Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Are opioid receptor antagonists adequate for “Opioid” overdose in a changing reality?
- Pages: 861-866
- First Published: 28 April 2021
Weight-adapted fixed-dose combined adult antiretroviral tablets for HIV-infected children
- Pages: 867-871
- First Published: 04 January 2021
Antibiotic therapy in sepsis: No next time for a second chance!
- Pages: 872-876
- First Published: 12 March 2021
Clinical and economic impacts of explicit tools detecting prescribing errors: A systematic review
- Pages: 877-886
- First Published: 25 March 2021
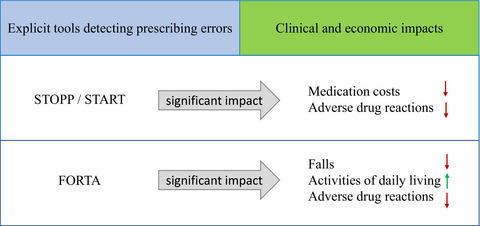
Very little is known regarding the clinical and economic impact of the prospective use of explicit tools detecting prescribing errors. We found a significant impact of STOPP/START on adverse drug reactions and medication costs and a significant impact of FORTA on falls, activities of daily living and adverse drug reactions. These findings suggest that explicit tools support reducing the complexity of therapeutic management and tools-based interventions could have a usefulness in clinical practice.
Albumin for cirrhosis-related complications
- Pages: 887-894
- First Published: 07 June 2021
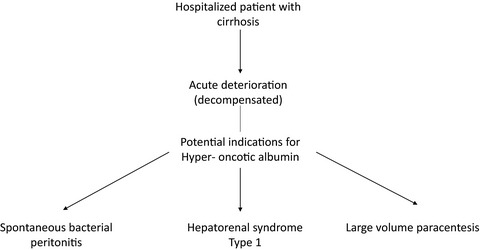
There is little evidence supporting the routine administration of albumin in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis except in cases of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and in selected patients who have hepatorenal syndrome or are undergoing large volume paracentesis. Recent evidence suggests possible benefits of longer-term albumin administration in subgroups of non-hospitalized patients with decompensated cirrhosis, but more research is needed.
Efficacy and safety of interleukin-17 inhibitors in the treatment of chronic rheumatic diseases: A combined and updated meta-analysis
- Pages: 895-906
- First Published: 25 March 2021
IL-17 inhibitors lead to a higher response rates in patients with AS or PsA. IL-17 inhibitors might be more effective for patients with AS or PsA who previously not used TNF inhibitors. IL-17 inhibitors might be well tolerated for patients with PsA, but increased treatment-emergent adverse events and infection in AS patients.
Clinical effects and safety of edaravone in treatment of acute ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 907-917
- First Published: 27 February 2021
Neurotoxicity associated with acyclovir and valacyclovir: A systematic review of cases
- Pages: 918-926
- First Published: 19 June 2021
Impact of corticosteroid use on outcomes of non–small-cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 927-935
- First Published: 17 June 2021
Polymorphisms of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor type 3B gene and clinical characteristics for vomiting after breast surgery in chinese han female population
- Pages: 936-941
- First Published: 19 February 2021
Association between interleukin 28B polymorphism and sustained virological response to sofosbuvir plus daclatasvir in chronic hepatitis C genotype 4 Egyptian patients
- Pages: 942-949
- First Published: 25 March 2021
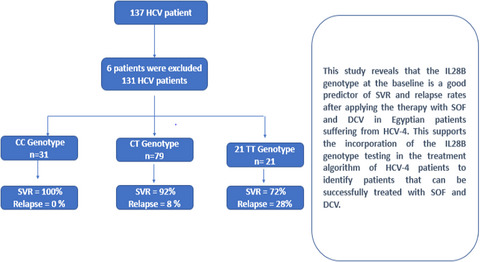
This study reveals that the IL28B genotype at the baseline is a good predictor of SVR and relapse rates after applying the therapy with SOF and DCV in Egyptian patients suffering from HCV-4. This supports the incorporation of the IL28B genotype testing in the treatment algorithm of HCV-4 patients to identify patients that can be successfully treated with SOF and DCV.
