Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image, Volume 50, Issue 7
- Pages: i-ii
- First Published: 22 February 2012
Electro-optic activity of a nonlinear optical polymer is stabilized by crosslinking of the hyperbranched polymer, as presented by Shiyoshi Yokoyama and colleagues on page 1254. Since a nonlinear optical chromophore attached to the polymer side-chain has large molecular hyperpolarizability, the resulting electric-poled polymer film shows large electro-optic activity. When polarized laser light is used to irradiate the polymer film, polarization is effectively modulated by applying an electric field with large electro-optic coefficient. Hyperbranching of the polymer enhances its glass transition temperature, so that the poled polymer film is extremely stable with little decay of electro-optic activity. Despite crosslinking of the as-synthesized hyperbranched polymer, it forms a high optical quality film from many common solvents. Optical propagation loss is small enough for application in optical waveguide devices.
Inside Cover, Volume 50, Issue 7
- Pages: iii-iv
- First Published: 22 February 2012

The image shows the process of morphology transition from the self-assembly behavior of fluorosilicone diblock copolymers with equal block length, as presented in the Rapid Communication by Hua Cheng, Jin-Jin Li, and Zheng-Hong Luo on page 1249. By changing the solvent quality, the morphology transition could bring about the generation of novel large compound rod micelles and micrometer-scale-sized vesicles. Interestingly, those vesicles are susceptible to the variation of pressure and regular polygonal micelles can be ultimately obtained. The micelles are also shown to be microporous materials with potential application for further fabrication of ordered microstructures.
Rapid Communications
Regular polygonal micelles induced from fluorosilicone diblock copolymers
- Pages: 1249-1253
- First Published: 29 December 2011
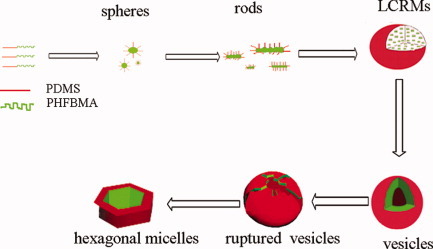
Charming polygonal micelles: The self-assembly bahavior of fluorosilicone copolymers with equal block length could bring about the generation of novel large compound rods micelles and microsize vesicles. Interestingly, those vesicles are susceptible to the variation of pressure and regular polygonal micelles can be ultimately obtained for the first time. The possible mechanism can be proposed for the micelles morphology transition (see picture).
Articles
Large electro-optic activity and enhanced temporal stability of methacrylate-based crosslinking hyperbranched nonlinear optical polymer
- Pages: 1254-1260
- First Published: 03 February 2012
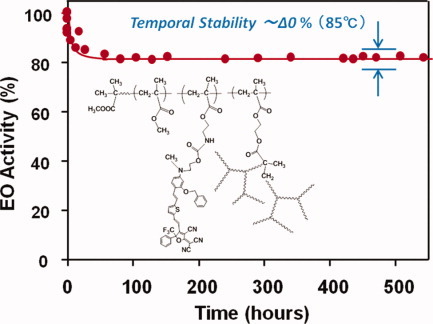
Electro-optic crosslinking polymers have been synthesized through initiator-fragment incorporation radical polymerization. Therefore, resulting EO polymers have hyperbranched type polymer chain and show improved glass transition temperature at 170 °C. Synthesized crosslinking polymers exhibited excellent solubility in common solvents to prepared high quality optical films. Electro-optic measurement of the electric-poled films showed electro-optic coefficient of 139 pm/V at the laser wavelength of 1.31 μm. Long term decay of EO activity was almost 0% at 85 °C for 500 h.
A novel benzimidazole moiety-containing benzoxazine: Synthesis, polymerization, and thermal properties
- Pages: 1261-1271
- First Published: 29 December 2011
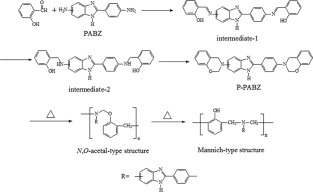
A novel benzoxazine-containing benzimidazole moiety with low-polymerization temperature and good thermal properties was synthesized and characterized. With the aid of differential scanning calorimetry and in situ Fourier transform infrared, its polymerization behavior was probed, and its favored polymerization pathway was given. The favored polymerization pathway was probably that formed N,O-acetal-type structure firstly and generated Mannich-type structure at elevated temperature. In order to decrease the polymerization temperature, the possibility of using this benzoxazine to blend with another benzoxazine was also explored. These blends exhibited lower processing temperature, and their polymers had higher glass transition temperature and enhanced thermal stability.
