Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
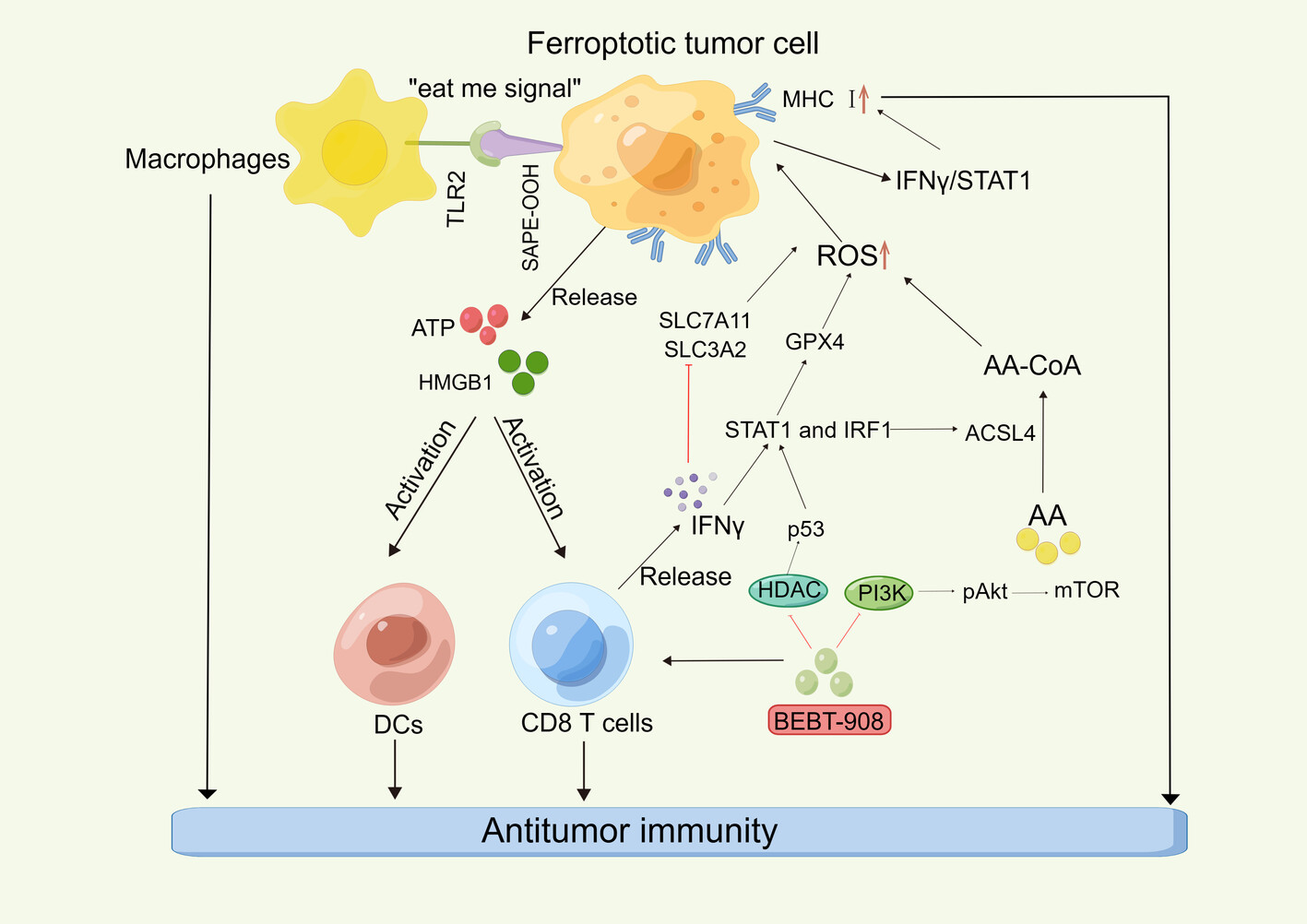
The engineered exosomes targeting ferroptosis: A novel approach to reverse immune checkpoint inhibitors resistance
- Pages: 7-18
- First Published: 27 March 2024
SHORT REPORT
Cancer Epidemiology
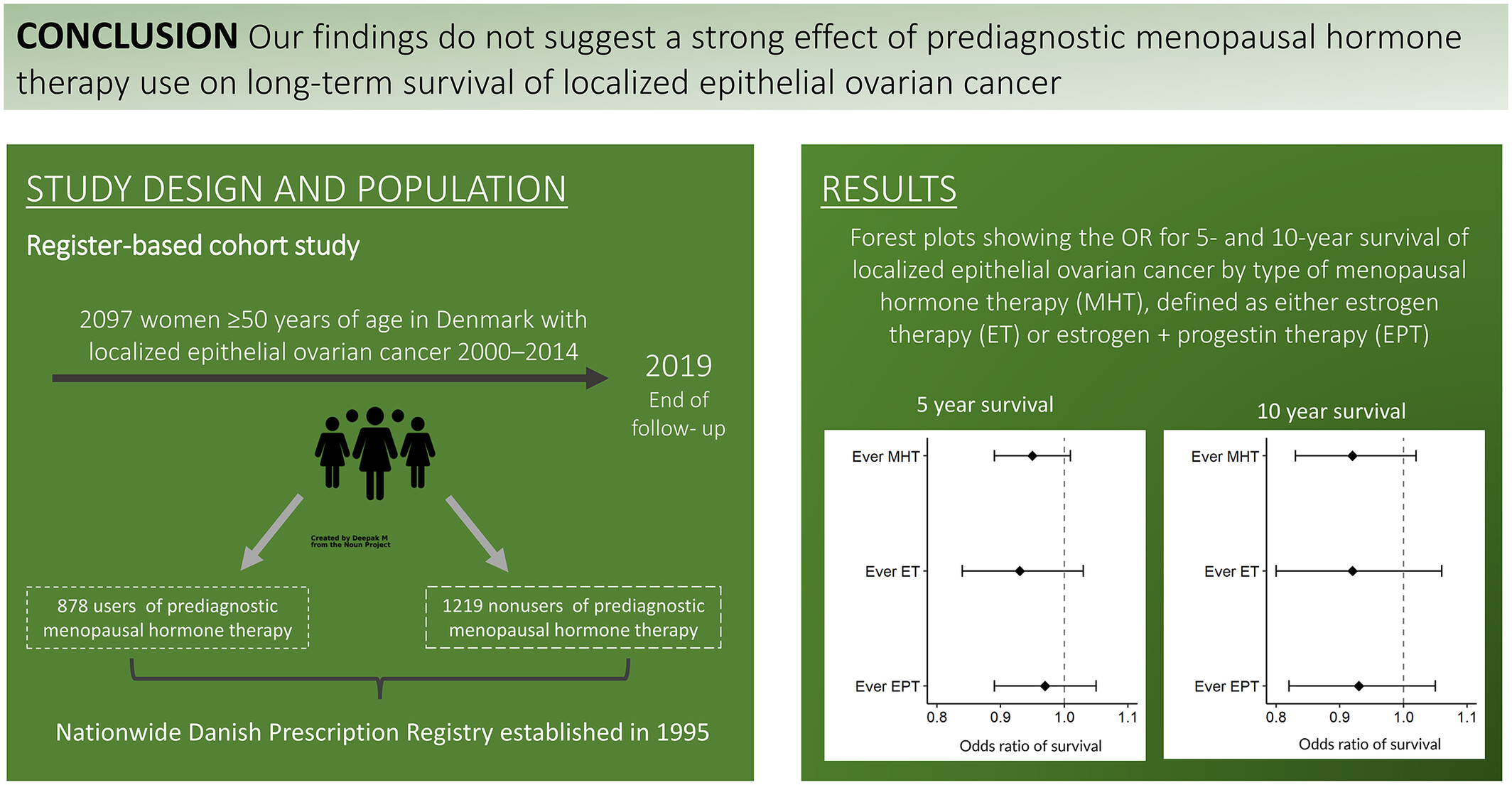
Prediagnostic use of menopausal hormone therapy and long-term survival of localized epithelial ovarian cancer: The Extreme study
- Pages: 19-26
- First Published: 26 March 2024
What's new?
While prediagnostic menopausal hormone therapy has been suggested to have a positive effect on epithelial ovarian cancer survival, studies remain inconsistent. Based on a large nationwide study of women 50 years or older