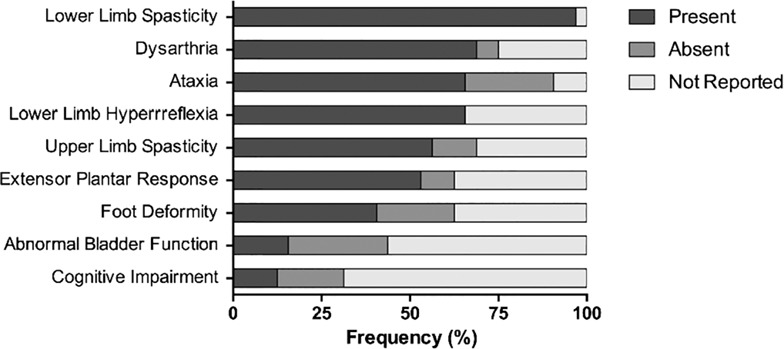
Novel SBF2 mutations and clinical spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 4B2
- Pages: 467-472
- First Published: 20 July 2018
Novel SBF1 splice-site null mutation broadens the clinical spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B3 disease
- Pages: 473-479
- First Published: 24 July 2018
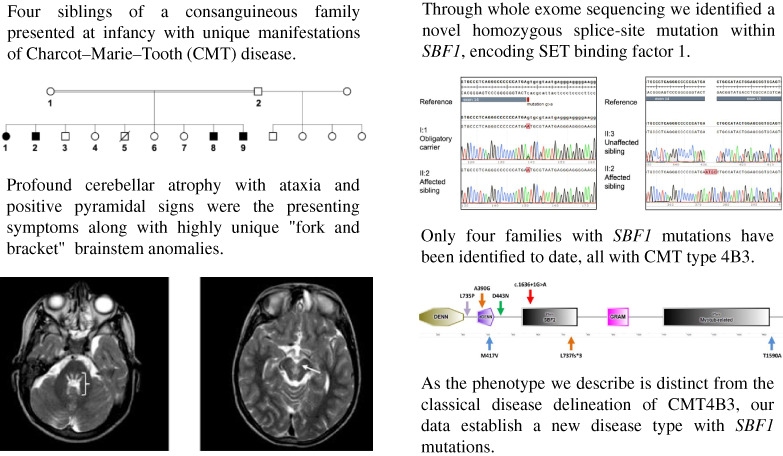
Four siblings of a consanguineous family presented at infancy with unique manifestations of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. Profound cerebellar atrophy with ataxia and positive pyramidal signs were the presenting symptoms along with highly unique “fork and bracket” brainstem anomalies. Through whole exome sequencing, we identified a novel homozygous splice-site mutation within SBF1, encoding SET binding factor 1. Only four families with SBF1 mutations have been identified to date, all with CMT type 4B3. As the phenotype we describe is distinct from the classical disease delineation of CMT4B3, our data establish a new disease type with SBF1 mutations.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
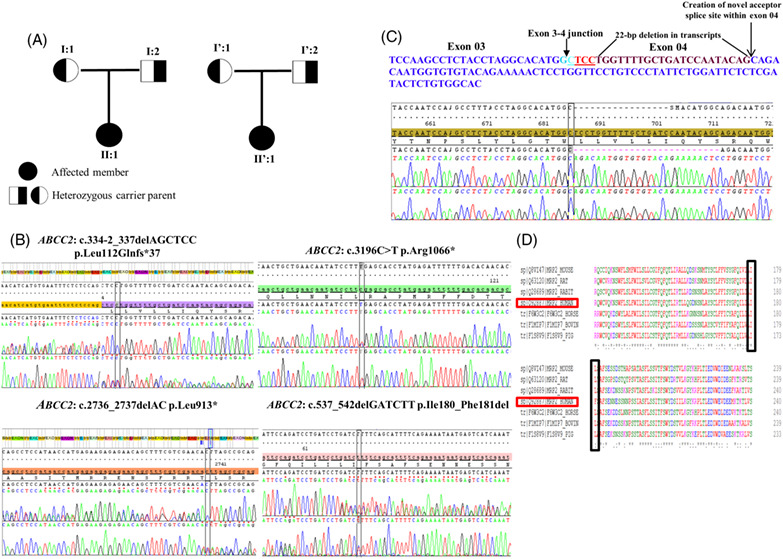
Novel compound heterozygous ABCC2 variants in patients with Dubin-Johnson syndrome and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- Pages: 480-481
- First Published: 09 August 2018
Clinical aspects of hereditary spastic paraplegia 76 and novel CAPN1 mutations
- Pages: 482-483
- First Published: 10 September 2018
Clinical, radiographic, and genetic characteristics of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: A cross-sectional study
- Pages: 484-486
- First Published: 07 September 2018
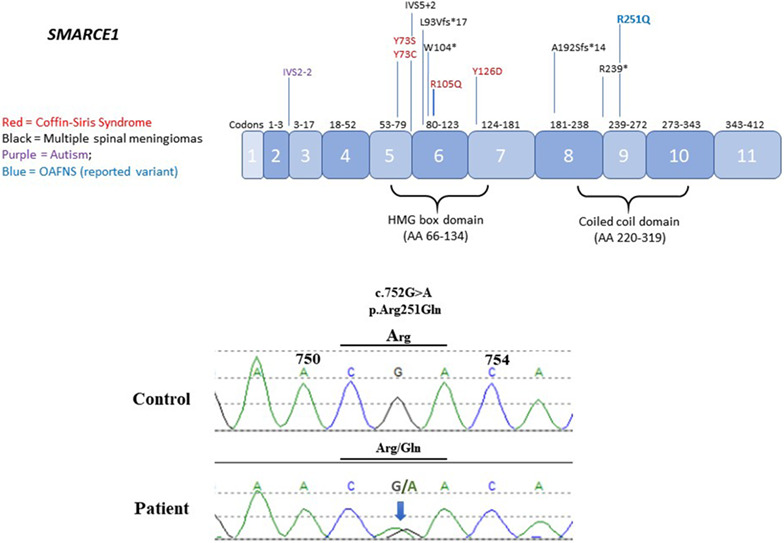
