Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Solving dynamic electric circuit with nonlinear hysteretic inductor using harmonics interpolation method
- Pages: 545-570
- First Published: 02 July 2024
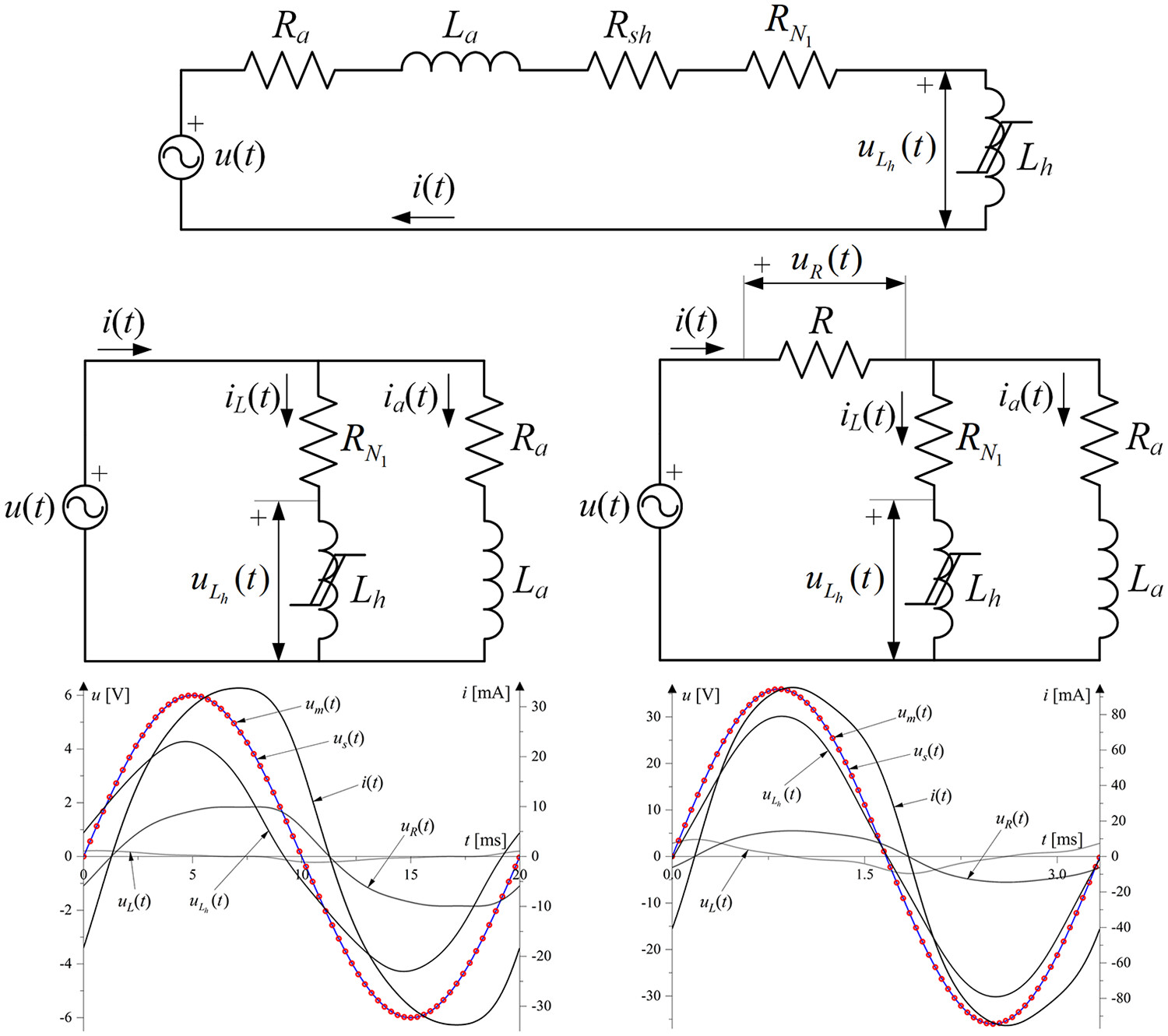
This paper presents a methodology for solving а dynamic electric circuit with nonlinear hysteretic inductor. Nonlinear and hysteretic behaviour of the magnetic core is considered by applying harmonics interpolation method (HIM), without the use of hysteresis model or equivalent circuit. The solution for electric current of the circuit is obtained by solving equations derived from Kirchhoff's laws through a series of successive iterations.
An ultra-low-power low-noise amplifier using a combination of current reuse and self-forward body bias techniques for biomedical applications
- Pages: 571-594
- First Published: 16 June 2024
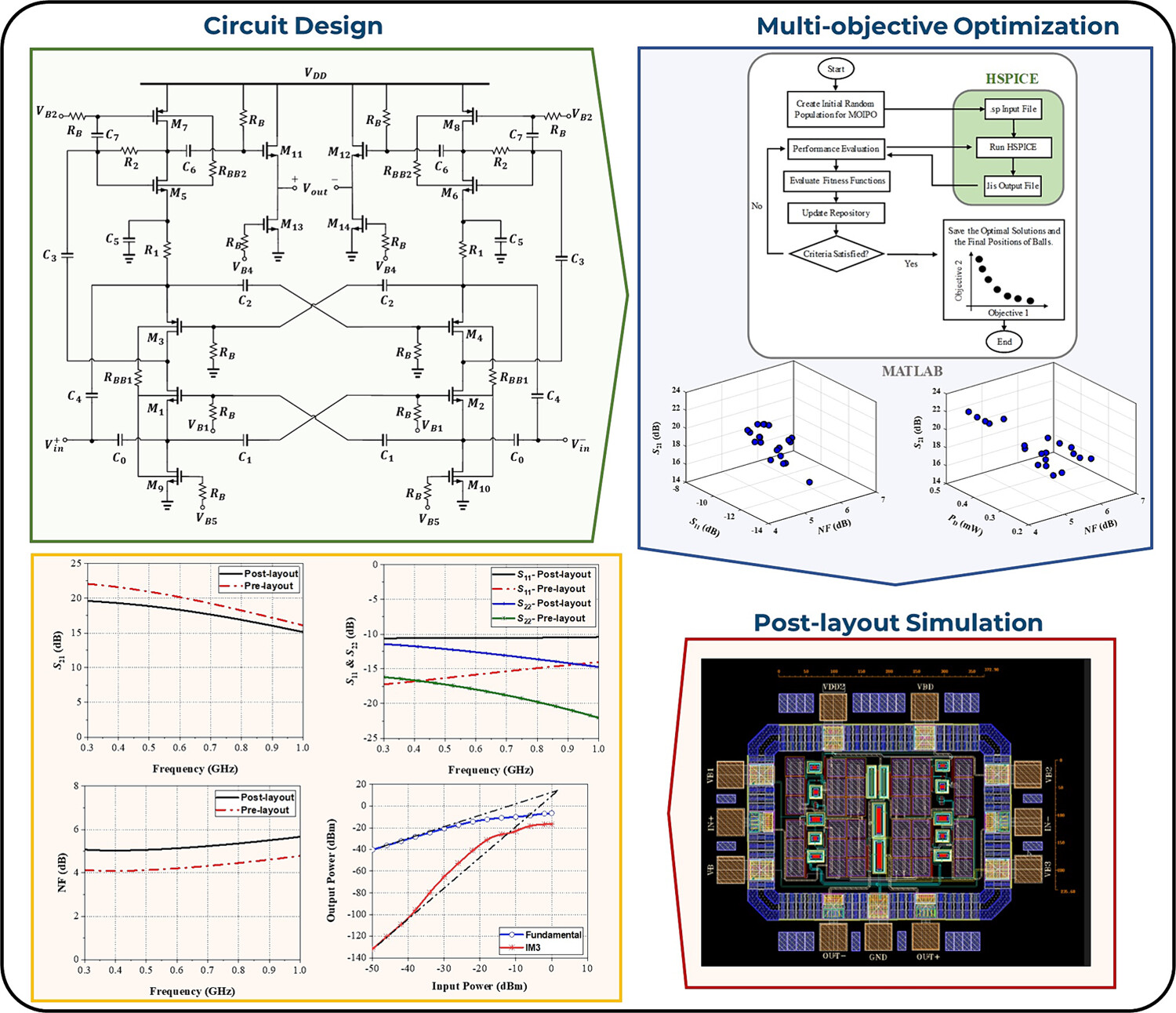
The proposed ultra-low-power low noise amplifier utilizes multiple gm-boosting and self-forward body bias techniques, with certain transistors operating in weak inversion. Additionally, the Multi-Objective Inclined Planes System Optimization algorithm is employed to determine the optimal values of the circuit components, thereby achieving the best trade-off among the various performance parameters.
Design of a transistor-based broadband high-efficiency class-F−1 rectifier
- Pages: 595-606
- First Published: 17 June 2024
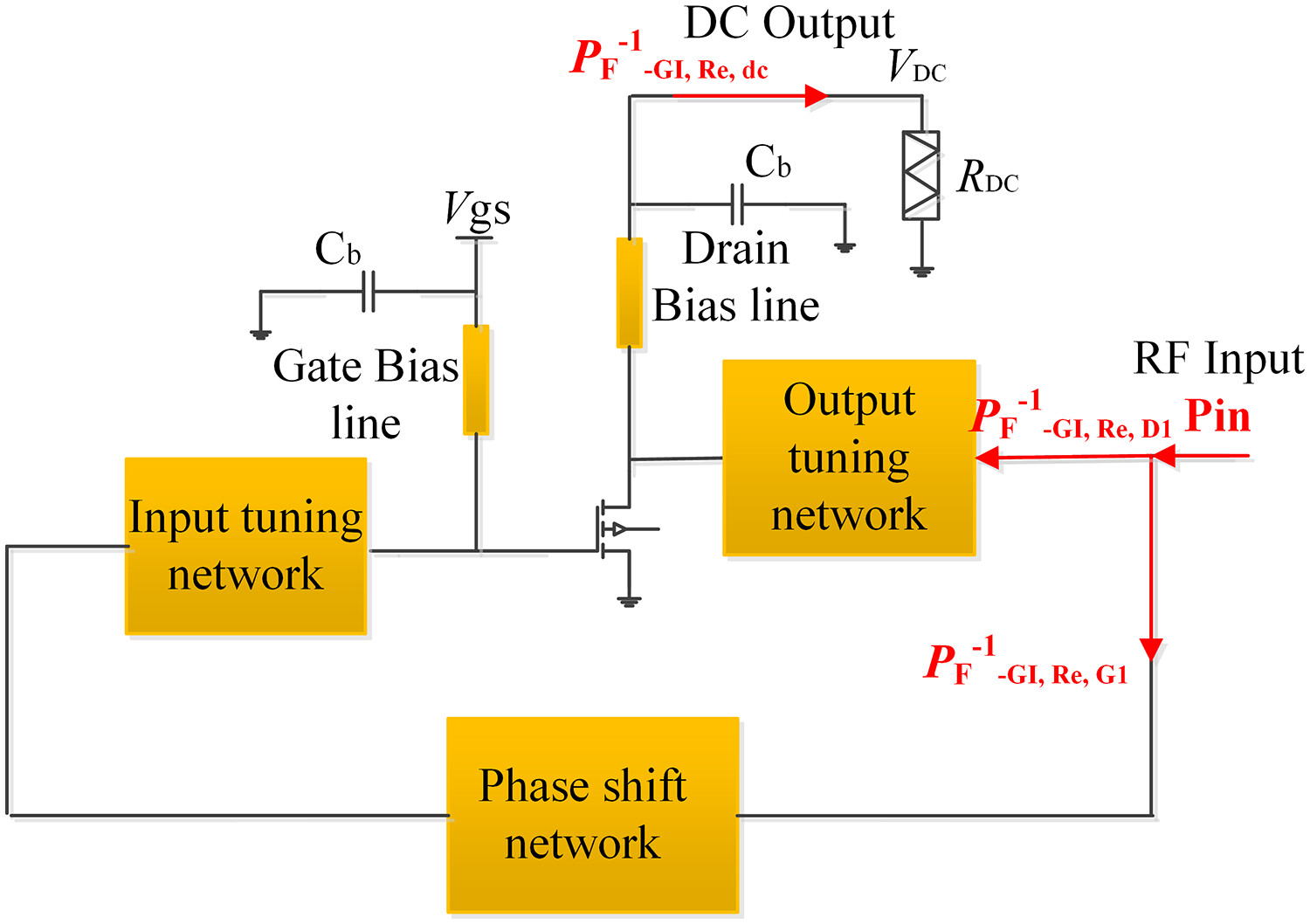
The theory of the transistor-based class-F−1 rectifier with the input second harmonic component is explored. A broadband high-efficiency class-F−1 rectifier (operating in 1.6–2.6 GHz) using a GaN transistor is realized. Measurements indicate a rectification efficiency of between 72.1% and 82.4% under the condition of Rdc = 67 Ω and Pin = 40 dBm.