with nonlocalized epithelial ovarian cancer, the authors previously found an improved long-term survival in long-term users of prediagnostic menopausal hormone therapy. Exploring long-term survival in women with localized epithelial ovarian cancer from the same nationwide cohort, they observed no significant benefit. The findings do not suggest a positive benefit from prediagnostic menopausal hormone therapy on long-term survival in localized epithelial ovarian cancer.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cancer Epidemiology
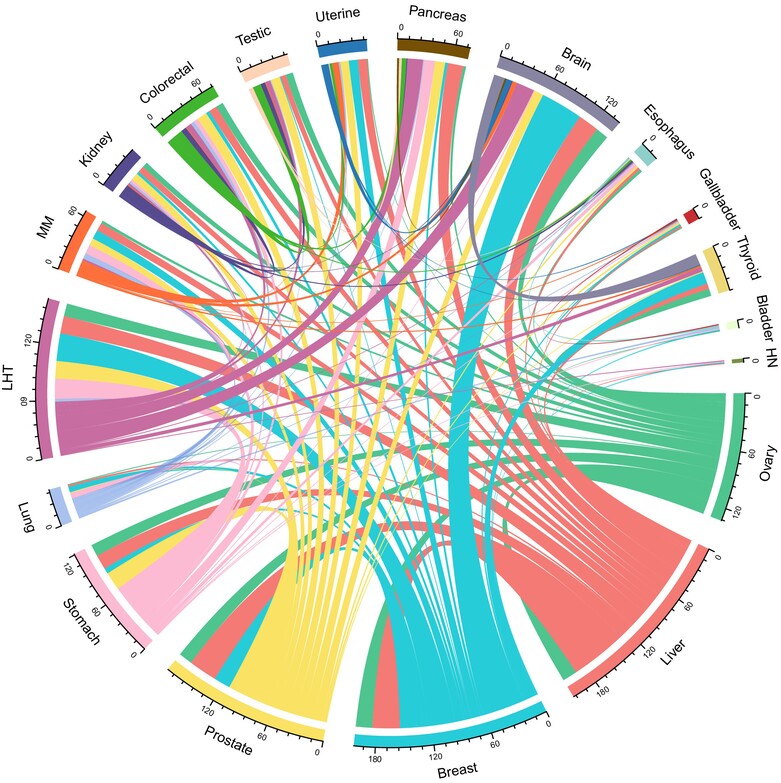
Metabolomic landscape of overall and common cancers in the UK Biobank: A prospective cohort study
- Pages: 27-39
- First Published: 02 March 2024
What's new?
