Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - COVER AND EDITORIAL BOARD
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE: GRAPHICAL ABSTRACTS
In this issue: Graphical abstract
- Pages: 7-14
- First Published: 29 December 2021
EDITORIAL
GUIDELINES
EAACI Biologicals Guidelines—Omalizumab for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria in adults and in the paediatric population 12–17 years old
- Pages: 17-38
- First Published: 29 July 2021

EAACI POSITION PAPER
Hypersensitivity reactions to biologicals: An EAACI position paper
- Pages: 39-54
- First Published: 22 June 2021

One Health: EAACI Position Paper on coronaviruses at the human-animal interface, with a specific focus on comparative and zoonotic aspects of SARS-CoV-2
- Pages: 55-71
- First Published: 28 June 2021

REVIEW ARTICLES
Regulatory concepts to guide and promote the accelerated but safe clinical development and licensure of COVID-19 vaccines in Europe
- Pages: 72-82
- First Published: 22 April 2021
The ingenious mast cell: Contemporary insights into mast cell behavior and function
- Pages: 83-99
- First Published: 06 May 2021
A bird's eye view on the role of dendritic cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Perspectives for immune-based vaccines
- Pages: 100-110
- First Published: 10 July 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
In vitro data suggest that Indian delta variant B.1.617 of SARS-CoV-2 escapes neutralization by both receptor affinity and immune evasion
- Pages: 111-117
- First Published: 28 August 2021
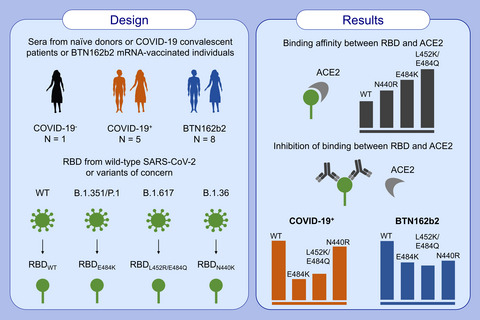
Binding assays using Biolayer Interferometry showed that the RBD containing L452R/E484Q present in the new SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.617 interacts with ACE2 with higher affinity than wild-type or single mutants N440K and E484K. Sera from convalescent and BTN162b2 vaccinated individual showed reduced ability to block the interaction between ACE2 and RBD mutants E484K and L452R/E484Q suggesting that the new SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.617 bypass immunity generated against the wild-type virus. Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; RBD, receptor binding domain; RBDE484K, RBD containing mutation E484K on S; RBDL452R/E484Q, RBD containing both mutations L452K and E484Q on S; RBDN440K, RBD containing mutation N440K on S; RBDWT, wild-type RBD; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2
Caspases and therapeutic potential of caspase inhibitors in moderate–severe SARS-CoV-2 infection and long COVID
- Pages: 118-129
- First Published: 15 May 2021
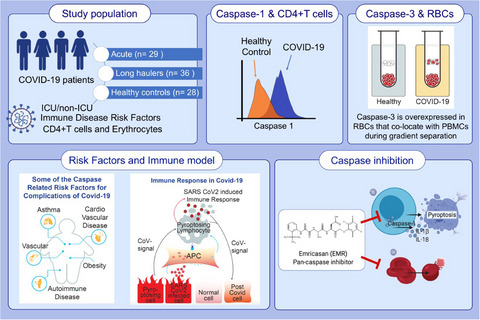
This study assesses transcriptional states of multiple caspases and the expression of active caspase-1 in blood cells from COVID-19 patients in acute and convalescent stages of disease. Elevated caspase-3/7 levels in red blood cells is observed in COVID-19 patients compared to controls. Post-COVID-19 patients with lingering symptoms show up-regulated caspase-1 activity in CD4+ T-cells that is attenuated ex vivo with a select pan-caspase inhibitor. An exuberant caspase response in COVID-19 that may facilitate immune-related pathological processes leading to severe outcomes.