Low-power multibit delta–sigma modulator based on passive and unattenuated summation scheme
- Pages: 607-620
- First Published: 18 June 2024
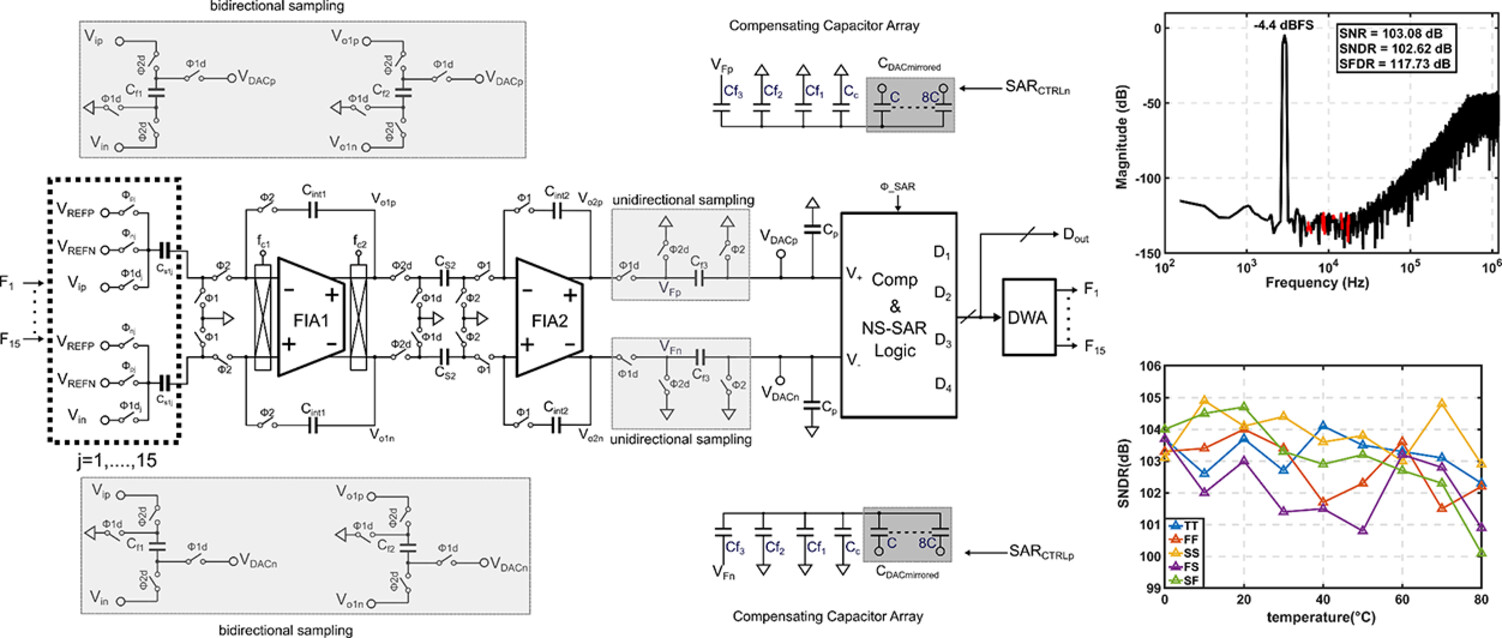
This paper presents a low-power multibit delta–sigma modulator based on a passive and unattenuated summation scheme. The summation circuit achieves multiplication of the voltage signal carried on the summation capacitor through a bidirectional sampling technique, thereby compensating for the inherent attenuation caused by passive summation.
Analysis and design of high-frequency multiple-output wireless power transfer system with load-independent class-E/F inverter
- Pages: 621-640
- First Published: 23 June 2024
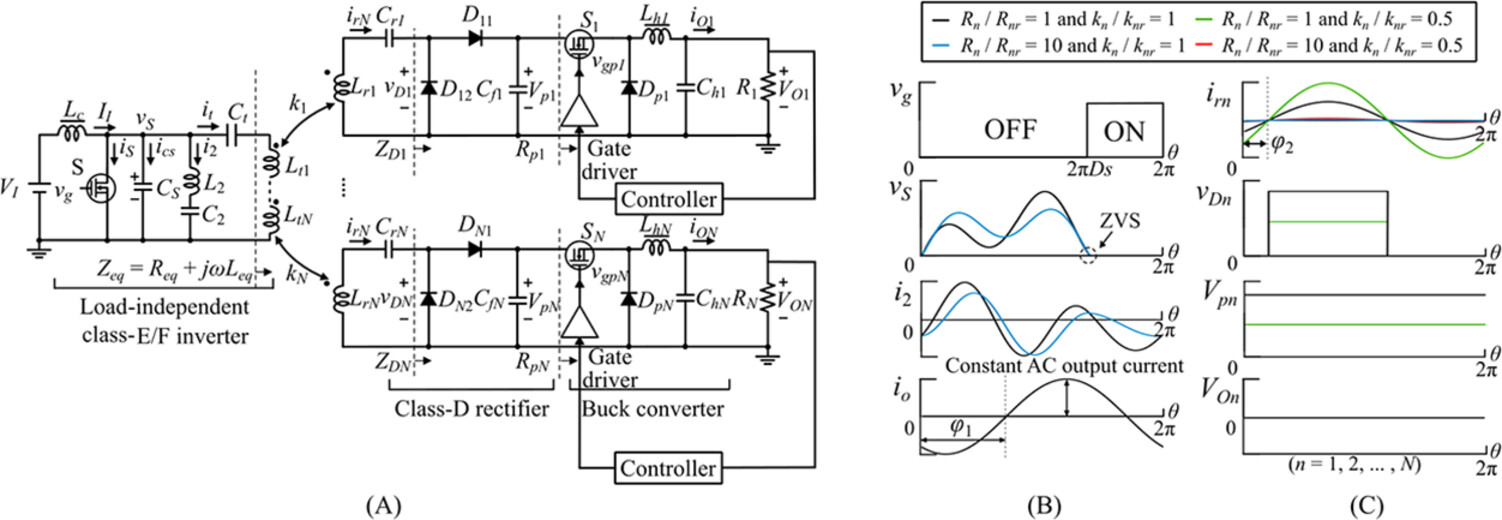
The proposed WPT system: (A) The circuit configuration; (B) The inverter waveforms. Green and red lines are overlapped with black and red lines, respectively, for and . All lines are overlapped for and it; and (C) The receiver waveforms. Blue and red lines are overlapped with black and green lines, respectively, except . All lines are overlapped for .
A CV-type WPT system based on CLC-N compensation with compact receiver
- Pages: 641-654
- First Published: 20 June 2024
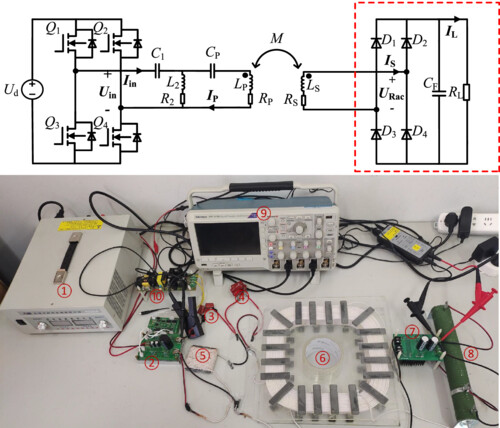
The proposed CV-type WPT system based on CLC-N compensation eliminates bulky filter inductors and secondary side components, achieving a compact and lightweight design. Its ability to achieve approximate ZPA and ZVS operations, as well as CVO characteristics without complex closed-loop control, highlights its simple structure and excellent functional performance.
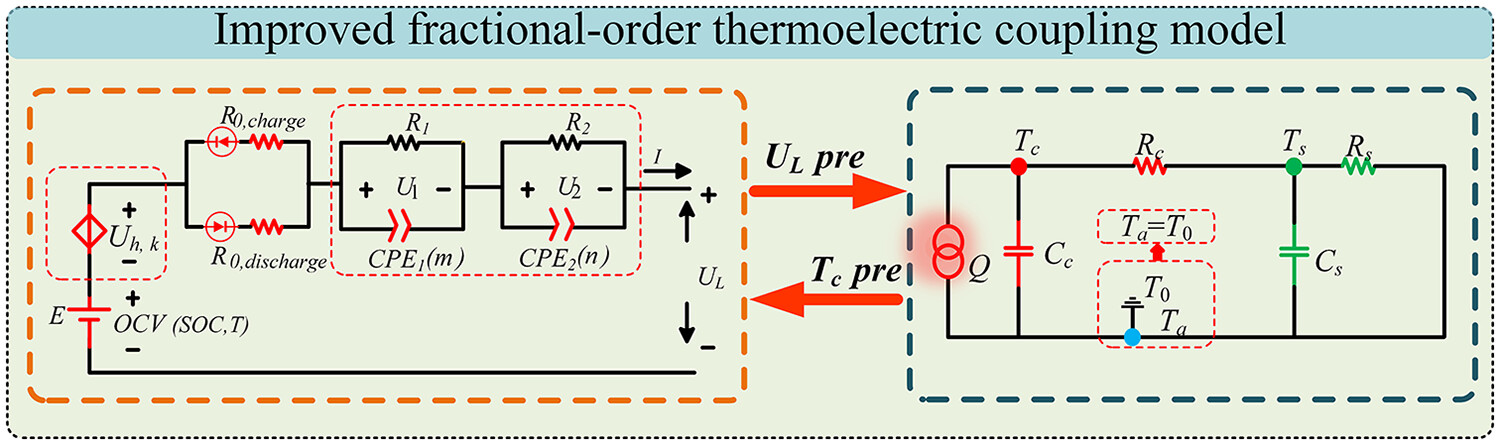
Battery lumped fractional-order hysteresis thermoelectric coupling model for state of charge estimation adaptive to time-varying core temperature conditions
- Pages: 655-680
- First Published: 23 June 2024
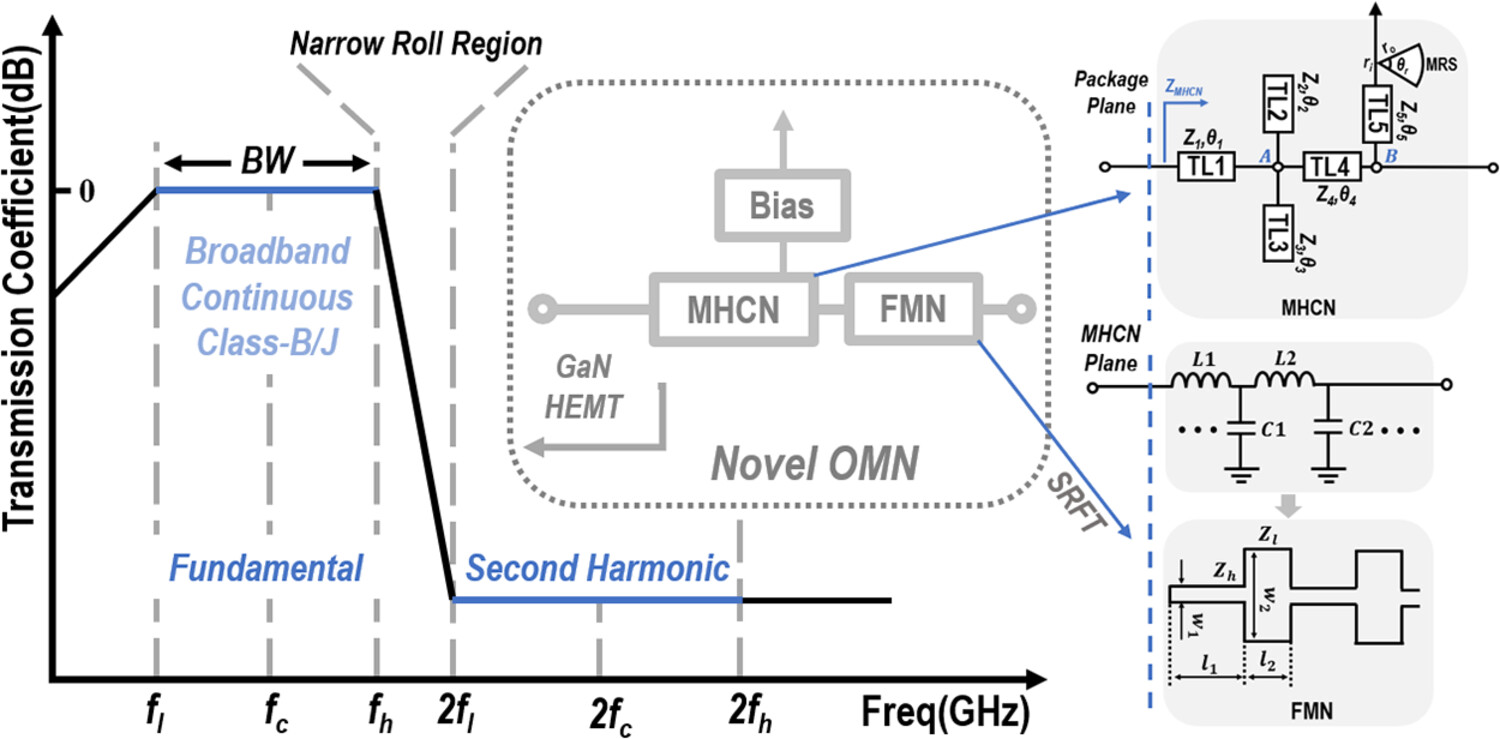
A broadband continuous class-B/J power amplifier with novel output matching network
- Pages: 681-693
- First Published: 24 June 2024
High PSR capacitor-less LDO with adaptive bulk-driven feedforward technique
- Pages: 694-707
- First Published: 27 June 2024
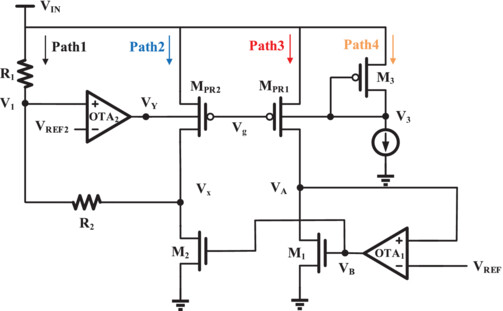
This article presents an adaptive bulk-driven feedforward (ABDFF) technique, which is implemented by two mirror transistors, MPR1 and MPR2, and two operational amplifier, OTA1 and OTA2, to track the load variations and generate an adaptive feedforward ripple at VY. The ripple is injected into the bulk of power transistor and the low dropout regulator (LDO) maintains a steady high power supply rejection (PSR) enhancement over a wide load range.
