Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Correlations among noninvasive right ventricular myocardial work indices and the main parameters of systolic and diastolic functions
- Pages: 873-884
- First Published: 09 August 2022
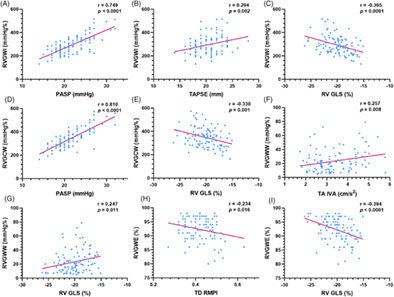
Right ventricular (RV) myocardial work (RVMW) is the latest indicator to assess right ventricular function. The figure shows the main correlations between RVMW indices and other parameters of RV function. Our study revealed RVMW indices could be reliable parameters of myocardial systolic performance.
COMMENTARY
Is noninvasive right ventricular myocardial work analysis the right way for functional assessment of the right ventricle?
- Pages: 885-886
- First Published: 07 September 2022
REVIEW
The impact of medical therapy on left ventricular strain: Current state and future perspectives
- Pages: 887-898
- First Published: 26 May 2022
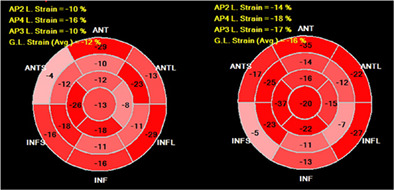
An example of GLS improvement in patient with hypertension and CHF with preserved EF initially and after 1 month of enhanced treatment with ACEi, diuretics (thiazide and loop) and BB. Left side – GLS = −12% on therapy with perindopril 10 mg, amlodipine 10 mg, spironolactone 25 mg; Right side – GLS = −16% on therapy with enalapril 40 mg, amlodipine 5 mg, spironolactone 25 mg, hydrochlorothiazide 12,5 mg, torasemide 5 mg, metoprolol 25 mg
CASE REPORT
Right ventricular postsystolic shortening: Resolution after opening a totally occluded right coronary artery
- Pages: 899-902
- First Published: 07 June 2022
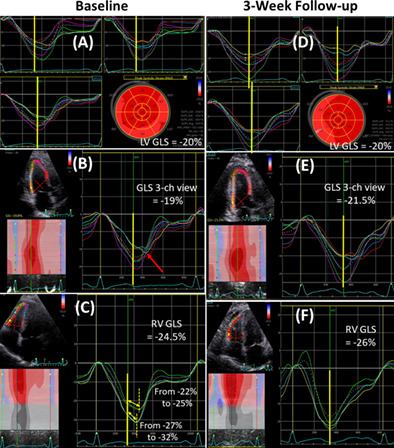
A 51-year-old woman was admitted with a non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Echocardiography showed significant post-systolic shortening (PSS) in the right ventricular (RV) free-wall segments, suggesting ongoing ischemia. Coronary angiography confirmed an occluded right coronary artery, treated by percutaneous coronary intervention. At 3-week follow-up, there was complete resolution of the RV-PSS.
CASE IMAGE
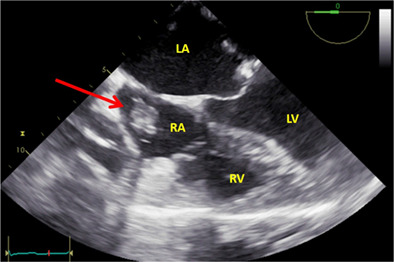
Mal-positioned coronary sinus catheter masquerading as right atrium mass – Thanks to transesophageal echocardiography!