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) enables detailed quantification and qualitative study of associations between metabolites and cancer. Owing to high reproducibility in particular, NMR could greatly facilitate the identification of biomarkers for cancer detection and prognosis. In this study, using a cohort from the UK Biobank, the authors explored associations between NMR metabolites and risk of 20 common cancers. Each of the 20 most frequently identified metabolites were associated with overall cancer risk. Relationships between the same metabolite and different cancer types varied by tumor site. Mediation effects on traditional risk factors, including age and diet, were observed for 13 metabolites.
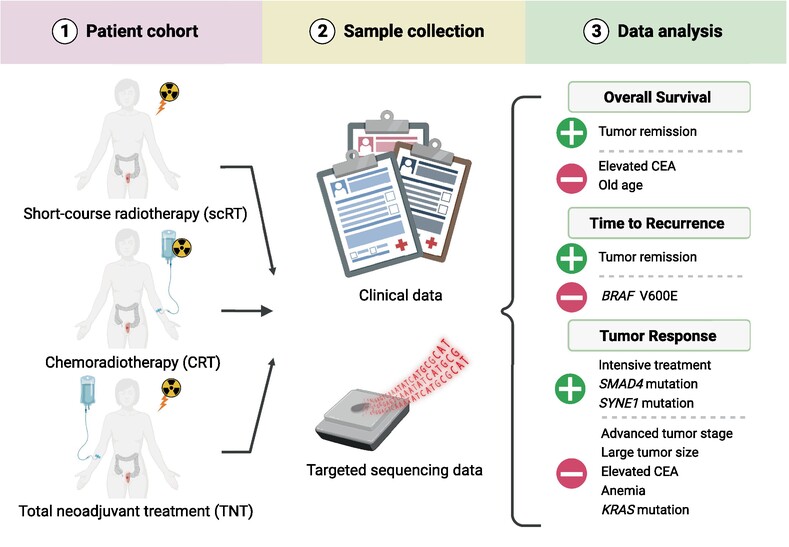
Clinical and genetic factors associated with tumor response to neoadjuvant (chemo)radiotherapy, survival and recurrence risk in rectal cancer
- Pages: 40-53
- First Published: 20 February 2024
What's new?
The response to preoperative radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer is highly heterogeneous, with up to 30% of patients showing a complete pathological response at surgery. This large study combining clinical and sequencing data from a cohort of patients with locally advanced rectal cancer found that mutations in SMAD4 and SYNE1 were associated with higher complete response rates. However, inclusion of mutation status for specific genes only marginally improved complete response prediction models. The findings may pave the way for personalised interventions, optimising outcomes and addressing current challenges in rectal cancer pre-operative treatment.
Stage at diagnosis of colorectal cancer in the Middle East and Northern Africa: A population-based cancer registry study
- Pages: 54-60
- First Published: 08 March 2024
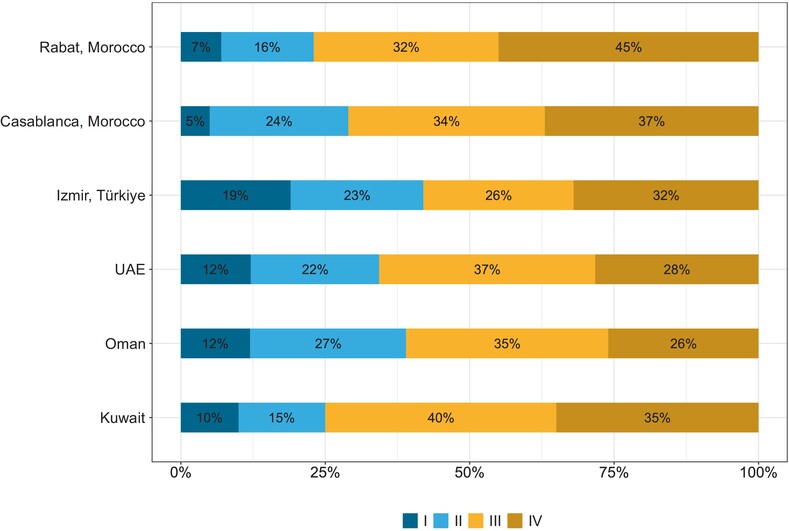
What's new?
The Middle East and Northern Africa (MENA) region faces an increasing prevalence of lifestyle risk factors for colorectal cancer. The authors collected colorectal cancer stage data (TNM and/or SEER) from 12 population-based cancer registries in nine MENA countries. About one third of cases were diagnosed with distant metastases. The metastatic cancer proportions were lower in Oman, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates compared to other MENA countries, but still less favourable than in Europe and the United States. Harmonising the use of staging systems and focusing data collection on major cancers is needed to inform colorectal cancer control in MENA.
The risk of vaginal, vulvar and anal precancer and cancer according to high-risk HPV status in cervical cytology samples
- Pages: 61-70
- First Published: 28 February 2024
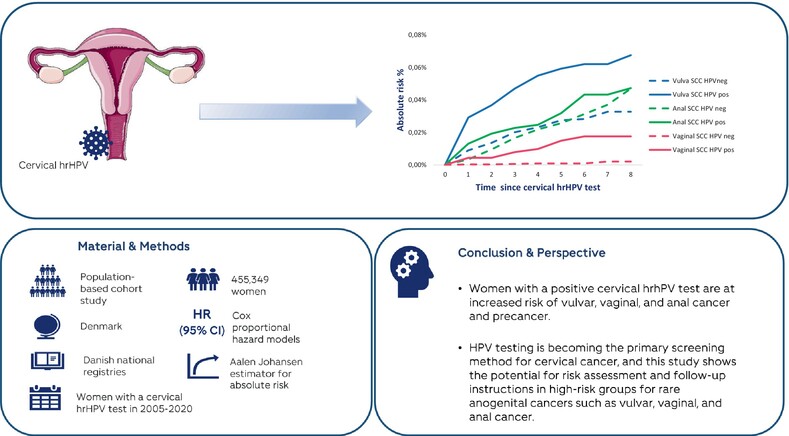
What's new?