Memristor-based dual mode whole-process Pavlov associative memory circuit
- Pages: 708-723
- First Published: 12 June 2024
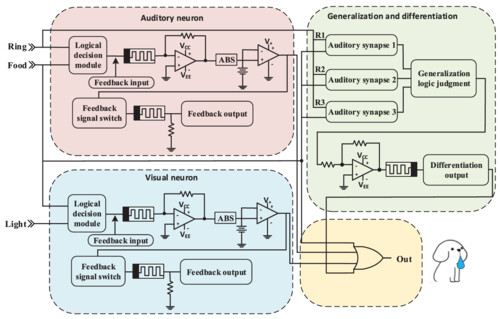
Based on voltage threshold memristor, a memristor associative memory circuit is constructed, and the whole process of acquisition, extinction, generalization, and differentiation of Pavlov associative memory experiment is realized. Compared with the traditional auditory Pavlov experiment, the visual learning mode is added, and the mutual inhibition between the two learning modes is explored. Compared with the traditional generalization and differentiation process, the process in this paper can be realized from every input signals.
A 0.05%–0.08% THD, 762.9 Hz–10 MHz direct digital frequency synthesizer using a reconfigurable DAC for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements
- Pages: 724-744
- First Published: 03 July 2024
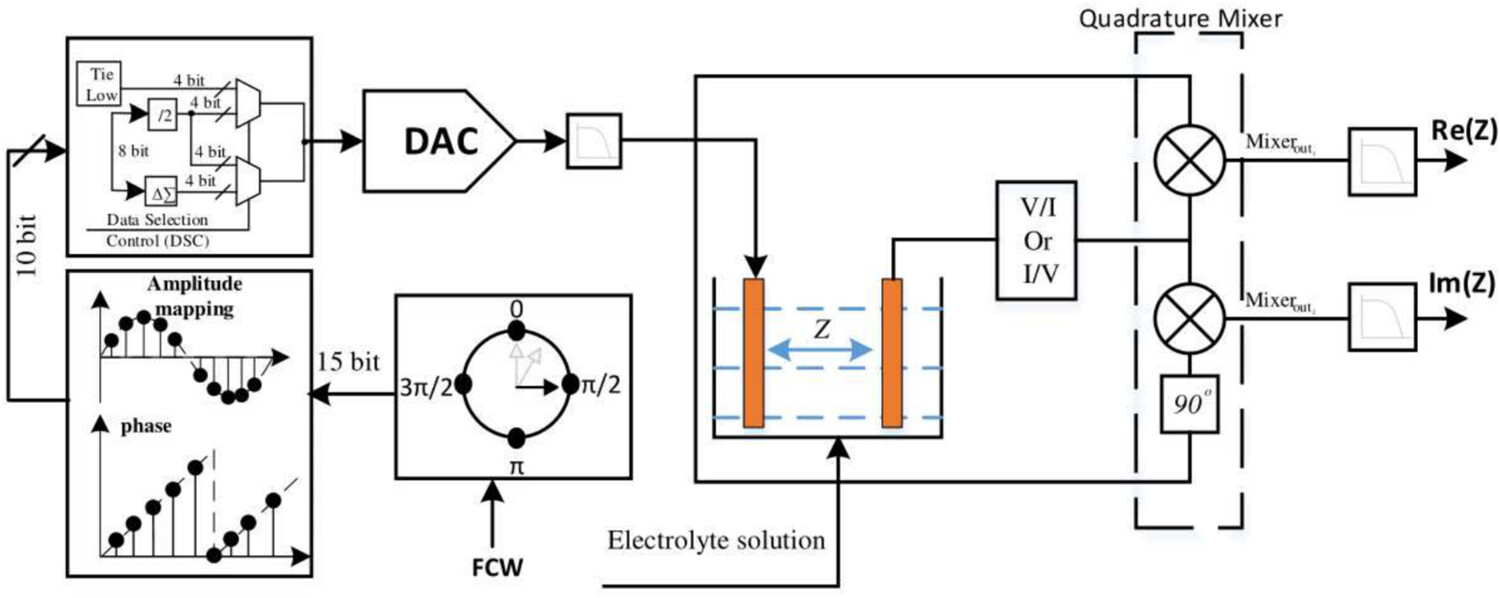
This paper introduces a wide range DDS complete system and circuit designs for electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements. The proposed DDFS-based reconfigurable DAC excites the electrochemical sensor with a pure sin wave for impedance-measuring purposes. The designed DDS system achieves THD less than 0.05% with superior free dynamic range (SFDR) 66 dBc for low-frequency range and 0.08% with SFDR 62 dBc for high-frequency range.
Low power and noise-immune 9 T compute SRAM cell design based on differential power generator and Schmitt-trigger logics with14 nm FinFET technology
- Pages: 745-770
- First Published: 27 June 2024
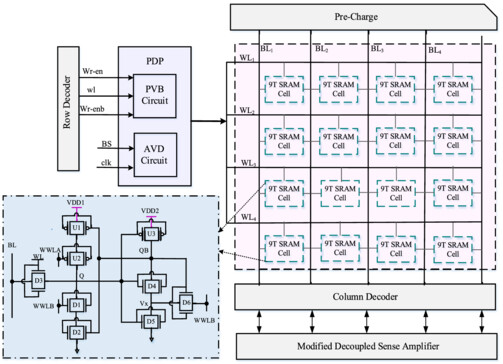
The Schmitt-trigger-based 9 T SRAM cell achieves an excellent read stability result by using a one-sided Schmitt-trigger inverter via a single bitline (BL) layout. The standard AND gates are combined with Schmitt-trigger logic AND gates to improve noise tolerance while consuming less power and taking up less space. Instead of using a power-gating mechanism, this research focuses on modifying a power delay product (PDP) circuit to increase the cell's read-and-write operation efficiency. The modified decoupled sensing amplifier plays a major role in the access time and provides significant benefits in terms of read latency.
Novel optimized implementations for the Piccolo cipher based on field-programmable gate arrays
- Pages: 771-789
- First Published: 07 July 2024

To optimize implementations for resource-constrained Internet of Things (IoT) devices, new, efficient circuit structures for key schedules and round functions of the Piccolo are proposed. Furthermore, three iterative architectures are presented, showing improved area and efficiency compared with existing designs, particularly enhancing the performance of Piccolo-80/128 against other block ciphers. In addition, the scalar architectures with the highest throughput compared with existing architectures are designed.
Hybrid image compression algorithm based on wavelet transform and number theoretic transformation
- Pages: 790-803
- First Published: 12 June 2024
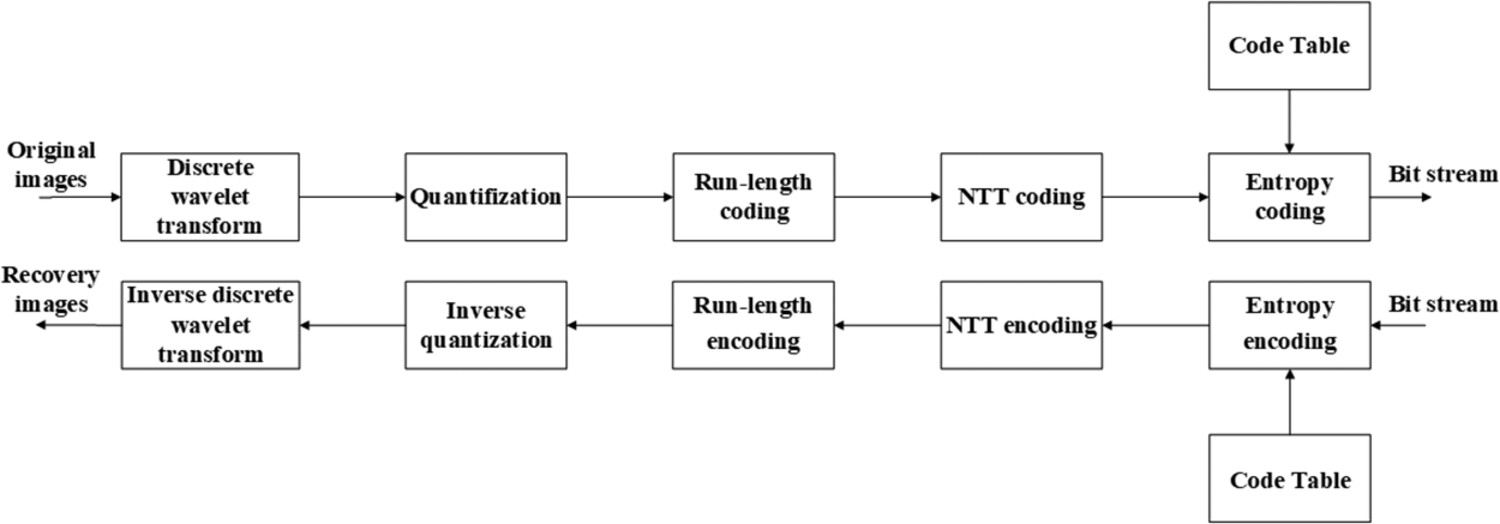
In this paper, we propose a lightweight image compression method (HICA-WT-NTT), which is based on NTT and WT to improve the compression ratio (CR), so as to reduce the transmission rate requirement for IoT devices. Simulation tests images with different qualities and CRs, and results show that the proposed method usually produces better CR as well as runtime performance than other tested methods, while all tested methods maintain almost the same recovered image quality or the same CR. Thus, the proposed method has adaptability to various IoT application scenarios.
