Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Cover Image, Volume 50, Issue 3
- First Published: 28 May 2024
The cover image is based on the Original Article Perineuronal nets are phagocytosed by MMP-9 expressing microglia and astrocytes in the SOD1G93A ALS mouse model by Sang Won Cheung et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12982.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Artificial intelligence in histopathological image analysis of central nervous system tumours: A systematic review
- First Published: 13 May 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Interferon-gamma contributes to disease progression in the Ndufs4(−/−) model of Leigh syndrome
- First Published: 28 April 2024
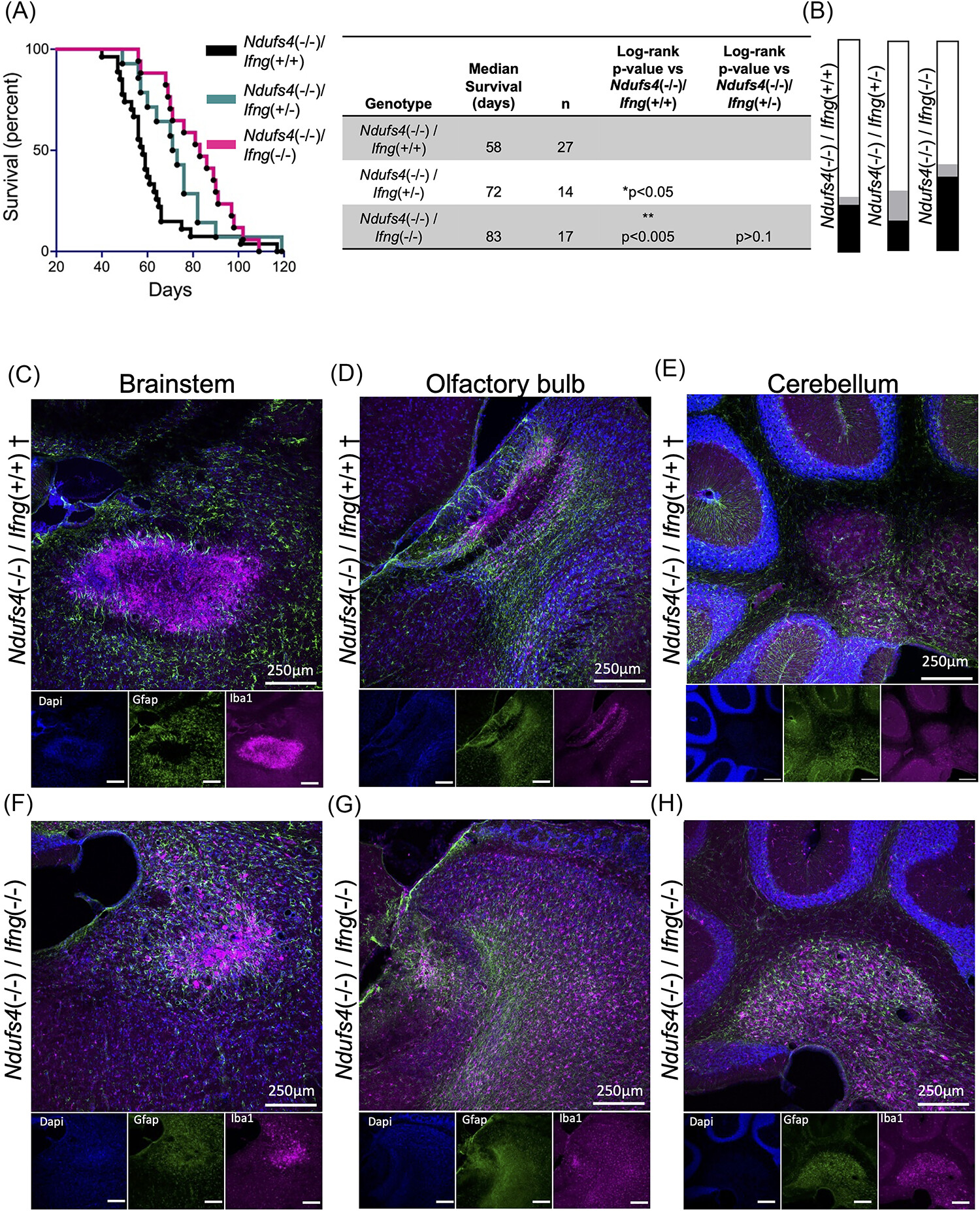
The brainstems of diseased Ndufs4(−/−) mice—a mouse model of the genetic mitochondrial disease Leigh syndrome (LS)—have elevated levels of cytokines IP10 and IFNγ. To explore the role of these two factors in LS, we generated IFNγ and IP10 deficient Ndufs4(−/−) mice and evaluated survival and disease pathology. Loss of IP10 does not impact disease in Ndufs4(−/−) mice, but IFNγ loss prolongs survival and delays disease progression, indicating that IFNγ signaling contributes to disease onset and progression in LS.
