Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
How Badly Does India Need Biologics for Severe Asthma?
- Pages: 518-520
- First Published: 25 June 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Advancing Remission in Severe Asthma With Benralizumab: Latest Findings, Current Perspectives and Future Direction
- Pages: 521-531
- First Published: 30 May 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Risk Factors for Fatal and Near-Fatal Food Anaphylaxis: Analysis of the Allergy-Vigilance Network Database
- Pages: 532-540
- First Published: 29 May 2025
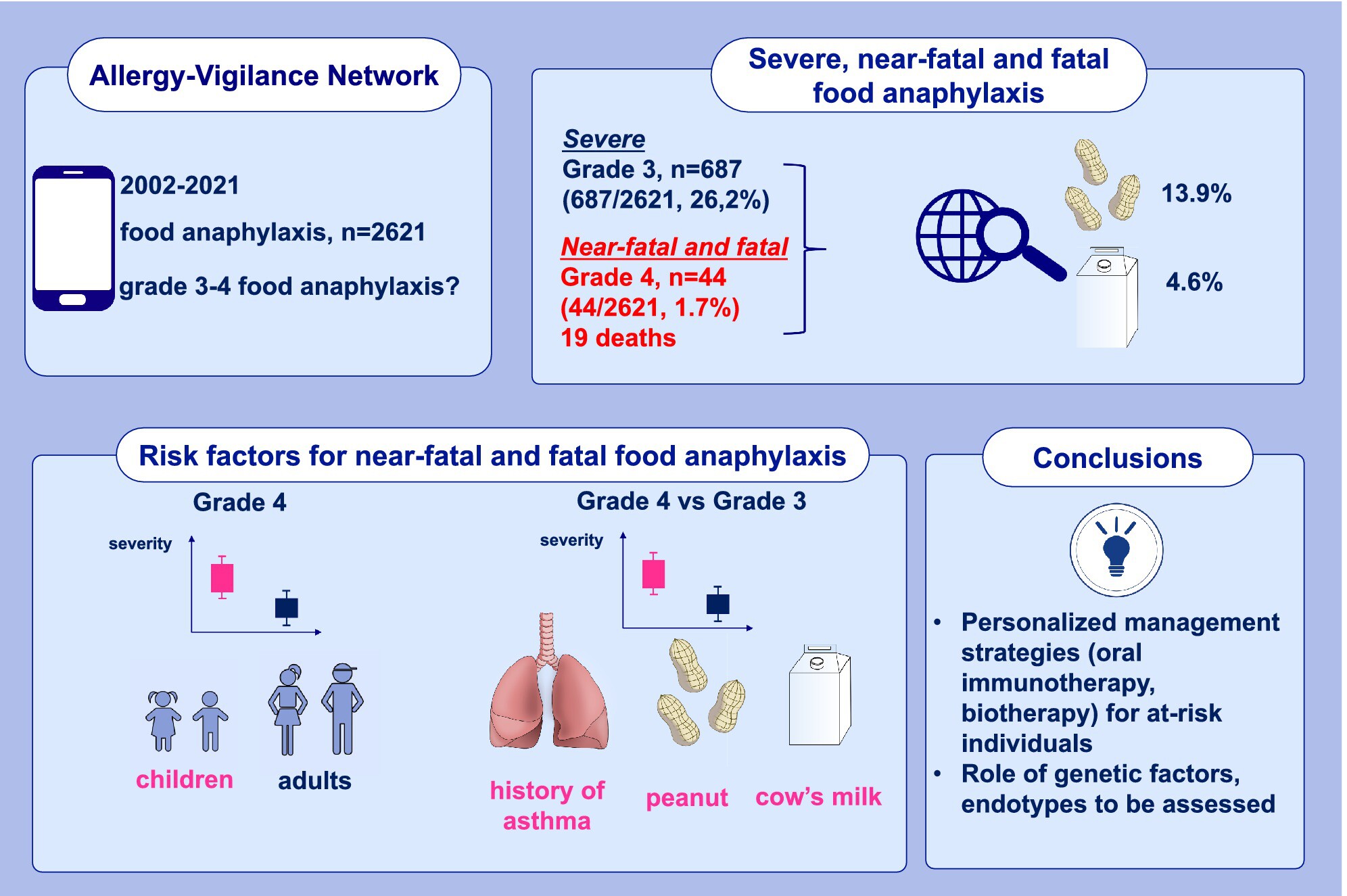
- Of the 2621 food anaphylaxis cases, 731 (27.9%) were considered as severe (grade 3, [94%] and grade 4 [6%]; 19 deaths).