Abbreviations: APC, antigen-presenting cell; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; ICU, intensive care unit; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; RBC, red blood cell; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
Experimental rhinovirus infection induces an antiviral response in circulating B cells which is dysregulated in patients with asthma
- Pages: 130-142
- First Published: 25 June 2021
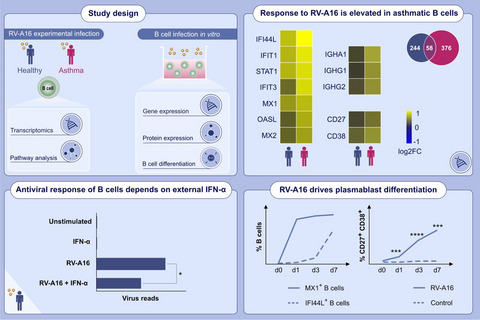
Intranasal infection with rhinovirus-A16 elicits antiviral response in peripheral B cells, characterized by upregulated antiviral response and cytokine genes. Peripheral B cells are dependent on external type-I-IFN to develop an antiviral activation state. Rhinovirus stimulation induces strong antiviral response in plasmablasts. Dysregulated expression of antiviral response and antibody genes in individuals with asthma is observed after rhinovirus infection. Abbreviations: IFI44L, interferon induced protein 44 like; IFIT, interferon induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats; IGHA, immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha; IGHG, immunoglobulin heavy constant gamma; IFN- α, IFN-alpha; MX, MX dynamin like GTPase; OASL, 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase like; RV-A16, rhinovirus-A16; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
Molecular definition of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 receptor-binding domain mutations: Receptor affinity versus neutralization of receptor interaction
- Pages: 143-149
- First Published: 08 July 2021
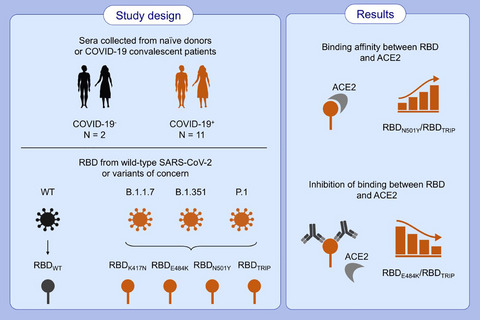
In this study, we tested RBD of the spike protein with single mutations or with all three mutations combinations for binding to sera from naïve donors and convalescent COVID-19 patients. Convalescent sera recognize RBD of the early SARS-CoV-2 emerged from Wuhan, China. Single mutations (E484K or N501Y) either affect receptor affinity to ACE2 or immune recognition of RBD by convalescent sera. Combining three-point mutations (K417N, E484K, and N501Y) in RBD increased binding to ACE2 and abolished recognition of RBD by sera of convalescent patients.
Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; B.1.1.7., SARS-CoV-2 UK variant; B.1.351, SARS-CoV-2 Japan/Brazil variant; B.1.6.1.7, SARS-CoV-2 India variant; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; P.1, SARS-CoV-2 South Africa variant; RBD, receptor-binding domain; RBDWT, RBD wild type; RBDTRIP, RBD N501Y, E484K, K417N mutations; RBDN501Y, RBD N501Y mutation; RBDE484K, RBD E484K mutation; RBDK417N, RBD K417N mutation; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; WT, wild type.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Benralizumab improves symptoms of patients with severe, eosinophilic asthma with a diagnosis of nasal polyposis
- Pages: 150-161
- First Published: 12 May 2021
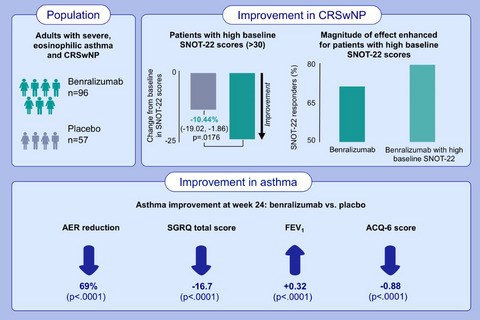