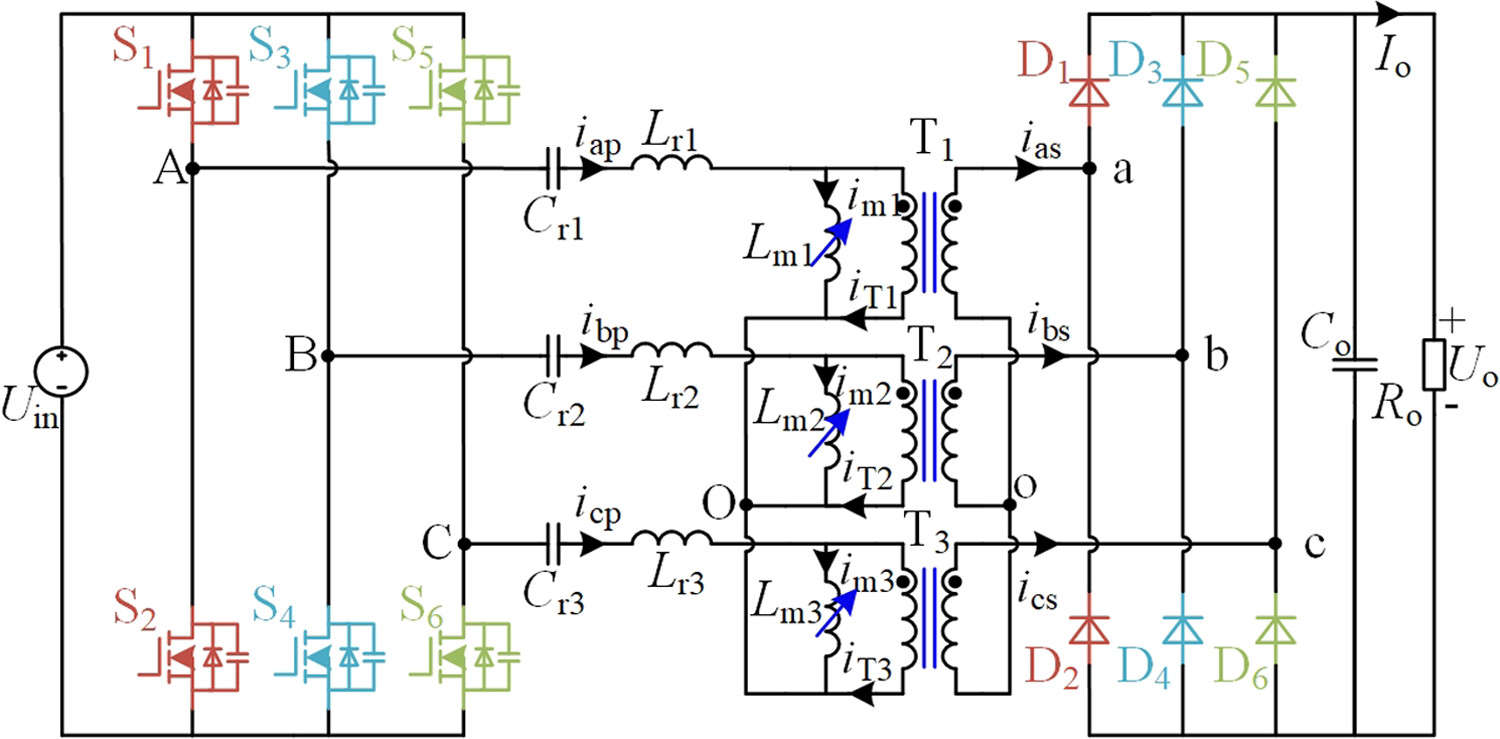
Three-phase LLC resonant converter with variable magnetizing inductance to extend gain range
- Pages: 804-822
- First Published: 14 June 2024
Channel and misalignment characterization for simultaneous wireless power and data transfer system based on moving average filter
- Pages: 823-839
- First Published: 14 June 2024
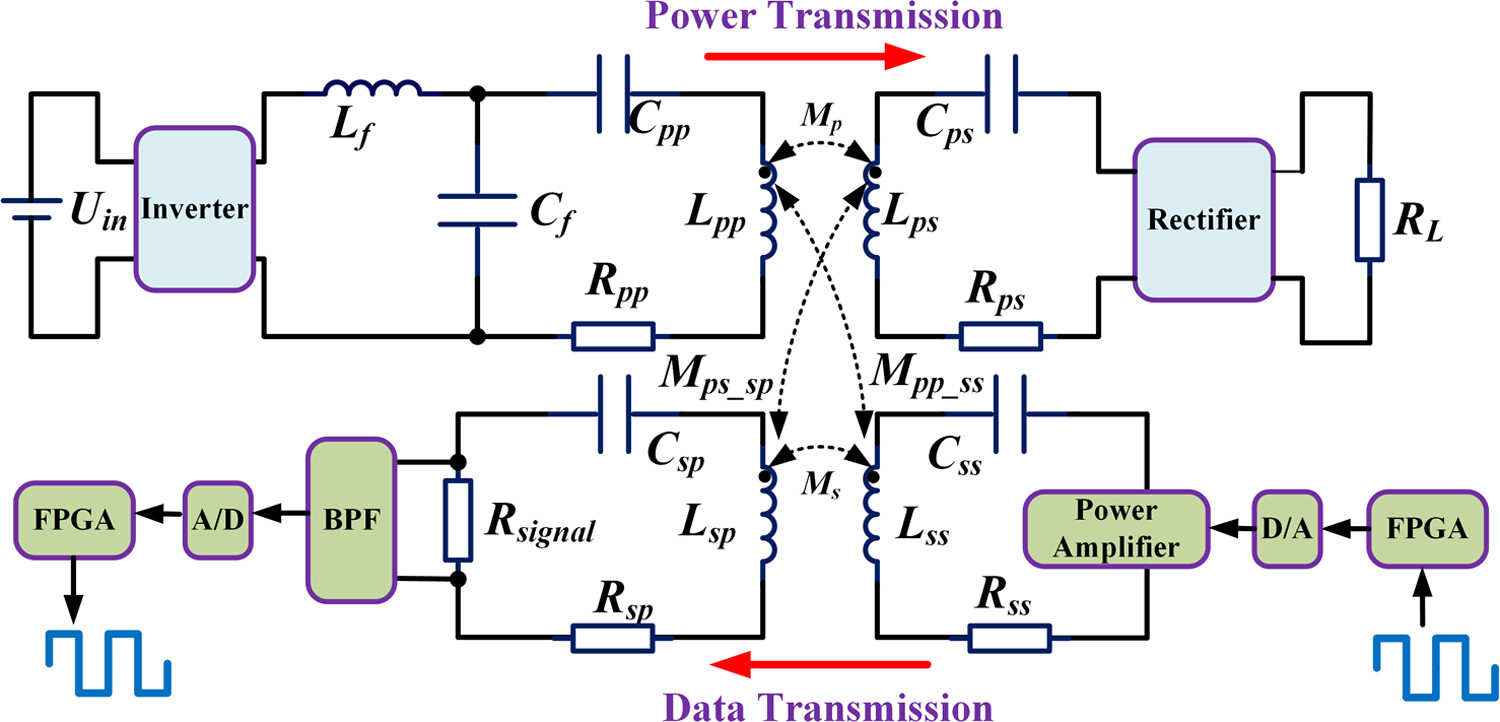
Based on the moving average filter algorithm, this article investigated a simultaneous wireless power and data transfer system. The channel and misalignment characterization is analyzed in detail for DDQ style of magnetic coupling mechanism and LCC-S topology in this article.The communication system is still able to operate stably and reliably even when the coil is misaligned by 6 cm in the x-direction and y-direction, respectively.
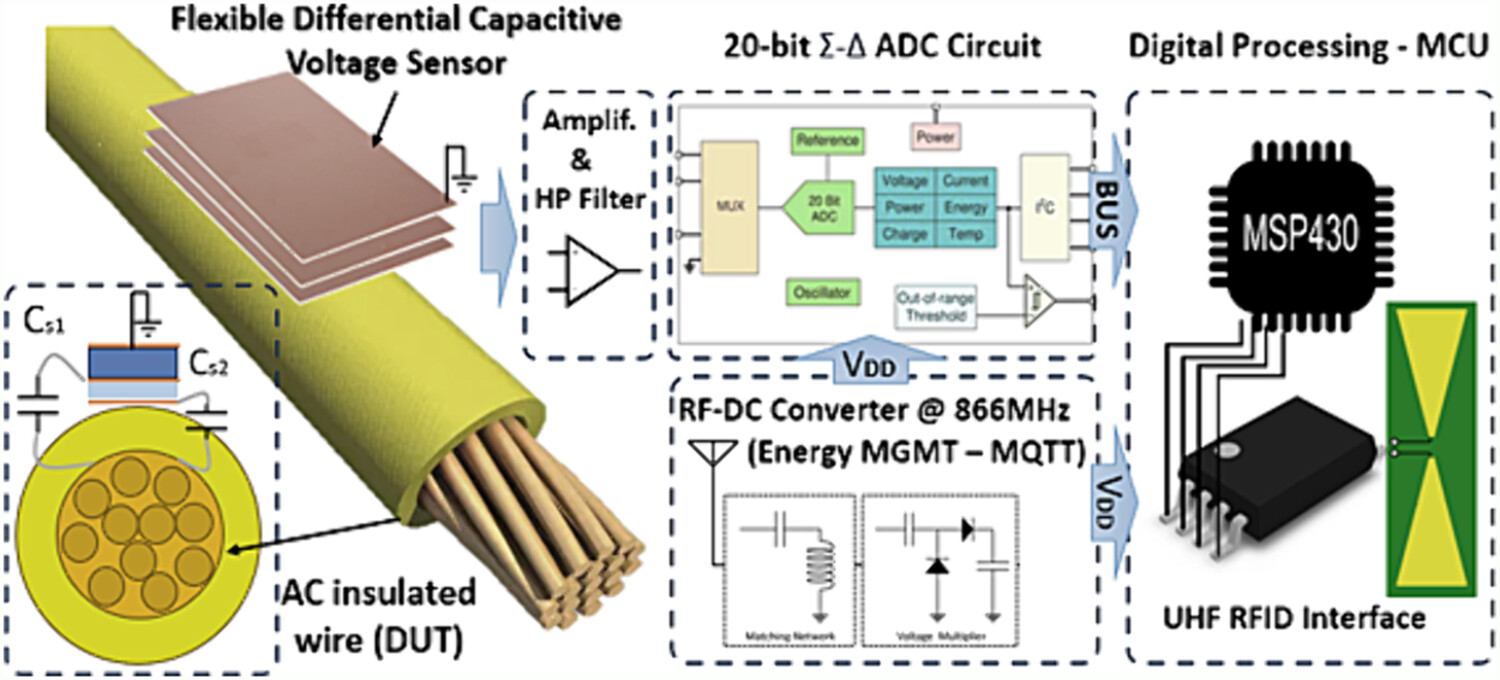
Battery-less RF-powered circuits for non-contact voltage monitoring of electric systems: Circuit modeling and SPICE analysis
- Pages: 840-860
- First Published: 14 June 2024
A single-phase AC-AC converter with continuous input current and without commutation problem
- Pages: 861-882
- First Published: 24 June 2024
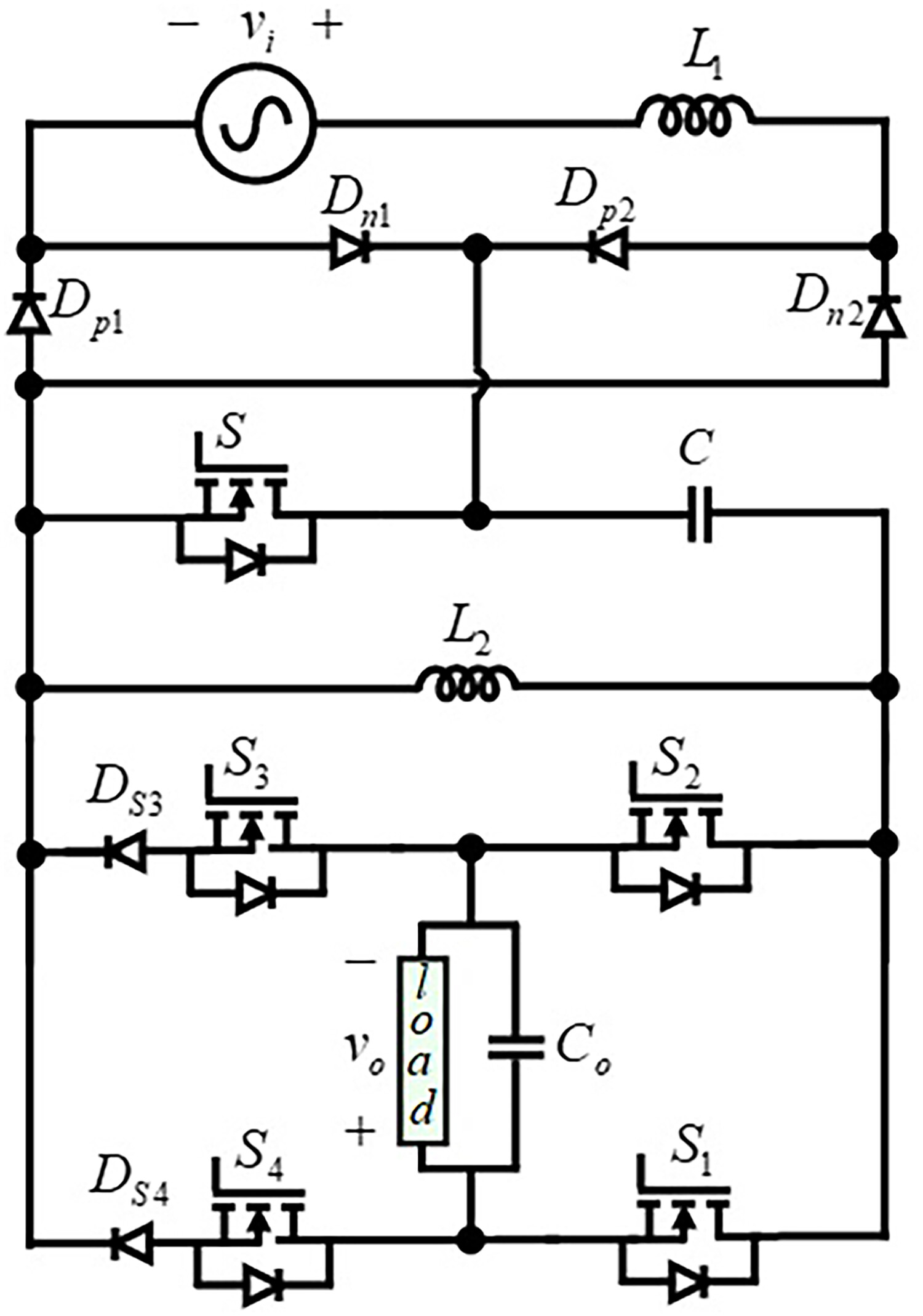
In this paper, a single-phase AC-AC converter with continuous input current and without commutation problem is proposed. The output voltage regulation achieved using a single high-frequency switch eliminates the need for complementary switches, thereby resolving high-frequency commutation issues and obviating the necessity for snubber circuits and a safe commutation strategy. The proposed converter operates with a continuous input current, eliminating the need for a bulky LC filter. Low-frequency switches on the output side allow for step-changed frequency operation without encountering commutation problems. A straightforward and adaptable switching strategy generates the step-changed frequency at the output.