Hard-block degradable thermoplastic urethane-elastomers for electrospun vascular prostheses
- Pages: 1272-1280
- First Published: 29 December 2011
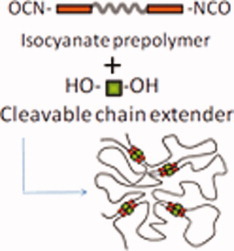
Thermoplastic polyurethanes were synthesized with two different ester containing chain extenders, and accelerated rates of hydrolysis were measured and compared to polylactic acid as a simple approximation to biodegradation. The thermoplastic polyurethanes were electrospun as tubular conduits, and a section was implanted into a rat as an infrarenal aorta graft. Initial histology indicates that biodegradation of the conduit is beneficial to endothelialization.
Acid-promoted double ring-opening reaction of bicyclobis (γ-butyrolactone) with alcohol and its application to polyester synthesis
- Pages: 1281-1289
- First Published: 29 December 2011
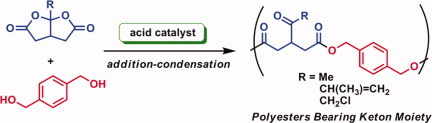
An acid-promoted reaction of bicyclobis(γ-butyrolactone) (BBL) and alcohol was investigated. BBL bearing methyl group reacted with benzyl alcohol in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid through the double- ring- opening of the bislactone structure to afford the corresponding diester. Based on these results, the reaction of BBLs having functional group with xylene-α,α-diol was carried out to obtain the corresponding polyesters bearing ketone group in the side chain.
Homopolymerization and copolymerization of a dilactone, 13,26-dihexyl-1,14-dioxa-cyclohexacosane-2,15-dione: Synthesis of bio-based polyesters and copolyesters consisting of 12-hydroxystearate sequences
- Pages: 1290-1297
- First Published: 29 December 2011
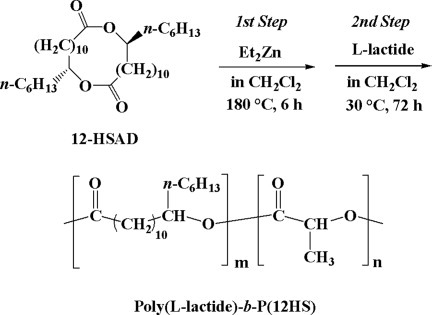
A dilactone, 13,26-dihexyl-1,14-dioxacyclohexacosane-2,15-dione (12-HSAD), was synthesized by lipase-catalyzed reaction of 12-hydroxystearic acid (12-HSA) in high yield. It was subjected to the ring-opening polymerization with various catalysts to obtain poly(12-hydroxystearate) (PHS). The polymerization system of 12-HSAD showed an interesting polymerization behavior because of its large ring system. The polymers produced by this polymerization were directly reacted with L-lactide to obtain a diblock copolymer of poly(L-lactide)-block-poly-(12-hydroxystearate) (PLLA-b-PHS). Characterization of the resultant copolymers was also performed.
Intramolecular friedel-crafts cyclization and subsequent hydrogenation of styrene-isoprene random copolymers prepared by anionic polymerization for thermally-resistant and optical applications
- Pages: 1298-1307
- First Published: 04 January 2012

The Friedel-Crafts alkylation of random styrene (St)-isoprene (Ip) rubbers (r-SIRs), which were prepared by anionic copolymerization, afforded cyclized r-SIR (C-r-SIR) to give thermoplastics with a high glass transition temperature (Tg ∼ 130 °C), good mechanical properties, and good transparency. Subsequent hydrogenation of the small amount of remaining CC double bonds in the uncyclized Ip units and cyclized Ip-–Ip units yielded hydrogenated C-r-SIR (HC-r-SIR) and increased the degradation temperature (Td5 ≥ 380 °C). These HC-r-SIRs display good flexural moduli and strength, good transparency, and refractive indices. The birefringence of HC-r-SIR was successfully tuned by adjusting the comonomer content to obtain near-zero birefringence high-performance plastics.
New hybrid membranes based on phosphonic acid functionalized silica particles for PEMFC
- Pages: 1308-1316
- First Published: 03 January 2012
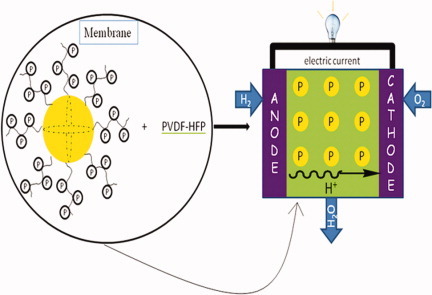
This work presents the elaboration of hybrid membranes based on both PVDF-HFP and functionalized silica. Silica nanoparticles were functionalized by a phosphonated polymer. Incorporation of silica nanoparticles into the polymer matrix allowed application as proton exchange membrane fuel cell used at high temperature and low relative humidity, thanks to the water retention ability of silica nanoparticles. A low IEC (1.08 meq g−1) could lead to high proton conductivity thanks to membrane structuration (hydrophilic silica domains into hydrophobic polymer matrix). Indeed, a proton conductivity of 65 mS cm−1 at 80 °C was measured in immersed conditions.
