Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
The Role of Innate Immunity in Healthy Aging Through Antimicrobial Peptides
- Pages: 375-383
- First Published: 21 January 2025
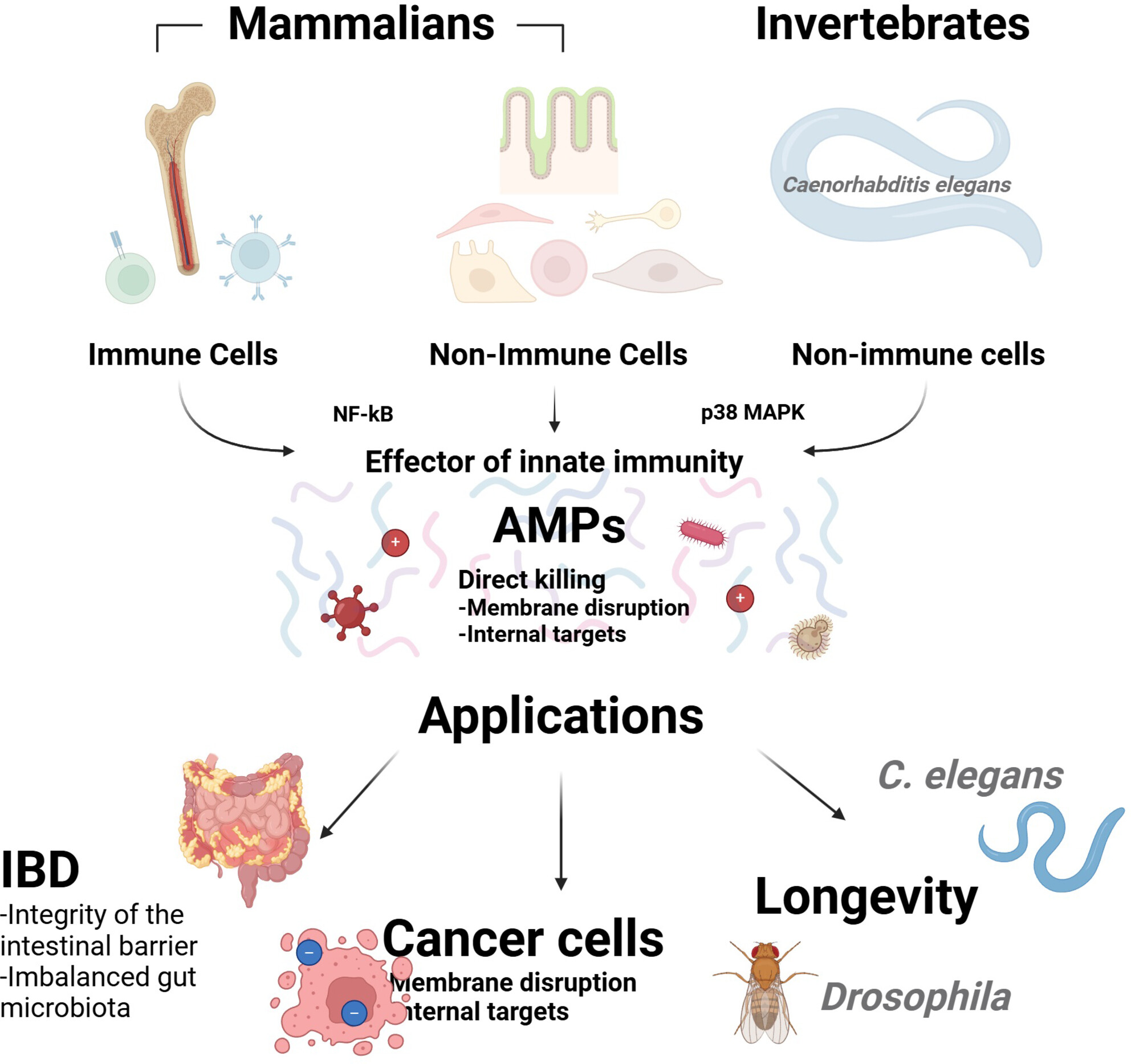
This study investigates the role of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in innate immune responses, focusing on their function in pathogen defence and aging regulation. The research reveals a conserved mechanism across species, from invertebrates to humans, highlighting AMPs' potential in addressing age-related challenges. These findings open new avenues for therapeutic interventions targeting innate immunity through AMPs to combat age-associated diseases and promote healthy aging.