Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
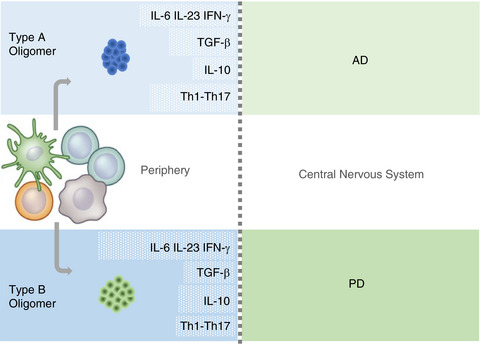
Do peripheral protein oligomers in neurodegenerative diseases shape T cell responses beyond the brain?
- Pages: 209-210
- First Published: 15 September 2021
REVIEWS
Influence of chronic stress on the mechanism of the cytotoxic system in common carp (Cyprinus carpio)
- Pages: 211-222
- First Published: 30 April 2021
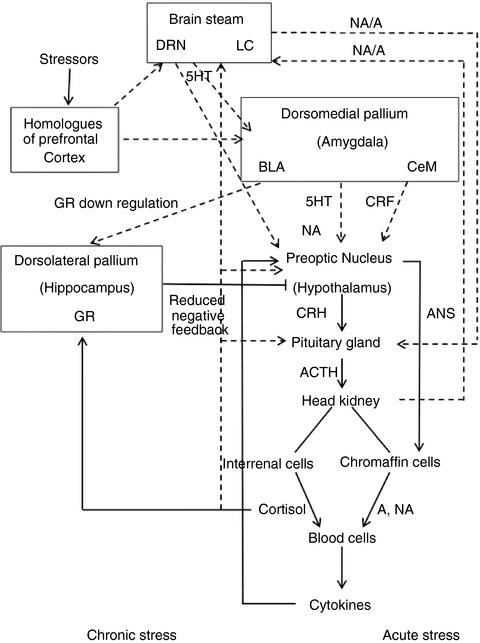
Chronic stress suppresses the immune system and especially the metabolism of components in the cytotoxic system, and the proliferation and maturation of cells essential for the body's protection against disease agents. This may be the reason for the increase in morbidity in chronic stressful situations.
Biological functions of IL-17-producing cells in mycoplasma respiratory infection
- Pages: 223-230
- First Published: 30 April 2021
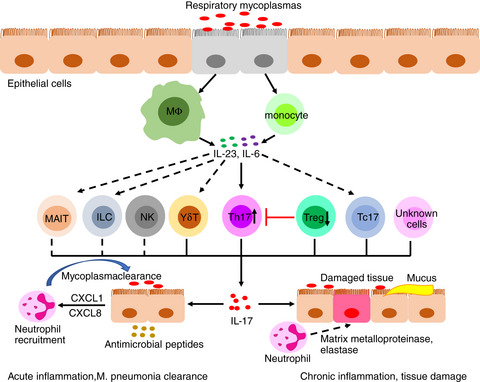
At the early stage of mycoplasma respiratory infection, IL-17 can be protective as it can induce epithelial cell activation-secreting chemokines to recruit neutrophils for host defence, producing antimicrobial peptides to maintain the lung barrier function; however, aberrant release of IL-17 in the lung results in persistent neutrophil recruitment, degranulation and tissue damage and even asthma during chronic infection.