- There were more grade 4 anaphylaxis cases in children than in adults (p = 0.01).
- In the multivariate analysis, individuals with a grade 4 anaphylaxis were more likely to have a history of asthma (OR [95% CI]: 5.46 [2.02–14.73], p < 0.001), peanut and cow's milk as culprit food triggers (OR: 4.94 [1.50–16.23], p = 0.009; OR: 6.44 [1.20–34.56], p = 0.03; respectively), compared to individuals with grade 3 anaphylaxis.
Identification of the Top 15 Drugs Associated With Anaphylaxis: A Pharmacovigilance Study
- Pages: 541-551
- First Published: 08 June 2025

This pharmacovigilance study identified the 15 most-reported drugs linked to anaphylaxis, including antibiotics and NSAIDs. The majority of drug-associated anaphylaxis reports were reported to occur within 2.5 h for most drugs. Despite being life-threatening yet recoverable, delayed recognition highlights the need for improved guidelines and enhanced pharmacovigilance systems for better management.
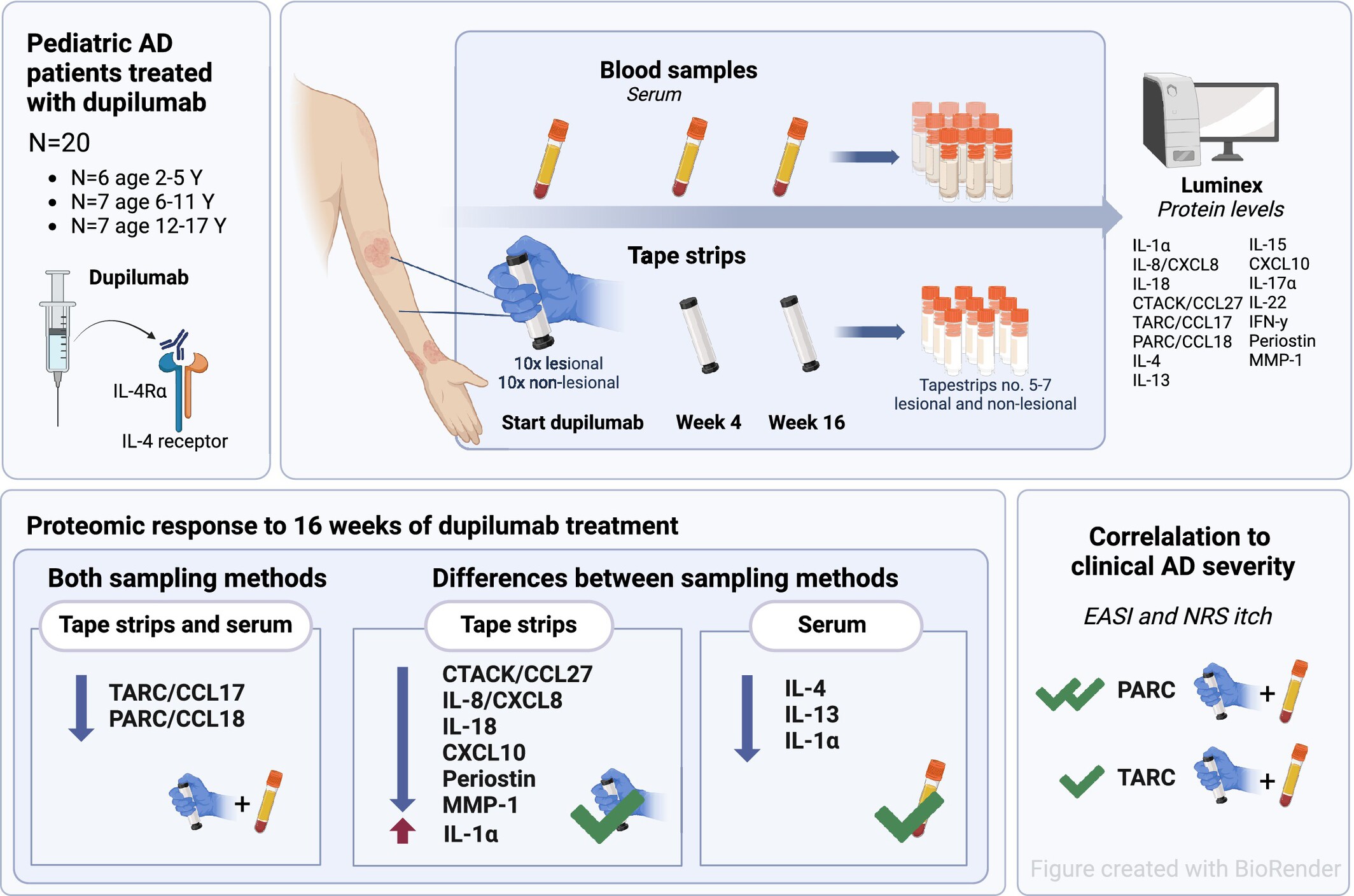
Complementary Analysis of Local and Systemic Effects of Dupilumab in Paediatric AD Using Tape Strips and Serum
- Pages: 552-563
- First Published: 15 May 2025
RESEARCH LETTER
Interaction of Atopy and Airway Dysbiosis Promotes Asthma Persistence in Children With Chronic Rhinosinusitis—5 Years Prospective Study
- Pages: 564-566
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Polyphenol Intake During Pregnancy and Childhood Asthma and Atopic Disorders: A Systematic Review
- Pages: 567-570
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Adult Asthma Diagnosis Based on the Japanese Practical Guideline: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Study