Perineuronal nets are phagocytosed by MMP-9 expressing microglia and astrocytes in the SOD1G93A ALS mouse model
- First Published: 14 May 2024
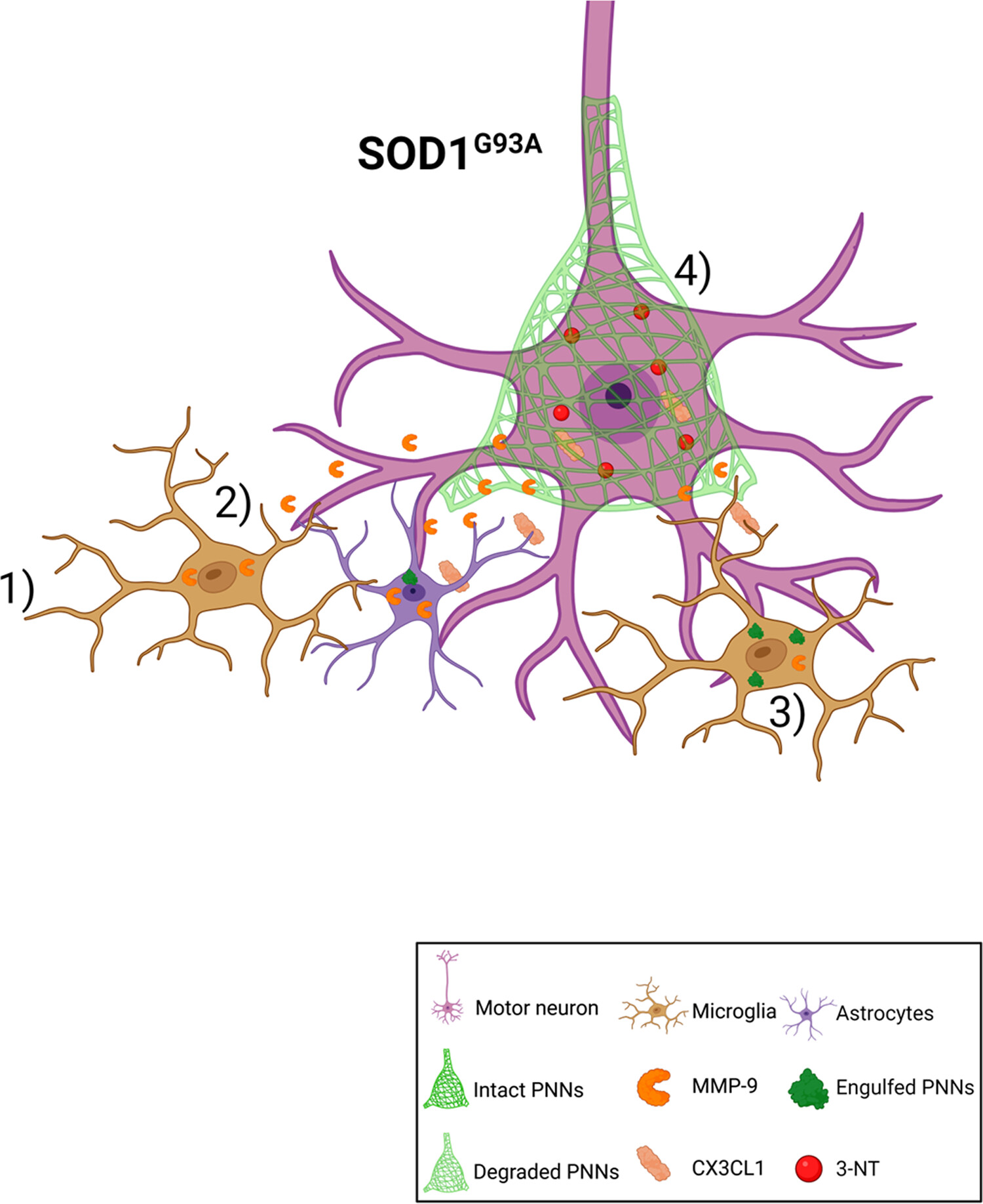
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) surrounding motoneurons in ALS model mice are broken down by a process of MMP-9 release from and engulfment by microglia and astrocytes, during disease progression. (1) Activated microglia and astrocytes are recruited to motoneurons. (2) MMP-9 released by these microglia assist in the breakdown of PNNs around motoneurons and digest PNN fragments. (3) CX3CL1 released from motoneurons triggers microglia to phagocytose PNNs. (4) These motoneurons are then made vulnerable to stress as seen by the upregulation of 3-NT.