The combination of asthma and nasal polyposis provides significant treatment challenges and substantial disease burden, including a greater number of asthma exacerbations annually, which negatively impacts quality of life. Clinically meaningful improvement in the SNOT-22 was observed early and maintained over time for patients with severe, eosinophilic asthma and nasal polyposis treated with benralizumab in the ANDHI trial. This ANDHI substudy demonstrated that benralizumab is safe and efficacious for patients with severe, eosinophilic asthma and nasal polyposis, with improvement in SNOT-22 total scores and asthma outcomes. Abbreviation: ACQ-6, Asthma Control Questionnaire-6; AER, asthma exacerbation rate; CRSwNP, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; SGRQ, St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; SNOT-22, Sino-Nasal Outcome Test
The maternal diet index in pregnancy is associated with offspring allergic diseases: the Healthy Start study
- Pages: 162-172
- First Published: 21 May 2021
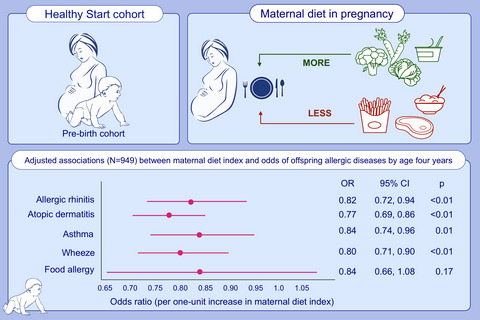
The maternal diet in pregnancy appears to be associated with offspring allergy outcomes. A maternal allergy-preventive diet index in pregnancy was developed and validated. Vegetables and yogurt were associated with the prevention of any allergy, while red meat, cold cereals, fried potatoes, rice/grains, and 100% fruit juice were associated with increased disease. For a one-unit increase in the maternal diet index, the odds of allergic diseases in offspring were significantly reduced by 18% for allergic rhinitis, 23% for atopic dermatitis, 16% for asthma, and 20% for wheeze.
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio.
Asthma phenotypes, associated comorbidities, and long-term symptoms in COVID-19
- Pages: 173-185
- First Published: 03 June 2021
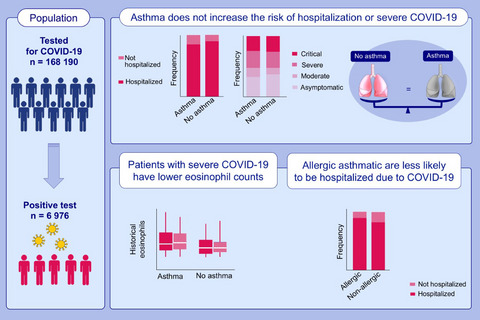
Asthma is not a risk factor for more severe COVID-19 disease. Allergic asthmatics are half as likely to be hospitalized compared with non-allergic asthmatics and lower levels of eosinophil counts (allergic biomarkers) are associated with a more severe COVID-19 disease trajectory. Recovery is similar among asthmatics and non-asthmatics. Abbreviation: COVID, coronavirus disease 2019.
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, and Upper Airway Disease
Dupilumab efficacy in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps from SINUS-52 is unaffected by eosinophilic status
- Pages: 186-196
- First Published: 16 May 2021
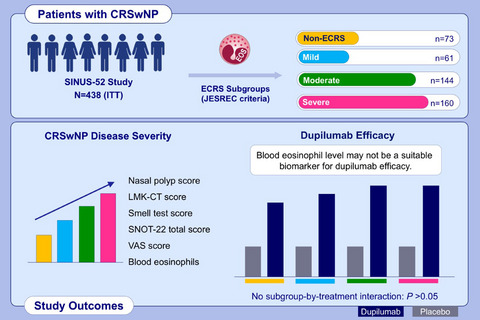
Patients with CRSwNP from SINUS-52 were classified by eosinophilic status (ECRS subgroup; JESREC criteria). Although moderate/severe ECRS shows greater baseline disease burden than mild/no ECRS, improvements in disease control, symptom burden, sense of smell, and HRQoL with dupilumab versus placebo are unaffected by ECRS status. Eosinophilic status is not a biomarker for dupilumab efficacy in CRSwNP patients meeting SINUS-52 inclusion criteria. Abbreviations: CRSwNP, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; ECRS, eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis; EOS, eosinophil; HRQoL, health-related quality of life; ITT, intention-to-treat; JESREC, Japanese Epidemiological Survey of Refractory Eosinophilic Rhinosinusitis; LMK-CT, Lund-Mackay score assessed by CT; SINUS-52, controlled clinical study of dupilumab in patients with nasal polyps; SNOT-22, 22-item sinonasal outcome test; VAS, visual analog scale.