Most high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia cases and cervical cancers are caused by high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) infection. Other anogenital cancers also share an etiological link with hrHPV. Here, the authors investigated associations between persistent cervical hrHPV infection and risk of non-cervical anogenital precancers and cancers. Data show that women who test positive for cervical hrHPV are at increased risk of subsequently developing vulvar, vaginal and anal cancer and precancer. Risk was highest among hrHPV-positive women who were older, who had a history of anogenital precancer and who were not vaccinated against HPV. Further study is needed to identify risk thresholds.
Healthy dietary patterns and risk of prostate cancer in men at high genetic risk
- Pages: 71-80
- First Published: 01 March 2024
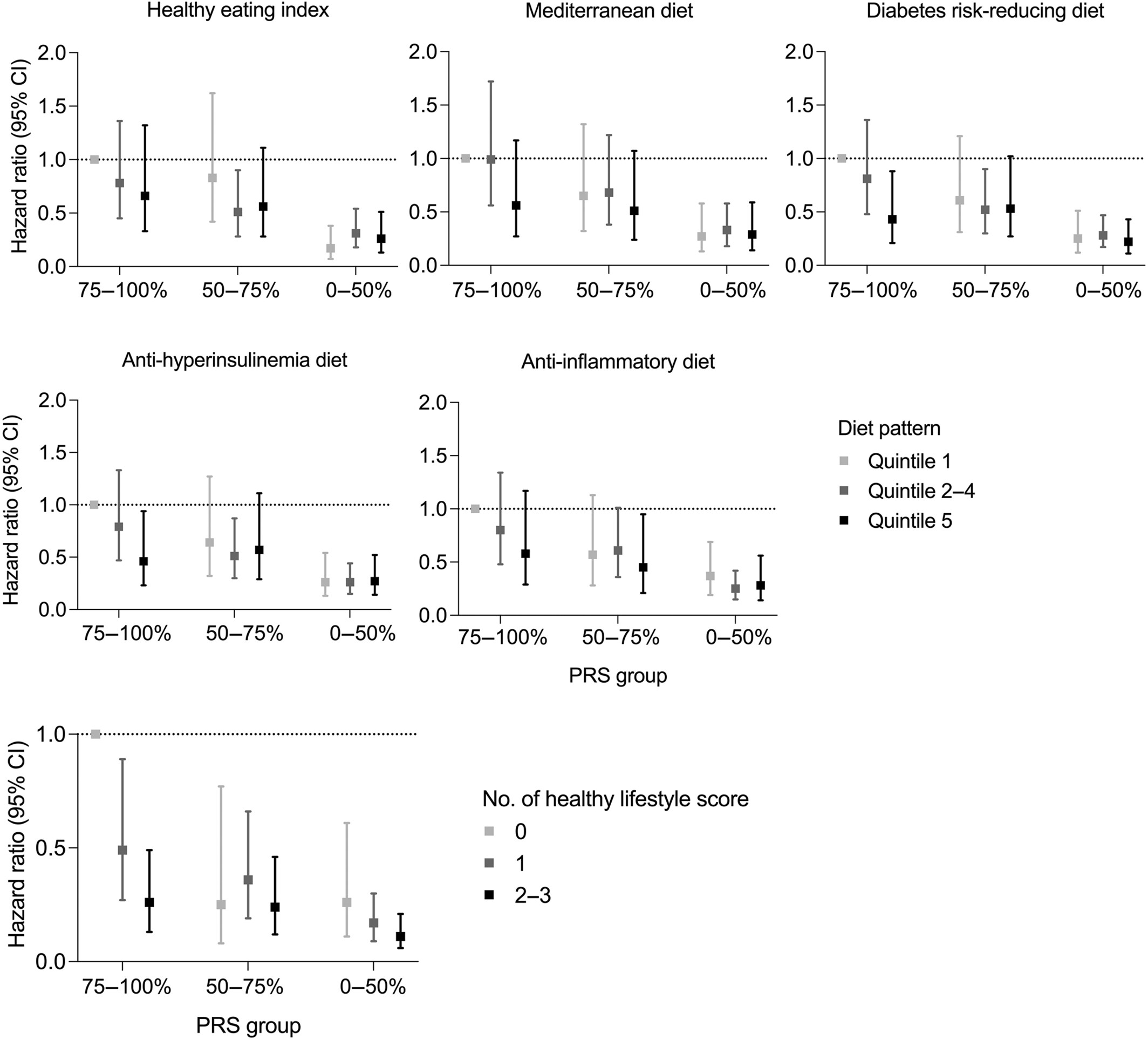
What's new?
While healthy dietary patterns are linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer, whether this is true for men with increased genetic susceptibility to prostate cancer remains unclear. Here, using data from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study, the authors examined links between five dietary patterns and prostate cancer risk among men at high genetic risk. Healthy lifestyle, based on body weight, physical activity, and low insulinemic diet, was associated with a significantly reduced rate of lethal prostate cancer. The findings suggest that higher adherence specifically to a low insulinemic diet reduces lethal prostate cancer risk in genetically predisposed men.