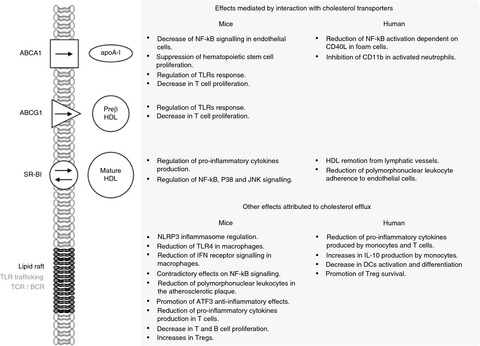
The role of high-density lipoprotein in the regulation of the immune response: implications for atherosclerosis and autoimmunity
- Pages: 231-241
- First Published: 02 May 2021
Endocannabinoids in immune regulation and immunopathologies
- Pages: 242-252
- First Published: 30 May 2021
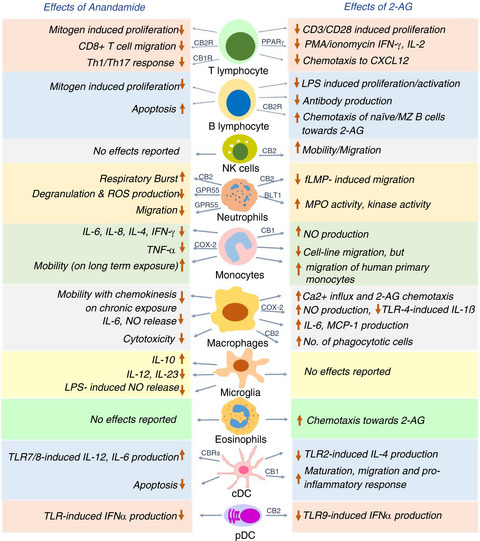
Endocannabinoids are key bioactive components of the endocannabinoid system, and the profound influence of endocannabinoids on the modulation of the immune system is being increasingly appreciated. Endocannabinoids seem to exert both anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory effects in specific contexts; thus, knowledge on endocannabinoid–immune cell crosstalk will pave the way to therapeutic implications of modulators of this pathway in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory disorders.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
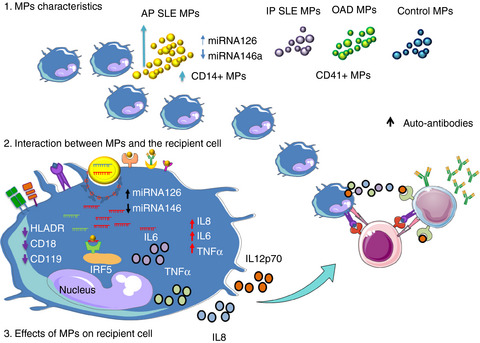
Plasma microparticles from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus modulate the content of miRNAs in U937 cells
- Pages: 253-265
- First Published: 18 May 2021
The detection of long-lasting memory foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) virus serotype O-specific CD4+ T cells from FMD-vaccinated cattle by bovine major histocompatibility complex class II tetramer
- Pages: 266-278
- First Published: 18 May 2021
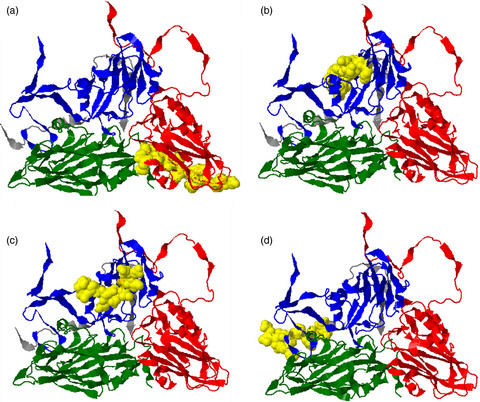
We have used bovine MHC II tetramers and PBMC from cattle vaccinated against foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) to identify novel CD4+ T-cell epitopes in the capsid of FMD virus (FMDV) and to confirm the presence of long-lasting FMDV-specific CD4+ T cells. Ex vivo analyses revealed the presence of CD45RO+CCR7+ central memory cells in higher frequency and epitope-expanded T-cell populations produced IFN-γ in vitro indicating a Th1 cell phenotype. This work indicates an important role in maintaining cell adaptive immunity after FMD vaccination and contributes to our understanding of vaccine efficacy.