- Pages: 571-573
- First Published: 11 March 2025
Incidence and Prevalence of Childhood Atopic Diseases in Dutch Primary Care
- Pages: 574-576
- First Published: 14 March 2025
Global Trends in Atopic Dermatitis Burden Among Individuals Under 19 Years From 1990 to 2021
- Pages: 577-579
- First Published: 18 March 2025
DIFENSE Study Protocol: Early Intervention With Difamilast Ointment in Infantile Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis for Prevention of Transcutaneous Sensitisation
- Pages: 580-582
- First Published: 26 March 2025
Association Is Not Prediction—A Pervasive Issue in the Medical Literature
- Pages: 583-585
- First Published: 26 March 2025
Asthma Associated Cytokines Regulate Gasdermin A and Gasdermin B Expression by Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells
- Pages: 586-588
- First Published: 31 March 2025
Differential Expression of Type 1 and Type 17 Immune Pathways and Chemokines in Mild-to-Severe Asthma With Mid to High Neutrophilic Inflammation
- Pages: 589-591
- First Published: 31 March 2025
CORRECTION
Correction to “Biomarkers predicting the controller dose of omalizumab in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria”
- Page: 592
- First Published: 24 March 2025
Correction to “Adherence to Treatment in Allergic Rhinitis During the Pollen Season in Europe: A MASK-air Study”
- Page: 593
- First Published: 24 March 2025
Correction to Water hardness and atopic dermatitis in the first year of life in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study
- Pages: 594-595
- First Published: 05 May 2025