Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlights from the Editors 2023
Open Access
oa
Association of glycemic gap with stroke recurrence in patients with ischemic stroke
缺血性卒中患者血糖间隙与卒中复发的相关性
- First Published: 09 June 2023
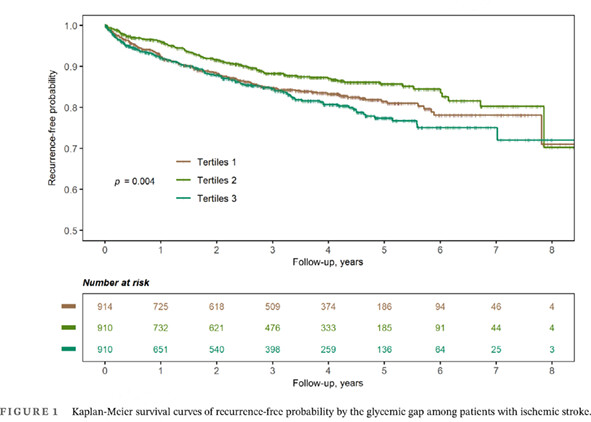
Highlights
- There was a U-shaped relationship between glycemic gap and stroke recurrence during a long-term follow-up in a Chinese ischemic stroke registry.
- Clinical physicians should remain vigilant in the fluctuation of glucose level and use individualized glucose control strategies in patients with ischemic stroke.
Open Access
oa
Association between follicle-stimulating hormone and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus
绝经后2型糖尿病女性中卵泡刺激素与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性
- First Published: 23 May 2023
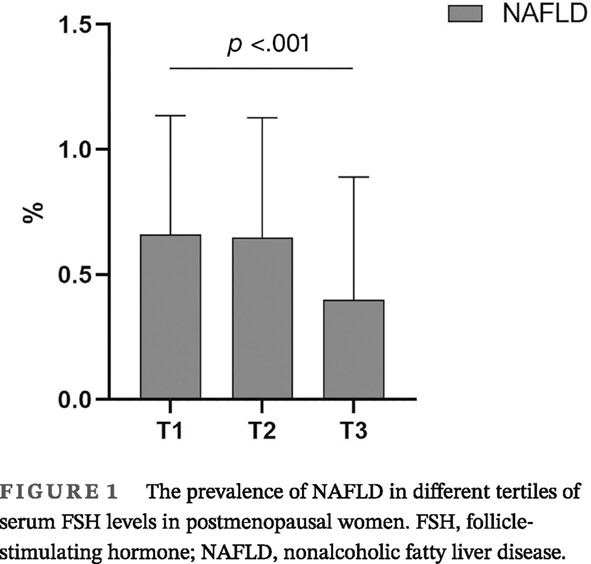
Highlights
- In Chinese postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus, serum follicle-stimulating hormone levels were negatively and independently associated with the prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Metabolic conditions, including overweight/obesity, central obesity, hyperuricemia, hypertension, and dyslipidemia did not interact with this association.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone might be a potential independent index for screening and identifying individuals with high risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Open Access