Conductive networked polymer gel electrolytes composed of poly(meth)acrylate, lithium salt, and ionic liquid
- Pages: 1317-1324
- First Published: 04 January 2012
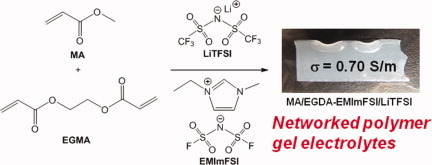
(Meth)acrylate-based networked polymer gel electrolytes with high ionic liquid content (80 wt %) were prepared by in situ radical copolymerization of mono-functional and di-functional (meth)acrylates in an ionic liquid in the presence/absence of a lithium salt. The acrylate-based polymer gel electrolyte with EMImFSI and LiTFSI showed higher ionic conductivity (0.70 S/m) with moderate thermal stability and good non-flammability.
Aqueous cationic olefin polymerization using tris(pentafluorophenyl)gallium and aluminum
- Pages: 1325-1332
- First Published: 29 December 2011
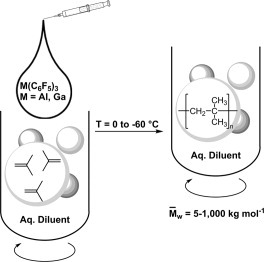
Isobutene and styrene are polymerized to medium-high molecular weight products in aqueous media using tris(pentafluorophenyl)gallium and aluminum. Compared to perfluoroarylated chelating diborane or diborole coinitiators, these Lewis acids are readily obtained by transmetalation of Group 13 metal halides with bis(pentafluorophenyl)zinc and afford polymers of higher MW (in some instances with narrow molecular weight distributions) at increased reaction temperatures.
Synthesis of ladder-like polynorbornenes with n-type perylenendiimide derivatives as bridges
- Pages: 1333-1341
- First Published: 04 January 2012
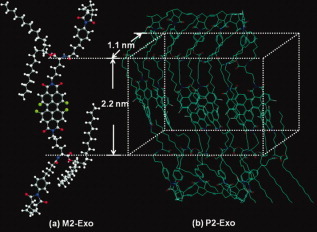
Endo/Exo-type soluble high molecular weight ladder-like polynorbornenes with perylenediimide (PDI) as bridges were synthesized by ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) with the 2nd generation Grubbs catalyst. Polynorbornenes show excellent solubility, thermal stability, and direct photovoltaic responses without losing PDI's photophysical and electrochemical properties.
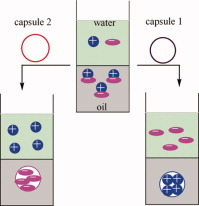
Charge selective encapsulation by polymeric micelles with cationic, anionic, or zwitterionic cores
- Pages: 1342-1350
- First Published: 04 January 2012
Functionalized block copolymers for preparation of reactive self-assembled surface patterns
- Pages: 1351-1361
- First Published: 29 December 2011
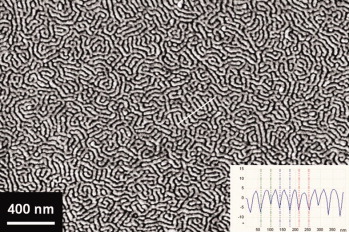
Block copolymers which are characterized by the presence of reactive functional groups in the segments undergo self-assembly to form non-regular but distinct surface nanostructures in thin films on silica. The reactive films are stable on exposure to various solvents and the self-assembled surface patterns turned out to be resistant toward ethanol.
Tunable light-harvesting polymers containing embedded dipolar chromophores for polymer solar cell applications
- Pages: 1362-1373
- First Published: 04 January 2012
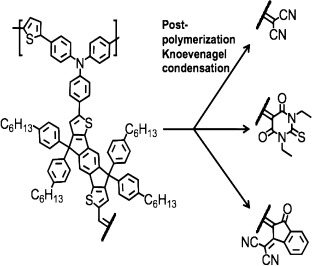
A series of tunable light-harvesting conjugated polymers comprising pushpull dipolar chromophores contained in its thiophenetriphenylamine backbone were designed and synthesized for polymer solar cells. By varying the electron withdrawing strength of the chromophore electron acceptor, the bandgap of the polymer could be modified by as much as 0.3 eV. A sufficiently strong acceptor was required to overcome the high stabilization energy of the indacenodithiophene–bridge and to achieve efficient charge transfer. Although these polymers have reasonable hole mobility (10−3 to 10−4 cm2 V−1 s−1) and absorbance, their performance is ultimately limited by poor morphology and high recombination rates.