- Pages: 903-904
- First Published: 11 May 2022
VASCULAR IMAGING
REVIEW
Imaging diagnosis and research progress of carotid plaque vulnerability
- Pages: 905-912
- First Published: 08 July 2022
CASE REPORT
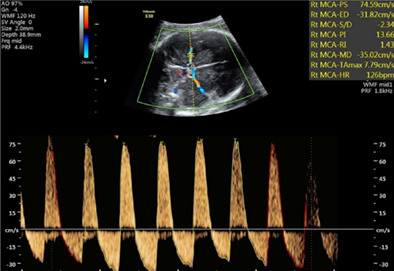
Persistent reversed end-diastolic flow of the middle cerebral artery: A rare and concerning finding
- Pages: 913-917
- First Published: 30 December 2021
GENERAL ULTRASOUND
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Differential diagnostic value of periampullary mass: A nomogram established by random forest based on clinical characteristics and contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- Pages: 918-928
- First Published: 23 June 2022
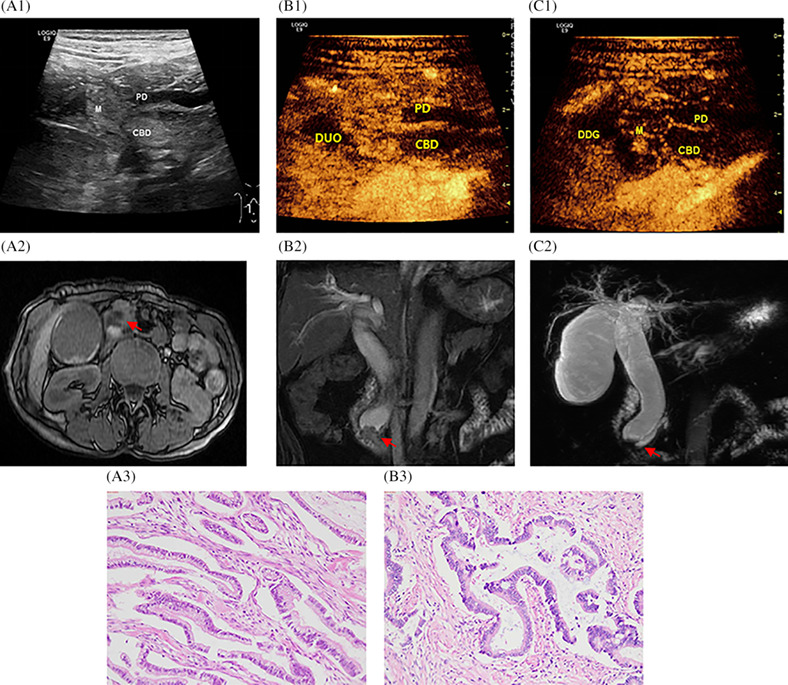
A 62-year-old female with ampullary carcinoma. The gray-scale ultrasound with gastrointestinal filling (a1); In the arterial phase, hyper-enhanced and inhomogeneous-enhanced of ampulla carcinoma with DCEUS (b1); In the venous phase, hypor-enhanced and inhomogeneous-enhanced of ampulla carcinoma with DCEUS (c1); Comparison with DCEUS, MRI Axial (a2)and coronal (b2 and c2) T1-weighted and T2-weighted in displaying the same patient, MRCP manifests as CBD proportional expansion, sudden narrowing of the distal CBD lumen (arrow). Histological outcomes: Pancreatobiliary-type Adenocarcinomas H&E 4× (a3) and H&E 100× (b3); M: mass CBD: common bile duct; PD: pancreatic duct; DUO: duodenum.
COMMENTARY
New horizon of contrast-enhanced sonography in the differential diagnosis of periampullary mass: A random forest nomogram
- Pages: 929-930
- First Published: 07 September 2022
This article has two important future possibilities. This random forest nomogram system can serve to overcome the disadvantage of the poor generalizability of contrast-enhanced sonography. Its routine use is expected to improve young doctors' diagnostic confidence of periampullary mass.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Intravenous combined with intrabiliary contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the evaluation of resectability of hilar cholangiocarcinomas
- Pages: 931-939
- First Published: 08 July 2022
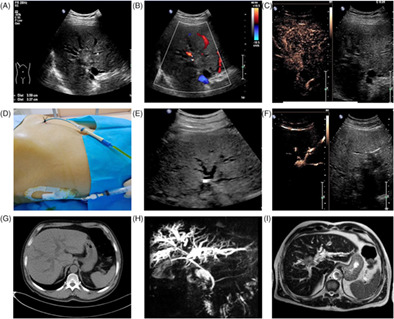
Ultrasonography and MRCP of a Bismuth-Corlette type IV HCCA patient. (A) The tumor invaded the grade 2 bifurcation of left and right hepatic duct in MRCP; (B) Traditional ultrasound showed that there was a space-occupying lesion in the hilar bile duct; (C) IV-CEUS showed that the tumor invaded the common hepatic duct, the left and right hepatic ducts. (D) Percutaneous transhepaticcholangial drainage was performed on the left and right intrahepatic bile ducts; (E) Contrast agent was injected through the drainage tube; (F) IB-CEUS showed that the tumor invaded the common hepatic duct, the left and right hepatic ducts.