New SMARCE1 variant in a patient with features overlapping with oculoauriculofrontonasal syndrome
- Pages: 487-488
- First Published: 12 September 2018
Androgen receptor mRNA analysis from whole blood: a low-cost strategy for detection of androgen receptor gene splicing defects
- Pages: 489-490
- First Published: 07 September 2018
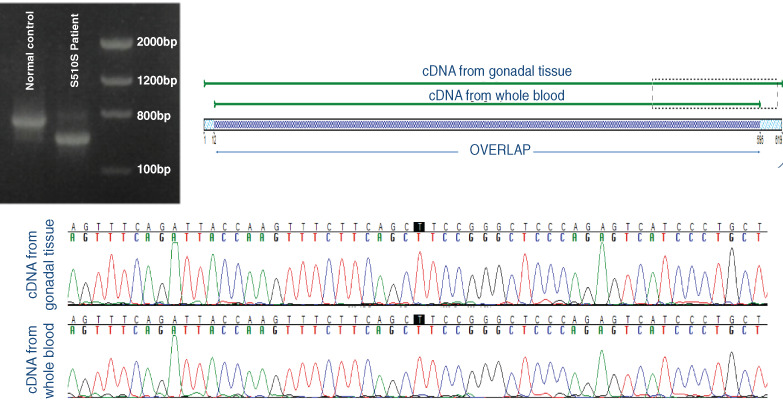
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) is caused by defects in the androgen receptor (AR) gene and is the most common aetiology of 46,XY disorders of sex development. Allelic variants in the AR gene are found in 90% of complete AIS (CAIS), but in only 28% to 50% of cases of partial AIS. Even a single nucleic acid change can disrupt splicing sites or splicing regulatory sequences, resulting in inadequate exon and intron recognition, ultimately leading to an aberrant transcript. Therefore, we tested the feasibility of conducting AR cDNA analysis from whole blood and from gonadal tissue in a patient with CAIS due to AR synonymous mutation (c.1530C > T, p.Ser510Ser; NM_000044.3), which led to an aberrant splicing site causing deletion of 92 nucleotides resulting in a very short transcript. AR cDNA sequencing was similar in the whole blood and in the gonadal tissue, with similar evidence of a consequent altered AR transcript. We propose that analysis of AR RNA extracted from whole blood with AR DNA sequencing can help to improve the frequency of molecular diagnosis, particularly for partial AIS.
CORRIGENDUM
Correction to: Polymorphisms of genes involved in inflammation and blood vessel development influence the risk of varicose veins
- Page: 491
- First Published: 08 October 2018