oa
Stress hyperglycemia ratio is associated with systemic inflammation and clinical outcomes in diabetic inpatients with pneumonia on admission
糖尿病合并肺炎住院患者的应激性高血糖率与全身性炎症和临床结局相关
- First Published: 05 May 2023
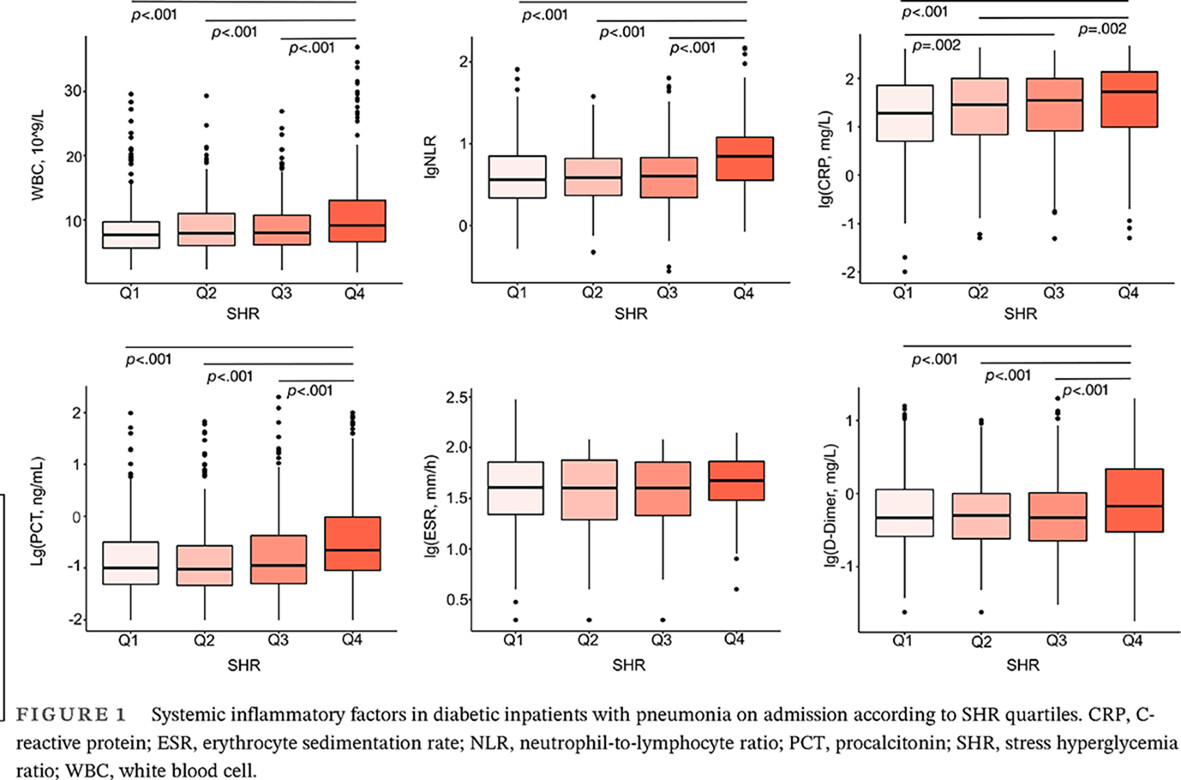
Highlights
- High stress hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) was associated with elevated systematic inflammation in diabetic inpatients with pneumonia on admission.
- In the absence of hypoglycemia on admission, SHR was of J-shaped associations with adverse clinical outcomes in diabetic inpatients with pneumonia of different severity.
- In diabetic inpatients with pneumonia on admission, predictive value of SHR for adverse clinical outcomes was greater than that of fasting blood glucose and was further elevated when the nonlinear association was taken into consideration.
Open Access
oa
Stress hyperglycemia ratio and long-term prognosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A multicenter, nationwide study
急性冠状动脉综合征患者应激性高血糖率与长期预后:一项多中心全国性研究
- First Published: 03 May 2023
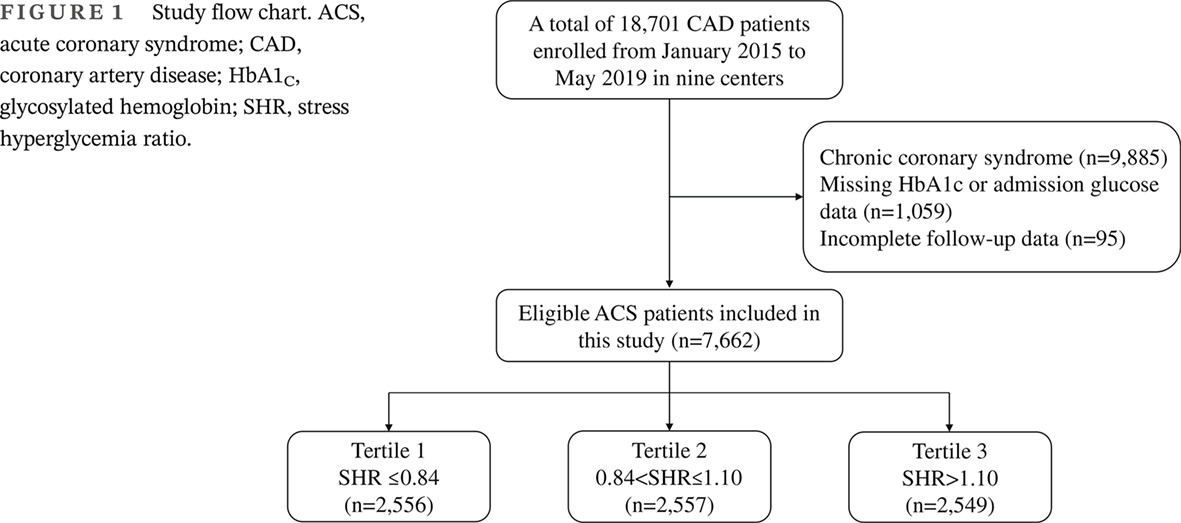
Highlights
- The association between stress hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) and long-term outcomes was still controversial.
