Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 02 August 2023
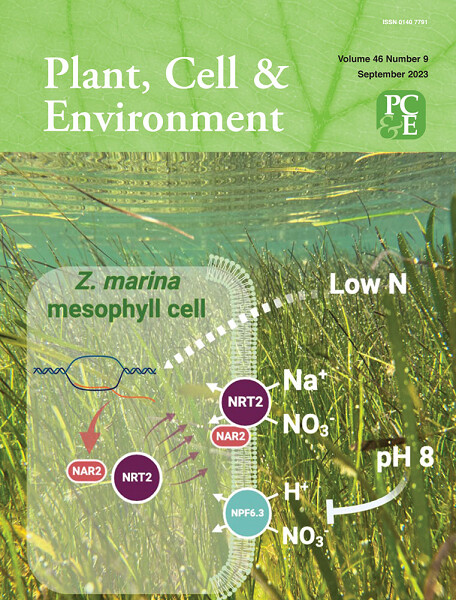
The cover image is based on the Original Article Identity and functional characterisation of the transporter supporting the Na+-dependent high-affinity NO3− uptake in Zostera marina L. by Lourdes Rubio et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.14660.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Plastid-mediated RNA interference: A potential strategy for efficient pest control
- Pages: 2595-2605
- First Published: 18 June 2023
We review the recent progresses in the plastid-mediated RNAi (PM-RNAi) approach for pest control and the factors influencing its efficacy, and propose the strategies for further efficiency improvement. We also discuss the current challenges and the biosafety-related issues of PM-RNAi technology that need to be addressed for commercial production.
Updating the dual C and O isotope—Gas-exchange model: A concept to understand plant responses to the environment and its implications for tree rings
- Pages: 2606-2627
- First Published: 07 June 2023
We analysed >300 studies making use of the dual carbon and oxygen isotope model (DI-model). Based on the isotopic patterns, we can draw conclusions on how environmental variables impact photosynthesis and stomatal conductance. The concept was well received and applied to interpret plant environment interactions. Yet, some studies reported nonplausible model results. Evaluating all publications applying the DI-model revealed most causes for nonplausibility.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
18O enrichment of sucrose and photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic leaf water in a C3 grass—atmospheric drivers and physiological relations
- Pages: 2628-2648
- First Published: 27 June 2023
The 18O enrichment of water in the two functionally distinct water pools of grasses—photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic tissue water—revealed opposite responses to atmospheric humidity in Lolium perenne. 18O enrichment of sucrose was close to equilibrium with evaporative site enrichment.
Drivers of intra-seasonal δ13C signal in tree-rings of Pinus sylvestris as indicated by compound-specific and laser ablation isotope analysis
- Pages: 2649-2666
- First Published: 13 June 2023
Intra-annual tree-ring δ13C signal of Scots pine recorded faithfully the environmental signal in leaf sucrose δ13C, with no clear signs of reserve use. The 13C-enrichment of studied sink organs relative to leaves was dominated by post-photosynthetic fractionations, such as sink organ respiration.
Revisiting yield in terms of phloem transport to grains suggests phloem sap movement might be homeostatic
- Pages: 2667-2679
- First Published: 11 June 2023
The role of phloem sap transport limitation in wheat yield is examined, using field data obtained from 466 wheat plots grown with various cultivars, with or without irrigation. We find that phloem transport properties change little with environmental conditions. Phloem transport adjusts to sustain grain filling and is likely not a limitation for yield in wheat.
Differences between tree stem CO2 efflux and O2 influx rates cannot be explained by internal CO2 transport or storage in large beech trees
- Pages: 2680-2693
- First Published: 23 May 2023
Our field experiment in mature beech trees, measuring CO2 and O2 fluxes simultaneously, showed that 30% of the respired CO2 is retained in the stem. However, CO2 internal fluxes could not explain the difference between CO2 efflux and O2 influx. The internal carbon recycling mechanism mediated by PEPC is active in mature trees and can be considered as a missing C sink.
Leaf cell wall properties and stomatal density influence oxygen isotope enrichment of leaf water
- Pages: 2694-2710
- First Published: 23 May 2023
The greater apoplastic permeability in maize (Zea mays) mutants that had a compromised ultrastructure of the suberin lamellae in the bundle sheath led to higher transpiration rates and lower isotopic mixing length than wildtype, resulting in lower oxygen isotope enrichment of leaf water (Péclet effect). In rice (Oryza sativa) wild type and mutants with no mixed linkage glucan in the cell wall, oxygen isotope enrichment in leaf water in response to growth light intensity co-varied with stomatal density, showing that differences in stomatal density modulate oxygen isotopic enrichment in leaf water.
Plant size directly correlates with water use efficiency in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 2711-2725
- First Published: 10 July 2023
The relationship among transpiration and water use efficiency, thermoregulation, nutrition, and growth was studied in natural Arabidopsis thaliana accessions grown under consistent conditions. We found a direct correlation between water use efficiency and leaf area, suggesting that larger plants utilise water more efficiently. Genome-wide association studies supported these findings, identifying specific genetic factors associated with water use efficiency. These findings highlight the importance of plant size as an adaptive trait for water usage in A. thaliana. Overall, our study enhances understanding of plant adaptation to water availability, with potential implications for crop productivity and water management.
