Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 141, Issue 1
- First Published: 22 November 2023

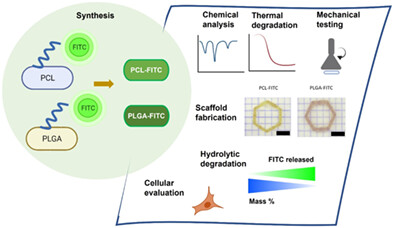
The cover depicts polymeric scaffolds made of polycaprolactone and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) functionalized with a fluorescent molecule that monitors the scaffold's degradation for potential tissue engineering applications. The graphic was created under the direction and editing of Dr. Lilith Caballero Aguilar and in collaboration with STUDIO TULUM graphic design sole trader- in kind contribution. DOI: 10.1002/app.54759
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
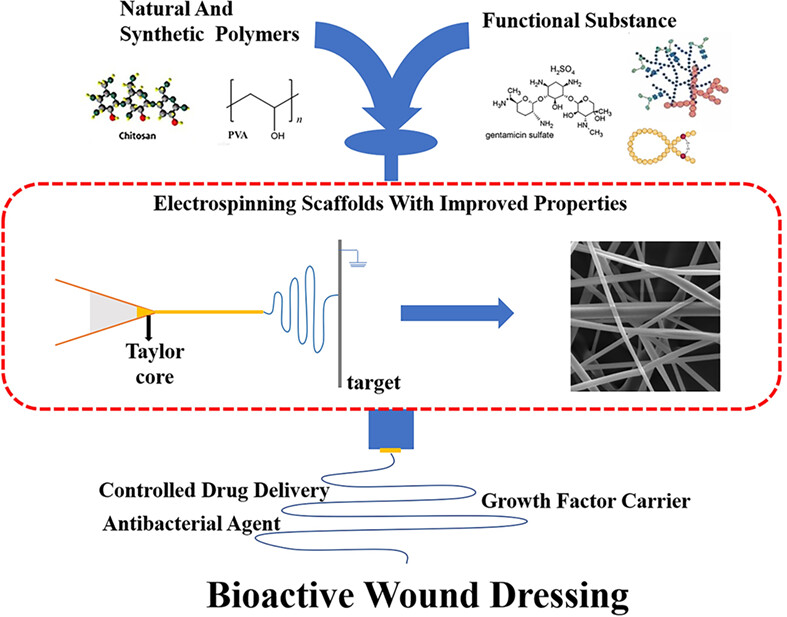
Advances in wound dressing based on electrospinning nanofibers
- First Published: 03 October 2023
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Scalable production of hydrophobic starch/beeswax films by continuous solution casting
- First Published: 01 November 2023
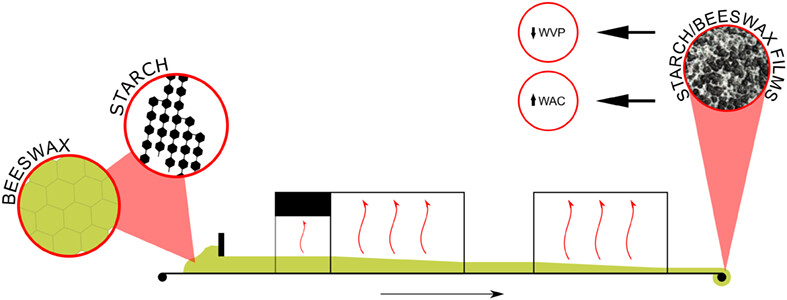
- Production of hydrophobic starch/beeswax (BW) films was scaled by continuous casting, with a productivity at least 50-fold larger than typical bench casting.
- BW was evenly distributed in the starch film matrix without using surfactants, which granted an over doubled water contact angle at lowest BW content and notable moisture barrier properties.
- Incorporation of BW to starch films reduced their environmental impact.