Accurate and comprehensive evaluation of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation by nanopore sequencing
- First Published: 23 May 2024
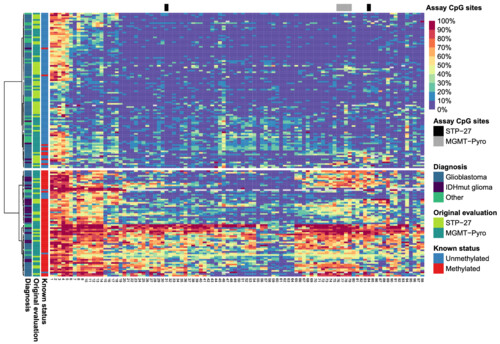
We assessed the effectiveness of nanopore long-read sequencing for evaluatingmethylation levels across the MGMT CpG-island, crucial for prognosis in glioblastomapatients. Using 165 CNS tumour samples, nanopore sequencing was compared toestablished techniques, showing a strong correlation with pyrosequencing and effectivepatient stratification via hierarchical clustering. Nanopore sequencing provided rapid,high-confidence results and expanded analysis to all 98 CpGs of the MGMT CpG-island,suggesting its utility for clinically relevant patient subgroup identification and warranting further exploration in clinical settings.
Amino-terminally elongated Aβ peptides are generated by the secreted metalloprotease ADAMTS4 and deposit in a subset of Alzheimer's disease brains
- First Published: 12 June 2024
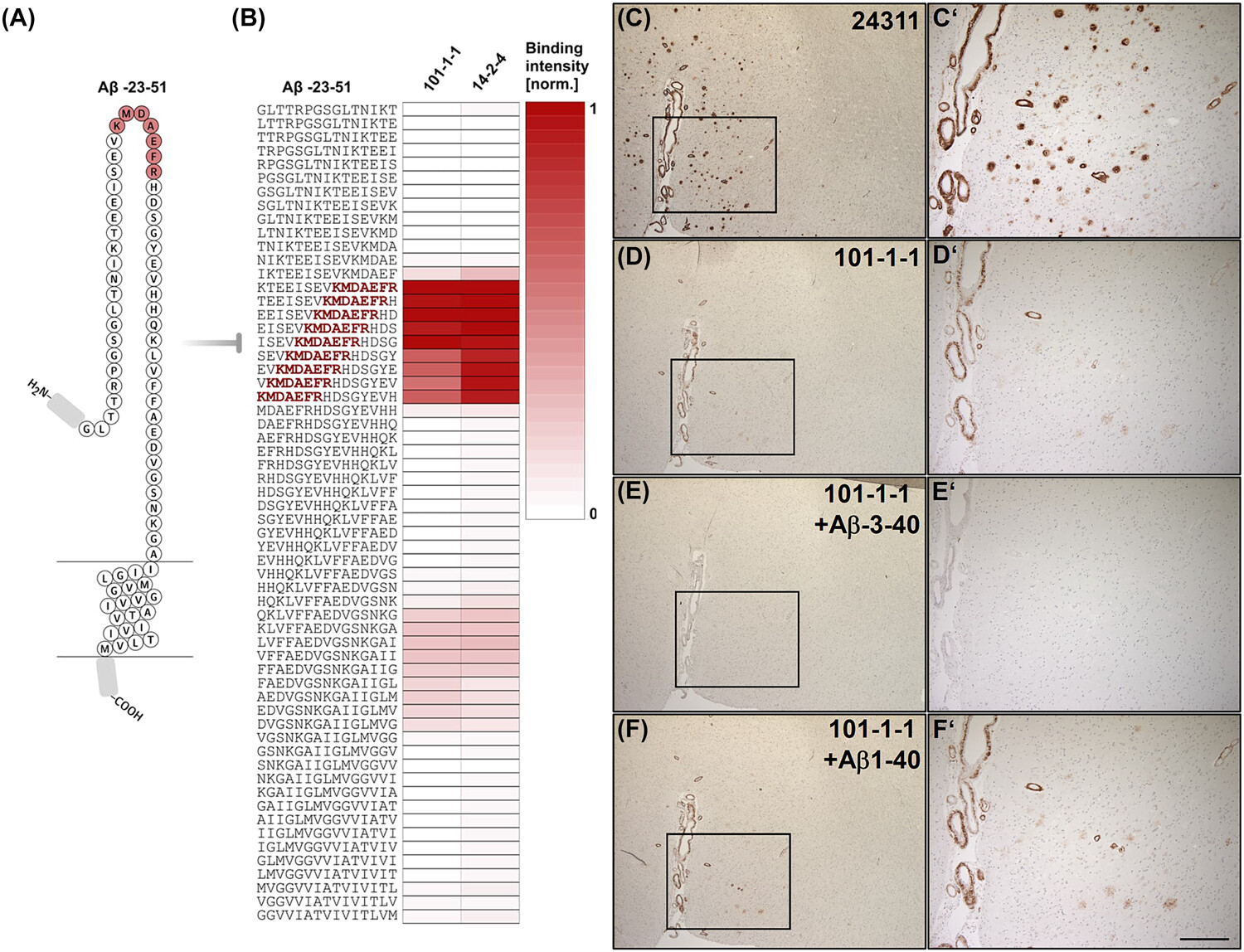
The role of the metalloproteinase ADAMTS4 in the generation of N-terminally elongated Aβ peptide species has been characterized with cell-free and cell-based assays in combination with mass spectrometry. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed the deposition of N-terminally elongated Ab variants in the brains of a subset of AD patients.
NLRP3 promotes radiation-induced brain injury by regulating microglial pyroptosis
- First Published: 03 June 2024
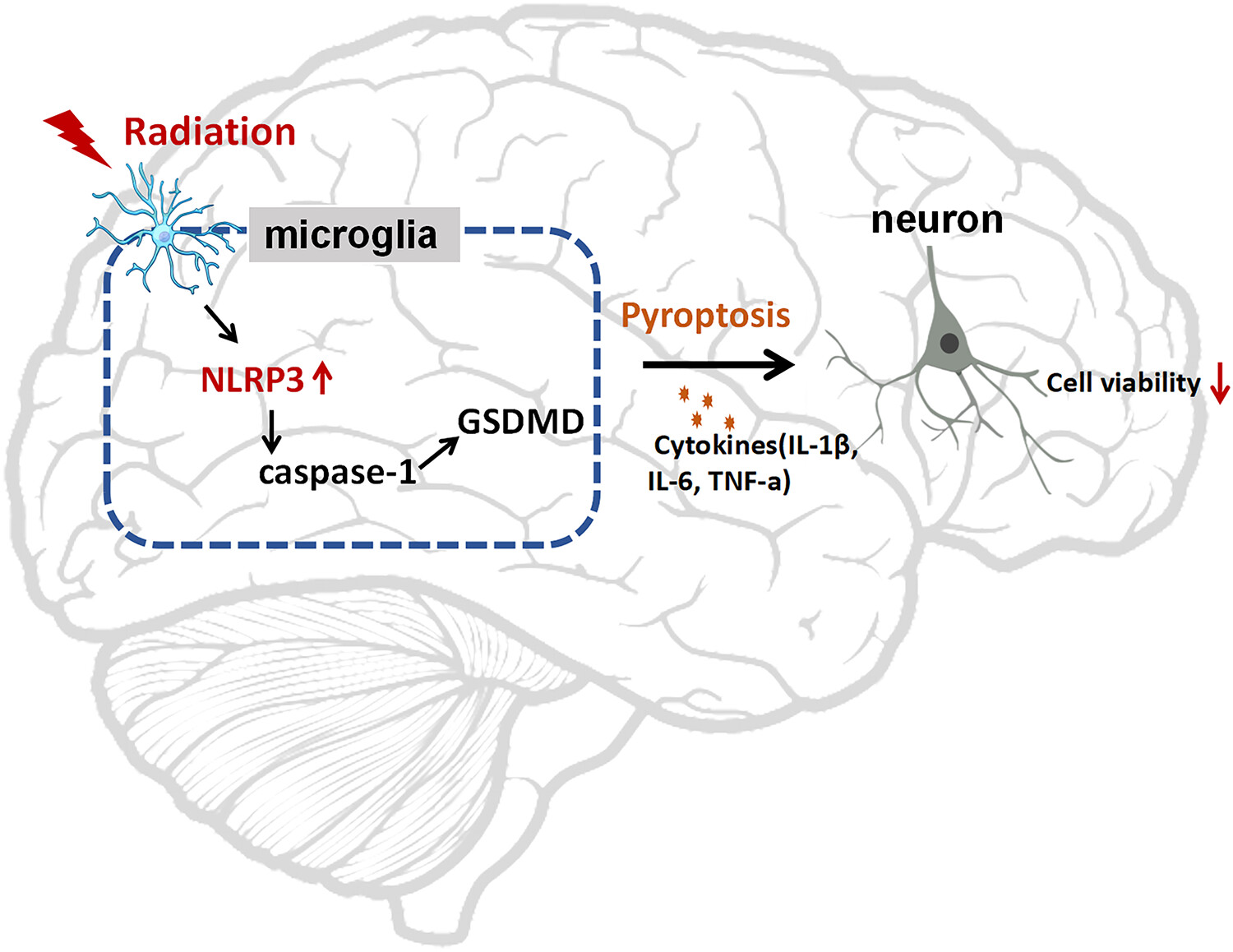
Radiation induced pyroptosis in microglia, promoting radiation-induced brain injury via the secretion of neurotoxic cytokines. NLRP3 was