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Newly Found Rat CD103 − Dendritic Cells Represent a Highly Immunogenic Subpopulation of Type-2 Conventional Dendritic Cells, Corresponding to Known Dendritic Cell Subsets in Mice and Humans
- Pages: 384-401
- First Published: 04 January 2025
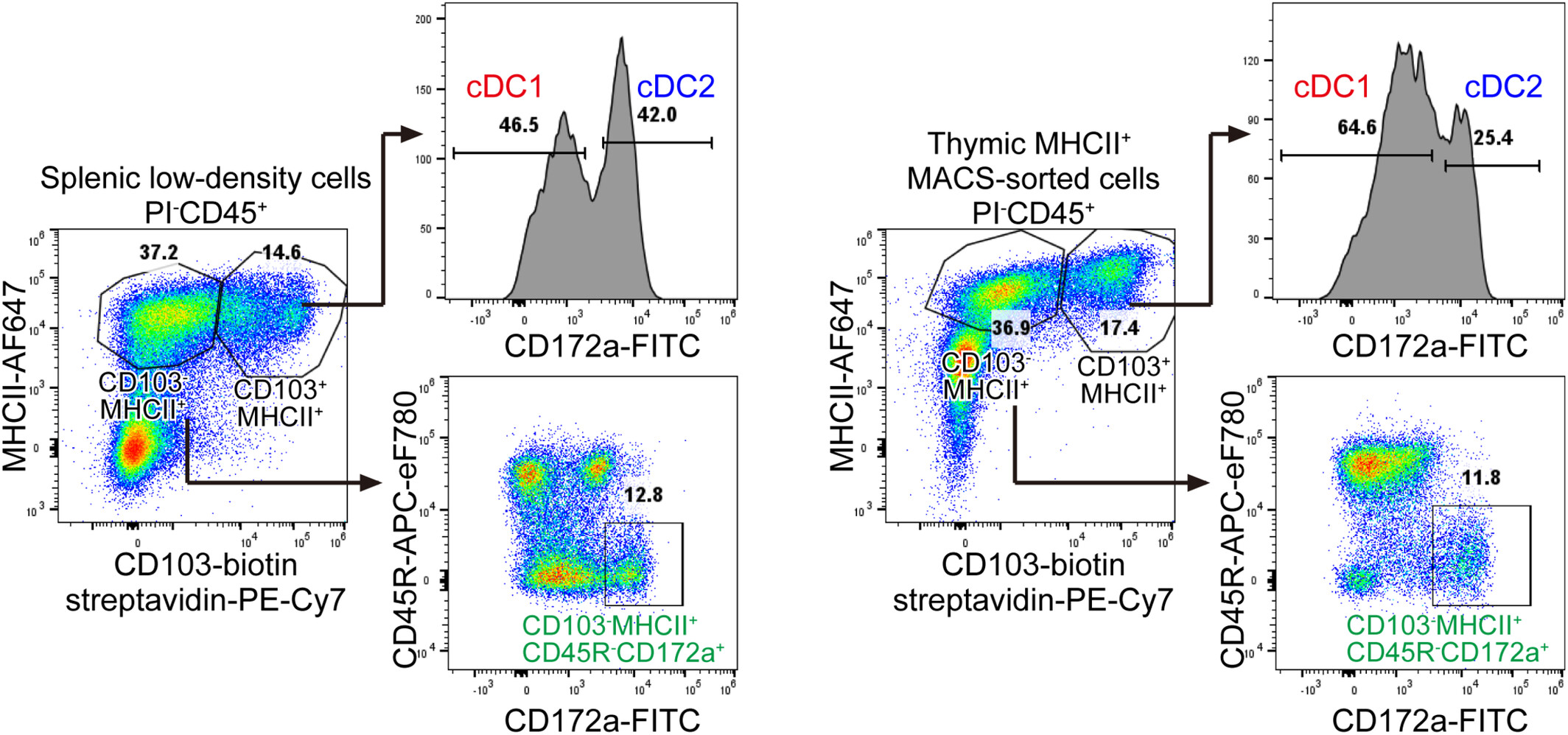
CD103−MHCII+CD45R−CD172a+ cells, which lack the classic rat dendritic cell marker CD103, were identified in the spleen and thymus of rats. Transcriptomic analyses revealed that these cells represent a highly immunogenic subpopulation of the conventional dendritic cell 2 (cDC2) subset, leading us to designate them as CD103− cDC2. This subset demonstrated pronounced immunogenic activity in vitro. Comparative transcriptomic and gene set enrichment analyses further showed that rat CD103− cDC2 corresponds to cDC2b, moDC, and inf-cDC2 in mice and humans, sharing their markers and adaptive immunity-associated GO terms.