CASE IMAGE
Multiple organ dysfunction due to inferior vena cava thrombosis diagnosed by point-of-care ultrasound in the intensive care unit
- Pages: 940-941
- First Published: 18 May 2022
HEAD AND NECK ULTRASOUND
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Differential diagnosis of diffuse sclerotic thyroid papillary carcinoma and Hashimoto's thyroiditis using fine-needle aspiration cytology, BRAFV600E, and ultrasound elastography
- Pages: 942-950
- First Published: 02 July 2022
COMMENTARY
Expanding the role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of thyroid carcinoma and the wish for adjunctive diagnostic tools
- Pages: 951-952
- First Published: 07 September 2022
CASE IMAGE
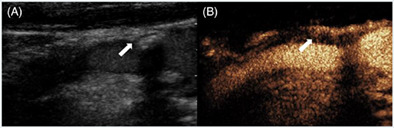
Usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the diagnosis of neck cavernous hemangioma in adults
- Pages: 953-954
- First Published: 28 July 2022
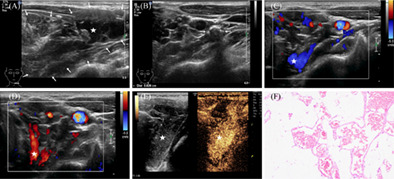
Cavernous hemangioma is a rare, benign tumor and usually uncommon in adults. It is often difficult to diagnose in time because conventional medical imaging examinations usually fail to provide valid information. Clinicians should attach importance to the value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound as an adjunct to rapidly diagnose cavernous hemangioma.
BREAST IMAGING
CASE IMAGE
Male breast cancer presenting in accessory axillary breast
- Pages: 955-957
- First Published: 15 June 2022
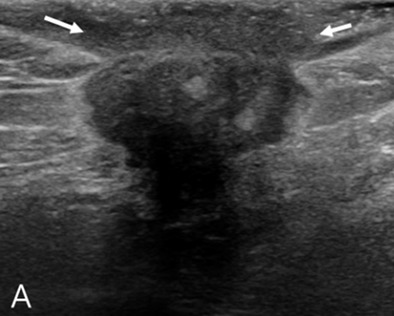
We present a rare case of male axillary accessory breast cancer, which is extremely rare and is indistinguishable from lymphadenopathy and other malignancies, such as lymphoma and skin-derived tumors. Clinicians should consider accessory breast cancer in the differential diagnosis even in men, particularly in those who present with superficially located tumors with adjacent accessory breast tissue.
