Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Feedback modulation of Orai1α and Orai1β protein content mediated by STIM proteins
- First Published: 02 October 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Signaling Regulation of FAM134-Dependent ER-Phagy in Cells
- First Published: 25 November 2024
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
Review Article
Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer
Mitochondrial metabolism: A moving target in hepatocellular carcinoma therapy
- First Published: 26 September 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Phenomics Demonstrates Cytokines Additive Induction of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition
- First Published: 20 November 2024
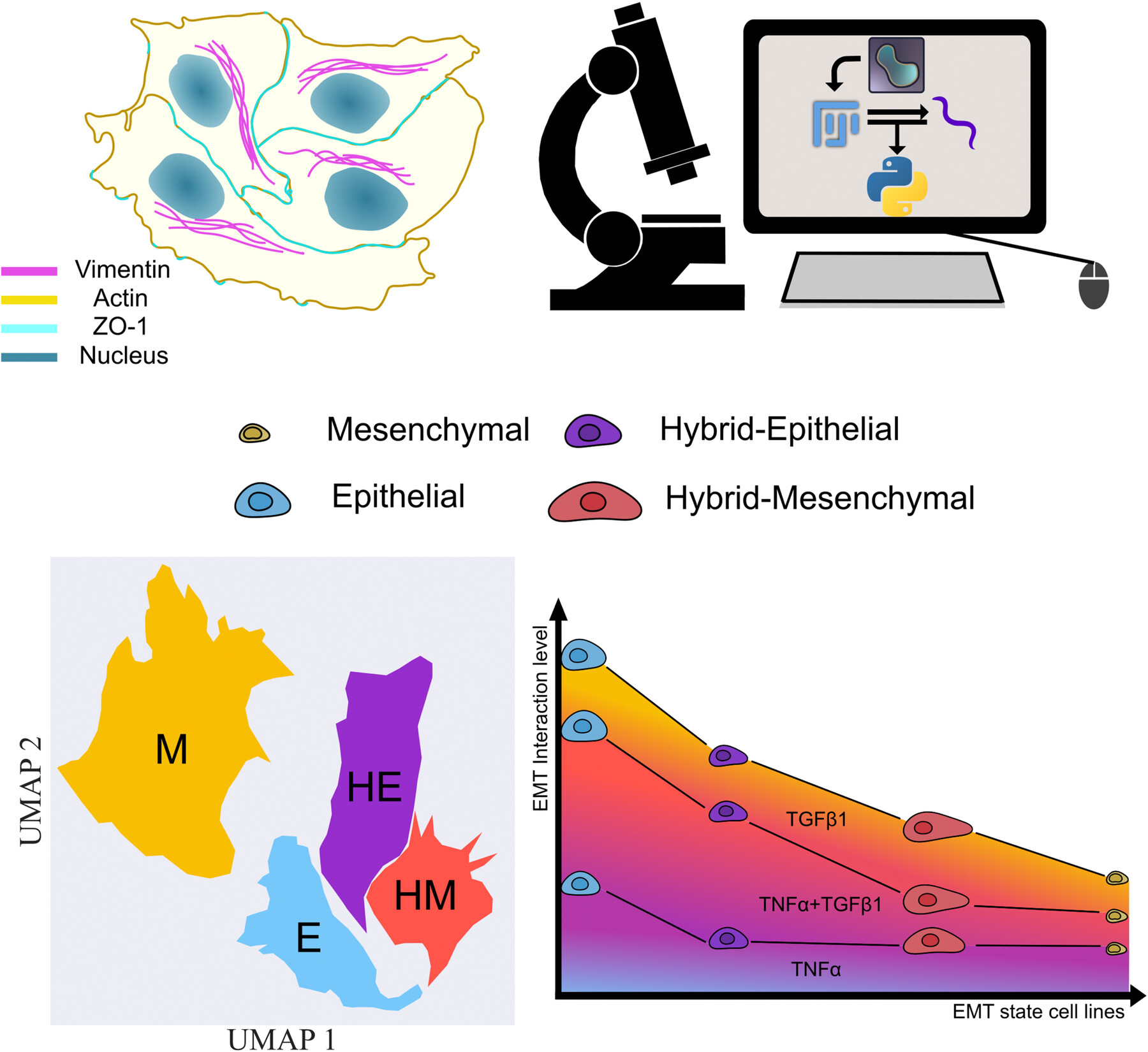
An image based, low experimental cost single cell phenomics identifies epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) states. Clustering discriminates 4 cell lines spanning across cancer EMT spectrum. A single normalised value of EMT induction is made, based on 50 single cell features. Cytokines combination in EMT induction is additive regardless of cancer cell line.
Carboxyl Terminal Modulator Protein Induces Cell Senescence and Is Upregulated With Aging by Zic2 in Rats
- First Published: 30 January 2025
Serinc5 Regulates Sequential Chondrocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Sox9 Function in Pre-Hypertrophic Chondrocytes
- First Published: 20 November 2024
CORRECTION
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
Review Article
Cancer knocks you out by fasting: Cachexia as a consequence of metabolic alterations in cancer
- First Published: 08 September 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Rho GTPase Signaling: A Molecular Switchboard for Regulating the Actin Cytoskeleton in Axon Guidance
- First Published: 30 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