Chronological Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Pages: 402-410
- First Published: 08 January 2025
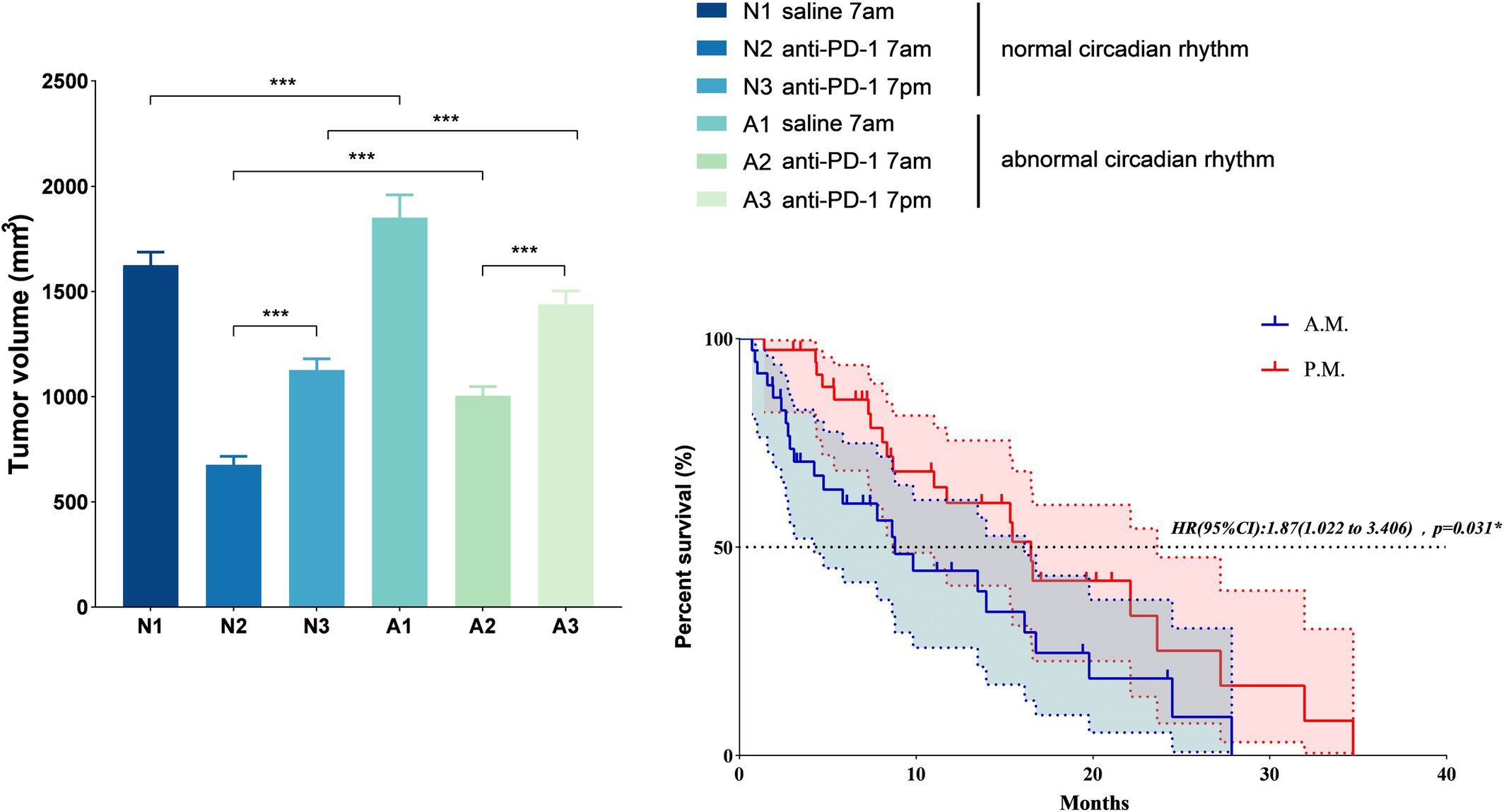
Our animal experiments showed that mice treated with ICIs in the morning showed slower tumour growth and smaller tumour volumes than those in the afternoon, accompanied by increased expression of BMAL1 and PER2 and suppression of PD-L1 expression. Retrospective analysis showed that patients who received ICIs in the afternoon (after 12:00) had significantly longer progression-free survival than those in the morning (before 12:00) (median was 16.5 months versus 9.8 months, respectively, p = 0.031, hazard ratio = 1.87).