FETAL ULTRASOUND
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Intertwin membrane cord insertion in dichorionic twin pregnancy: The description and comparison with other umbilical cord insertion types
- Pages: 958-963
- First Published: 03 June 2022
COMMENTARY
Intertwin-membrane insertion: An ultrasound marker of defective growth in dichorionic/diamniotic twins
- Pages: 964-966
- First Published: 07 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLE
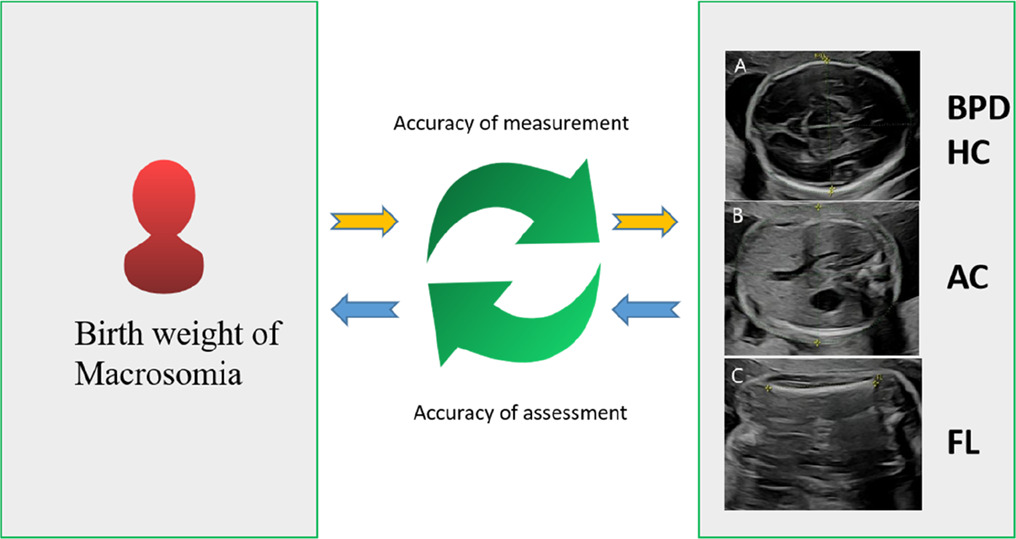
The birth weight of macrosomia influence the accuracy of ultrasound estimation of fetal weight at term
- Pages: 967-973
- First Published: 18 June 2022
COMMENTARY
Can we improve the diagnosis of fetal macrosomia?
- Pages: 974-975
- First Published: 07 September 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLE
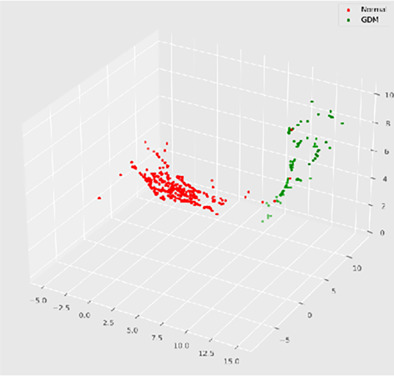
Model application to quantitatively evaluate placental features from ultrasound images with gestational diabetes
- Pages: 976-983
- First Published: 10 July 2022
REVIEWS
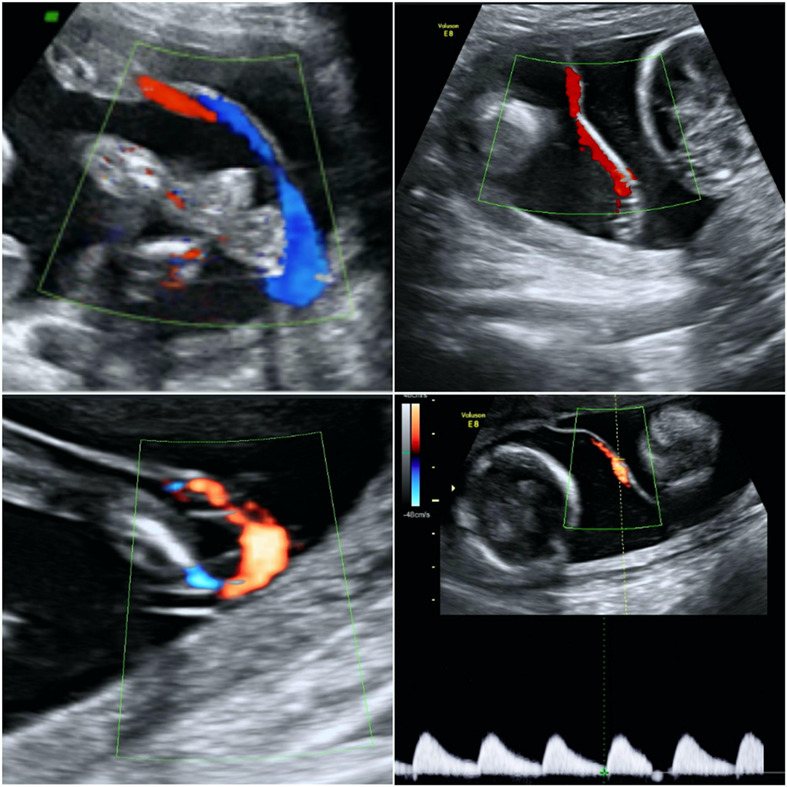
Assessment of pericallosal artery at 11–14 weeks of gestation: Cohort study and meta-analysis
- Pages: 984-988
- First Published: 22 March 2022
Fetal corpus callosum abnormalities: Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging role
- Pages: 989-1003
- First Published: 30 April 2022
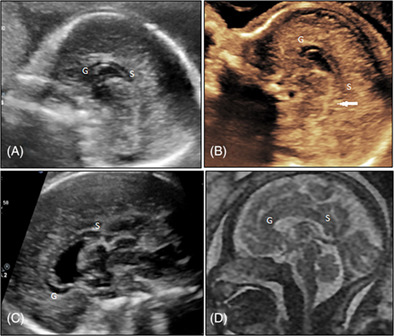