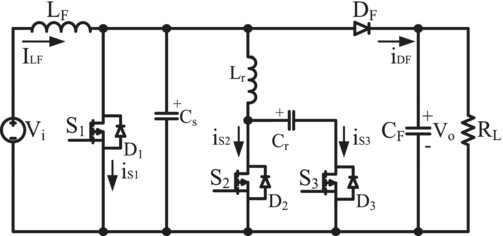
Design, analysis, and implementation of DC-DC boost converter with new active snubber cell
- Pages: 883-901
- First Published: 27 June 2024
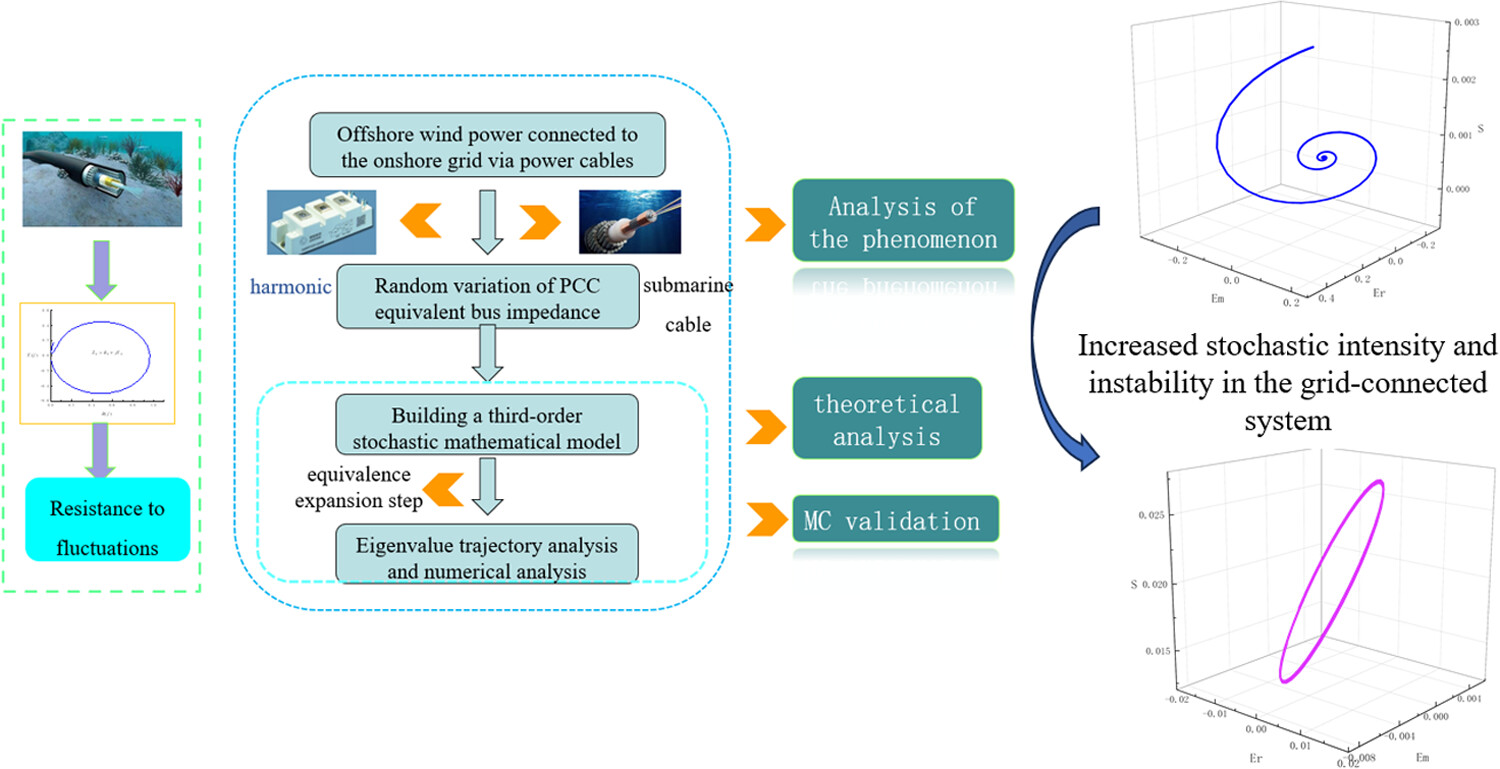
Stochastic stability analysis method for offshore doubly-fed wind power systems considering frequency variation of power cable parameters
- Pages: 902-914
- First Published: 14 June 2024
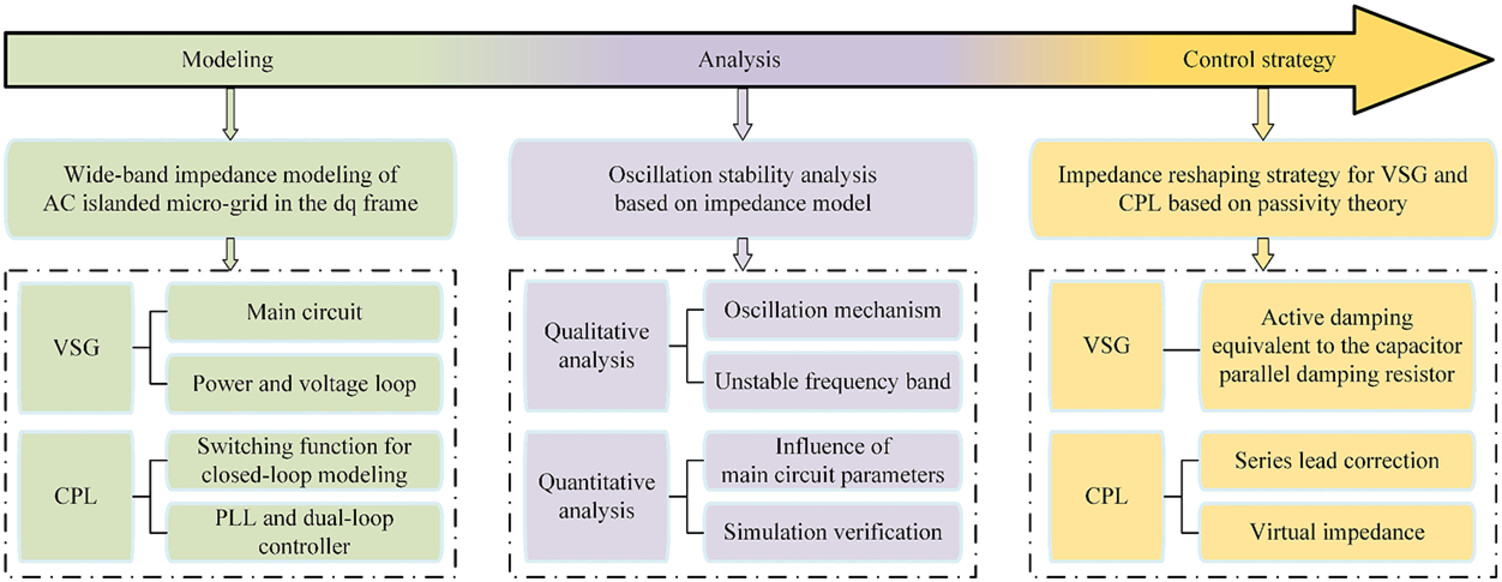
A novel impedance modeling and stability analysis paradigm of microgrids consisting of virtual synchronous generators and constant power loads
- Pages: 915-932
- First Published: 14 June 2024
Voltage-based fault arc detection based on PCA-RF
- Pages: 933-947
- First Published: 09 June 2024
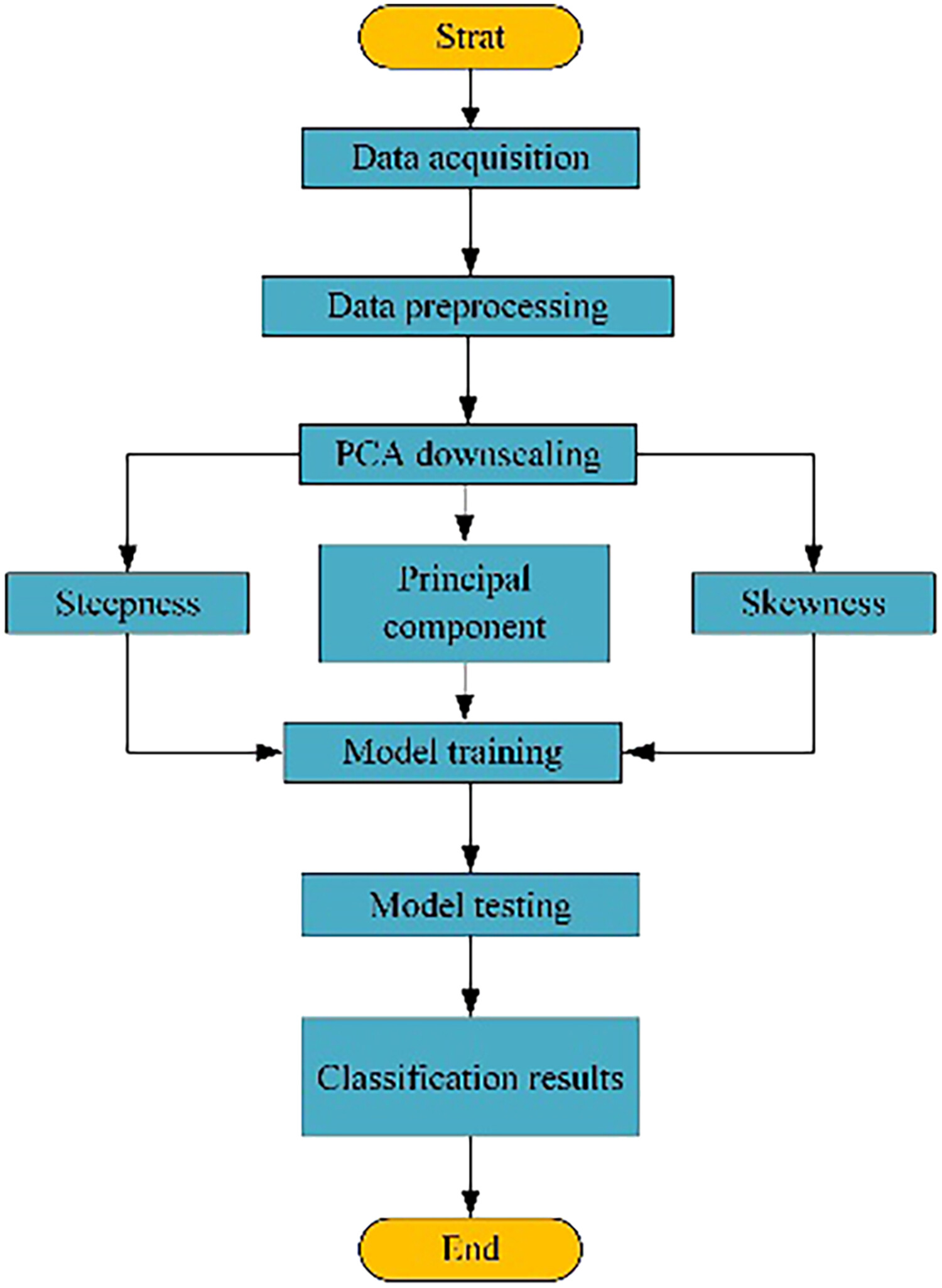
The arc fault characteristics of certain loads lack significance, making it difficult to efficiently detect the line current characteristics. This research presents a novel approach for detecting arc faults using a combination of Principal Component Analysis and Random Forest based on voltage measurements. The experimental results demonstrated that the approach exhibits superior accuracy and a reduced false alarm rate.