Synergistic toughening and reinforcement of poly(lactic acid) with epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polymers
- First Published: 29 September 2023
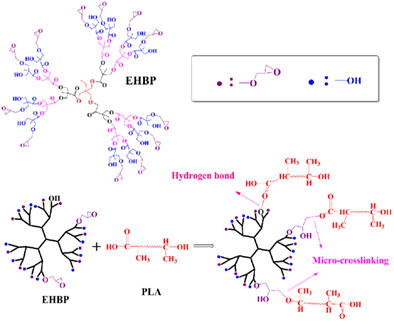
Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) was an eco-friendly and biodegradable material. However, its molecular chain was inflexible and showed limited toughness. In this work, PLA was modified with epoxy-terminated hyperbranched polymer (EHBP) by melt blending to improve the toughness of PLA. The results showed that epoxy groups within EHBP reacted with carboxyl and hydroxyl groups of PLA, forming chemical micro-crosslinking. In addition, intermolecular hydrogen bonds were formed between hydroxyl groups on EHBP and PLA, and the combined action of the two ultimately improved the toughness and strength of PLA. Chemical micro-crosslinking was validated via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and gel content analysis. By observing the microscopic morphology of the impact fracture of the blends, it was found that the interface adhesion of the blends increased with the addition of EHBP, enhancing the corresponding mechanical properties. The best interface adhesion was achieved when 2.5 phr EHBP was added to PLA. At this point, compared with neat PLA, the maximum tensile strength, impact strength, elongation at break, and flexural modulus of PLA/EHBP increased by 17.4%, 54.5%, 107.1%, and 25.8% respectively, achieving the goal of simultaneously enhancing the toughness and strength of PLA. The simultaneous improvement in the strength and toughness of PLA expands its potential application value.
Optimizing natural rubber blends for examination gloves: Vacuum radiation for mechanical strength and solvent barrier
- First Published: 26 September 2023
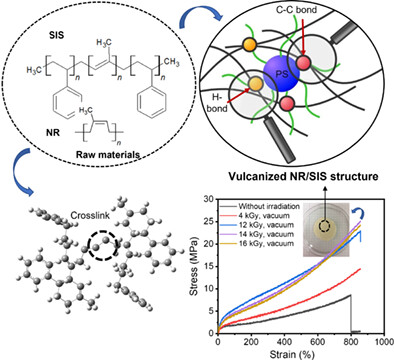
This manuscript introduces the ability of the vacuum radiation strategy as a green process that can replace conventional chemical vulcanization methods, resulting in natural rubber (NR)/poly(isoprene-b-styrene-b-isoprene) (SIS) films with high mechanical and barrier performance. The proposed method is an interesting, fast reaction time and energy-saving method because the samples packed in vacuum condition before the irradiation have produced vulcanized NR/SIS blend films. Moreover, this approach is greener than the conventional sulfur vulcanization method because it does not contain vulcanization agents.
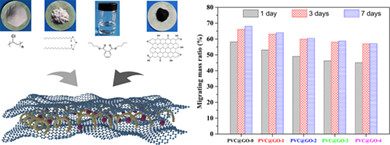
Improving the migration resistance against phthalate plasticizer in polyvinyl chloride/graphene oxide composites
- First Published: 18 October 2023