Exploring within-plant hydraulic trait variation: A test of the vulnerability segmentation hypothesis
- Pages: 2726-2746
- First Published: 20 June 2023
Using a hydraulic model, we examine how vulnerability segmentation interacts with other traits to impact plant conductance loss. We show that vulnerability segmentation impacts depend on other traits, which potentially helps explain variable observations of vulnerability segmentation.
High vapour pressure deficit enhances turgor limitation of stem growth in an Asian tropical rainforest tree
- Pages: 2747-2762
- First Published: 10 July 2023
Root relative water content is a potential signal for impending mortality of a subtropical conifer during extreme drought stress
- Pages: 2763-2777
- First Published: 12 June 2023
Hydraulic failure and multiorgan dehydration triggered seedling mortality of Pinus massoniana, with root relative water content (RWC) exhibiting faster decline than other organ RWCs in extreme drought.
Multifactorial in vivo regulation of the photoreceptor channelrhodopsin-1 abundance
- Pages: 2778-2793
- First Published: 28 June 2023
How Chlamydomonas controls the level of ChR1, the main photoreceptor for its movement responses, is largely unknown. Here we show that regulatory elements involved in photoprotective gene expression are parts of this cascade(s), supporting an integrating link between phototaxis and photoprotection.
A MYB activator, DcMYB11c, regulates carrot anthocyanins accumulation in petiole but not taproot
- Pages: 2794-2809
- First Published: 20 June 2023
Here, we described a MYB gene, DcMYB11c, which was highly expressed in the purple pigmented petioles. The orchestrated regulation mechanism in carrot might be conserved across the plant kingdom and useful for other researchers working on anthocyanins accumulation in different tissues.
B-Box proteins BBX28 and BBX29 interplay with PSEUDO-RESPONSE REGULATORS to fine-tune circadian clock in Arabidopsis
- Pages: 2810-2826
- First Published: 13 June 2023
BBX28/29 interact with PRR to augment their transcriptional repressive activity, while PRR proteins feedback inhibit the transcription of BBX28/29, which cooperatively orchestrates the circadian clock.
Substrate and adenylate limit subtropical tree fine-root respiration under soil warming
- Pages: 2827-2840
- First Published: 06 June 2023
Fine-root respiration of subtropical Chinese fir plantation showed partial thermal acclimation to warming only during summer and was limited by substrate and adenylate rather than enzyme capacity, which is conducive to mitigate the potential positive effect of warming on ecosystem carbon emissions.
Nighttime hypoxia effects on ATP availability for photosynthesis in seagrass
- Pages: 2841-2850
- First Published: 18 June 2023
- 1.
Hypoxia lowers respiratory ATP production and prevents ATP from being transported into the chloroplasts, thus inhibiting high-light-damaged photosystem II (PSII) recovery of Enhalus acoroides at night.
- 2.
The inhibition of PSII recovery reduces the photosynthetic capacity of E. acoroides after reillumination.
Identity and functional characterisation of the transporter supporting the Na+-dependent high-affinity NO3− uptake in Zostera marina L.
- Pages: 2851-2866
- First Published: 05 July 2023
The work shows evidence that ZosmaNRT2 functions as a Na+-dependent NO3− transporter that requires ZosmaNAR2 to achieve high affinity for NO3−. This mechanism, the first characterised in the marine angiosperm Zostera marina, changes the paradigm of high-affinity NO3− transport in vascular plants.
ZmEREB57 regulates OPDA synthesis and enhances salt stress tolerance through two distinct signalling pathways in Zea mays
- Pages: 2867-2883
- First Published: 16 June 2023
As an important cereal crop worldwide, however, the yield and quality of maize are severely affected by salt stress. This study identified that ZmEREB57, a AP2/ERF transcription factor, contributes to salt tolerance in maize. The ZmEREB57-mediated salt stress response can be achieved by binding to the ZmAOC2 promoter, which is a positive regulator of OPDA biosynthesis. Although as being a precursor for JA synthesis, OPDA functions independently of JA as a signalling molecule in the salt response.
An ancient route towards salicylic acid and its implications for the perpetual Trichormus–Azolla symbiosis
- Pages: 2884-2908
- First Published: 02 July 2023
Azolla spp. live in perpetual symbioses with cyanobacteria. We pinpoint the presence of salicylic acid (SA) via UPLC-MS/MS, analyze an evolutionary framework for SA biosynthesis, and, based on RNAseq data and SA levels upon removal of the symbiont, postulate links of SA to symbiotic communication.
DATA INSIGHT
Integrative time-scale and multi-omics analysis of host responses to viroid infection
- Pages: 2909-2927
- First Published: 28 June 2023
Here we show that viroid infection promotes a dynamic redesign of the host regulatory pathways. This first comprehensive map of the plant-response reveals the molecular basis of the multifaceted defence and counter-defence layout associated with viroid-infection.
TECHNICAL REPORT
A rapid method to quantify vein density in C4 plants using starch staining
- Pages: 2928-2938
- First Published: 23 June 2023
Preferential accumulation of starch in bundle sheath cells of C4 plants allows high-throughput phenotyping of vein density.