Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2018
no
Assessment of factors determining an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5% in patients with type 1 diabetes: 评估决定1型糖尿病患者HbA1c≤7.5%的因素
- First Published: 22 May 2017
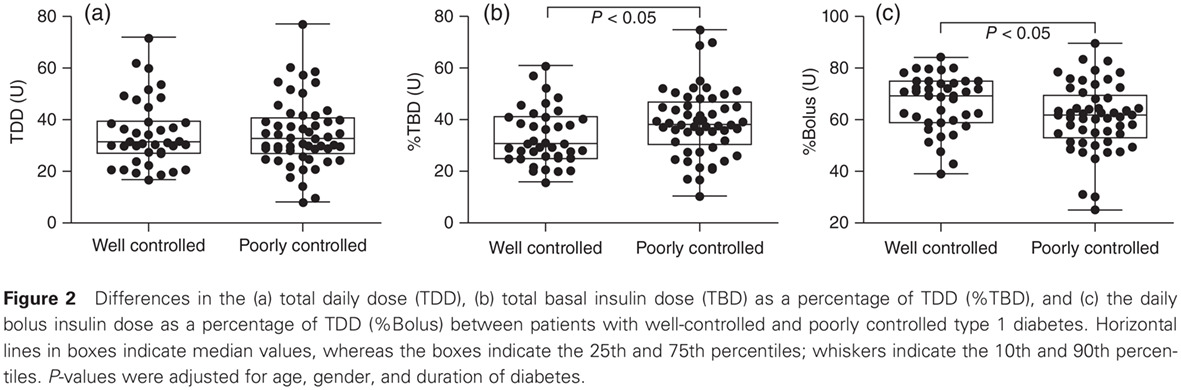
Highlights
- Appropriate insulin dose required for maintaining good glycemic control were assessed in patients with type 1 diabetes.
- Glycemic control did not depend on the total daily insulin dose; rather, the ratio of basal: bolus insulin is important.
- To achieve an HbA1c concentration ≤7.5%, the total daily insulin dose (TDD) should be based on body weight, and the total basal insulin dose as a percentage of TDD should be set at 30% in the Japanese population.
no
Effectiveness of vildagliptin as add-on to metformin monotherapy among uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a real-world setting: 在一个真实世界环境中二甲双胍单药治疗后未控制的2型糖尿病患者加用维格列汀治疗的疗效
- First Published: 18 April 2017
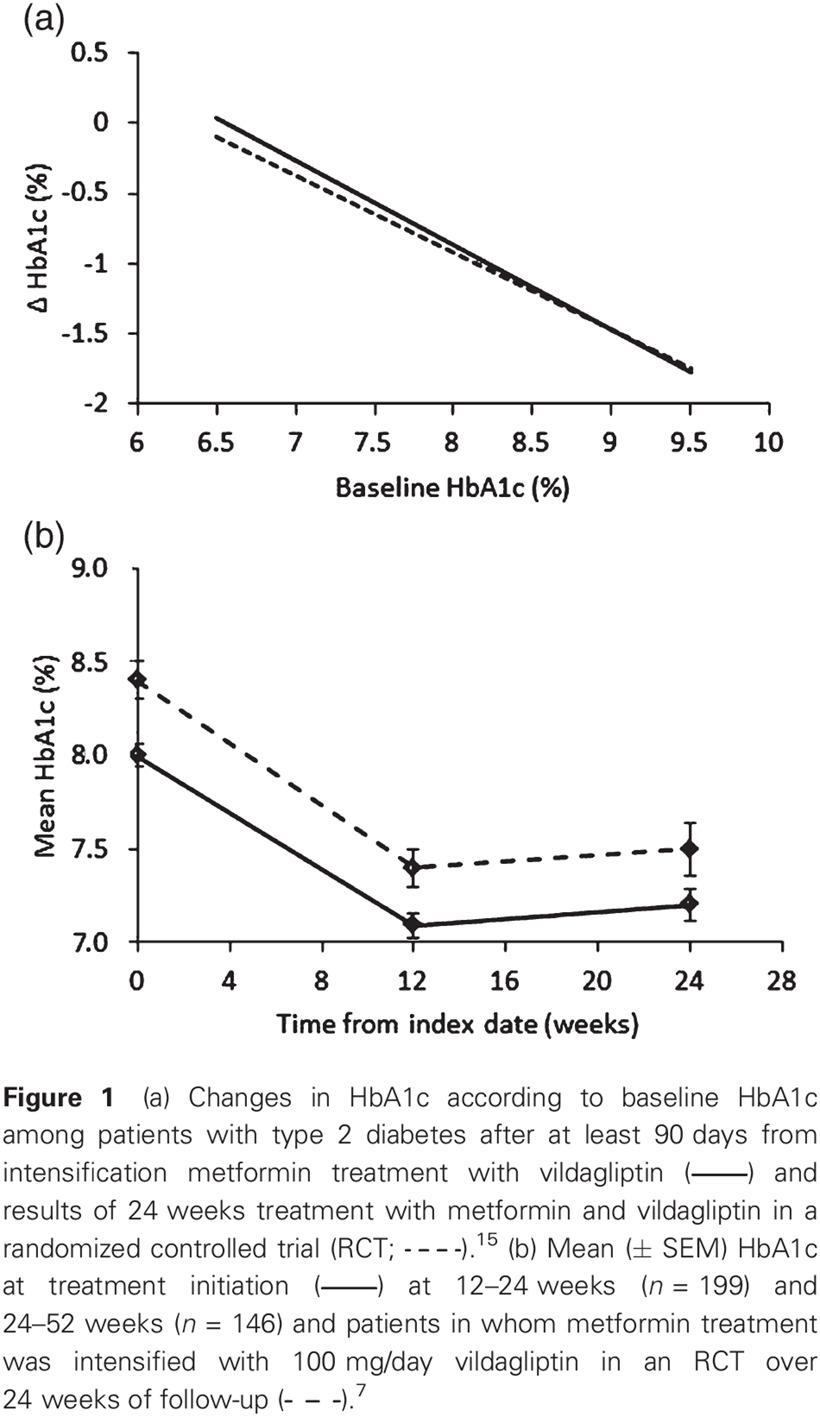
Highlights
- Add-on therapy with vildagliptin to a metformin monotherapy regimen in uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients is associated with a significant improvement in glycemic control, with no apparent increase in body weight.
- The real-world efficacy of vildagliptin as an add-on therapy to metformin is similar to that calculated in randomized controlled trials.




 This collection presents the recent progress and breakthrough in Clinical Science of Diabetes.
This collection presents the recent progress and breakthrough in Clinical Science of Diabetes.