Risk comparison of beta-lactam-induced anaphylaxis: Therapeutic stratification analysis in a Vietnamese pharmacovigilance database
- Pages: 950-956
- First Published: 10 February 2021
Efficacy and safety of restarting antiplatelet therapy for patients with spontaneous intracranial haemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 957-965
- First Published: 04 February 2021
A qualitative study on the development of pharmacist-managed clinics in Taiwan
- Pages: 966-974
- First Published: 10 February 2021
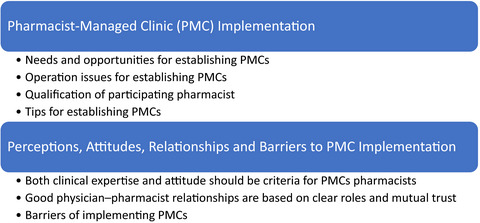
This study used semi-structured interviews to understand implementation issues and perceptions of pharmacist-managed clinics in Taiwan. Participants described influential factors in establishing PMCs, including clinical expertise, attitude towards patient care and trust building with collaborating physicians. Operational concerns included role clarifications, manpower shortage, inadequate advanced training or certification, regulatory issues and a lack of service promotion.
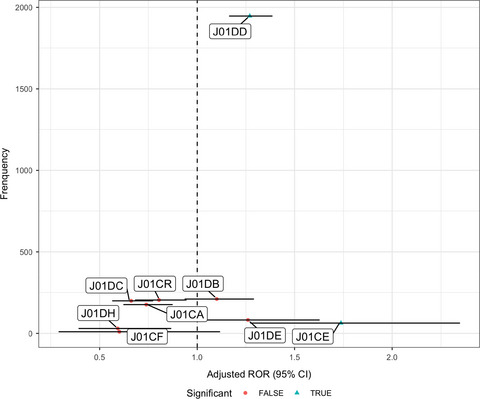
Estimation of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor–related genital and urinary tract infections via electronic medical record–based common data model
- Pages: 975-983
- First Published: 10 February 2021
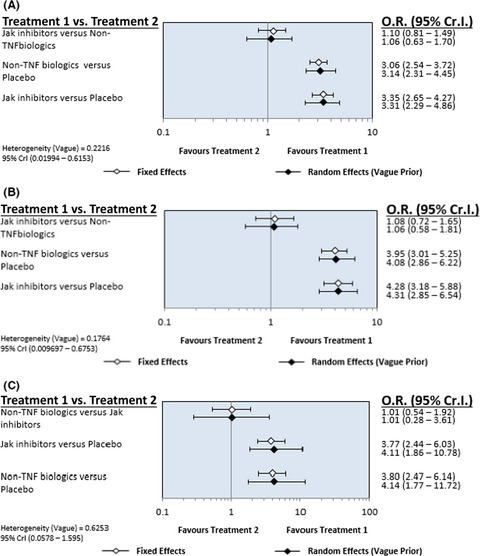
Comparative effectiveness and safety of non-tumour necrosis factor biologics and Janus kinase inhibitors in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis showing insufficient response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: A Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 984-992
- First Published: 18 February 2021
Effectiveness of fidaxomicin versus oral vancomycin in the treatment of recurrent clostridioides difficile
- Pages: 993-998
- First Published: 20 February 2021
Long-term efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in anaemia of chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis including 13,146 patients
- Pages: 999-1009
- First Published: 21 February 2021
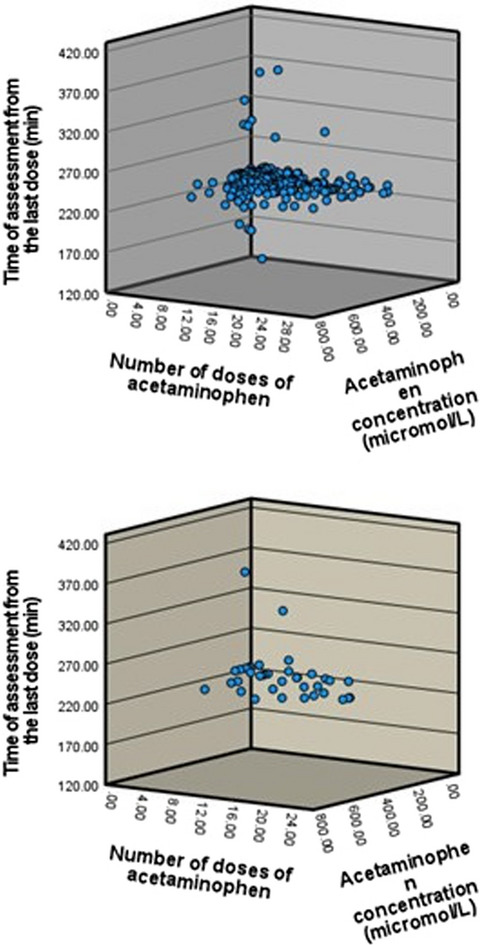