Long-term prediction by DNA methylation of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: Results of the ARTISTIC cohort
- Pages: 81-92
- First Published: 20 March 2024
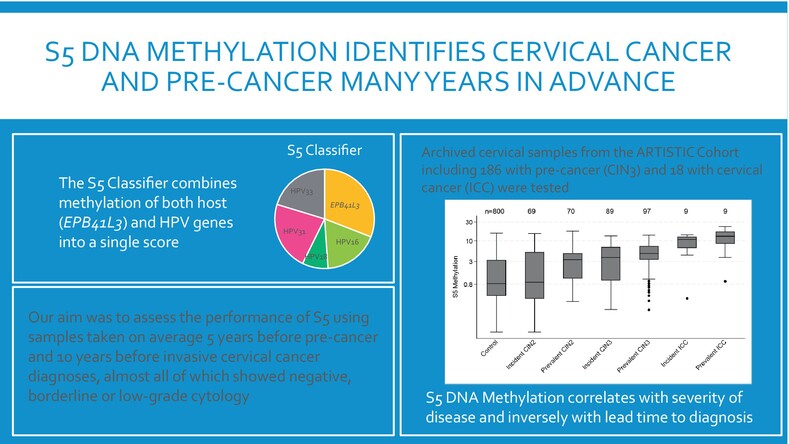
What's new?
Most human papillomavirus infections do not lead to pre-cancer, so a test is essential to triage high-risk HPV-positive women for treatment or further testing. While methylation markers have shown some success in triaging high-risk HPV samples for prevalent disease, their potential for long-term prediction of incident CIN3 and invasive cancer has yet to be revealed. In this case-control study, S5 DNA methylation correlated with increasing disease severity, and inversely with lead time to diagnosis. The S5 classifier could discriminate between high-risk HPV-positive women who developed CIN3 or invasive cancer and high-risk HPV-positive controls on average 5 years before diagnosis.
Cancer Genetics and Epigenetics
Germline variants of DNA repair and immune genes in lymphoma from lymphoma-cancer families
- Pages: 93-103
- First Published: 06 March 2024
What's new?
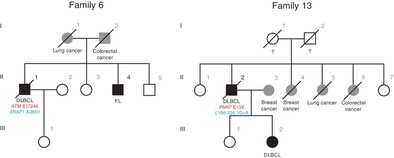
The genetic predisposition to lymphoma has yet to be fully understood. Here, the authors performed sequencing analyses in 13 lymphoma-cancer families, in which males tended to develop lymphomas and females to develop cancers. They identified germline variants for 25 DNA repair genes and 14 immune genes in 18 lymphoma patients, with more than one third of these mutations being protein truncating. Genome instability and oncogene activation were verified in lymphoma samples, and somatic mutations mediating immune evasion were also found. These germline defects of DNA repair and immune genes suggest germline double hits in lymphomagenesis.
Targeted DNA sequencing of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma reveals association of TP53 mutations with platinum resistance when combined with gene expression
- Pages: 104-116
- First Published: 06 March 2024
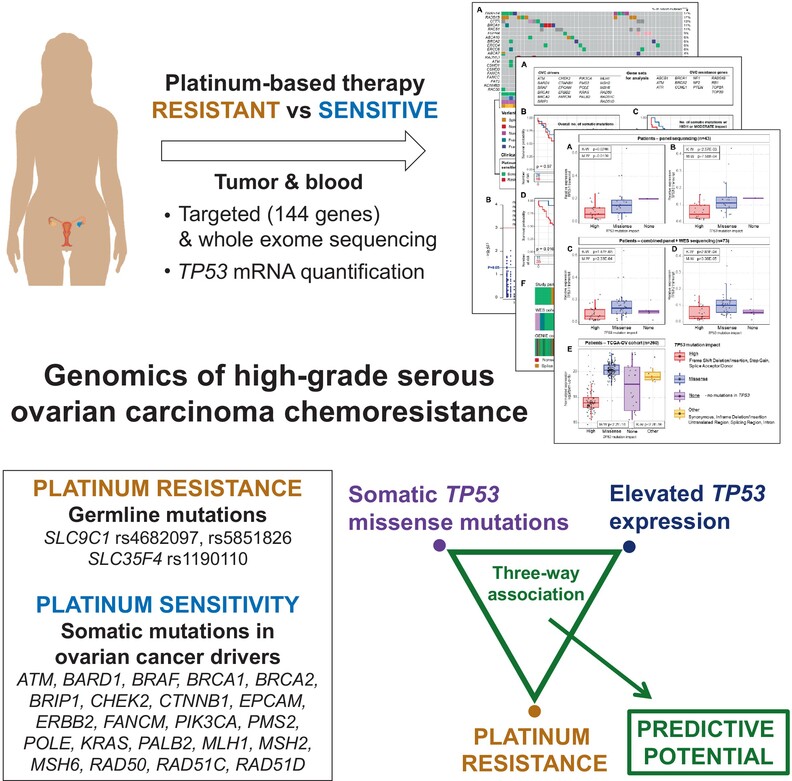
What's new?
Biomarkers for better stratification of patients with ovarian cancer into existing targeted therapy scenarios and clinical trials are still missing. In this analysis of somatic and germline genetic variability using a custom panel of 144 high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma-related genes, gene expression of highly somatically mutated TP53 correlated with mutation type and resistance to platinum therapy. Combined analysis of somatic genetic background and TP53 expression may thus be valuable in predicting therapy response. Furthermore, high-coverage custom-targeted sequencing was superior to whole-exome sequencing for identification of potentially clinically impactful TP53 variants, both somatic and germline.