Simultaneous Blockade of CD209 and CD209L by Monoclonal Antibody Does Not Provide Sufficient Protection Against Multiple Viral Infections In Vivo
- Pages: 411-422
- First Published: 09 January 2025
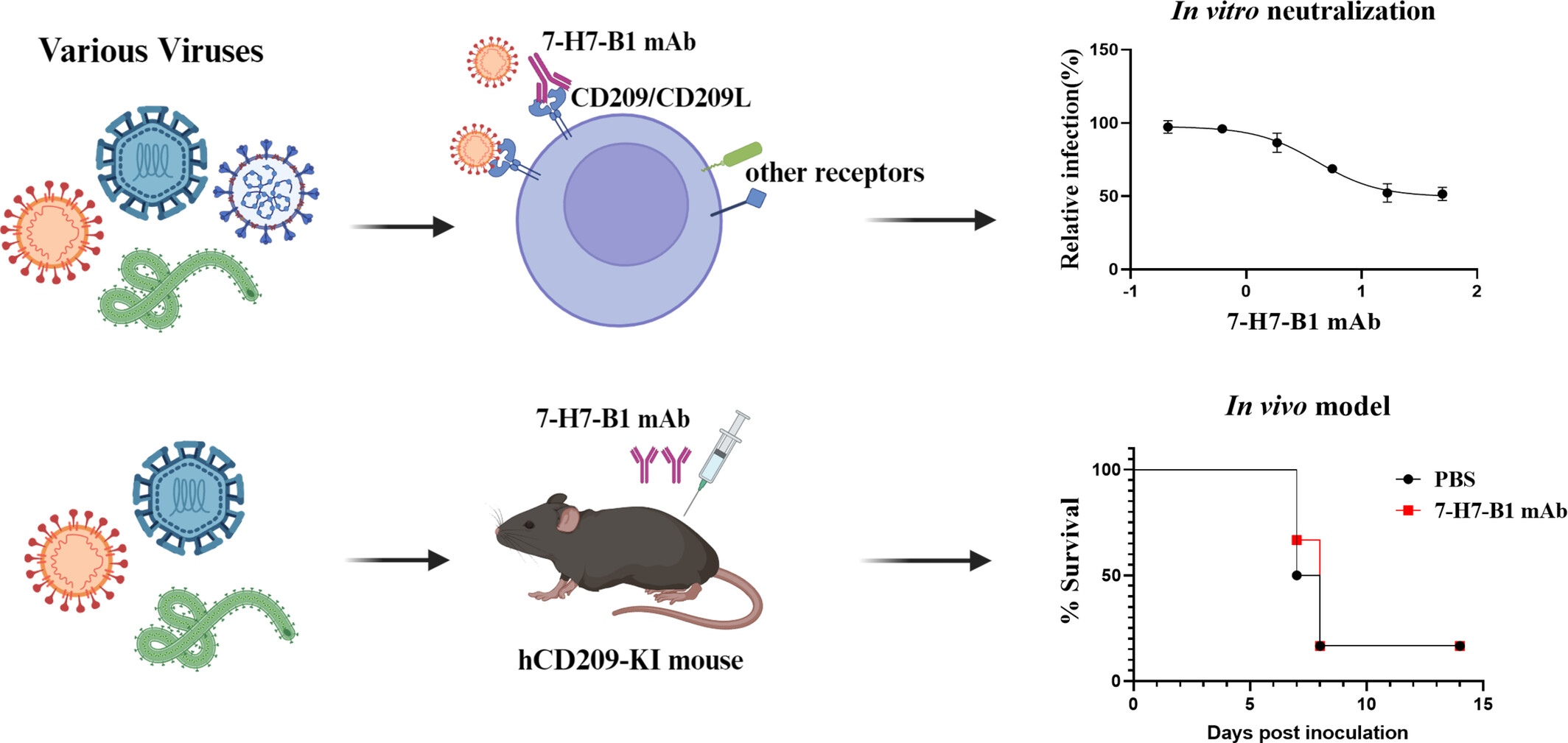
Many virus species, including Ebola virus, Marburg virus, SARS-CoV-2, DENV and ZIKV, exploit CD209 and CD209L as alternative or attachment receptors for viral infection. The 7-H7-B1 mAb, which blocks CD209 and CD209L, can effectively inhibit multiple pseudotyped or live viral infections in vitro. However, the 7-H7-B1 mAb does not provide favourable protection against Zaire Ebola virus or ZIKV infection in hCD209 knock-in mice in vivo.