CD44/Integrin β1 Association Drives Fast Motility on Hyaluronic Acid Substrates
- First Published: 21 January 2025
CCL2-CCR2 Axis Inhibition in Osteosarcoma Cell Model: The Impact of Oxygen Level on Cell Phenotype
- First Published: 25 November 2024
CORRECTION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
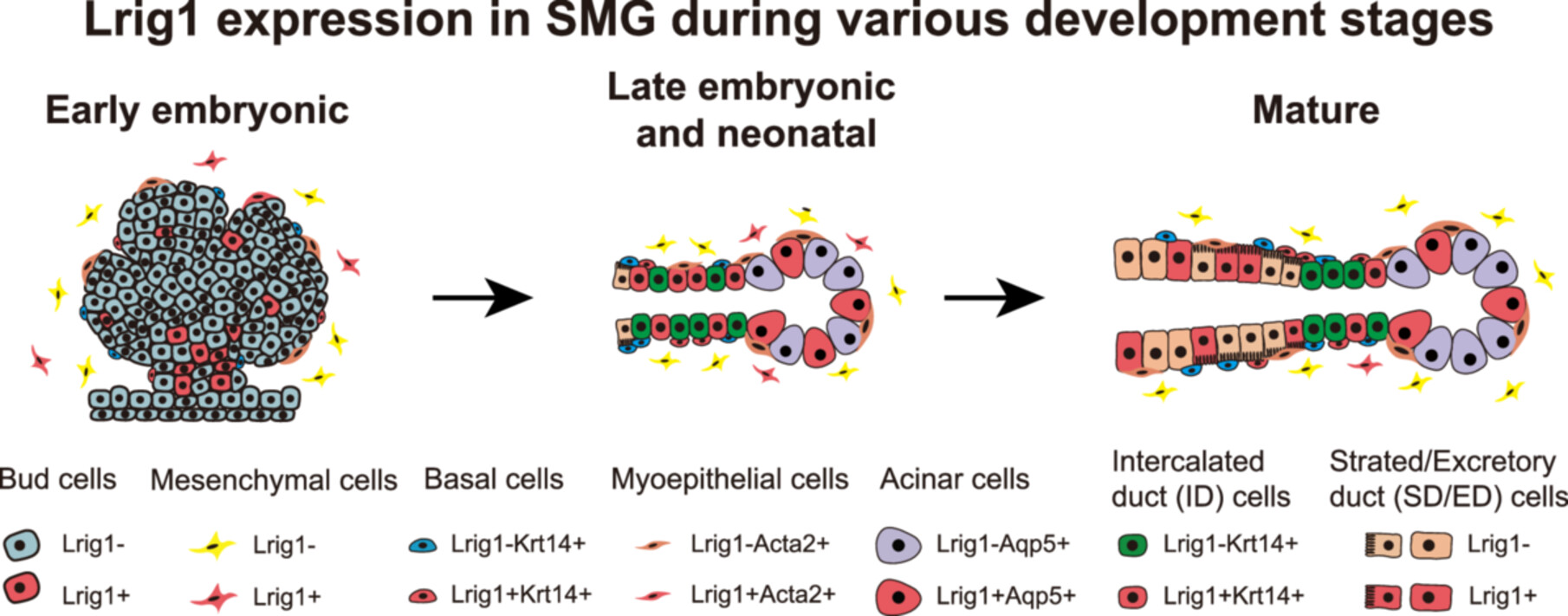
Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Histological Analysis Reveals Dynamic Lrig1 Expression During Salivary Gland Development
- First Published: 25 November 2024
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
Research Article
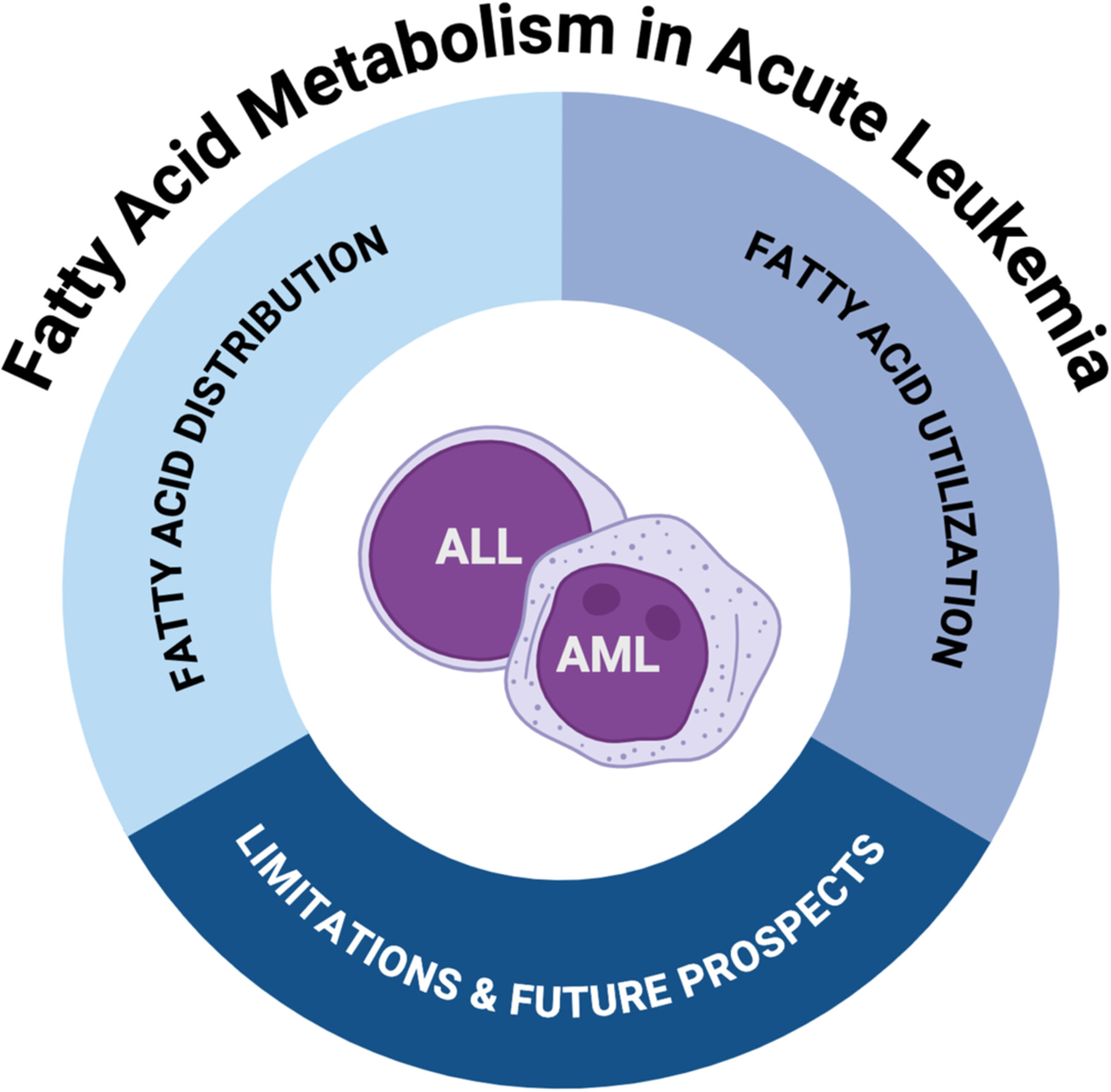
Reprogramming of Fatty Acid Metabolism in Acute Leukemia
- First Published: 21 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
WHAMM Inhibits Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell EMT by Mediating Autophagic Degradation of TGF-β1 in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- First Published: 20 November 2024
RETRACTION
RETRACTION NOTICE
REVIEW ARTICLE
Osteoclast Secretes Stage-Specific Key Molecules for Modulating Osteoclast–Osteoblast Communication
- First Published: 28 November 2024
RETRACTION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
High Glucose Inhibits O-GlcNAc Transferase Translocation in Early Osteoblast Differentiation by Altering Protein Phosphatase 2A Activity
- First Published: 12 January 2025
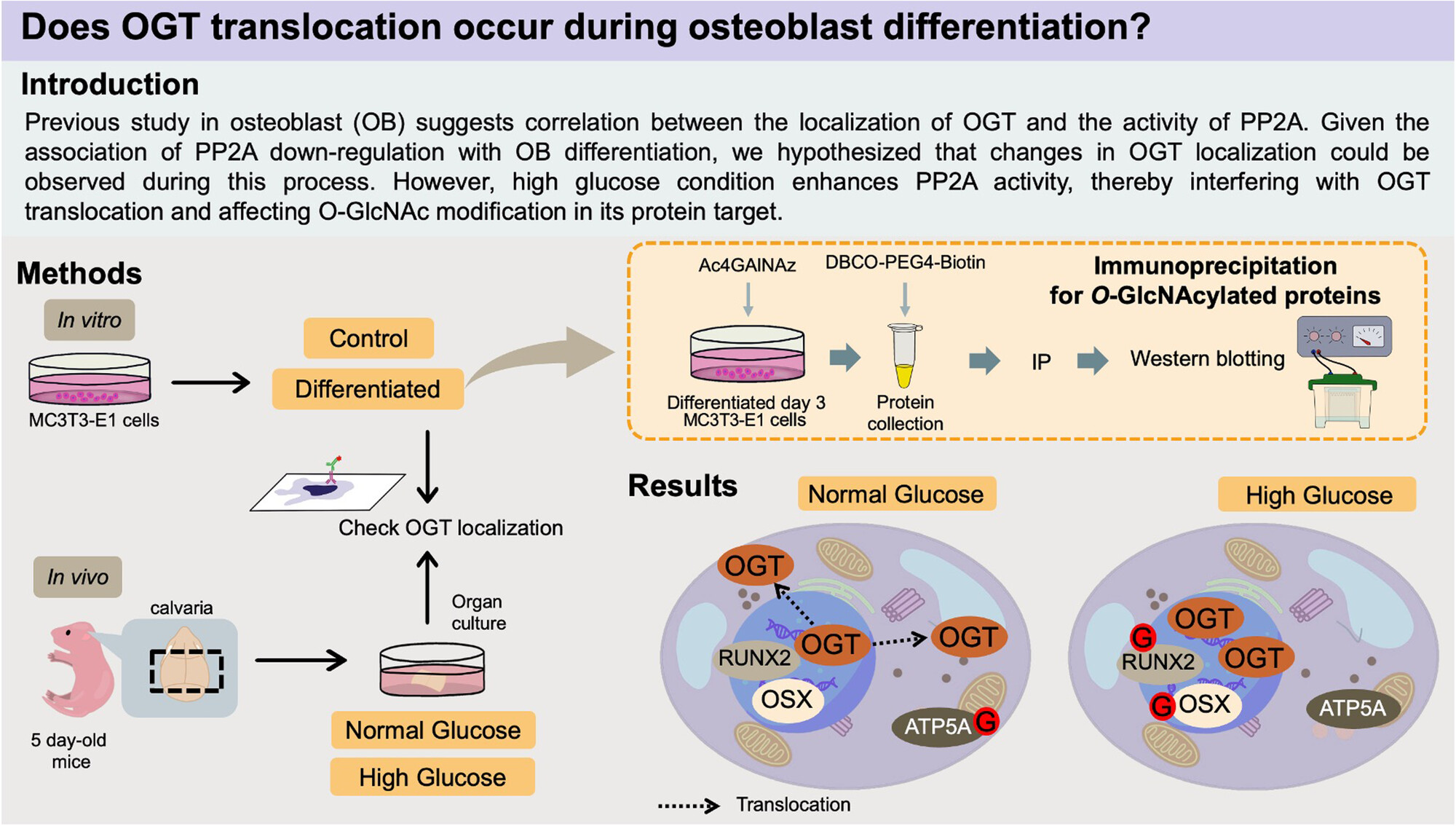
-
OGT translocation from the nucleus to the cytoplasm can be observed in early osteoblast differentiation.
-
High glucose condition disrupts OGT translocation in differentiating osteoblast, but this condition can be alleviated by PP2A inhibition.
-
Changes in OGT localization affect O-GlcNAcylation level of proteins in nucleus and cytoplasm.
-
Ser73 is identified as potential O-GlcNAc modification site in Osterix.