evaluated as an important mediator in radiation-induced pyroptosis and a promising therapeutic target of radiation-induced brain injury. The patients after irradiation with higher IL-6 were found to have a decreased MMSE score, indicating that the level of IL-6 could serve as a valuable biomarker for radiation-induced brain injury.
Proteomic profiling of polyglucosan bodies associated with glycogenin-1 deficiency in skeletal muscle
- First Published: 24 June 2024
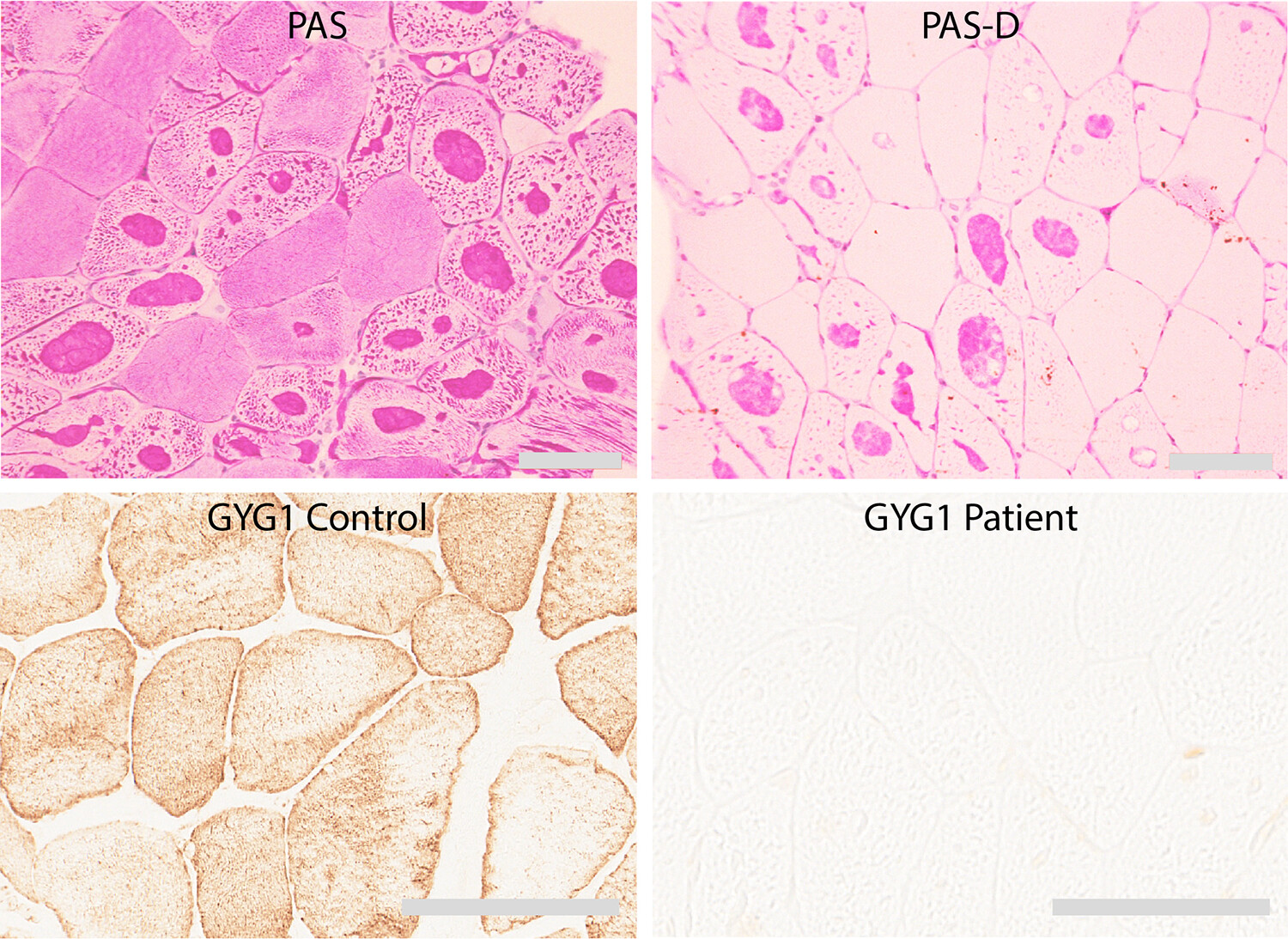
Polyglucosan storage disorders represent an emerging field within neurodegenerative and neuromuscular conditions. We combined molecular genetic analyses, quantitative mass spectrometry of laser micro-dissected polyglucosan bodies, immunohistochemistry and western blot, and show that the absence of glycogenin-1 (GYG1), a protein important