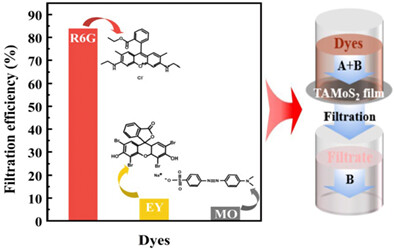
Selective filtration of dye by tannic acid-molybdenum disulfide composite nanofiltration membrane
- First Published: 25 September 2023
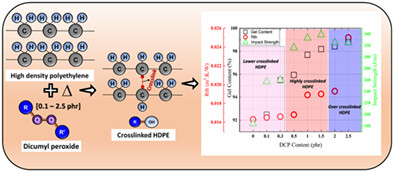
The effect of chemical crosslinking on the properties of Rotomolded high density polyethylene
- First Published: 29 September 2023
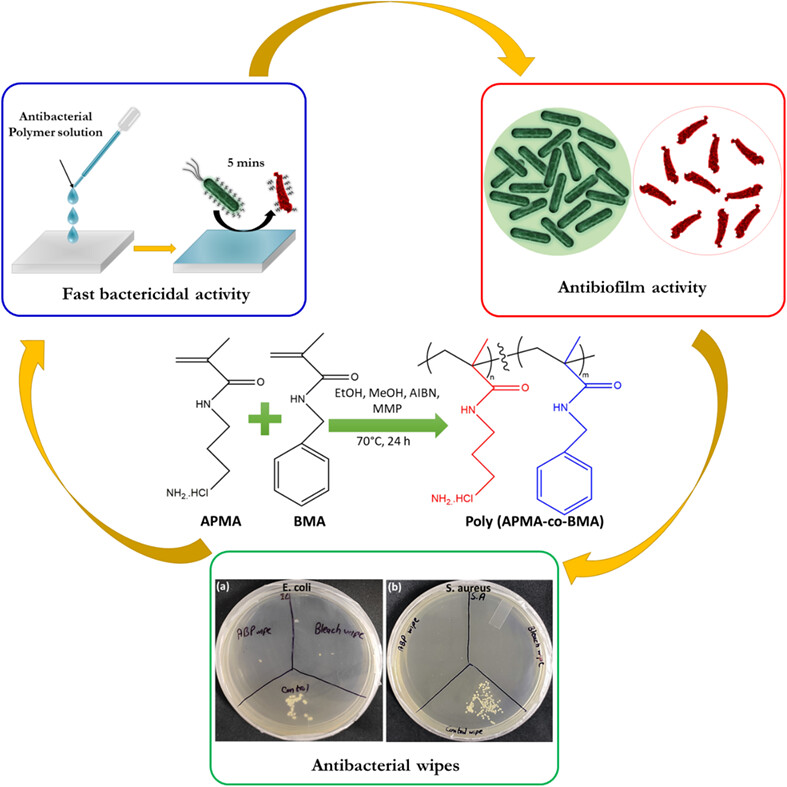
Long-term and fast-bactericidal activity of methacrylamide-based copolymer for antibiofilm coatings and antibacterial wipes applications
- First Published: 29 September 2023
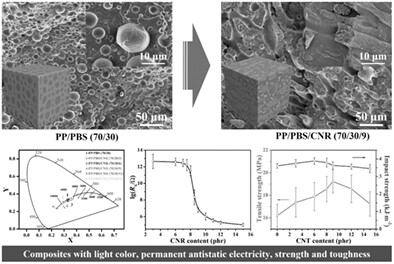
Light-colored conductive nanorod-mediated co-continuous polypropylene/poly(butylene succinate) blends: Regulatory mechanism, morphology evolution, electrical, and optical properties
- First Published: 29 September 2023
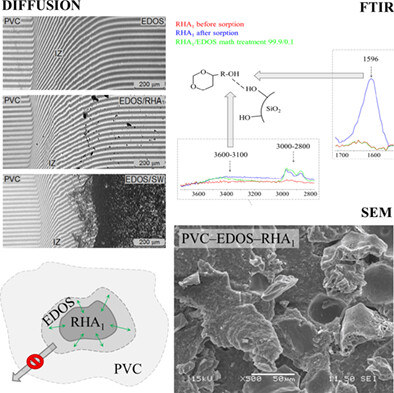
Influence of rice husk ash and wollastonite on plasticizer migration in polyvinyl chloride system
- First Published: 29 September 2023
Enhanced desalination performance and arsenate removal using semi-aromatic polyamide-based pervaporation membranes by modifying with amino-acids via interfacial polymerization
- First Published: 03 October 2023
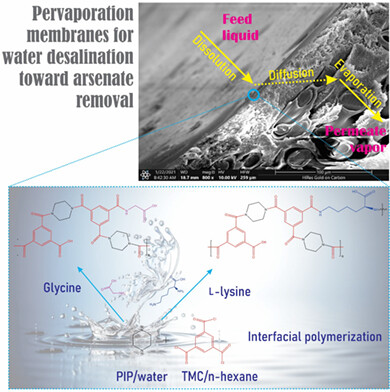
This concept is to modify the semi-aromatic PA thin-film composite membrane by adding glycine and lysine into the PA selective layer, resulting in increasing the hydrophilic properties and reducing the thickness of the modified membrane. Also, it could improve permeability without sacrificing the selectivity of the membrane.
Influence of annealing-induced phase separation on the shape memory effect of graphene-based thermoplastic polyurethane nanocomposites
- First Published: 03 October 2023
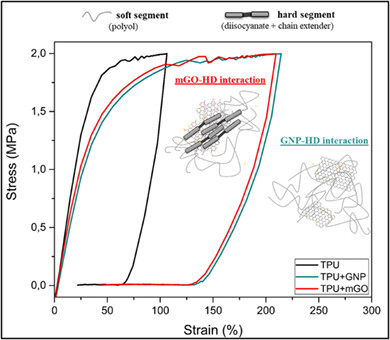
Solution casting processing was used to incorporate 0.1 wt% of graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) or 0.1 wt% of multilayers graphene oxide (mGO) into TPU matrix. The results have shown that GNP with less functional groups than mGO, is mainly disperse in the soft segment, while mGO acting as nucleating agent mainly interacts with the hard segments. According to the shape-memory thermomechanical cycle, analyzed in terms of stress and strain, higher strains are observed for all nanocomposites when compared to neat TPU. Among the graphene nanoparticles, GNP presented higher strains, mostly due the lubricating effect of graphene, as mGO, presents greater stiffness which can be explained by the higher polarity inherent to the functional groups that present better affinity with the TPU, which anchors the polymeric chains.