Estrogen Regulates Mitochondrial Activity Through Inducing Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression in Skeletal Muscle
- First Published: 12 November 2024
Glucose Transporter 1 Deficiency Impairs Glucose Metabolism and Barrier Induction in Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocytes
- First Published: 14 January 2025
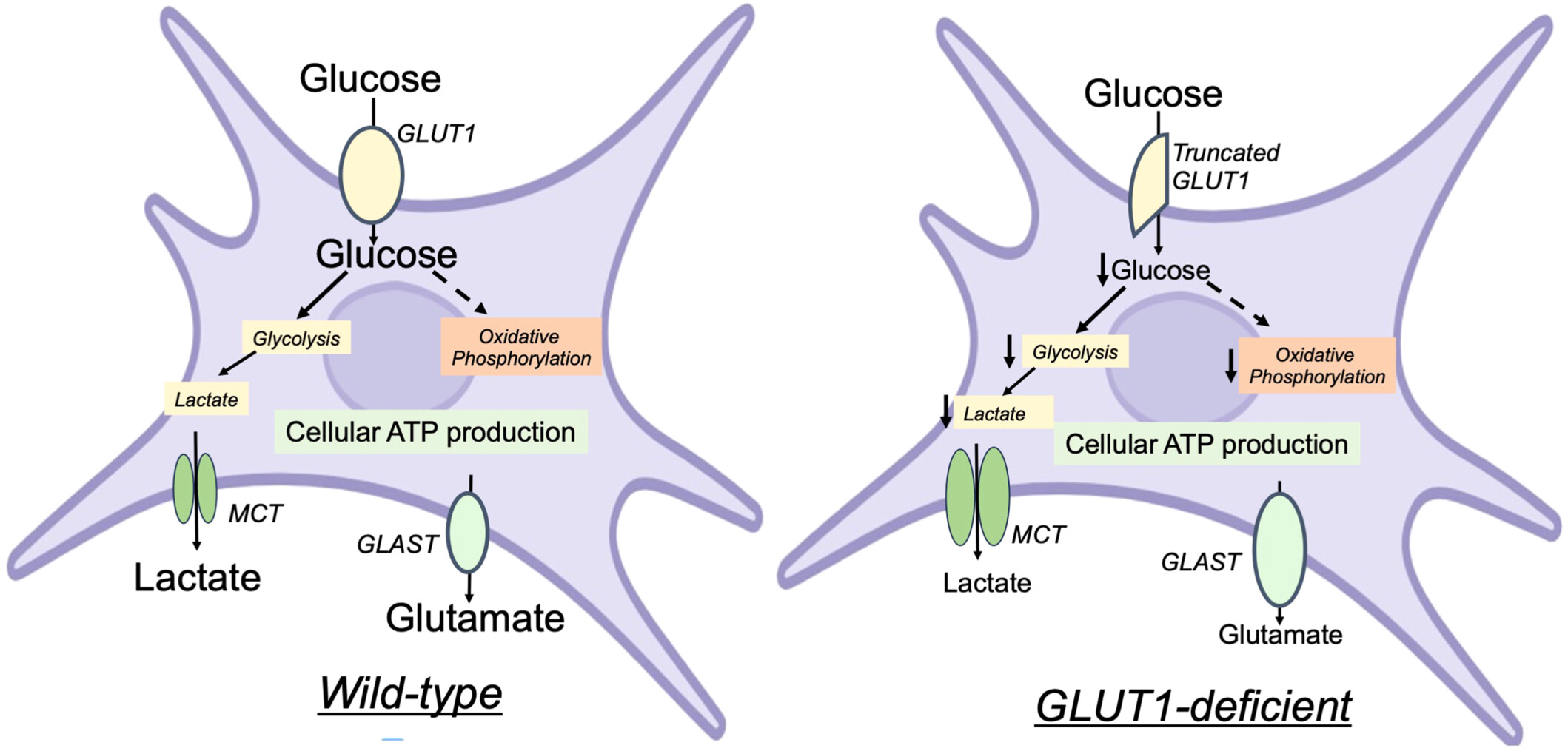
Graphical Abstract
Schematic representation of the major phenotype differences observed in GLUT1DS-iAstrocytes (iAstros) compared to their parental control clones. GLUT1DS-iAstros displayed reduced glucose uptake, reduced glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation and reduced extracellular glutamate and lactate release.
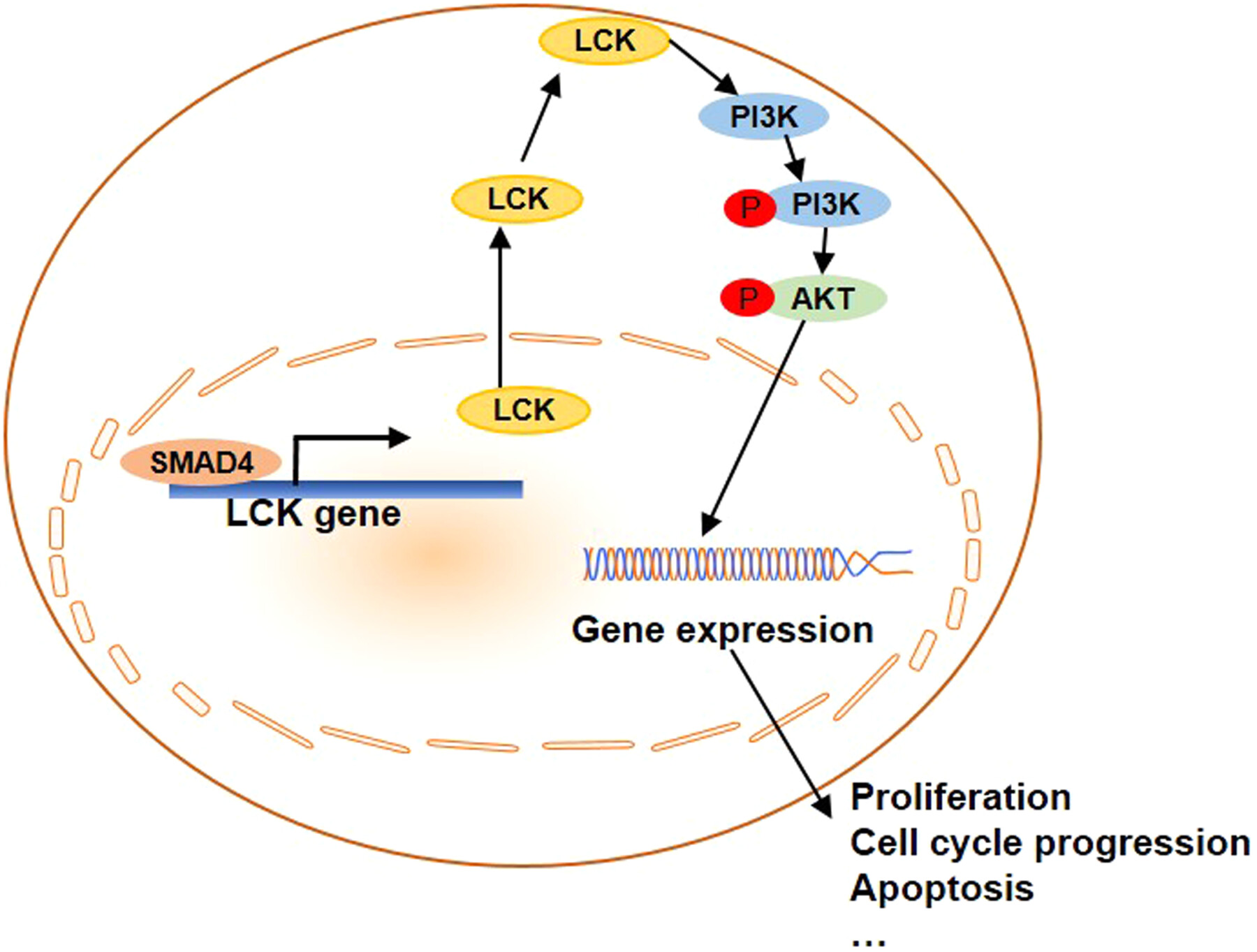
SMAD4 Regulates the Expression of LCK Affecting Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Cells Proliferation Through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 06 January 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Function and Regulation of Age-Associated B Cells in Diseases
- First Published: 03 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Spontaneously Immortalised Nonhuman Primate Müller Glia Cell Lines as Source to Explore Retinal Reprogramming Mechanisms for Cell Therapies
- First Published: 28 November 2024
Point of No Return—What Is the Threshold of Mitochondria With Permeability Transition in Cells to Trigger Cell Death
- First Published: 06 January 2025
FMNL3 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells via Inhibiting Rad23B-Induced Ubiquitination of Twist1
- First Published: 25 November 2024
RETRACTION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
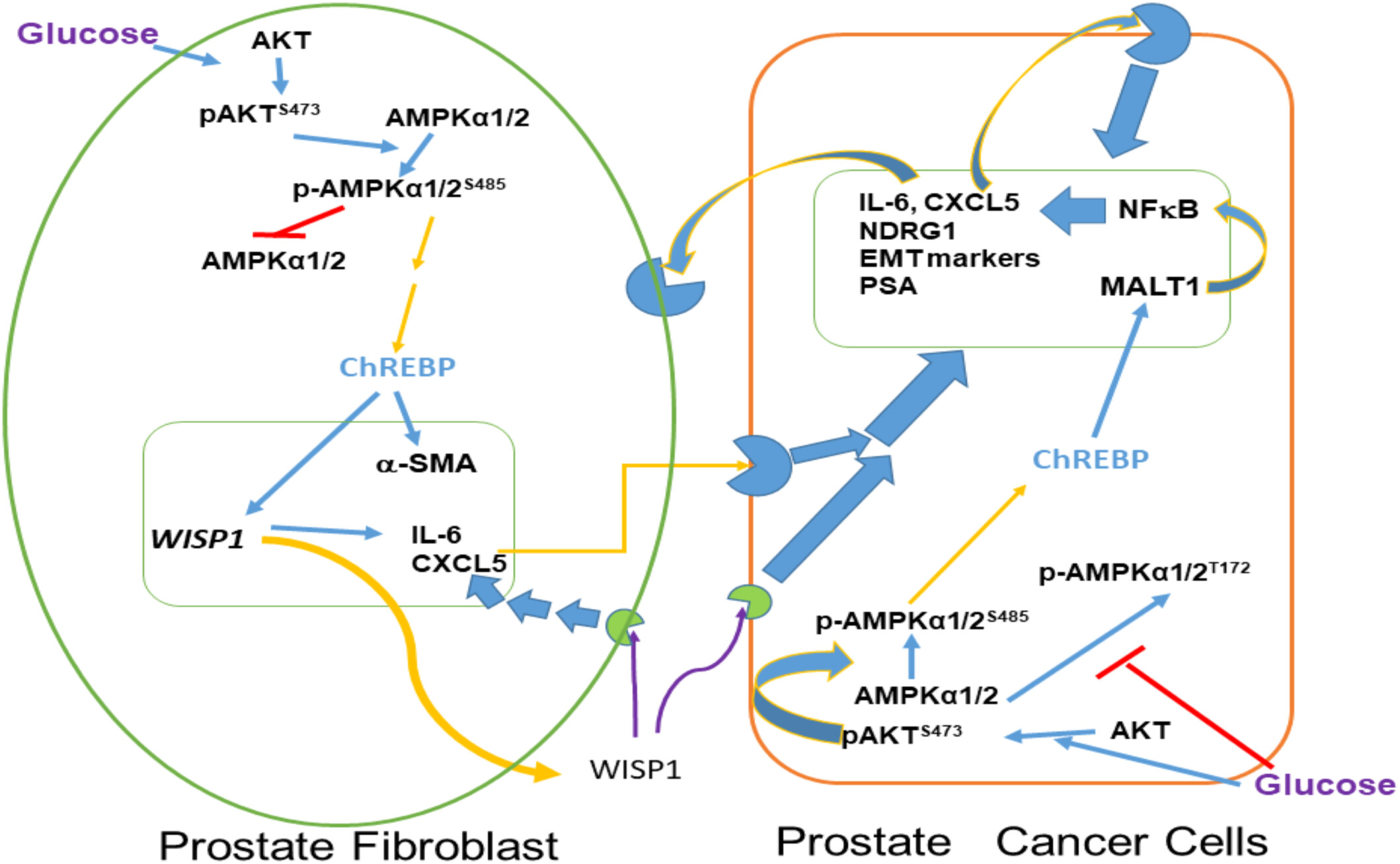
Glucose Upregulates ChREBP via Phosphorylation of AKT and AMPK to Modulate MALT1 and WISP1 Expression
