Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - TABLE OF CONTENTS
Free Access
free
Issue Information - Table of Contents
- Pages: 567-569
- First Published: 21 February 2019
REVIEW ARTICLE
Full Access
full
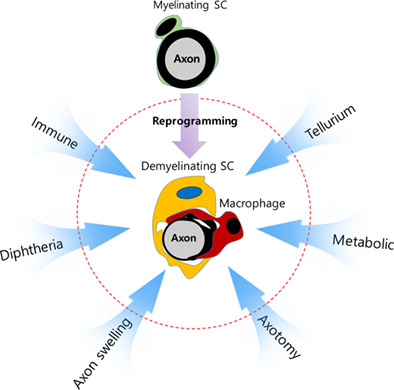
The conceptual introduction of the “demyelinating Schwann cell” in peripheral demyelinating neuropathies
- Pages: 571-581
- First Published: 30 October 2018
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Full Access
full
Helper CD4 T cells expressing granzyme B cause glial fibrillary acidic protein fragmentation in astrocytes in an MHCII-independent manner
- Pages: 582-593
- First Published: 16 November 2018
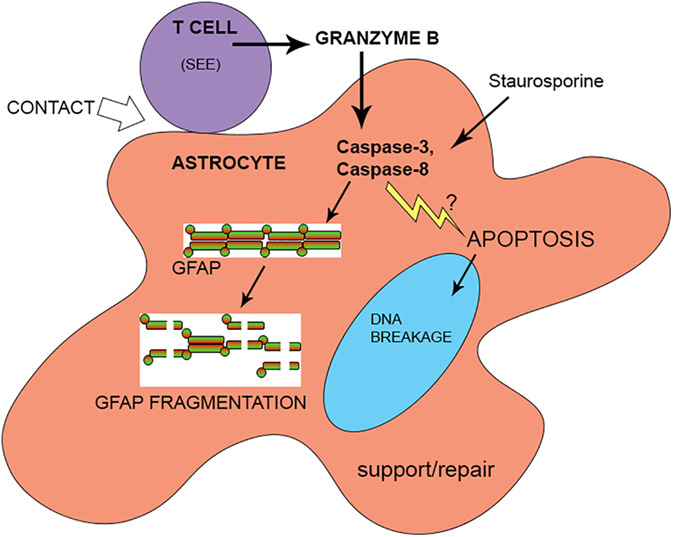
Main Points
- Helper T cells released granzyme B upon contact with cultured human astrocytes in an MHCII-independent manner.
- Helper T cells caused GFAP fragmentation in a granzyme B and caspase-dependent manner.
- Sub-lethally injured astrocytes were not apoptotic but had a reduced ability to migrate and to support oligodendrocytes.
Full Access
full
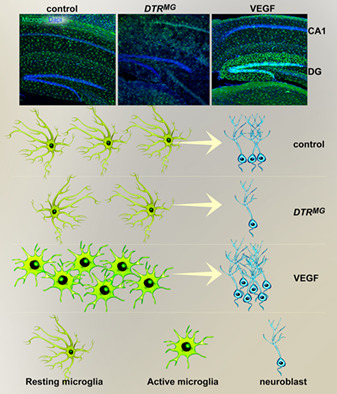
Unique role for dentate gyrus microglia in neuroblast survival and in VEGF-induced activation
- Pages: 594-618
- First Published: 19 November 2018
Full Access
full
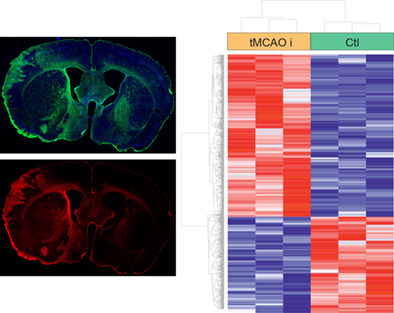
Stroke target identification guided by astrocyte transcriptome analysis
- Pages: 619-633
- First Published: 26 December 2018
Full Access
full
Maintenance of high proteolipid protein level in adult central nervous system myelin is required to preserve the integrity of myelin and axons
- Pages: 634-649
- First Published: 14 January 2019
Full Access
full