Intravenous acetaminophen (at 15 mg/kg/dose every 6 hours) in critically ill preterm neonates with patent ductus arteriosus: A prospective study
- Pages: 1010-1019
- First Published: 27 February 2021
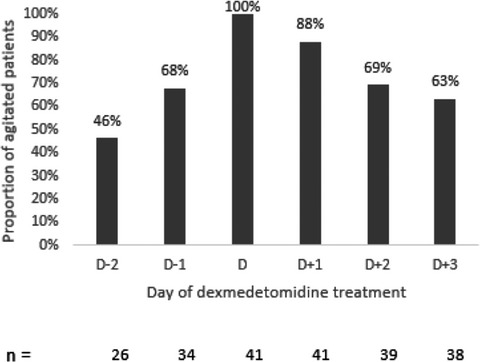
Safety of dexmedetomidine for the control of agitation in critically ill traumatic brain injury patients: a descriptive study
- Pages: 1020-1026
- First Published: 19 February 2021
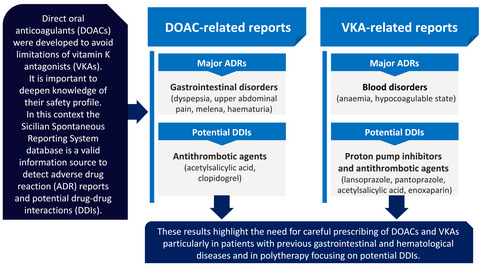
Adverse drug reactions with oral anticoagulants: data from sicilian spontaneous reporting system database
- Pages: 1027-1040
- First Published: 01 March 2021
Curbing proton pump inhibitor overprescribing: Multifaceted strategies in an academic hospital
- Pages: 1041-1045
- First Published: 24 February 2021
The association between statins exposure and peripheral neuropathy risk: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 1046-1054
- First Published: 25 February 2021
Impact and barriers of a pharmacist-led practice with computerized reminders on intravenous to oral antibiotic conversion for community-acquired pneumonia inpatients
- Pages: 1055-1061
- First Published: 07 June 2021
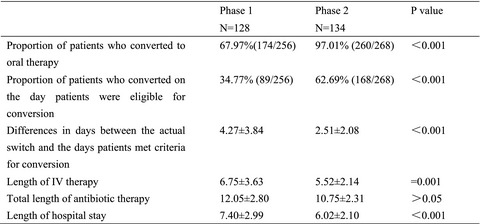
The proportion of patients who converted to oral therapy on the day patients were eligible for the conversion was significantly increased, and the length of IV antibiotic therapy days and the length of hospital stay for patients were both significantly shorter after the pharmacists’ intervention with computerized reminders on IV-PO antibiotic conversion for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) inpatients.
Safety of tocilizumab in COVID-19 pregnant women and their newborn: A retrospective study
- Pages: 1062-1070
- First Published: 26 February 2021
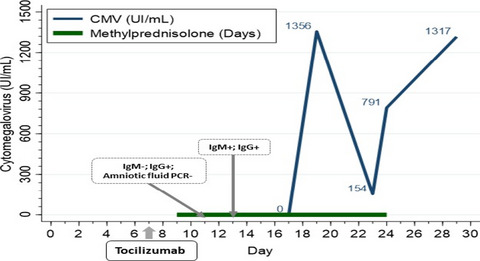
Evolution of cytomegalovirus viral load and serology tests in one pregnant patient, in which viral reactivation was detected. She received a single dose of tocilizumab and methylprednisolone therapy for 15 days. Baseline IgM antibodies and amniotic fluid polymerase-chain-reaction were negative, but they became positive 6 days after tocilizumab infusion and viral load was detected on day 13.