- First Published: 12 November 2024
Dynamic mRNA Stability Buffer Transcriptional Activation During Neuronal Differentiation and Is Regulated by SAMD4A
- First Published: 08 November 2024
Vacuolar H+-ATPase and Megalin-Mediated Prorenin Uptake: Focus on Elements Beyond the (Pro)Renin Receptor
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Muscle PGC-1α Overexpression Drives Metabolite Secretion Boosting Subcutaneous Adipocyte Browning
- First Published: 15 December 2024
Primary Cilia Regulate the Homeostasis and Regeneration of the Stem Cell Niche in the Tooth
- First Published: 29 December 2024
Cholesterol Depletion Activate Hepatic Stellate Cells Mediated Through SREBP-2 Signaling
- First Published: 13 November 2024
Shear stress effects on epididymal epithelial cell via primary cilia mechanosensory signaling
- First Published: 07 November 2024
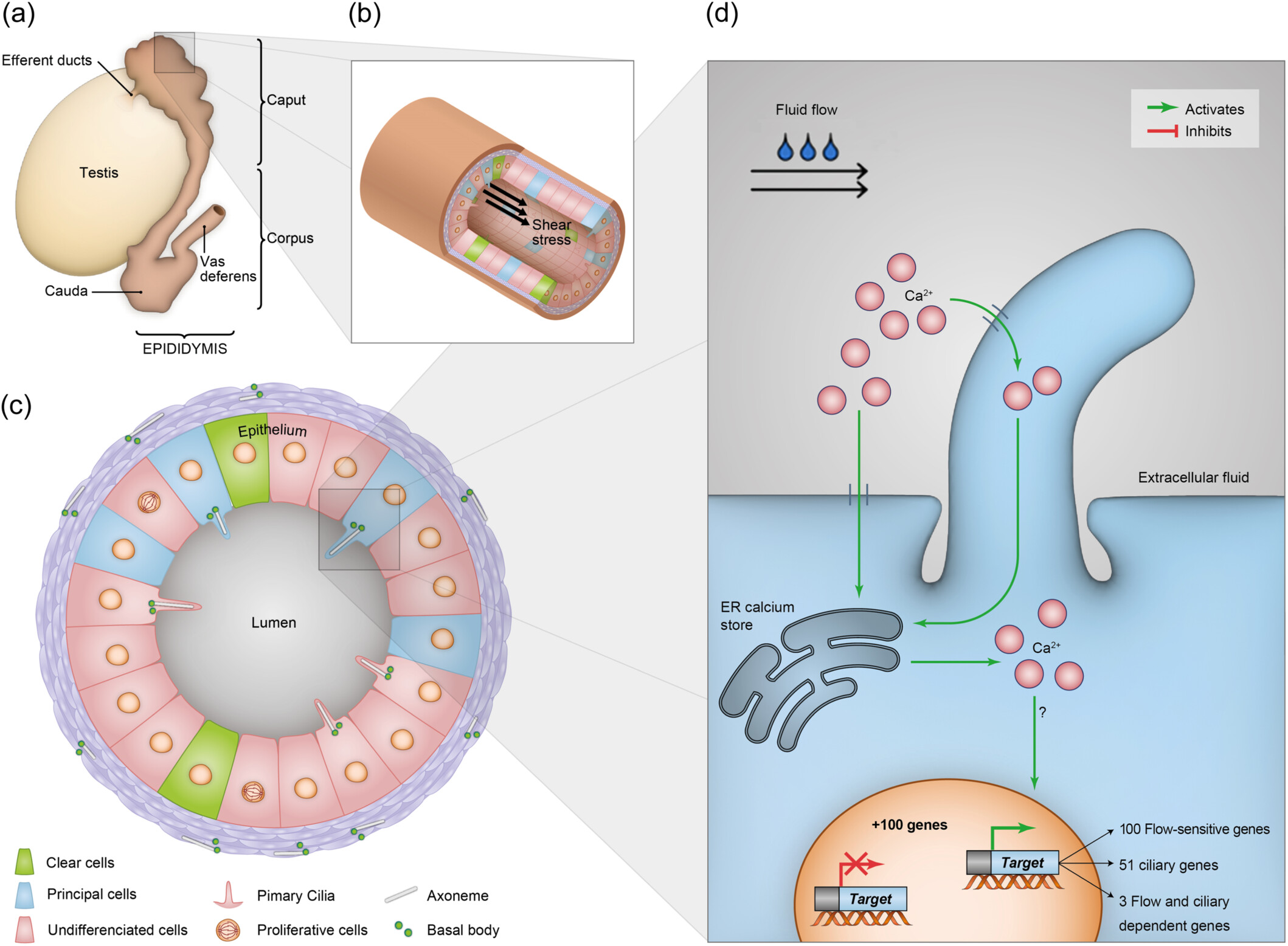
Influence of shear stress on epididymis epithelial cells through primary cilia mechanosensory signaling. (a) Anatomical illustration of the male reproductive system highlighting the epididymis three main segments: caput, corpus, and cauda. (b) Luminal fluid flow-induced shear stress within the epididymal duct. (c) Cross-sectional diagram of the epididymal epithelium showing various cell types including undifferentiated cells, differentiated principal, and clear cells. Primary cilia elongate from the basal body of undifferentiated cells and principal cells. (d) Fluid shear stress-induced calcium signaling and gene expression in principal cells. Fluid flow induces Ca²⁺ influx through the primary cilium, activating the release of calcium from endoplasmic reticulium (ER) and leading to the modulation of over 100 genes, including flow-sensitive genes, cilia-dependent genes, and genes dependent on both flow and the presence of cilia.