for glycogen synthesis initiation, causes storage of polyglucosan that displays accumulation of several proteins, including those essential for glycogen synthesis, sequestosome 1/p62 and desmin.
SHORT COMMUNICATIONS
Diffuse infiltrating tumour with the molecular profile of an atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumour (AT/RT SHH-1B) in an adult patient
- First Published: 06 May 2024
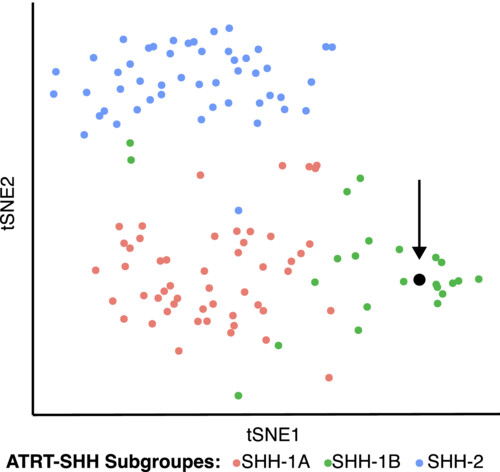
In this case report, we describe a 46-year-old patient with a brain lesion identified with imaging studies following a minor head injury. Initially suspected to be diffuse glioma, detailed histological, immunohistochemical and molecular investigations revealed characteristics consistent with an atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour (AT/RT), SHH-1B molecular subtype.