Efficacy of Subcutaneous, Sublingual and Oral Immunotherapy for Allergens: A Comparative Study
- Pages: 423-433
- First Published: 12 January 2025
The study evaluates subcutaneous, sublingual and oral immunotherapy for various allergens, highlighting their effectiveness and safety. Subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) was most effective for aeroallergens like pollen and dust mites but had a higher rate of side effects. Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) offered comparable efficacy with fewer side effects, making it safer for wider use. Oral immunotherapy (OIT) excelled in treating food allergies, particularly in elderly patients due to its tolerability. These findings underscore the importance of tailoring immunotherapy routes based on allergen type, patient profile and treatment goals. The research affirms the significant potential of these methods to improve allergic disease management.
IL-6 Signalling to Responding T Cells Is Key to Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide-Exposed Endothelial Cell Enhancement of Th17 Immunity During Langerhans Cell Antigen Presentation
- Pages: 434-449
- First Published: 19 January 2025
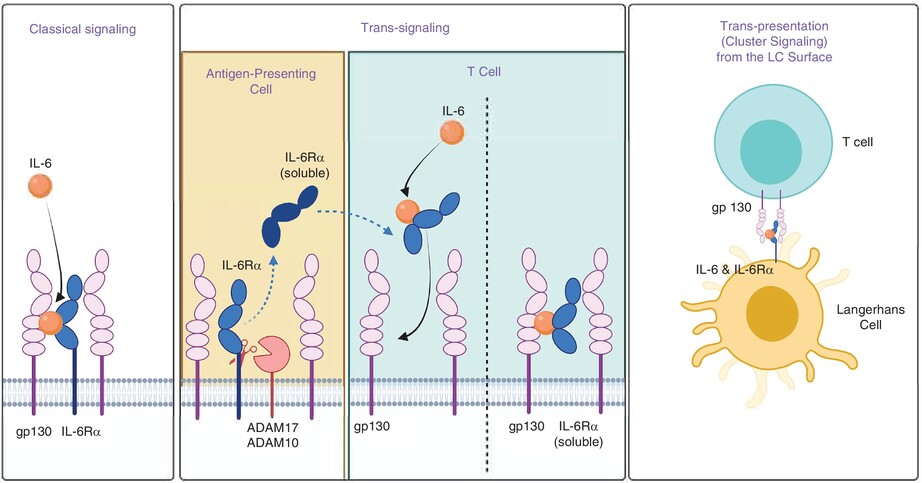
Classical presentation (left), trans-signalling (middle) and trans-presentation (right) of IL-6 to responding T cells. Left: Soluble IL-6 binds to a heterodimer made up of the IL-6Rα chain and gp130. Middle: Soluble complex of the IL-6Rα chain (cleaved by ADAM17 or ADAM10 from the APC surface) and IL-6 engages gp130 on the T-cell surface. Right: IL-6 bound to the IL-6Rα chain on the APC surface engages gp130 on the APC surface. Our data indicate that Langerhans cells exposure to IL-6 results in biasing of the outcome of antigen presentation towards the Th17/IL-17 pole due to nonclassical presentation of IL-6.