KIF18A Is a Novel Target of JNK1/c-Jun Signaling Pathway Involved in Cervical Tumorigenesis
- First Published: 03 January 2025
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
Review Article
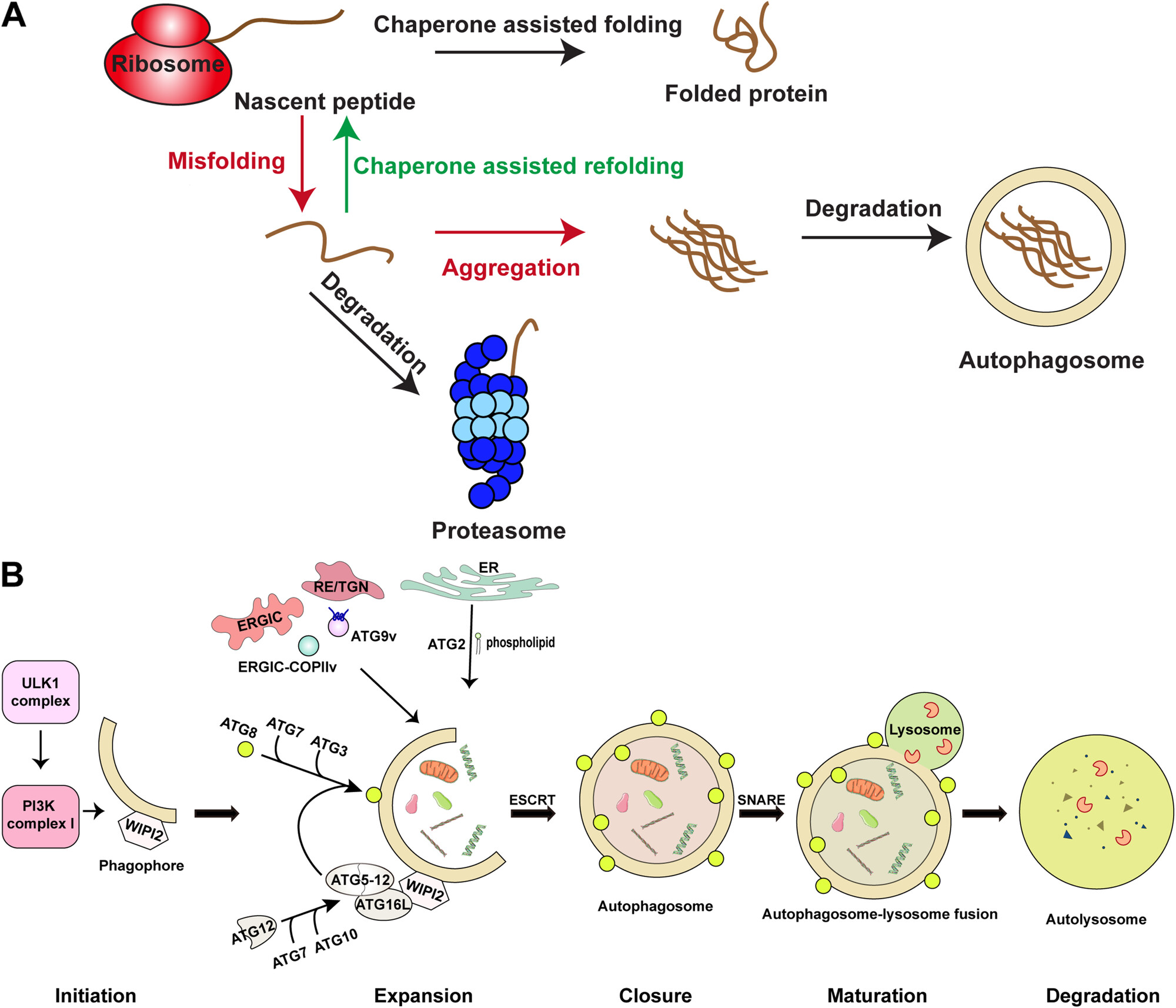
Advances in Aggrephagy: Mechanisms, Disease Implications, and Therapeutic Strategies
- First Published: 03 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
miR-1224 Controls Mammal Cerebral Cortex Development by Targeting the 3’-UTR of the Dlx1 mRNA
- First Published: 02 January 2025
NAT10 functions as a pivotal regulator in gastric cancer metastasis and tumor immunity
- First Published: 28 October 2024
RETRACTION
RETRACTION: MiR-145 Promotes MiR-133b Expression Through c-myc and DNMT3A-mediated Methylation in Ovarian Cancer Cells
- First Published: 13 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Biomechanical Loading-Induced Imbalance in Bone and Fat, Leading to Ossification in Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Nucleus Pulposus Degeneration
- First Published: 24 January 2025
Trial Registration: Clinical Registration number: ChiCTR2200064033 (Date: 2022-09-24, URL: https://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.html?proj=180927).
REVIEW ARTICLE
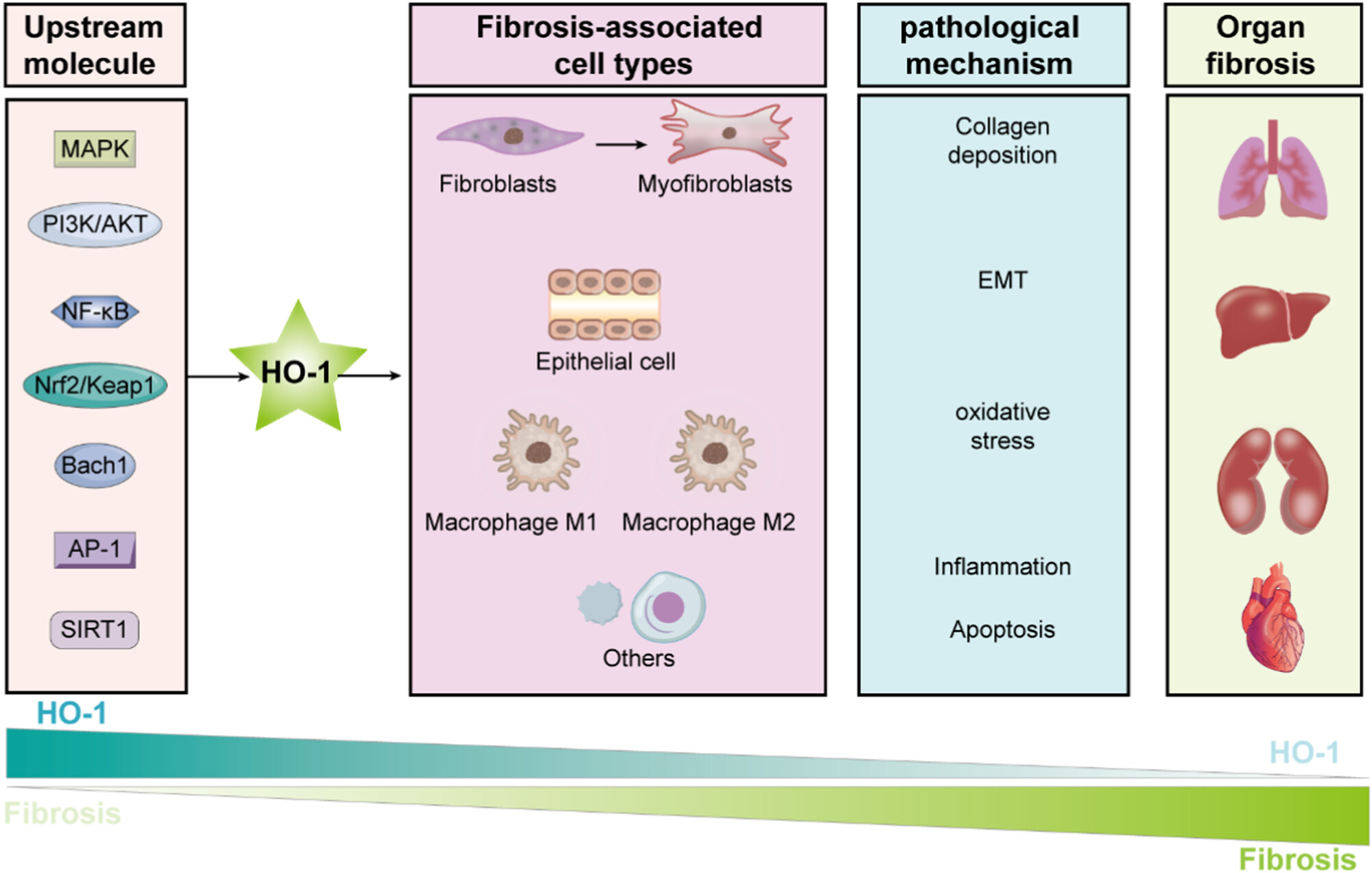
Novel Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Fibroblasts to Improve Heart Disease
- First Published: 17 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
CBFβ Regulates RUNX3 ADP-Ribosylation to Mediate Homologous Recombination Repair
- First Published: 18 December 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Physiological Insights Into the Role of Pericytes in Spinal Cord Injury