The non-visualization of cavum septum pellucidum and colpocephaly are critical signs in antenatal diagnosis of corpus callosum (CC) agenesis. More subtle findings (i.e., hypoplasia and partial agenesis) might also be recognized antenatally. In this review, the focus was given on the prenatal diagnosis of CC abnormalities in ultrasound (US) and magnetic resonance imaging.
CASE REPORT
Prenatal ultrasonic features of a mediastinal teratoma: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 1004-1012
- First Published: 08 April 2022
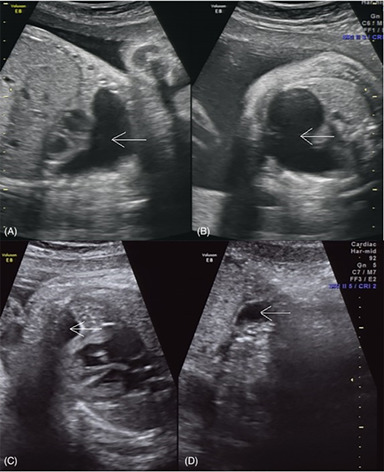
We report a case of a fetal unilocular cystic mediastinal teratoma. The tumor presented as a large simple cystic mass, which became smaller after aspiration of the fetal tumor cyst fluid. The infant was born in good condition without neonatal respiratory distress, and the tumor was successfully removed by elective surgery at age 1 year.
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Effect of beam attenuation on muscle ultrasound echogenicity measurement in muscular dystrophies
- Pages: 1013-1019
- First Published: 21 May 2022
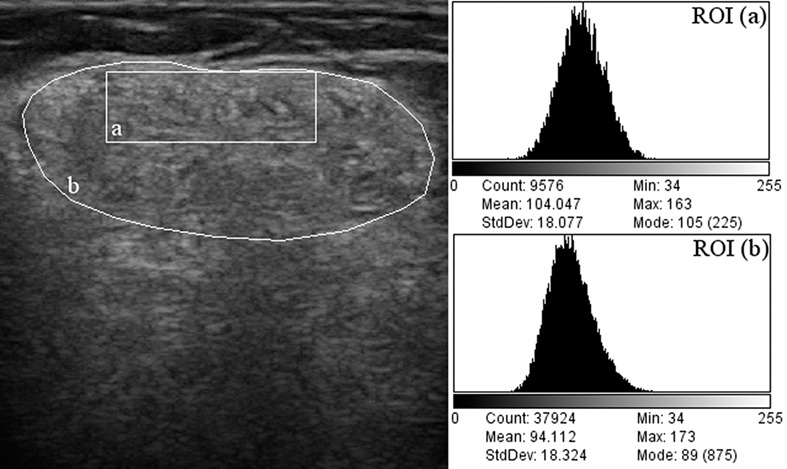
This study evaluated the effect of disease-related beam attenuation when quantifying muscle echogenicity in subjects with muscular dystrophies. Grayscale analysis was performed in three muscles using a superficial versus a whole-muscle region of interest (ROI). In severely affected dystrophic muscles, the analysis of a superficial ROI was more representative of muscle texture changes.