Design, analysis, and implementation of a phase-shift controlled cascaded H-bridge and anti-interleaved zeta converter-based E-bike battery charging circuitry
- Pages: 948-992
- First Published: 09 June 2024
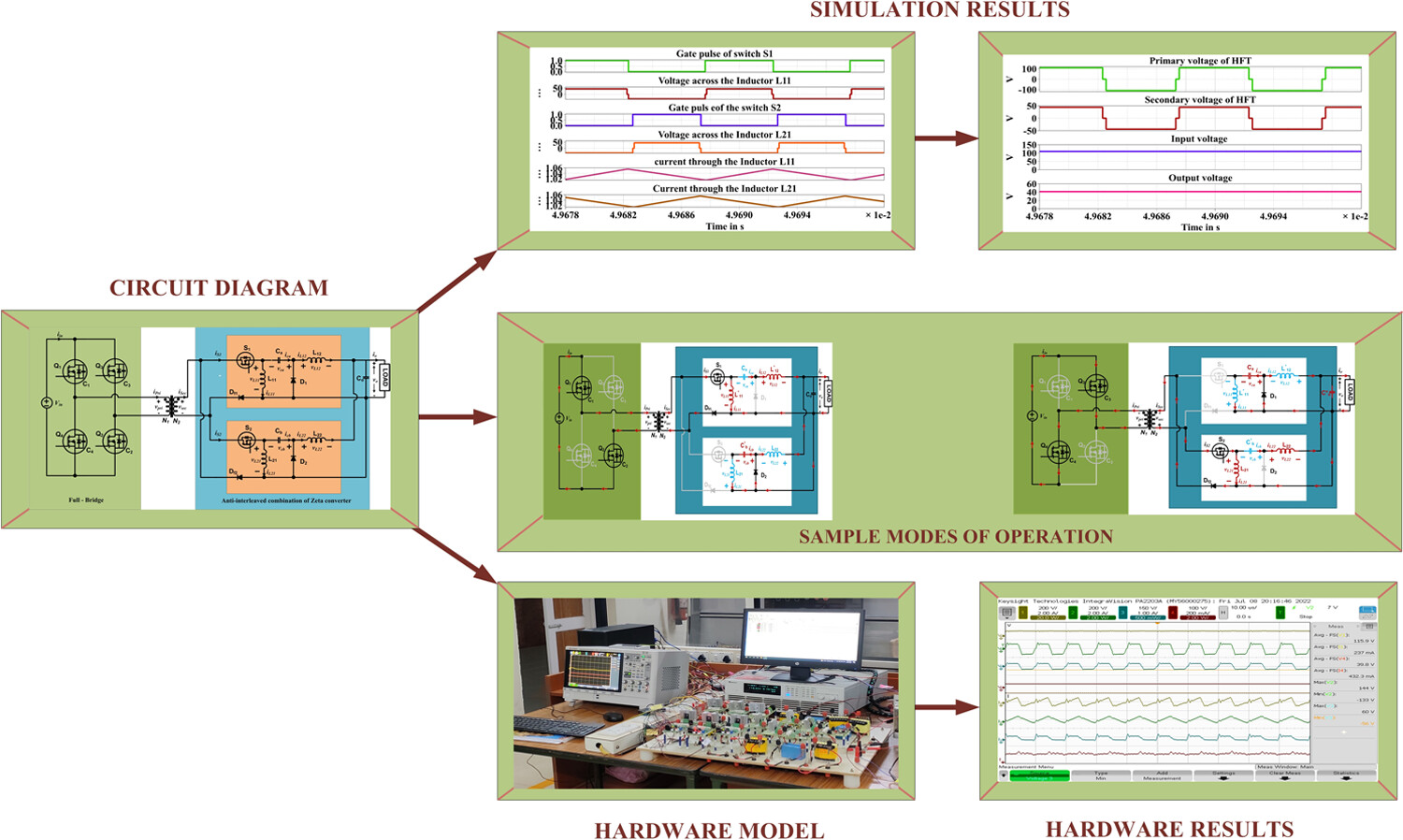
A phase-shifted full bridge zeta DC-DC converter is proposed for charging 36 V Li-ion battery for EV applications. The modes of operation of the proposed converter is explained, and the simulated results of the different parameters of the system are shown. The values of the energy, current, and voltage of various active and passive components are obtained. The hardware prototype of the proposed converter is developed, and the plots of the waveforms of the different parameters are presented. The various samples of the phase shift are chosen, and the effect of the phase shift on the different parameters like voltage and the current of the converter is observed.
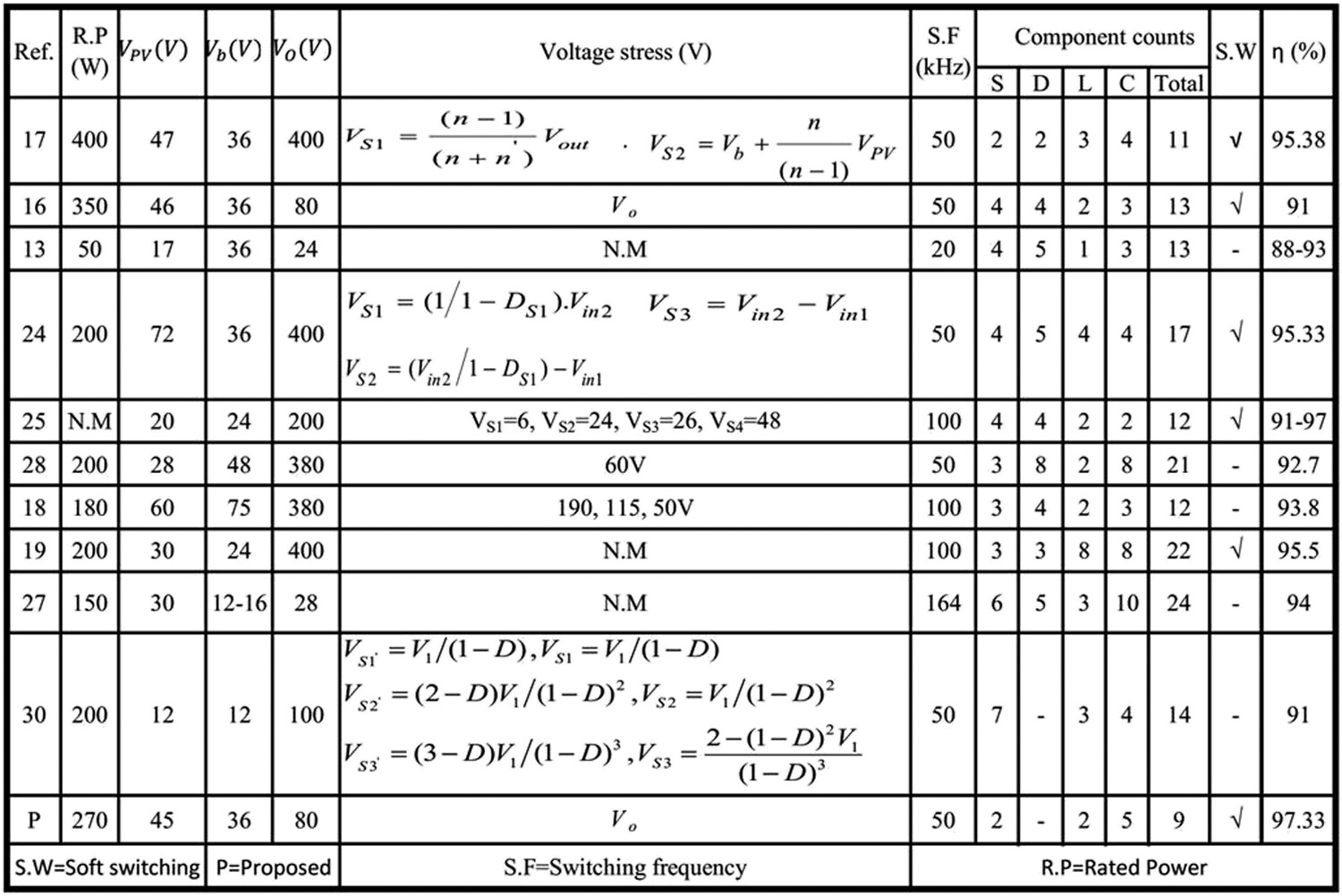
A new three-port DC/DC converter with soft switching, for PV applications
- Pages: 993-1009
- First Published: 16 June 2024
A solution on parameter fluctuation of integrated on-board battery chargers based on recursive least square algorithm
- Pages: 1010-1030
- First Published: 16 June 2024
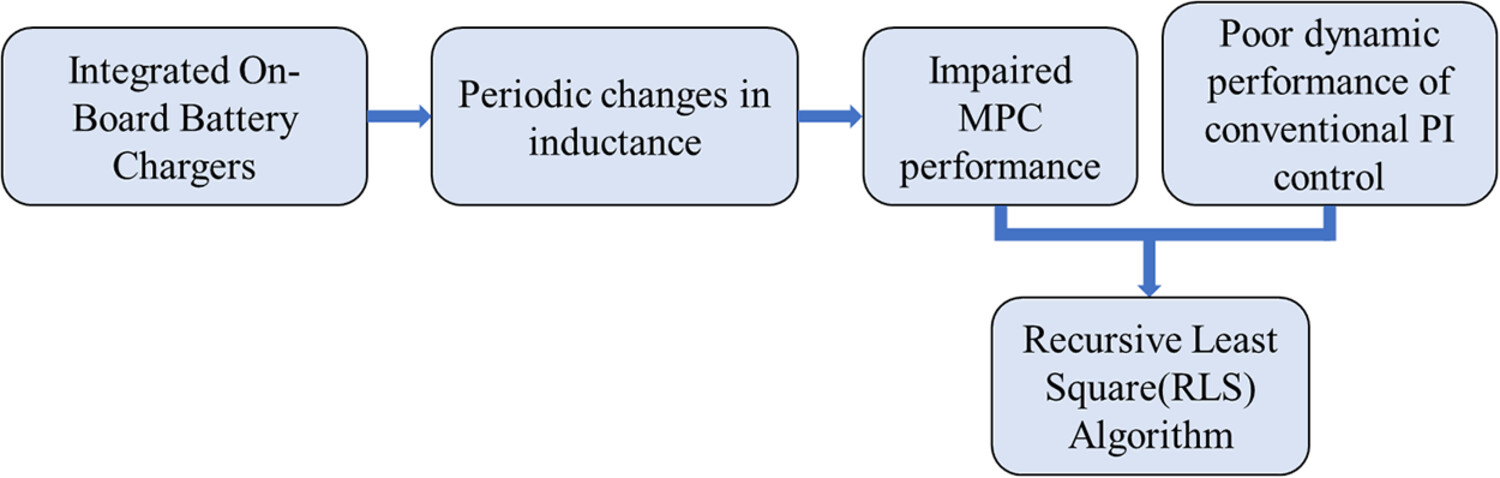
A common single-phase IOBC topology is used as an example, the causes of inductance fluctuations are analyzed, and finite element analysis (FEM) of motor inductance with different types of motor is carried out. A recursive least squares (RLS)-based solution method is proposed, and its convergence is analyzed.