Cancer Therapy and Prevention
Health utility values of breast cancer treatments and the impact of varying quality of life assumptions on cost-effectiveness
- Pages: 117-127
- First Published: 13 March 2024

What's new?
Utility scores facilitate calculations of quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), which represent a measure of the value of health outcomes. With regard to breast cancer, however, utility scores are inconsistent, with consequences for QALY evaluation and cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA). In our study, new utility values for breast cancer treatment were determined at different time points and stratified by different measures. Evaluation shows that normative utilities stratified by age and gender most reflected real-world situations and were therefore most meaningful for CEA. Likewise, patient-based breast cancer quality-of-life parameters stratified by age and treatment or by disease stage were most appropriate for CEA.
Efficacy and safety of everolimus plus exemestane in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER-2-negative advanced breast cancer: Results from the open-label, multicentre, non-interventional BRAWO study
- Pages: 128-138
- First Published: 06 March 2024
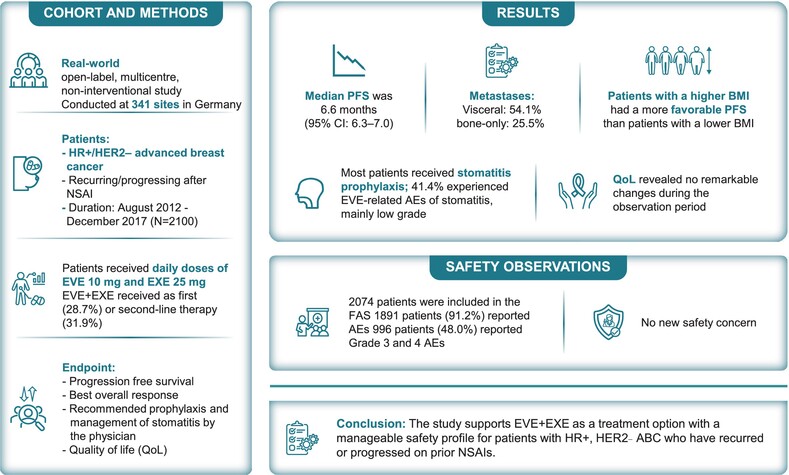
What's new?
The non-interventional BRAWO study assessed efficacy and safety of everolimus and exemestane (EVE + EXE) for patients with HR+, HER2-advanced breast cancer. The study also assessed patients' quality of life during the treatment. BRAWO assessed the combination treatment under real-world conditions using evidence from a clinical practice in Germany. They found a median progression-free survival of 6.6 months, which broadly agreed with the findings from earlier clinical trials. EVE + EXE did not significantly affects quality of life. Most common adverse events were stomatitis and fatigue; most patients did receive prophylactic treatment against stomatitis. Higher BMI and non-visceral metastases predicted longer progression-free survival.
Trends in management and outcomes of colon cancer in the United States over 15 years: Analysis of the National Cancer Database
- Pages: 139-148
- First Published: 07 March 2024
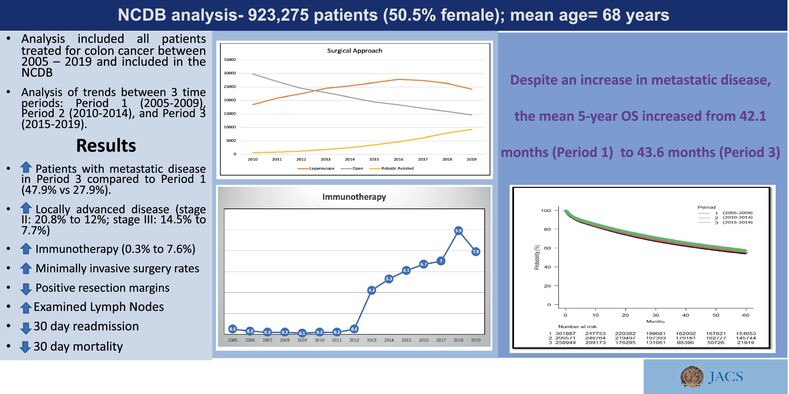
What's new?
Although colon cancer outcome remains strongly associated with disease stage at diagnosis, basic understanding and treatment of colon cancer have advanced significantly in recent years. The authors of the present study assessed the impact of these advances on trends in colon cancer treatment and outcomes using data from the US National Cancer Database over the period 2005–2019. Retrospective analysis revealed an increase in patients who presented with metastatic colon cancer within the study timeframe. Nonetheless, 5-year overall survival improved, possibly owing to enhanced use of immunotherapy and minimally invasive surgery, coupled with decreased resection margins and hospital stays.
Tumor Immunology and Microenvironment
Revealing genes associated with cervical cancer in distinct immune cells: A comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis
- Pages: 149-158
- First Published: 06 March 2024
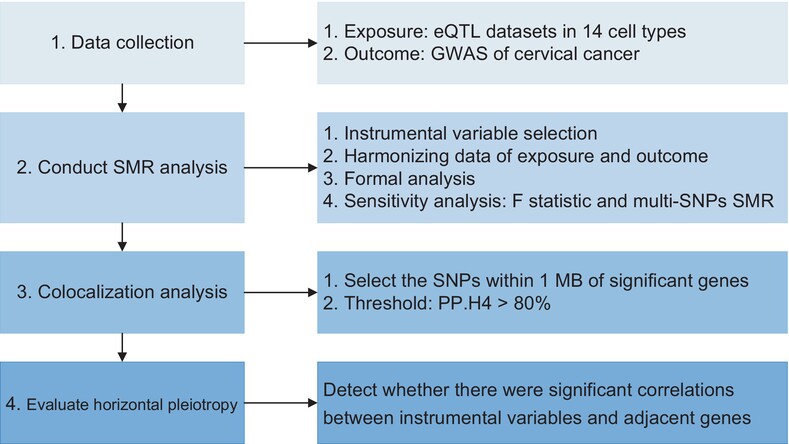
What's new?