- First Published: 06 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Pregnancy Entails a Metabolic Rewiring of Maternal Circulating Neutrophils
- First Published: 16 December 2024
RRM2 Is a Putative Biomarker and Promotes Bladder Cancer Progression via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway
- First Published: 16 December 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Regulation of the Cilia as a Potential Treatment for Senescence and Tumors: A Review
- First Published: 11 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
METTL3-Dependent YTHDF2 Mediates TSC1 Expression to Regulate Alveolar Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition and Promote Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- First Published: 28 November 2024
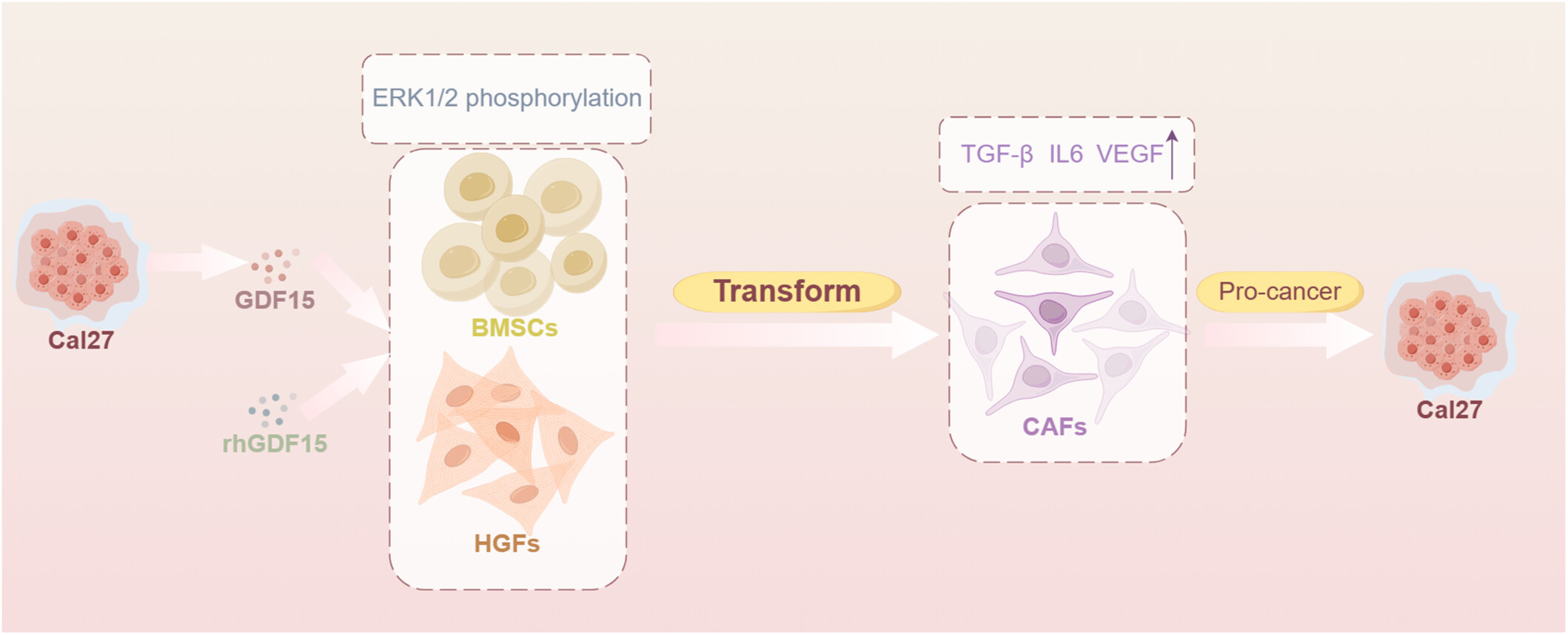
Tumor-Derived GDF15 Induces Tumor Associated Fibroblast Transformation From BMSCs and Fibroblasts in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- First Published: 05 December 2024
Fish collagen sponge with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic wound repair in rats
- First Published: 21 October 2024
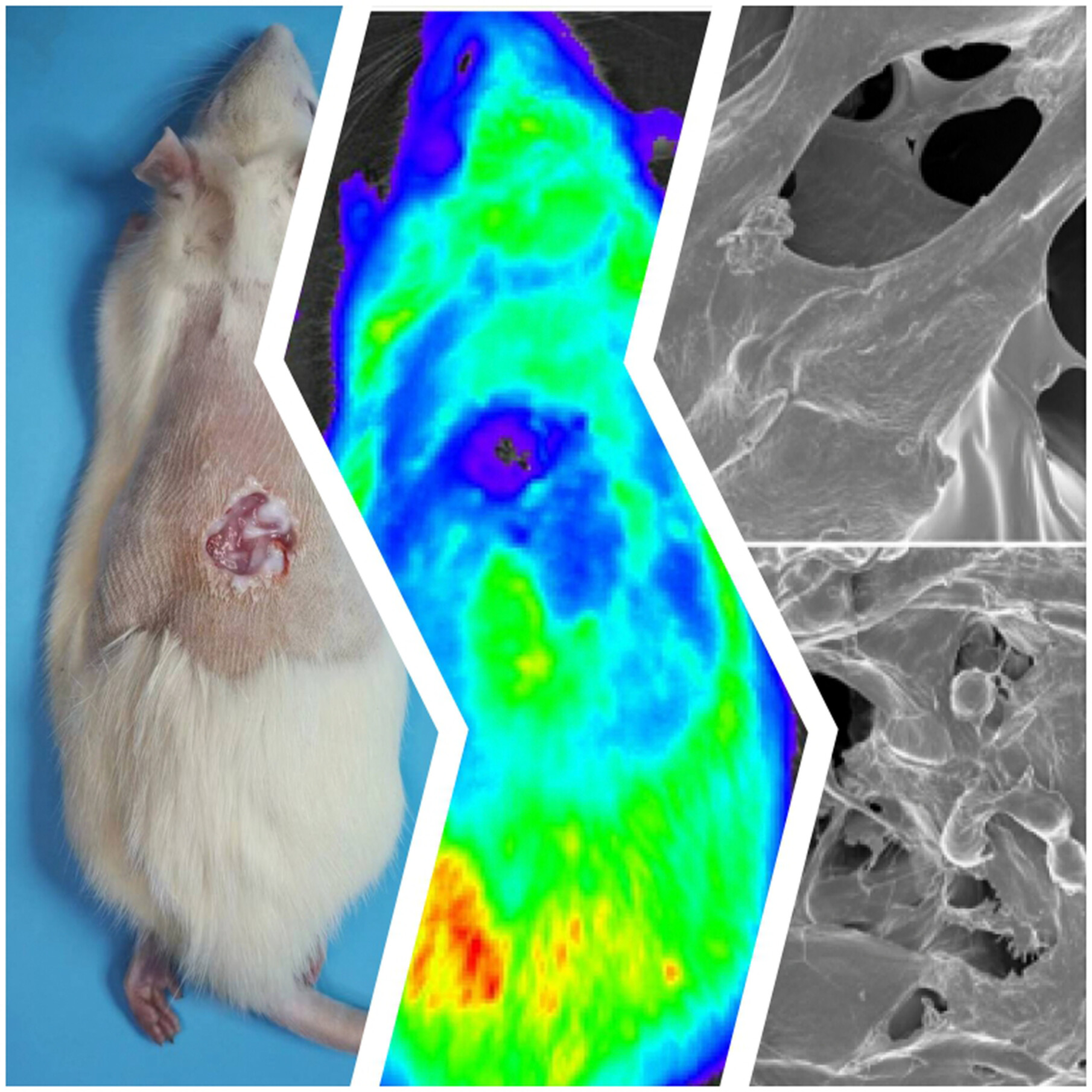
A study explored the effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells loaded onto a fish collagen sponge for wound healing in diabetic rats. Results showed improved wound repair time, healing outcomes, and collagen deposition regulation compared to self-healing methods, suggesting promise for treating diabetes-induced wounds with this innovative approach.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Maintenance of Cardiac Microenvironmental Homeostasis: A Joint Battle of Multiple Cells