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
Adherence to subcutaneous immunotherapy with aeroallergens in real-life practice during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 197-206
- First Published: 27 April 2021
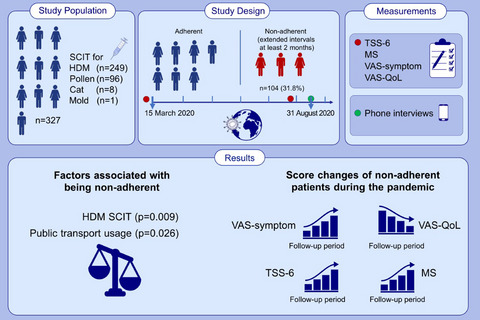
In this real-life study, the nonadherence rate of patients receiving SCIT during the COVID-19 pandemic is 31.8%. In the nonadherent patients, the use of HDM SCIT and the use of public transport for reaching the hospital are significantly higher. SCIT effectiveness and QoL levels are lower during the pandemic period than before the pandemic in the nonadherent patients. Abbreviations: HDM, house dust mite; MS, medical score; QoL, quality of life; SCIT, subcutaneous immunotherapy; TSS-6, total symptom score-6; VAS, visual analogue scale.
Epidemiology and Genetics
Epigenetic regulation of epithelial dectin-1 through an IL-33-STAT3 axis in allergic disease
- Pages: 207-217
- First Published: 12 May 2021
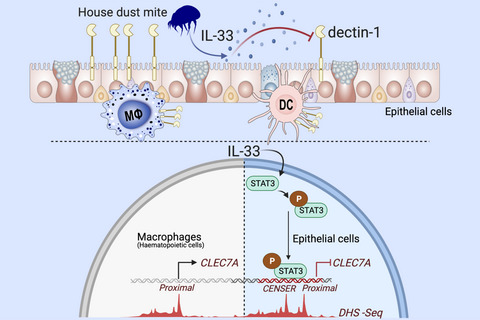
Dectin-1 is not only present on macrophages and DCs, but is also constitutively expressed by human and mouse respiratory epithelial cells where it has a protective role. Allergen induced IL-33 inhibits dectin-1 on epithelial, but not immune cells. IL-33-induced STAT3 represses dectin-1 through a newly identified enhancer region—CENSER—active in non-hematopoietic cells. Abbrreviations: MΦ, macrophage; DC, dendritic cell; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; DHS-seq, DNase I hypersensitive site sequencing.
Genome-wide association study identifies TNFSF15 associated with childhood asthma
- Pages: 218-229
- First Published: 22 May 2021
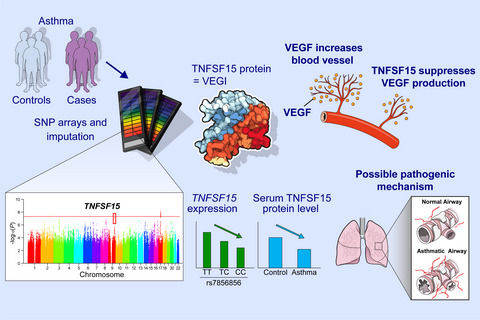
Our genome-wide association studies identify a new susceptibility gene, TNFSF15 for persistent asthma in children. Children with asthma have lower serum TNFSF15 levels than controls, and those with the asthma risk rs7856856-CC genotype exhibit the lowest serum TNFSF15 levels. This novel association may be mediated by loss of suppression of angiogenesis via lower expression of TNFSF15. Abbreviations: SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; TNFSF15, tumor necrosis factor superfamily 15; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGI, vascular endothelial growth inhibitor.