A novel myelin protein zero transgenic zebrafish designed for rapid readout of in vivo myelination
- Pages: 650-667
- First Published: 09 January 2019
Open Access
oa
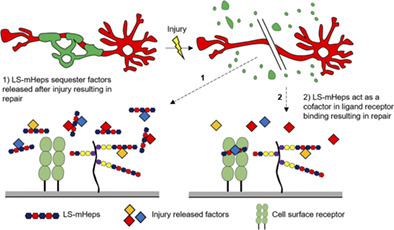
Low sulfated heparins target multiple proteins for central nervous system repair
- Pages: 668-687
- First Published: 26 December 2018
Full Access
full
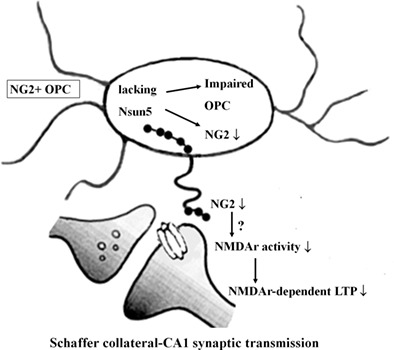
Cognitive deficits in mice lacking Nsun5, a cytosine-5 RNA methyltransferase, with impairment of oligodendrocyte precursor cells
- Pages: 688-702
- First Published: 28 November 2018
Full Access
full
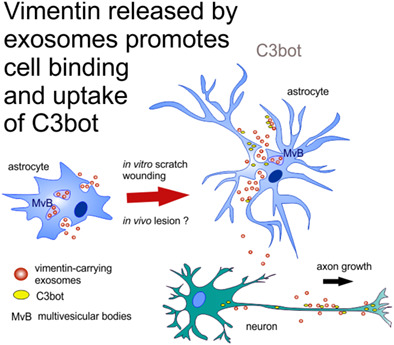
Release of astroglial vimentin by extracellular vesicles: Modulation of binding and internalization of C3 transferase in astrocytes and neurons
- Pages: 703-717
- First Published: 28 November 2018
Full Access
full
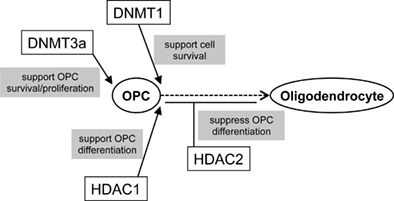
Differential roles of epigenetic regulators in the survival and differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells
- Pages: 718-728
- First Published: 28 November 2018
Full Access
full
Transcription factor MafB contributes to the activation of spinal microglia underlying neuropathic pain development
- Pages: 729-740
- First Published: 28 November 2018
Full Access
full
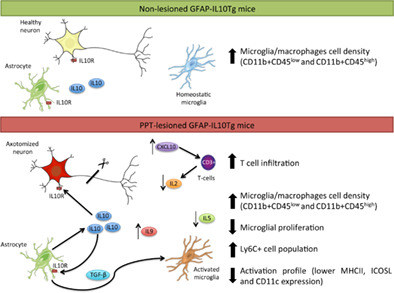
Astrocyte-targeted IL-10 production decreases proliferation and induces a downregulation of activated microglia/macrophages after PPT
- Pages: 741-758
- First Published: 11 December 2018
Full Access
full
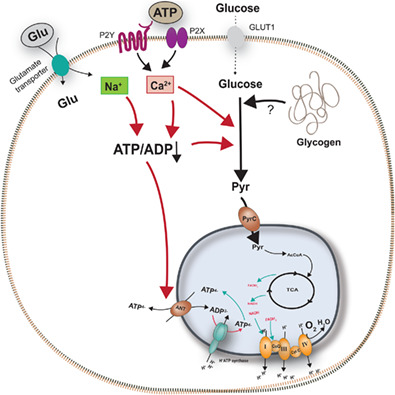
Extracellular ATP and glutamate drive pyruvate production and energy demand to regulate mitochondrial respiration in astrocytes
- Pages: 759-774
- First Published: 09 January 2019