Anion effects on the phase transition of N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogels
- Pages: 1374-1382
- First Published: 04 January 2012
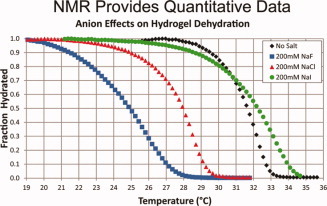
Additional insight into the Hoffmeister series salts and their effect on the NiPAAm phase transitions is found with high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) NMR spectroscopy. Iodide ions do not effect affect the LCST greatly, but they do impact enthalpy and entropy values. Fluoride change LCST significantly and also the thermodynamic variables compared to with other salts and water.
Dynamic modeling of the morphology of latex particles with in situ formation of graft copolymer
- Pages: 1383-1393
- First Published: 12 January 2012
Polymerization of free secondary amine bearing monomers by RAFT polymerization and other controlled radical techniques
- Pages: 1394-1407
- First Published: 24 January 2012
Energy transfer from fluorene-based conjugated polyelectrolytes to on-chain and self-assembled porphyrin units
- Pages: 1408-1417
- First Published: 24 January 2012
Theoretical studies on polyfluorene/porphyrin systems show that Förster electronic energy transfer depends on the orientation between donor and acceptor. To determine the factors that control the energy transfer, an anionic poly(fluorene-alt-phenylene) with on-chain porphyrin units was synthesized and its mechanism studied. In addition, calcium was used to induce self-assembly of anionic porphyrins with the anionic poly(fluorene-alt-phenylene) polyelectrolyte and the donor-acceptor energy transfer within the aggregates formed was observed.
Effect of graphene doping of holographic polymer-dispersed liquid crystals
- Pages: 1418-1423
- First Published: 20 January 2012
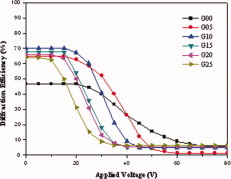
Doping a polymer matrix with a minute amount of graphene (0.05–0.25%) resulted in a significant increase in conductivity, up to several fold. This caused a decrease in driving voltage from 65 to 25 V and an increase in contrast ratio from 7 to 33 as well as a decrease in rise time and increase in decay time.
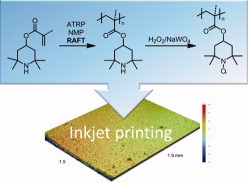
SET-RAFT of MMA mediated by ascorbic acid-activated copper oxide
- Pages: 1424-1433
- First Published: 20 January 2012
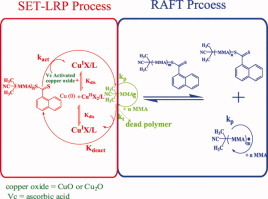
In this work, CuO or Cu2O was used as the catalyst for SET-RAFT of MMA under the activation of ascorbic acid at 25 °C. The polymerization occurred smoothly and conveyed features of “living”/controlled radical polymerizations. Based on experimental results, it was deduced that the polymerization proceeded via a conjunct mechanism of SET-LRP and RAFT polymerization.
The use of poly(alkylene oxide)s to achieve fast and controlled photochromic switching in rigid matrices†
- Pages: 1434-1444
- First Published: 24 January 2012
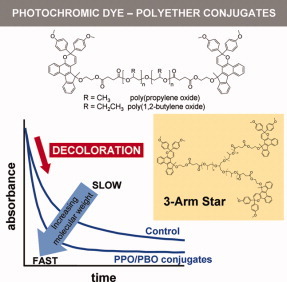
Photochromic dyes conjugated to soft poly(propylene oxide) and poly(1,2-butylene oxide) oligomers in telechelic and 3-arm star geometries show greatly accelerated decoloration performance compared to the non-conjugated control dye when incorporated in rigid polymeric matrices. These polyether precursors are chemically robust materials, allowing facile conjugate synthesis in high yield and purity using a variety of chemistries with the added benefit of being cheap and readily available materials.
Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of biodegradable block copolyesters based on poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s and poly(D,L-lactide)
- Pages: 1445-1455
- First Published: 28 January 2012
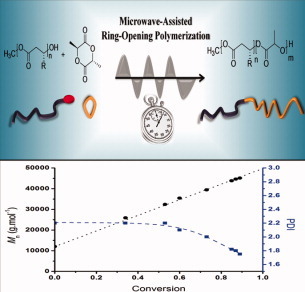
poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)-block-poly(D,L-lactide) (PHA-b-PLA) diblock copolymers with tunable compositions and controlled block lengths were synthesized within short reaction times (typically a few minutes) upon microwave irradiation through the ring-opening polymerization of D,L-lactide (LA) triggered by a series of monohydroxylated PHA-based macroinitiators. A kinetic investigation gave evidence of the “livingness” associated with the mechanism of microwave-assisted LA polymerization under the experimental conditions selected.