Autoimmunity and Clinical Immunology
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 requires antibodies against conformational receptor-binding domain epitopes
- Pages: 230-242
- First Published: 28 August 2021
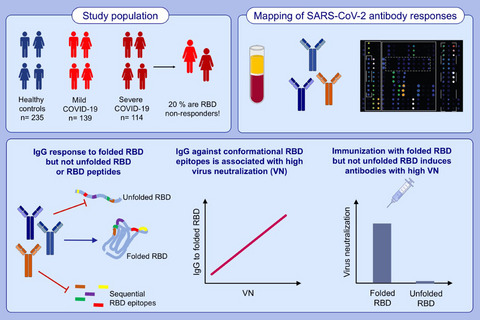
IgG response in convalescent COVID-19 patients is directed to folded but not to unfolded RBD or RBD peptides. IgGs to folded RBD are required for virus neutralization. Twenty percent of convalescent COVID-19 patients selectively lack RBD-specific IgG. Only immunization with folded, but not with unfolded RBD, induces antibodies with virus-neutralizing activity. Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; IgG, immunoglobulin G; RBD, receptor-binding domain; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
A scalable and highly immunogenic virus-like particle-based vaccine against SARS-CoV-2
- Pages: 243-257
- First Published: 08 September 2021
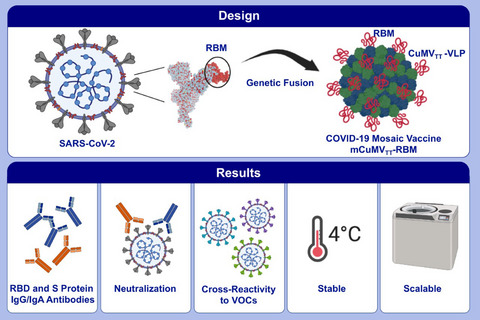
In this study, we describe a novel conventional COVID-19 vaccine that consists of the RBM of SARS-CoV-2 genetically grafted onto the surface of our optimized cucumber-mosaic virus-like particles. We demonstrate that the vaccine candidate (mCuMVTT-RBM) is highly immunogenic in mice and rabbits, can efficiently neutralize SARS-CoV-2, and is stable and highly scalable. The induced antibodies show cross-reactivity with VoC. Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; CuMVTT-VLPs, cucumber-mosaic virus-like particles; RBD, receptor-binding domain; RBM, receptor-binding motif; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; VOCs, variant of concerns.
Development and preclinical evaluation of virus-like particle vaccine against COVID-19 infection
- Pages: 258-270
- First Published: 14 September 2021
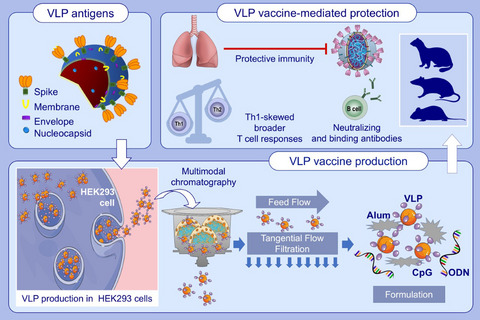
SARS-CoV-2 VLP vaccine that incorporates the four structural proteins of SARS-CoV-2 is reproducibly produced in suspension adapted HEK293 cells. Alum adsorbed, K3-CpG ODN-adjuvanted VLPs elicit high titer anti-S, anti-RBD, anti-N IgG, and neutralizing antibodies in mice, rats, and ferrets. The VLP vaccine supports multifunctional Th1-biased T-cell responses and demonstrate immunoprotective activity against live SARS-CoV-2 challenge in vaccinated mice. Abbreviations: Alum, aluminum hydroxide; CpG, cytosine-phosphate-guanosine dinucleotide; HEK293, human embryonic kidney cell line; ODN, oligodeoxynucleotide; RBD, receptor binding domain; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Th, T-helper cell; VLP, virus-like particle.
Antibody response after one and two jabs of the BNT162b2 vaccine in nursing home residents: The CONsort-19 study
- Pages: 271-281
- First Published: 19 July 2021

This study compares levels of IgG antibodies against the spike protein (S-RBD IgG) (S-RDB protein IgG) after one and two BNT162b2/Pfizer jabs in residents with and without prior COVID-19. One BNT162b2 jab is sufficient to reach an S-RBD protein IgG level of 1050 AU/ml in 98% of nursing home residents with prior COVID-19. After two jabs, levels of S-RBD IgG are below 1050 AU/ml in 29.5% of residents without prior COVID-19. Abbreviations: AU/ml, arbitrary units per ml; COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; RT-PCR, real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; S-RBD IgG, IgG antibodies against the spike protein.