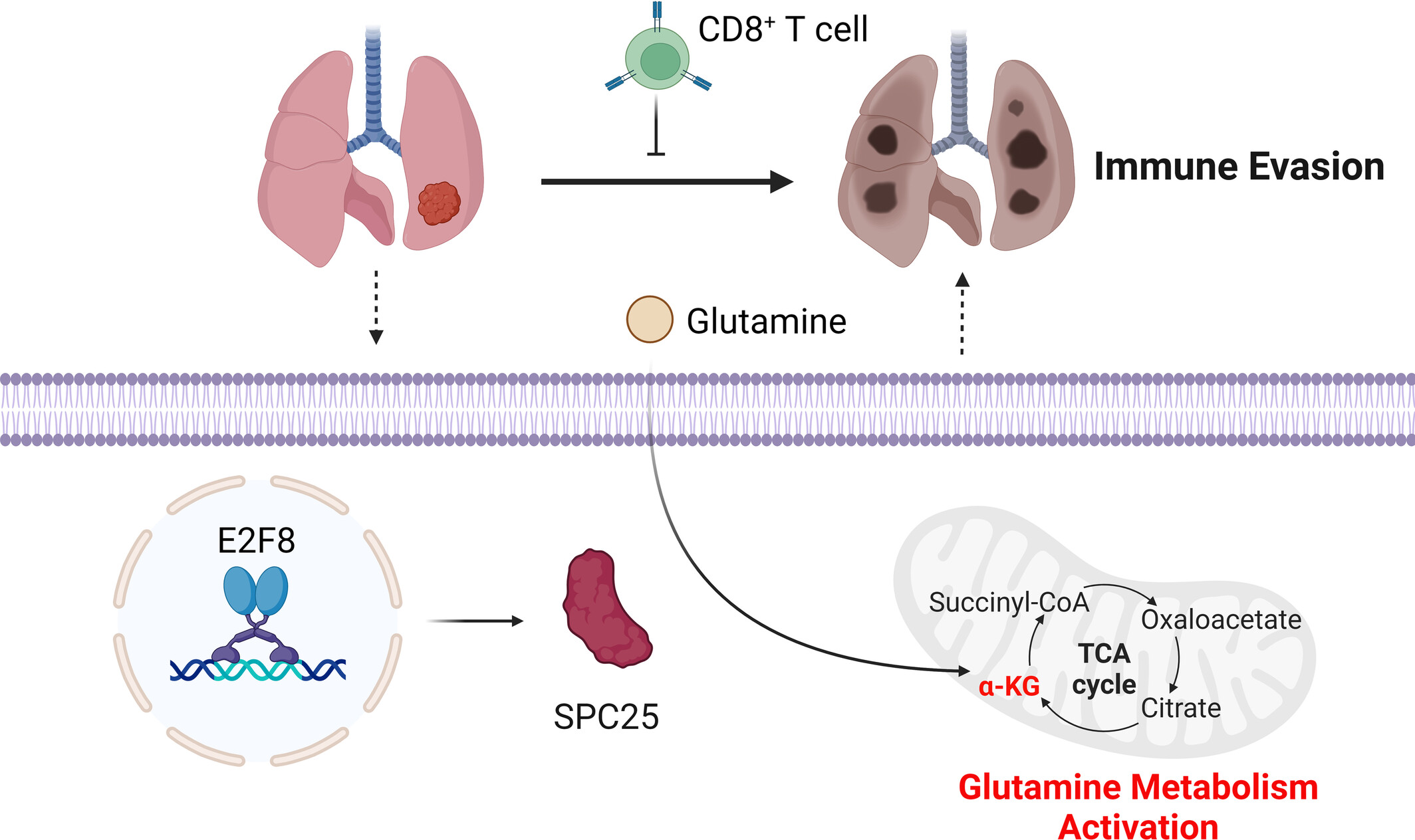
Mechanism Study of E2F8 Activation of SPC25-Mediated Glutamine Metabolism Promoting Immune Escape in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 450-461
- First Published: 19 January 2025
TYK2 :p.Pro1104Ala Variant Protects Against Autoimmunity by Modulating Immune Cell Levels
- Pages: 462-469
- First Published: 21 January 2025
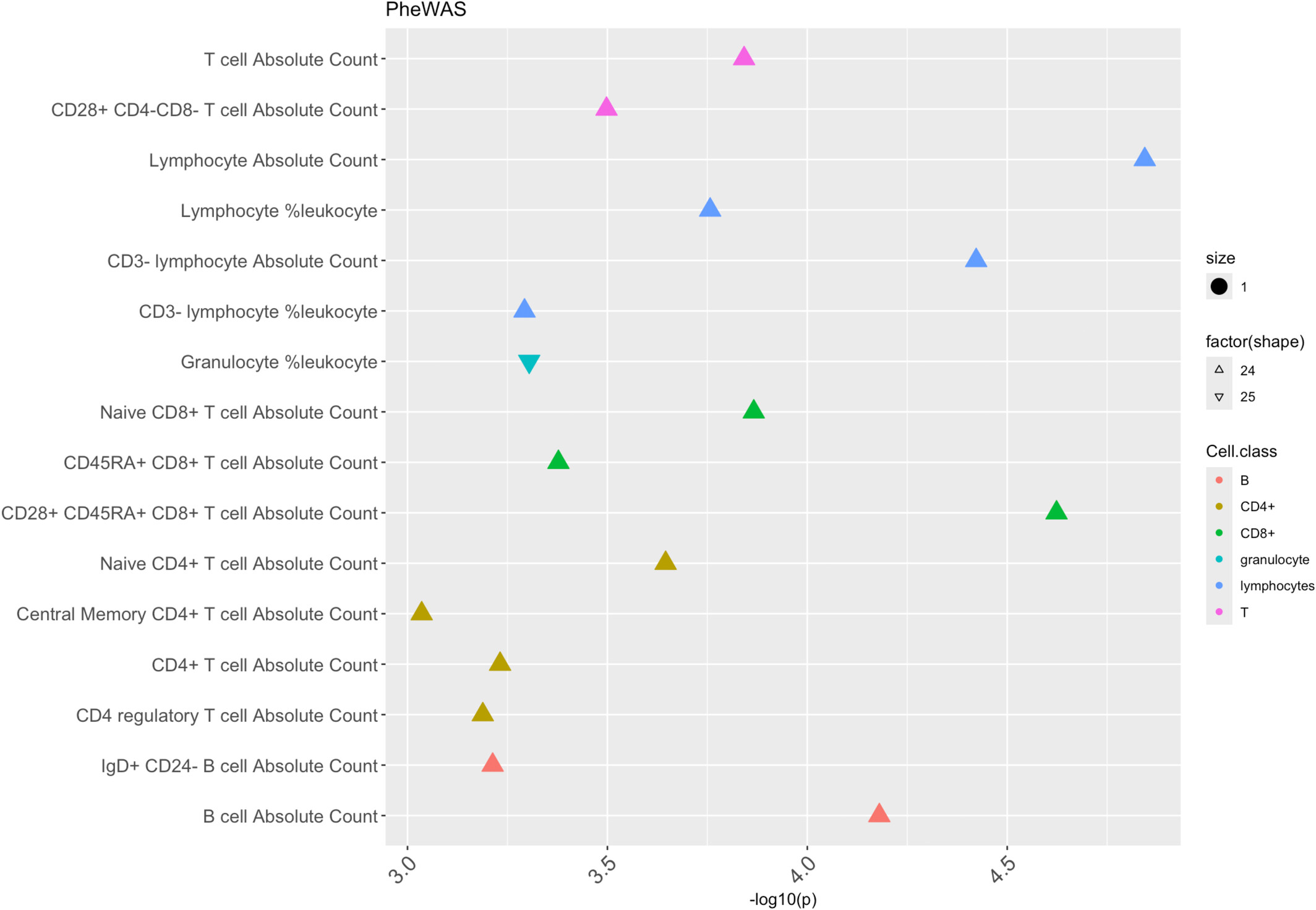
TYK2:p.Pro1104Ala variant confers protection from several autoimmune disorders but predisposes to infection and we show that the mechanism of its action includes an increase of the levels of lymphocytes in all compartments (CD4+, CD8+ and B), but these cells are mainly naive. Thus, this variant constrains immune activation thereby protecting from autoimmunity. Our work identifies the cellular mechanisms of regulation by the TYK2:p.Pro1104Ala variant providing novel hypotheses for the general immune mechanisms of protection from autoimmunity.