- First Published: 04 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
REVIEW ARTICLE
RHO subfamily of small GTPases in the development and function of hematopoietic cells
- First Published: 21 October 2024
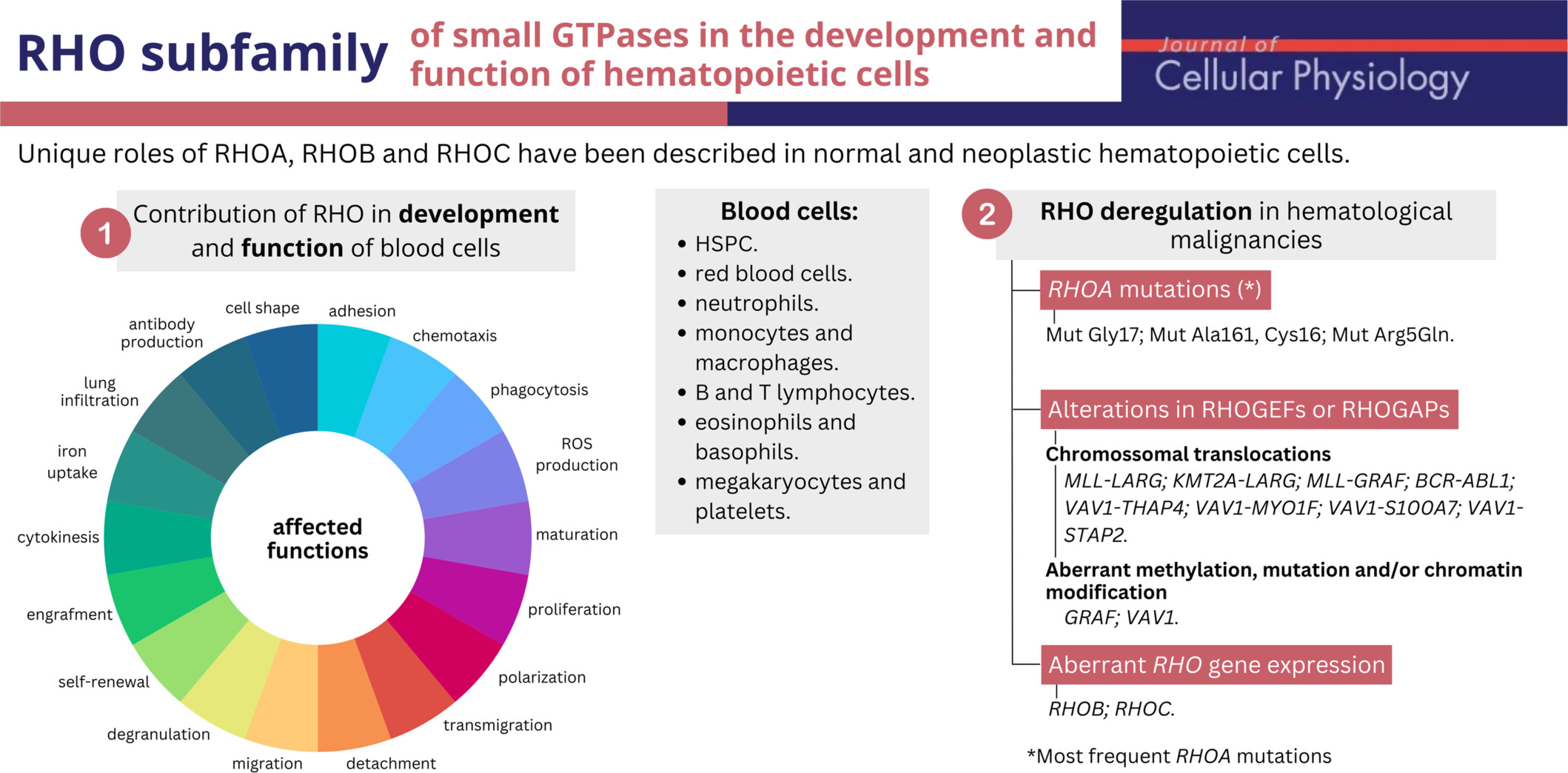
RHO subfamily of small GTPases in hematopoietic cells. Critical roles of RHOA, RHOB and RHOC have been described in hematopoietic cells. (1) Proper functioning of the RHO pathway is necessary for the normal development and activity of blood cells, (2) whereas several RHO abnormalities are found in hematological malignancies.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Leukotriene B4 is elevated in diabetes and promotes ventricular arrhythmogenesis in guinea pig
- First Published: 14 October 2024
N-terminomics profiling of naïve and inflamed murine colon reveals proteolytic signatures of legumain
- First Published: 11 October 2024
SPECIAL ISSUE ARTICLE
Research Article
Exploring Metabolic Approaches for Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Therapy
- First Published: 15 December 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
RESEARCH ARTICLE
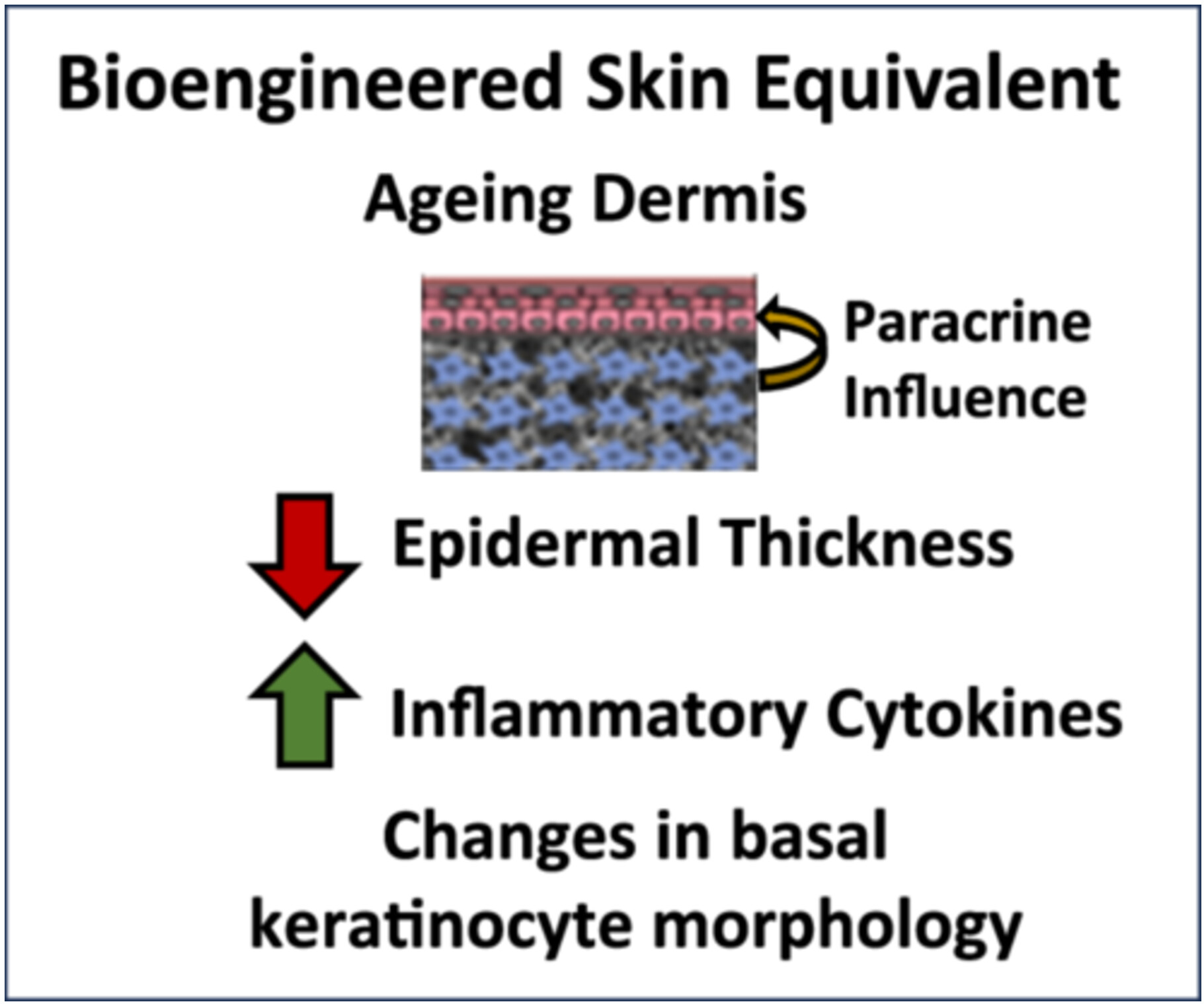
Investigation into the significant role of dermal-epidermal interactions in skin ageing utilising a bioengineered skin construct
- First Published: 08 October 2024
Taurine reduces glycolysis of pig skeletal muscle by inhibiting HIF-1α signaling
- First Published: 07 October 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Advances in the mechanisms of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease