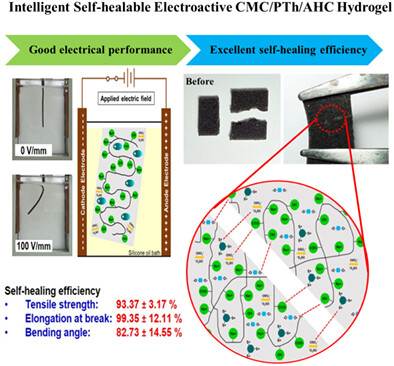
Intelligent self-healable electroactive carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel containing conductive polythiophene and acid hydrolyzed cellulose
- First Published: 04 October 2023
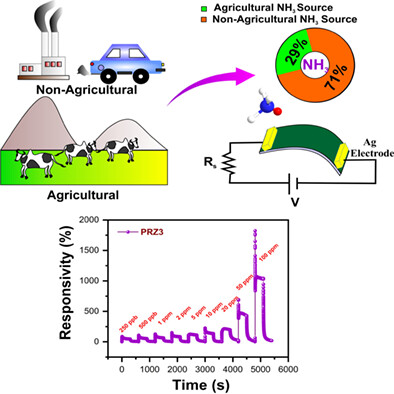
Superior ammonia sensing properties of PET-supported polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide/zinc ferrite ternary nanocomposite thin film at room temperature
- First Published: 18 October 2023
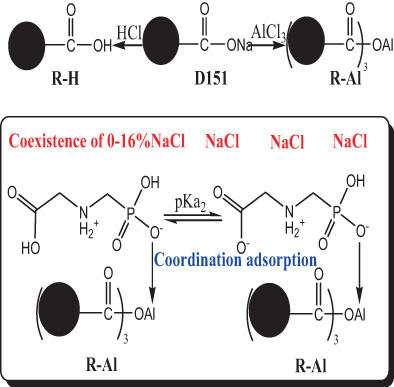
La3+ and Al3+ loaded D151 as salt-resistant resins for efficient adsorption of glyphosate: Effects of ionic radius
- First Published: 05 October 2023
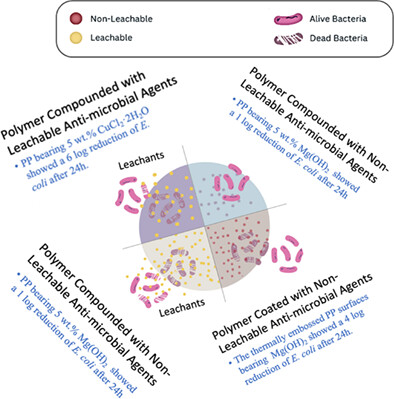
Fabrication methodologies for antimicrobial polypropylene surfaces with leachable and nonleachable antimicrobial agents
- First Published: 18 October 2023
Colorless, transparent, and shape memory polyurethane networks with high strength and recyclability
- First Published: 10 October 2023
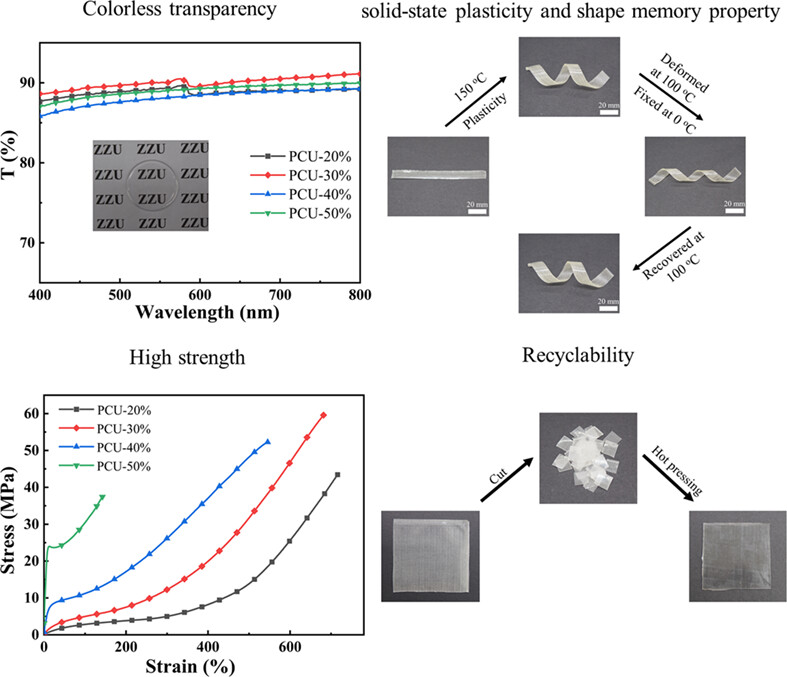
The colorless, transparent, and recyclable thermoset PCU fabricated in this work exhibits excellent mechanics with tensile strength of 59.2 ± 3.7 MPa, and shows solid-state plasticity and good shape memory performance, with shape fixity and recovery ratios above 90%. The PCU can achieve arbitrary shape manipulations by the combination of solid-state plasticity and shape memory property.