Optimal CD8+ T-cell memory formation following subcutaneous cytomegalovirus infection requires virus replication but not early dendritic cell responses
- Pages: 279-291
- First Published: 18 May 2021
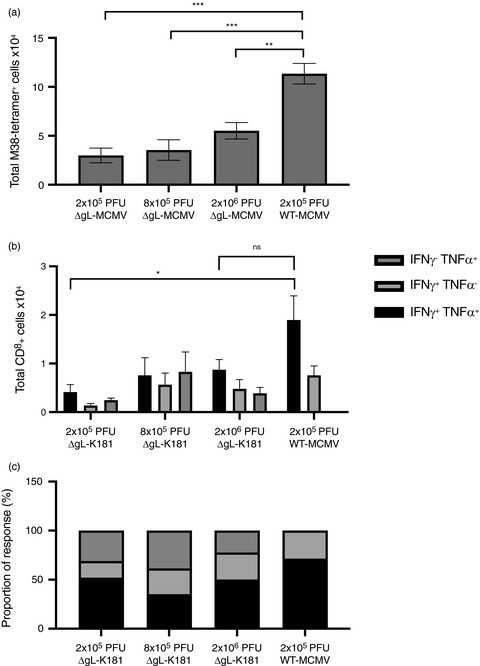
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a potentially exciting vaccine vector, but pathogenicity may preclude the use of replicating viruses. Here, we show that a spread-deficient CMV vector is attenuated in the ability to induce T-cell memory formation after subcutaneous immunization. This results in pronounced loss of polyfunctional T cells, possibly linked to reduced development of TCF1-expressing T cells.
Induction of the apoptosis, degranulation and IL-13 production of human basophils by butyrate and propionate via suppression of histone deacetylation
- Pages: 292-304
- First Published: 17 May 2021
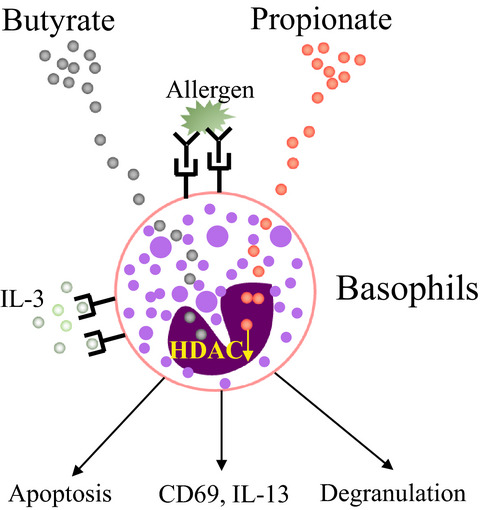
Butyrate and propionate but not acetate induced the apoptosis, degranulation and IL-13 expression of human basophils. Propionate and butyrate promoted histone acetylation of human basophils. Suppression of histone deacetylation by trichostatin A induced the apoptosis, degranulation and IL-13 expression of human basophils.
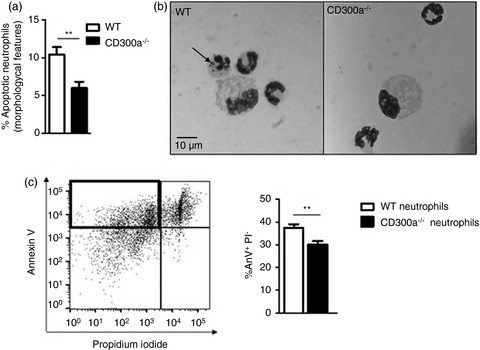
CD300a contributes to the resolution of articular inflammation triggered by MSU crystals by controlling neutrophil apoptosis
- Pages: 305-317
- First Published: 18 May 2021
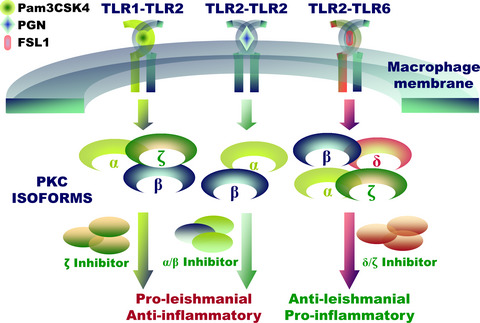
TLR2 dimer-specific ligands selectively activate protein kinase C isoforms in Leishmania infection
- Pages: 318-331
- First Published: 22 May 2021
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide limits reactive donor T cells and delays the development of graft-versus-host disease in a humanized mouse model
- Pages: 332-347
- First Published: 22 May 2021