Only a small proportion of human papillomavirus infections persist and may progress into cervical cancers, indicating a significant involvement of the immune system in cervical cancer development. However, the precise contributions of genes from different immune cell types to cervical cancers remain poorly understood. Here, by conducting summary data-based Mendelian randomization, the authors identified 10 genes across 11 immune cell types that showed significant associations with cervical cancer after false-discovery rate correction, with ORMDL3, BRK1 and HMGN1 gene expression levels showing notable associations in specific immune cell types.
Tumor Markers and Signatures
Exploring causal correlations between circulating levels of cytokines and colorectal cancer risk: A Mendelian randomization analysis
- Pages: 159-171
- First Published: 22 February 2024
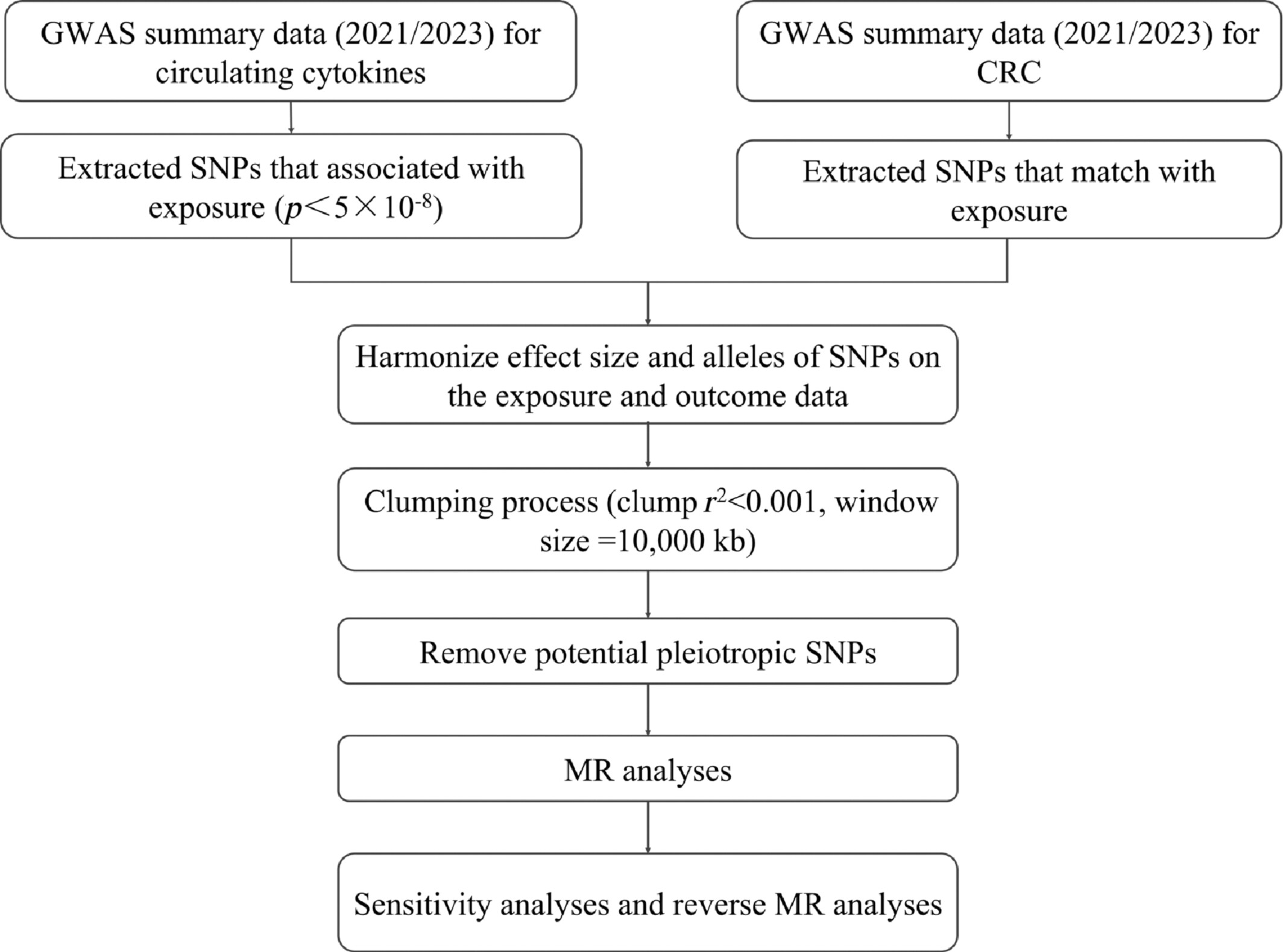
What's new?
Altered cytokine expression is linked to inflammation and cancer-related processes, including initiation, progression, and invasion. In colorectal cancer (CRC), however, which is closely associated with inflammation, whether cytokines influence disease processes remains uncertain. Here, the authors performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis to explore associations involving circulating cytokines and CRC risk. The cytokine IL-12p70 (IL-12B) was found to be associated with elevated CRC risk. CRC risk was further linked to five other cytokines, namely VEGF, M-CSF, IL-13, IL-10, and IL-7. The findings warrant further investigation to better understand relationships between cytokines and CRC risk and to identify possible therapeutic targets.