Noninvasive biosensing 3D scaffold to monitor degradation: The potential of fluorescent PCL and PLGA for tissue engineering
- First Published: 24 October 2023
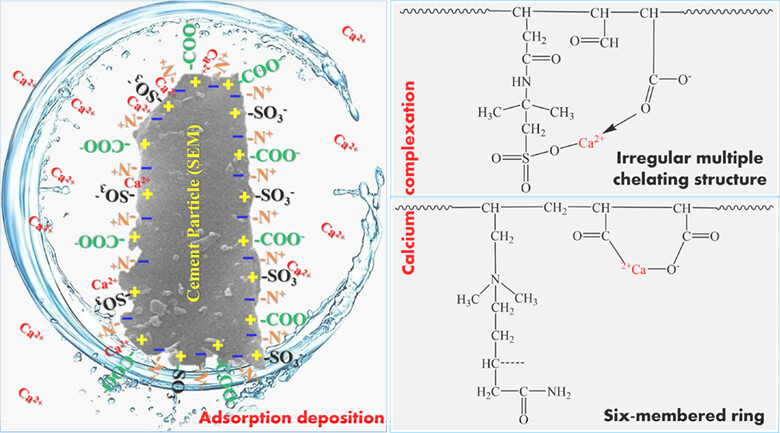
Preparation, characterization, and retarding mechanism of high temperature resistant amphoteric ion polymer oil well cement retarder Poly-AAMD for HTHP application
- First Published: 18 October 2023
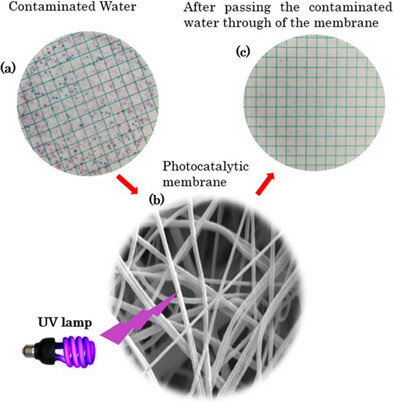
Photocatalytic and antimicrobial efficacy of PVDF/TiO2 membranes fabricated by solution blow spinning
- First Published: 10 October 2023
Polyurethane toughened covalent adaptive networks epoxy composite based on thermoreversible Diels-Alder reaction: Self-healable, shape memory, and recyclable
- First Published: 08 October 2023
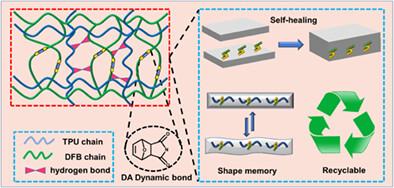
By introducing thermoplastic polyurethane as a toughening phase into DA reaction in-situ polymerization through solution blending, a uniform interlocking polymer network DFB-TPU can be formed. Due to the reversible covalent chemistry of DA reactions, new functionalities such as self-healing, shape memory and recyclability are introduced.