Renal and Peripheral Blood Transcriptome Signatures That Predict Treatment Response in Proliferative Lupus Nephritis—A Prospective Study
- Pages: 470-480
- First Published: 28 January 2025
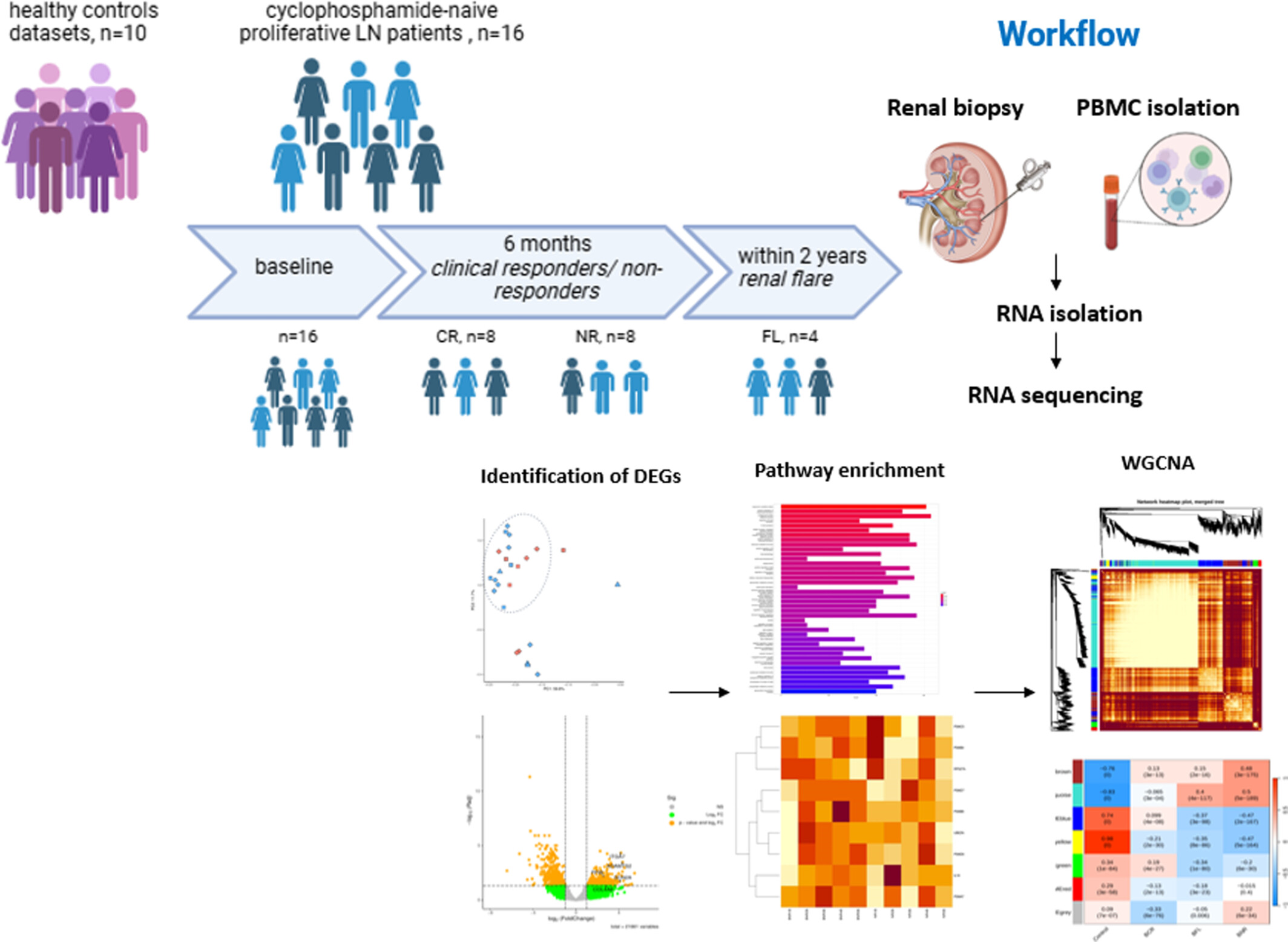
We identified significant genes and pathways exclusive to distinct cyclophosphamide-based treatment outcomes to in lupus nephritis (LN). TENM2, NLGN1 from PBMCs and AP005230.1 from PBMCs and renal tissue predicted non-response and a model combining these genes enhanced the predictive performance. AC092436.3 from PBMCs predicted renal flare. These findings highlight the complexity of LN and underscore the need for nuanced therapeutic strategies tailored for each individual.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Maternal Carriage of Prevotella copri Is Associated With Increased Thymus Derived Naïve Regulatory T Cells in Cord Blood
- Pages: 481-484
- First Published: 13 February 2025