Generalized state-space averaging modeling to fourth-order power converters operating in DCM
- Pages: 1031-1055
- First Published: 18 June 2024
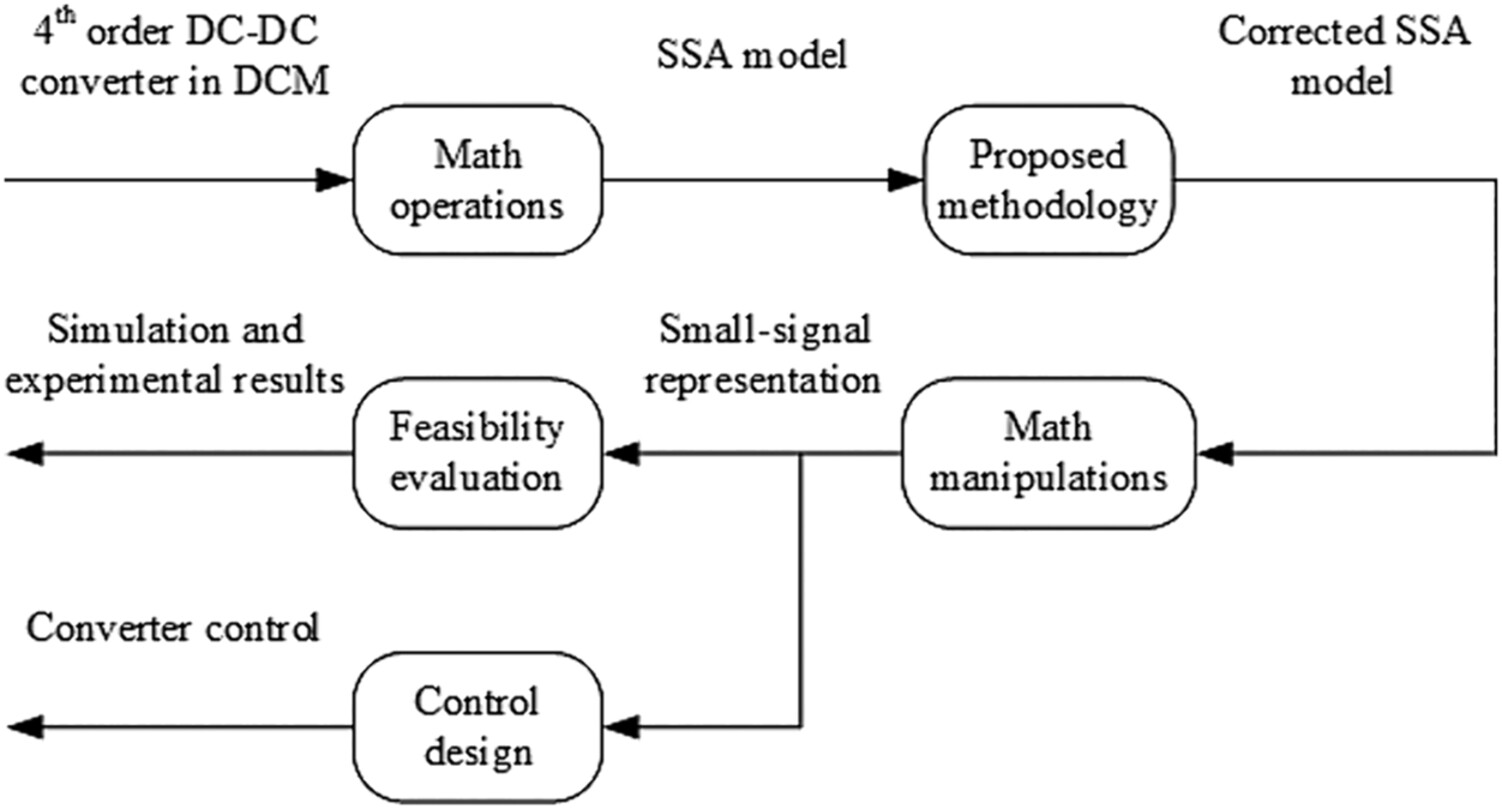
Initially, the main SSA models are obtained for fourth-order converters. The proposed method corrects the models by mathematical manipulations. Several modeling techniques can be applied. The model can be evaluated from the simulation and experimental results. In addition, proper control can be defined and tuned.
A new method for selecting optimum levels in asymmetric Cascaded H-Bridge-Multilevel Inveter with variable DC sources
- Pages: 1056-1071
- First Published: 23 June 2024
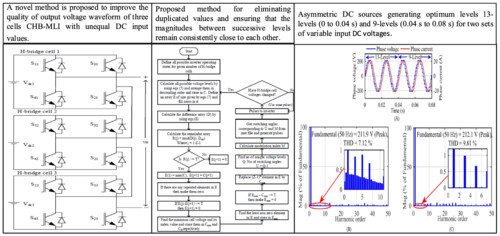
A novel method is proposed to improved the quality of output voltage waveform of three cells CHB-MLI with DC input values. Proposed method for eliminating duplicated values and ensuring that the magnitudes between successive levels remain consistently close to each other. Asymmetric DC sources generate optimum levels, 13 levels (0 to 0.04 s) and 9 levels (0.04 s to 0.08 s), for two sets of variable input DC voltages.
Reactive power management in variable frequency transformer (VFT)-integrated multi-machine power systems: A STATCOM-based approach
- Pages: 1072-1100
- First Published: 25 June 2024
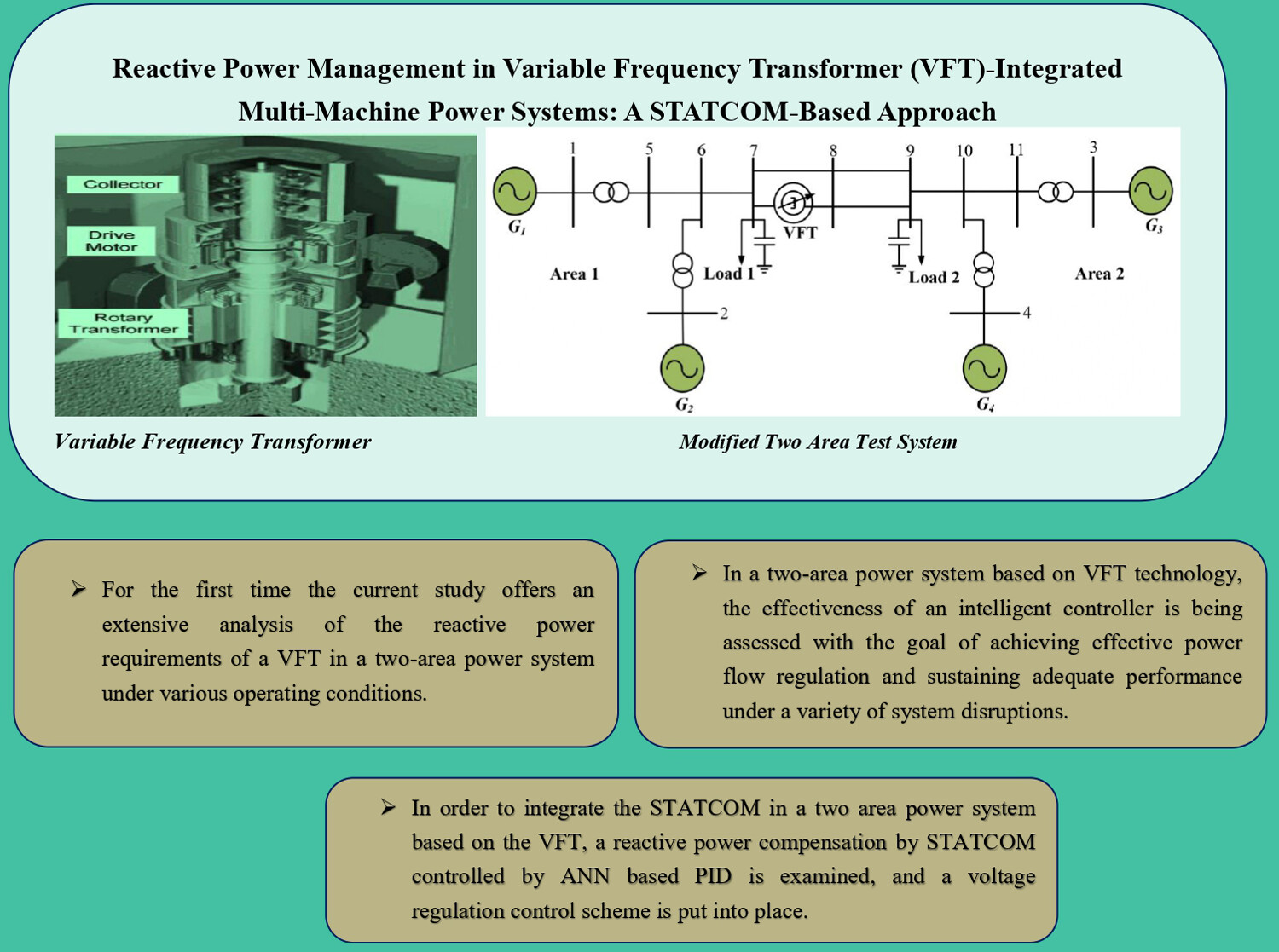
- For the first time, the current study offers an extensive analysis of the reactive power requirements of a VFT in a two-area power system under various operating conditions.
- In order to integrate the STATCOM in a two-area power system based on the VFT, a reactive power compensation by STATCOM controlled by ANN-based PID is examined, and a voltage regulation control scheme is put into place.