- First Published: 11 October 2024
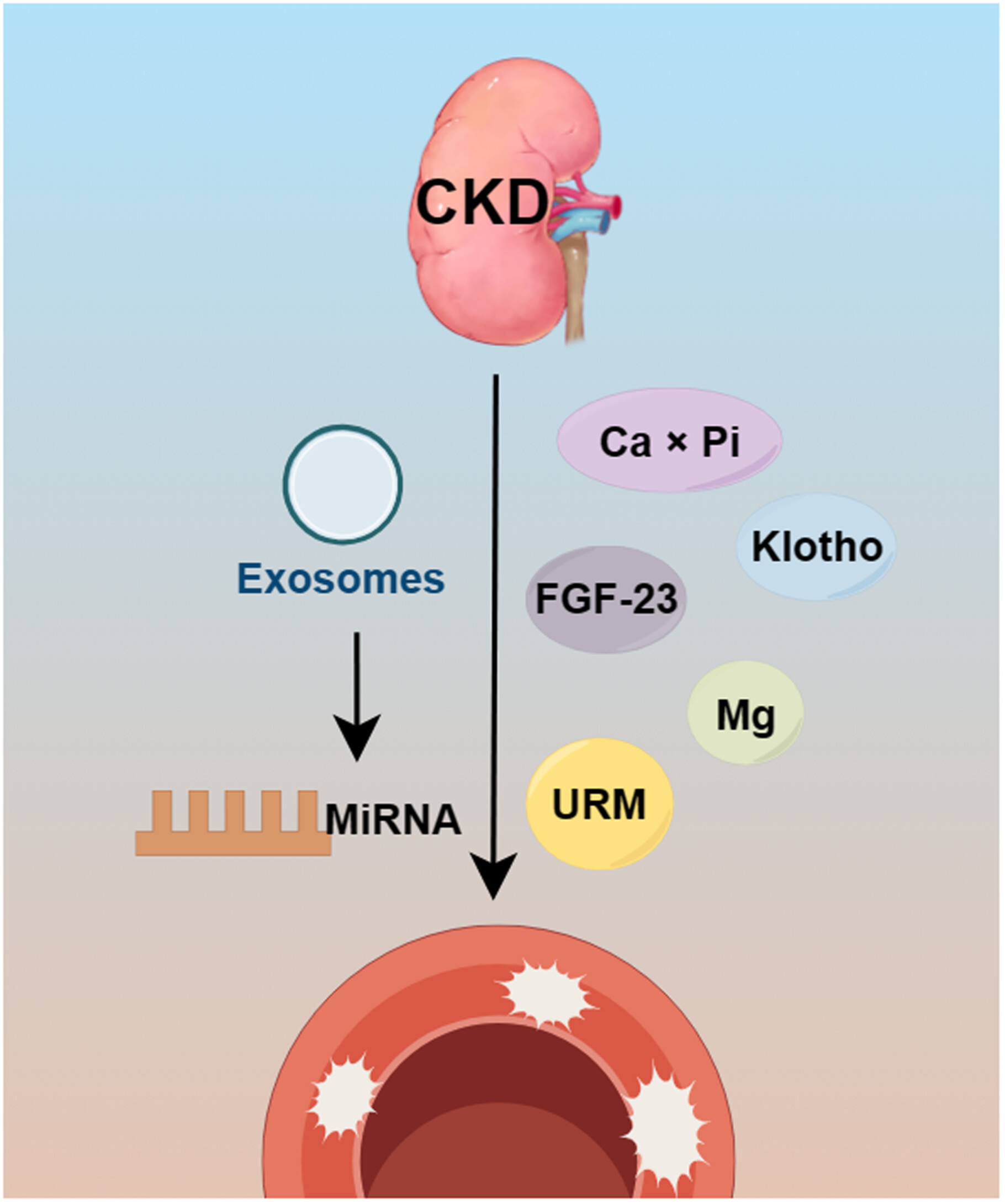
This article reviews how various factors, such as disturbances in calcium and phosphorus metabolism, imbalances in inhibitors of calcification, and accumulation of uremia toxins, promote vascular calcification (VC) in the chronic kidney disease state. Epigenetics provides new tools to study the mechanisms of VC and to discover excellent circulating markers.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A combination of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I overexpression and type I interferon induce mitochondrial dysfunction in human skeletal myoblasts
- First Published: 09 October 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Emerging understandings of the role of exosomes in atherosclerosis
- First Published: 06 October 2024
Pharmacological activity, phytochemistry, and organ protection of lithospermic acid
- First Published: 14 October 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Compensatory reactions of B cells in response to chronic HIV-1 Tat exposure
- First Published: 07 October 2024
Pressure loading regulates the stemness of liver cancer stem cells via YAP/BMF signaling axis
- First Published: 02 October 2024
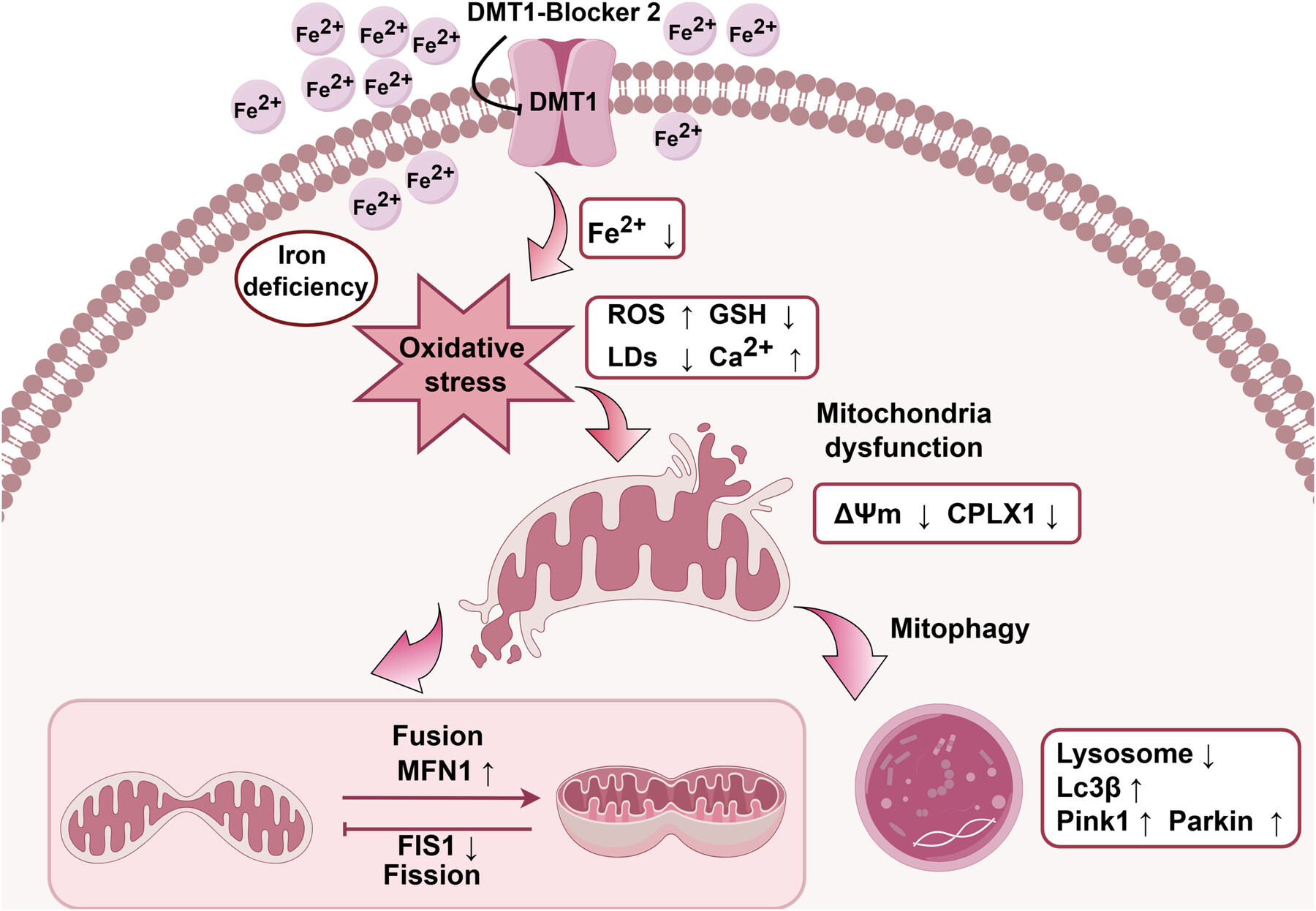
DMT1 Maintains Iron Homeostasis to Regulate Mitochondrial Function in Porcine Oocytes
- First Published: 05 December 2024
Ethionine-induced S-adenosylmethionine deficiency suppressed H3K27me3 and cell differentiation during neural tube development in mice
- First Published: 06 October 2024