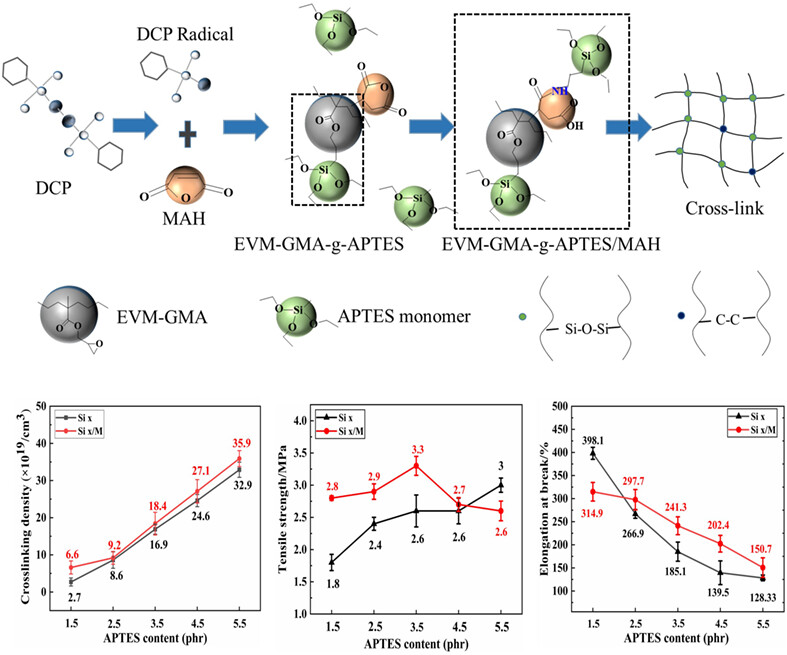
Effects of maleic anhydride on the moisture crosslinking of EVM-GMA grafted with amino silane
- First Published: 18 October 2023
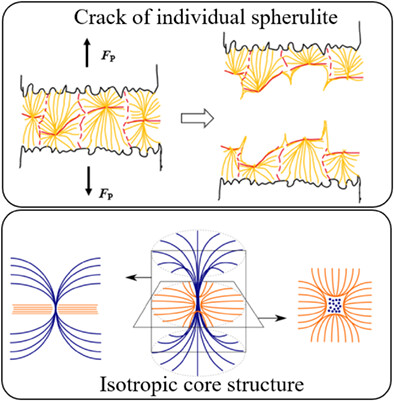
Direct observation of the fracture behavior of the polyether ketone ketone (PEKK) spherulites
- First Published: 08 October 2023
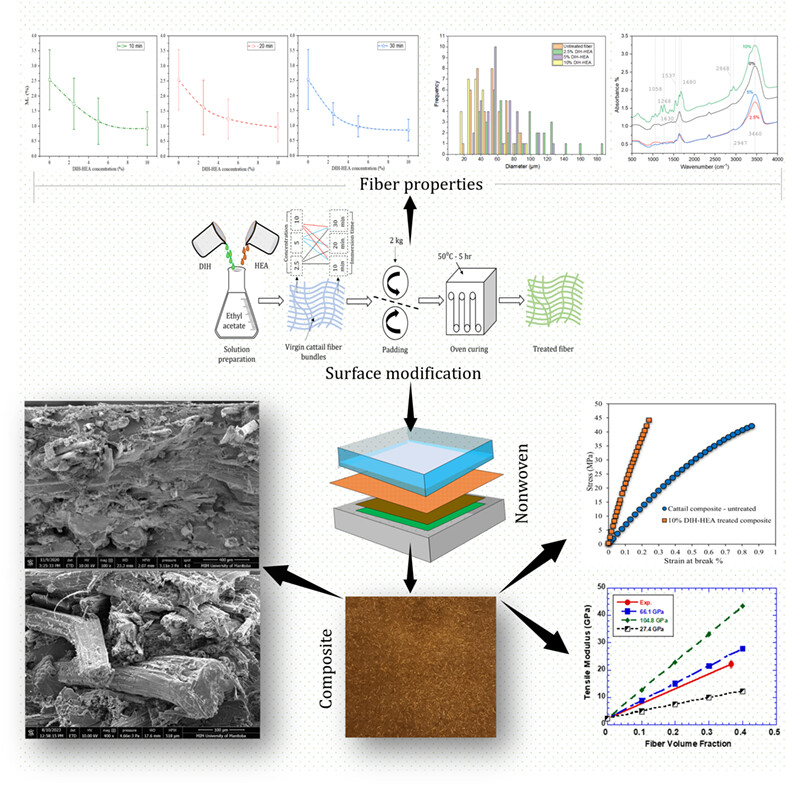
Effect of fiber surface treatment on mechanical, interfacial, and moisture absorption properties of cattail fiber-reinforced composites
- First Published: 15 October 2023
Preparation and characterization of high solid content cationic waterborne polyurethane with core-shell structures
- First Published: 10 October 2023