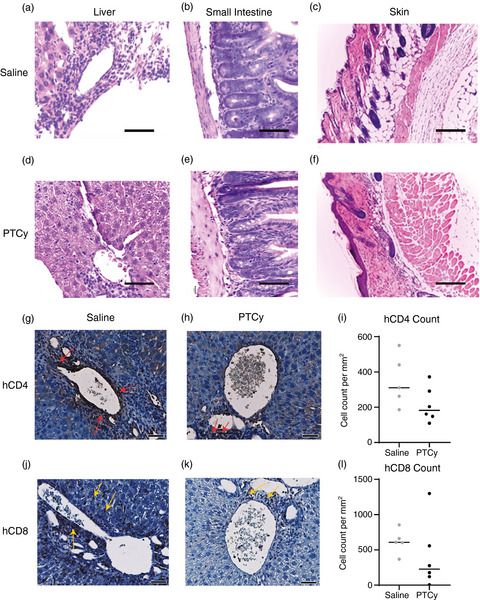
Graft-versus-host disease is a life-threatening complication of bone marrow transplantation. Post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) reduces clinical GVHD, but the mechanism is unclear. Using a humanized mouse model of GVHD, we demonstrate that PTCy not only reduces GVHD alongside reactive donor T cells in the liver, but also reduces human regulatory T cells, which are protective against disease.
Systemic and mucosal mobilization of granulocyte subsets during lentiviral infection
- Pages: 348-357
- First Published: 26 May 2021
Granulocyte subsets were characterized in systemic, mucosal and lymphoid tissues during lentiviral infection using the rhesus macaque model. We identified elevated neutrophils and eosinophils in the infected gastrointestinal mucosa, where significant inflammation and disruption occurs in lentivirus-induced disease.
Distinct responses of human peripheral blood cells to different misfolded protein oligomers
- Pages: 358-371
- First Published: 27 May 2021
Neutralizing interferon-α blocks inflammation-mediated vascular injury via PI3K and AMPK in systemic lupus erythematosus
- Pages: 372-385
- First Published: 02 June 2021
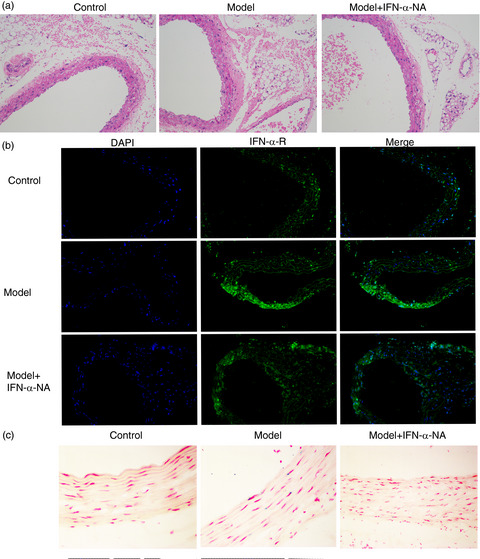
Pristane can cause obvious damage to the blood vessels of ApoE−/− mice, the pathological morphology of the arterial tissue of the SLE mouse model is disordered, and the basement membrane is thickened. The treatment of IFN-α-NA reverses these phenotypes. The expression of IFN-α receptor in the vascular endothelium is increased, and that of SA-β-Gal-positive EPCs in vascular endothelium is enhanced.
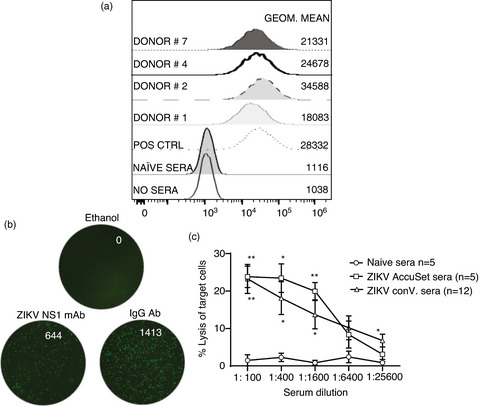
Non-structural protein 1-specific antibodies directed against Zika virus in humans mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
- Pages: 386-397
- First Published: 31 May 2021