A solar photovoltaic-fed three-phase multifunctional converter operation using nonlinear control strategy
- Pages: 1101-1117
- First Published: 27 June 2024
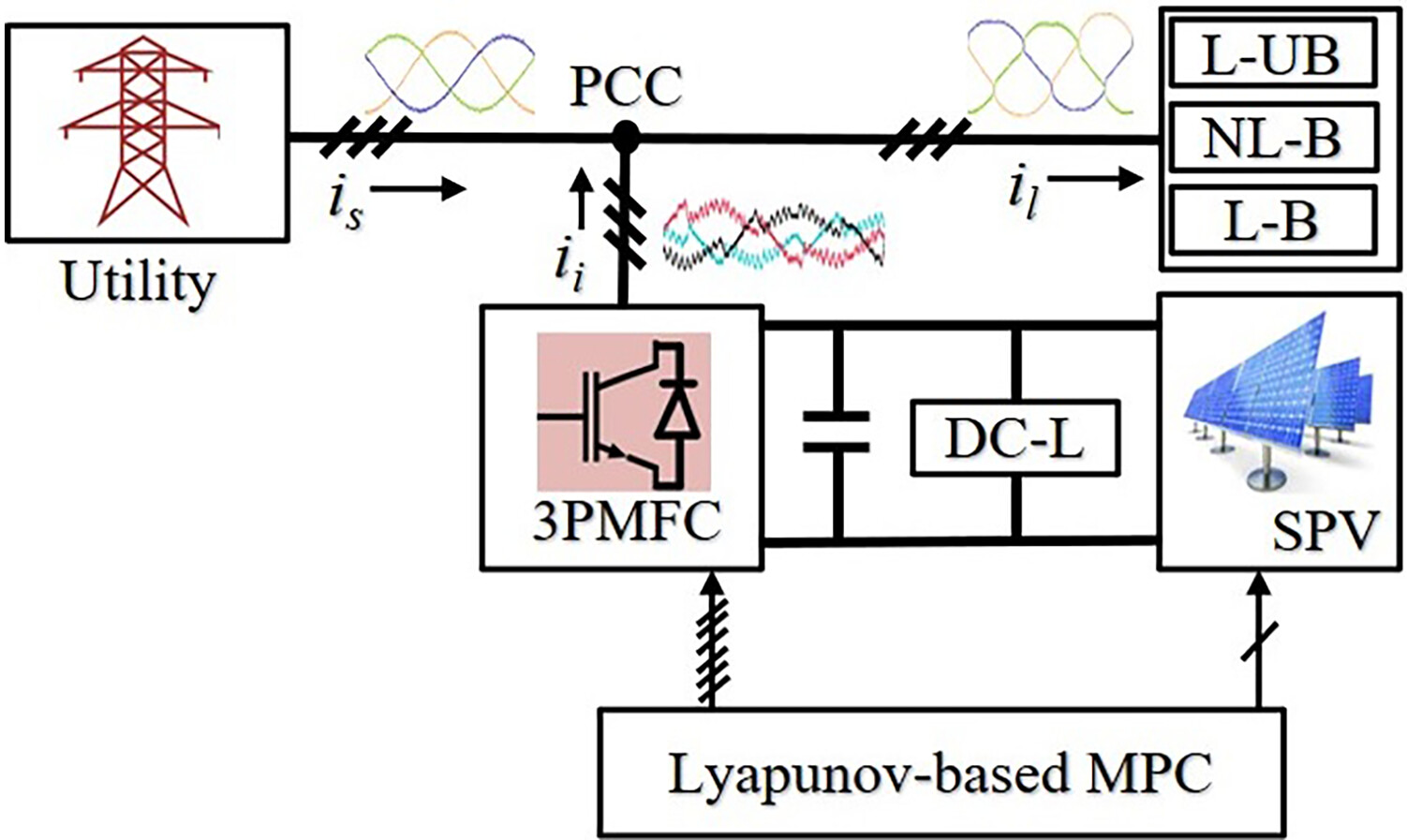
The elementary idea of this article comprises (i) reference current estimation using a Lyapunov function-based variable conductance factor approach for the flexible operation of a grid-integrated solar photovoltaic-fed three-phase multifunctional converter (3PMFC), resulting in less computational burden, and (ii) generation of optimal switching signals for the 3PMFC and the dc-dc boost converters using model predictive control under dynamic operation scenarios.
Hierarchical single-objective variable double voltage vector model predictive control with low computational burden for cascaded H-bridge multilevel converter
- Pages: 1118-1134
- First Published: 27 June 2024
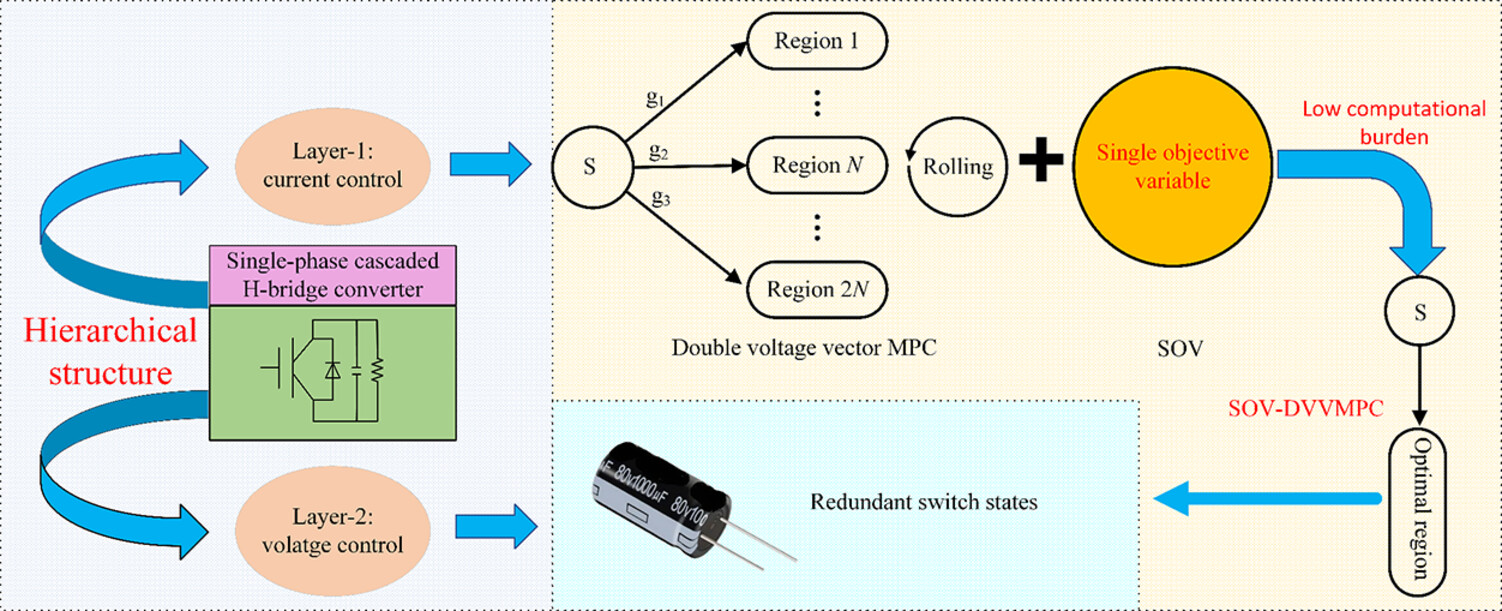
The method aims to reduce the computational burden of model predictive control of cascaded H-bridge multilevel converters. It uses a double-vector voltage control approach to achieve a fixed switching frequency, and a hierarchical structure to control the grid current and dc-side output capacitor voltages.
An Improved Model Predictive Current Control of BLDC Motor With a Novel Adaptive Extended Kalman Filter–Based Back EMF Estimator and a New Commutation Duration Approach for Electrical Vehicle
- Pages: 1135-1150
- First Published: 23 December 2024
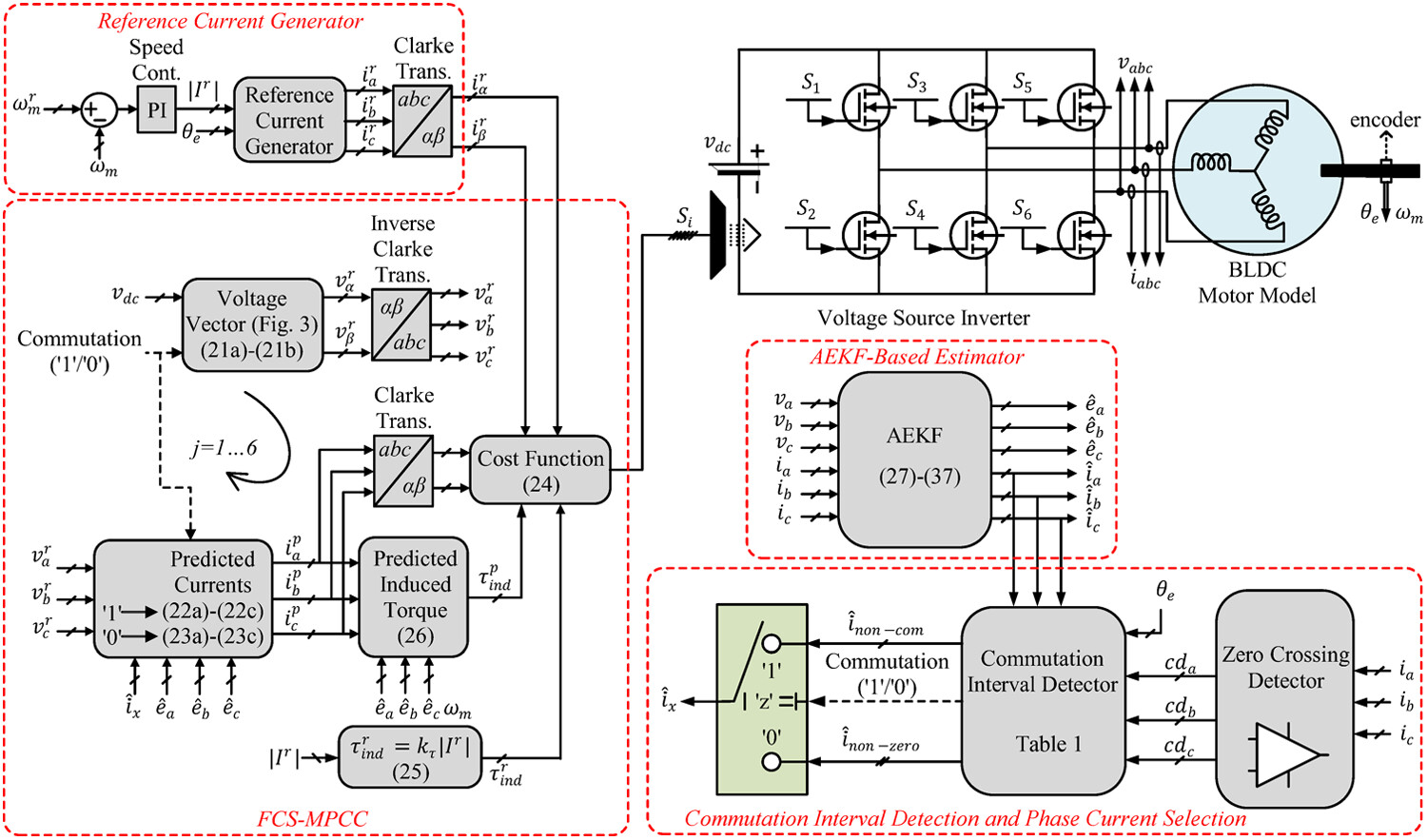
Commutation moments and durations of the FCS-MPCC of BLDC motor are captured and determined with a new approach. Moreover, three-phase back EMFs of the BLDC motor applied to FCS-MPCC to predict the stator phase currents are estimated with a novel adaptive extended Kalman filter which has the estimation capability without any speed sensor.
BRIEF REPORT
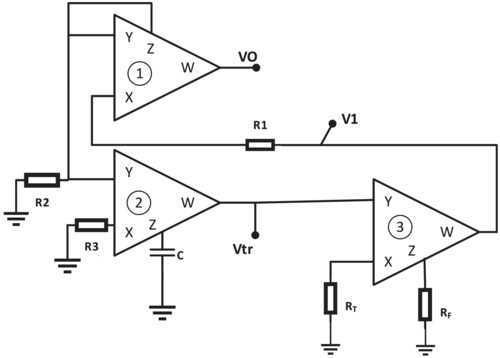
A novel compact and shadow resistance-to-frequency and resistance-to-time converter
- Pages: 1151-1158
- First Published: 07 August 2024
Non-overlapping placement of macro cells based on reinforcement learning in chip design
- Pages: 1159-1170
- First Published: 12 August 2024
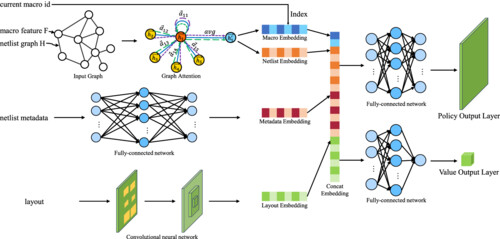
This paper introduces a novel end-to-end placement method of macro cells in chip design based on reinforcement learning. By assessing on the public benchmark ISPD2005, the proposed method can effectively solve the overlap problem between macro cells while considering routing congestion and shortening the total wire length to ensure routability.