Adverse COVID-19 outcomes in immune deficiencies: Inequality exists between subclasses
- Pages: 282-295
- First Published: 27 July 2021
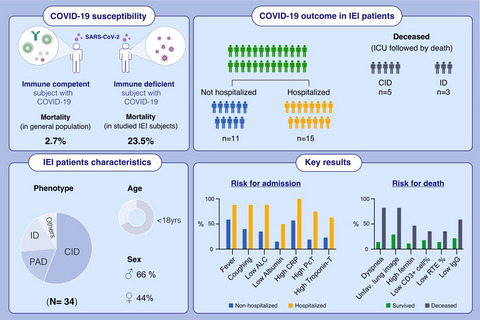
34 IEI patients aged between 0.6 and 43 years, eight patients (23.5%) succumbed to COVID-19, indicating a highly vulnerable condition to COVID-19. Laboratory markers associated with mortality included elevated acute phase reactants, ferritin, troponin T, TLS, and reduced ALC levels, albumin, and baseline IgG. Coughing, dyspnea, CORADS category 4–6, and negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR at admission were among the predictors of lethal outcome. Abbreviations: ALC, absolute lymphocye count; CID, combined immune deficiency; COVID-19, coronavirus infectious disease 2019; CRP, C-reactive protein; F, female; ICU, intensive care unit; ID, immune dysregulation; IEI, inbor errors of immunity; Ig, immunoglobulin; M, male; PAD, predominantly antibody deficiency; PcT, procalcitonin; RTE, recent thymic emigrants; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; Unfav, unfavorable.
LETTERS
A single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine elicits strong humoral response in SARS-CoV-2 seropositive individuals
- Pages: 296-298
- First Published: 12 August 2021
Antiviral response in vernal keratoconjunctivitis may be protective against COVID-19
- Pages: 298-300
- First Published: 14 August 2021
House dust mite sensitization and frequent antibiotic courses may suppress remission of rhinosinusitis and asthma symptoms in young children
- Pages: 301-304
- First Published: 12 September 2021
COVID-19 vaccination with BNT162b2 and ChAdOx1 vaccines has the potential to induce nasal neutralizing antibodies
- Pages: 304-307
- First Published: 20 September 2021
Nasal epigenetic age and systemic steroid response in pediatric emergency department asthma patients
- Pages: 307-309
- First Published: 19 September 2021
NK cells and lipoxin A4 promote resolution of eosinophilic inflammation after nasal allergen challenge
- Pages: 309-313
- First Published: 20 September 2021
Mass cytometry-based identification of a unique T-cell signature in childhood allergic asthma
- Pages: 313-316
- First Published: 26 September 2021
Selenomonas: A marker of asthma severity with the potential therapeutic effect
- Pages: 317-320
- First Published: 29 September 2021
Allergoid-mannan conjugates imprint tolerogenic features in human macrophages
- Pages: 320-323
- First Published: 03 October 2021
Identification of chronic urticaria subtypes using machine learning algorithms
- Pages: 323-326
- First Published: 04 October 2021
NEWS AND VIEWS
Algorithms in Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Medical algorithm: Aspergillus fumigatus components in the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Pages: 327-330
- First Published: 12 July 2021
Groundbreaking Discoveries in Clinical & Basic Science
Adding the variable of environmental complexity into the COVID-19 pandemic equation
- Pages: 331-333
- First Published: 28 May 2021
News & Views: Groundbreaking Discoveries in Clinical & Basic Science
The food, the bug, and the ugly: A recipe for food-induced gut pain
- Pages: 334-336
- First Published: 22 July 2021
CORRESPONDENCE
Successful administration of second dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine in two patients with potential anaphylaxis to first dose
- Pages: 337-338
- First Published: 29 December 2021