Adult epithelioid glioblastoma exhibits an extremely poor prognosis and high frequency of SWI/SNF complex mutation: Insights from a retrospective study
- Pages: 172-183
- First Published: 27 February 2024
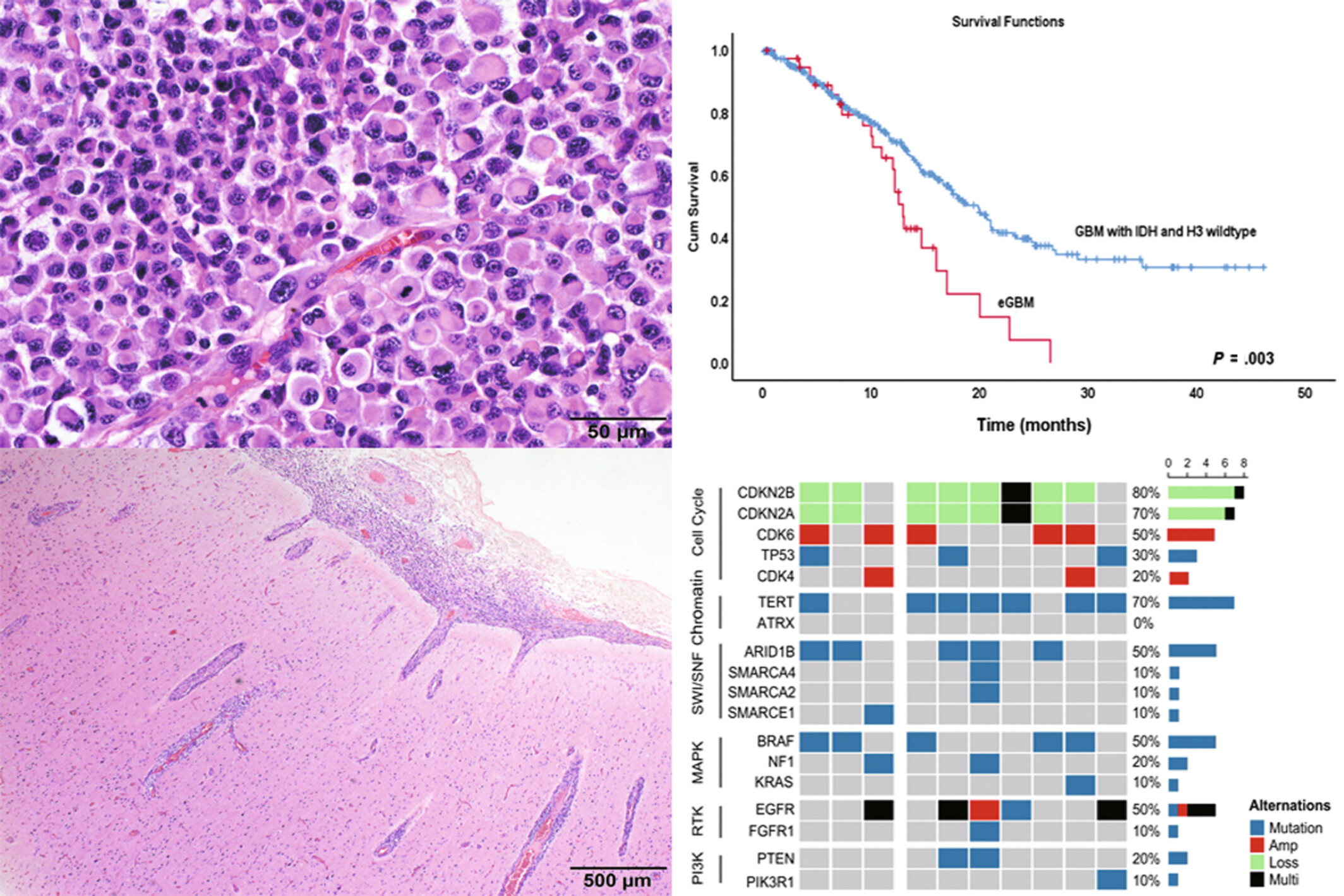
What's new?
Epithelioid glioblastoma (eGBM) is a rare subtype of glioblastoma multiforme. Following the update of the definition of glioblastoma multiforme, the understanding of the molecular characteristics and prognosis of adult eGBM remains limited. This retrospective, single-center study of a cohort comprising 39 adult eGBM cases found that eGBM was marked by specific histopathological characteristics and a high frequency of the 7+/10− signature, along with gene alterations in the SWI/SNF complex. The findings also indicate that eGBM carries a significantly worse prognosis than typical adult glioblastoma multiforme, even in cases without MGMT promoter methylation.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Comment on “Infectious pathogens and risk of esophageal, gastric and duodenal cancers and ulcers in China: A case-cohort study”
- Pages: 184-185
- First Published: 23 February 2024
ERRATA
Correction to “Triptolide reverses hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stem-like features in pancreatic cancer by NF-κB downregulation”
- Page: E1
- First Published: 23 March 2024
Correction to “Real-world treatment patterns for palbociclib plus an aromatase inhibitor, or an aromatase inhibitor alone, for patients with metastatic breast cancer in the Flatiron Database”
- Page: E2
- First Published: 30 March 2024