Safe handling and delivery of biological medications during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 1071-1082
- First Published: 18 March 2021
Clinical outcomes of pharmaceutical care intervention in HIV positive patients with hypertension: A randomized controlled study
- Pages: 1083-1094
- First Published: 05 March 2021
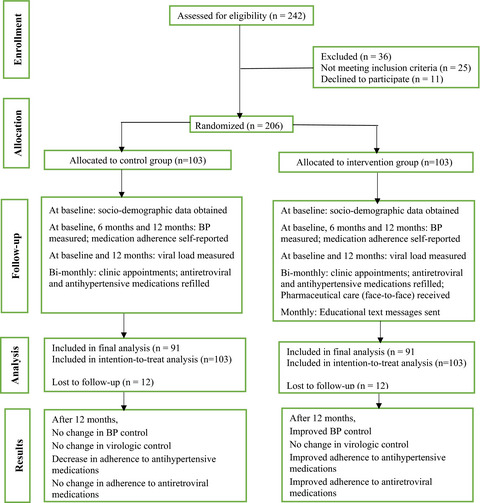
- This randomized controlled study evaluated the impacts of a 12-month pharmaceutical care intervention programme on clinical outcomes in HIV positive patients with hypertension.
- The interventions significantly improved blood pressure control and adherence to medications, but had no statistically significant effect on virologic control.
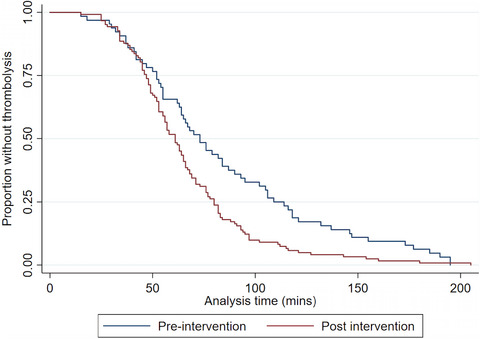
Involvement of emergency medicine pharmacists in stroke thrombolysis: A cohort study
- Pages: 1095-1102
- First Published: 22 March 2021
Outcomes of a pharmacist-driven vancomycin monitoring initiative in a community hospital
- Pages: 1103-1108
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Vancomycin administration requires close monitoring of serum vancomycin levels and appropriate dosing based on patients’ renal function, underlying infection type and serum concentration levels. This article explores the implications of a pharmacist-driven vancomycin monitoring initiative, which was implemented at Mercy Catholic Medical Center's Philadelphia Campus (MPC) in July 2016. Pharmacist-driven vancomycin monitoring significantly improved the monitoring compliance of vancomycin trough levels; specifically, the initiative improved the total percentage of patients attaining desired trough goals and helped reduce further renal insult from supratherapeutic vancomycin level.
Improving meningococcal MenACWY and 4CMenB/meningococcal group B vaccine-related health literacy in patients: Importance of readability of pharmaceutical Patient Leaflets
- Pages: 1109-1116
- First Published: 25 March 2021
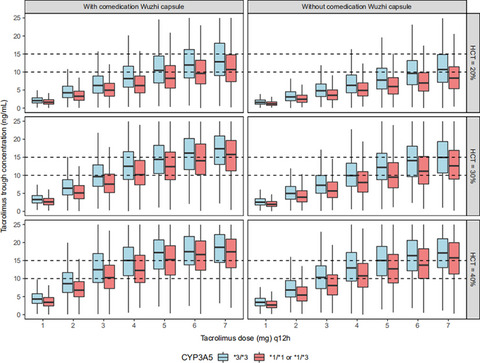
Population pharmacokinetic analysis and dosing guidelines for tacrolimus co-administration with Wuzhi capsule in Chinese renal transplant recipients
- Pages: 1117-1128
- First Published: 25 March 2021
The outcomes and acceptance of pressurized metered-dose inhaler bronchodilators with venturi mask modified spacer in the outpatient emergency department during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 1129-1138
- First Published: 25 March 2021
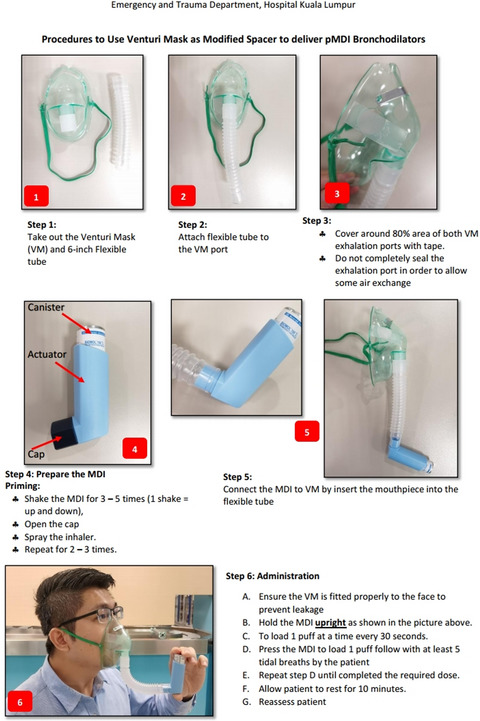
The use of nebulizer is discouraged during the COVID-19 pandemic. The pMDI bronchodilators delivered via Venturi mask modified spacer appeared to be comparable to nebulizer in treating mild to moderate asthma and COPD exacerbation in the outpatient ED setting. The Venturi mask modified spacer can be a cheap and effective alternative to the commercial spacer in a resource-limited situation.
Association between potentially inappropriate medication and adverse drug reactions in hospitalized elderly patients
- Pages: 1139-1147
- First Published: 27 April 2021
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced hepatic failure in lung cancer patients: A study of signal mining and analysis of the FDA adverse event reporting system database
- Pages: 1148-1154
- First Published: 25 March 2021
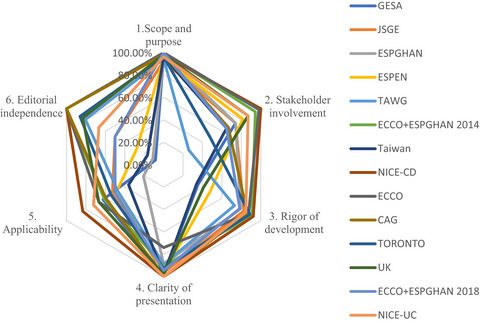
Quality assessment of clinical guidelines on probiotics therapy in children with IBD using the AGREE II instrument
- Pages: 1155-1165
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Pharmacokinetic comparison of nalbuphine with single injection and patient-controlled analgesia mimic method in healthy Chinese volunteers
- Pages: 1166-1172
- First Published: 03 May 2021
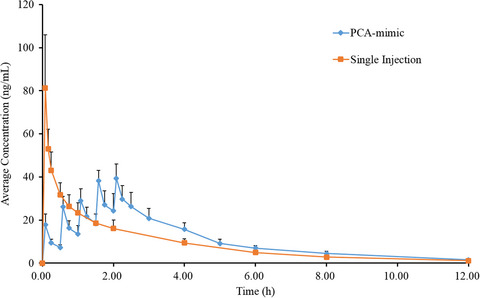
Compared with those in the single-injection group, the area under concentration-time curve (AUC0–t) and effective analgesic concentration durations in the patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) group were similar, whereas Cmax was decreased significantly. Therefore, the PCA method was more suitable for the clinical application of nalbuphine injection owing to the superiority of lower concentration fluctuation and the improved safety profile.
Severe thrombocytopenia induced by trastuzumab rechallenge: a case report and literature review
- Pages: 1173-1177
- First Published: 18 March 2021
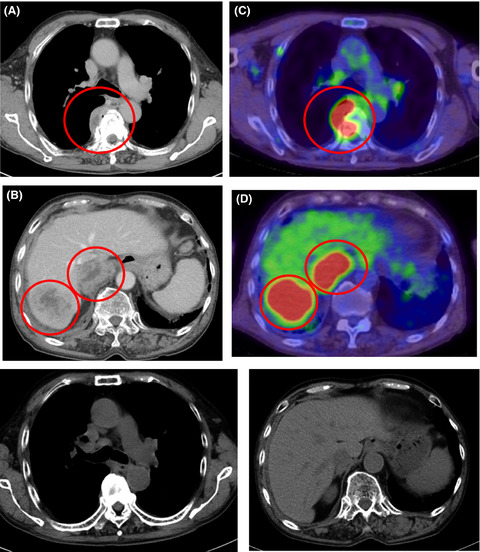
Methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorder with an osteolytic vertebral lesion in an elderly patient with rheumatoid arthritis: A case report
- Pages: 1178-1181
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Therapeutic Bayesian monitoring of sunitinib in two patients with impaired absorption or elimination
- Pages: 1182-1184
- First Published: 05 April 2021
Ibalizumab-uiyk as a bridge therapy for a patient with drug-resistant HIV-1 infection receiving chemotherapy: A case report
- Pages: 1185-1187
- First Published: 10 June 2021

Our case describes a patient with drug-resistant HIV infection and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), who initiated chemotherapy which had drug interactions with his antiretroviral therapy (ART). During chemotherapy, darunavir/cobicistat was held and ibalizumab-uiyk was initiated, as this medication has no known drug-drug interactions, to ensure he was on three active HIV medications. Ibalizumab-uiyk may be used as bridge therapy for patients with drug-resistant HIV infection undergoing chemotherapy.