- Based on a large prospective multicenter cohort, we found that high SHR levels were independently associated with increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), all-cause death, and unplanned revascularization. Associations between high SHR levels and risk of MACE and death remained positive in patients with or without diabetes.
- SHR was a potential biomarker for risk stratification after acute coronary syndromes.
Open Access
oa
Relative contributions of fasting and postprandial glucose increments, glycemic variability, and non-glycemic factors to HbA1c in individuals with type 1 diabetes
基于1型糖尿病患者的空腹和餐后血糖增量、血糖变异性和非血糖因素对HbA1C的相对贡献
- First Published: 04 May 2023
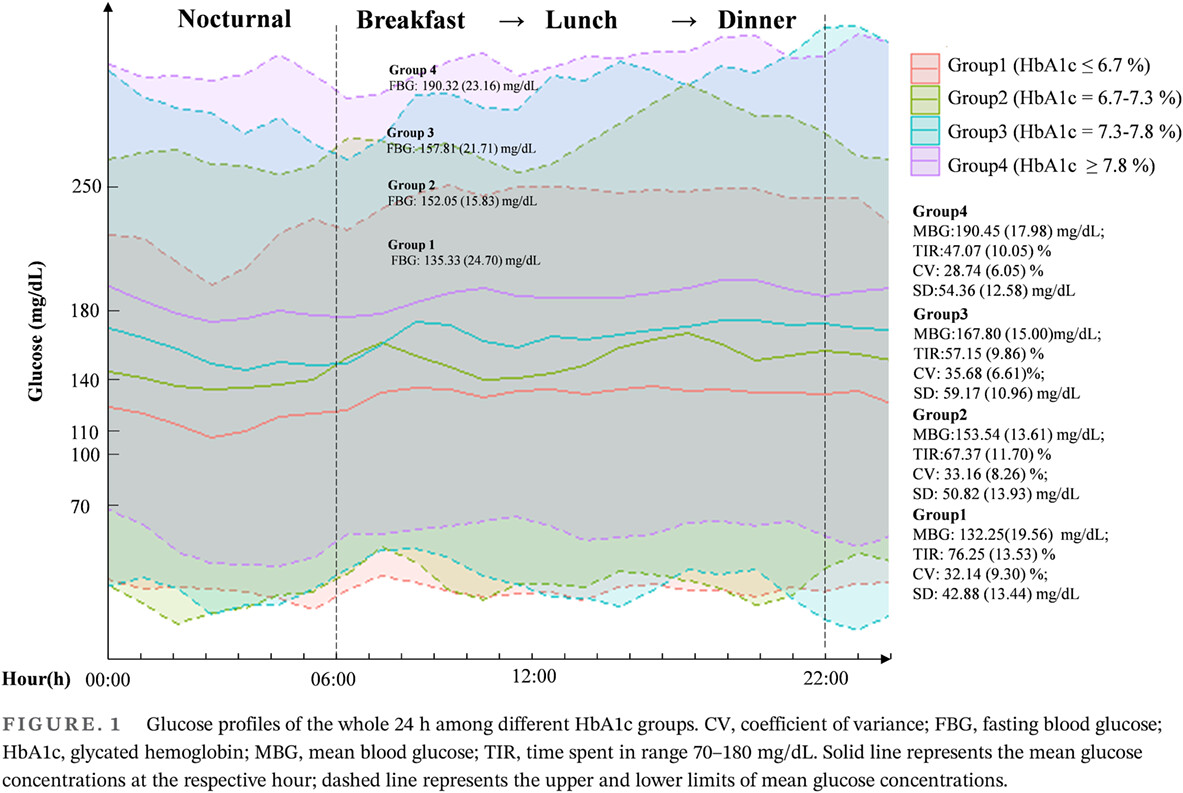
Highlights
- Evidence for contribution of basal and postprandial glucose increments and glycemic variability to glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) among adults with type 1 diabetes (T1D) is limited.
- In this study, after analyzing a total of 169 550 sensor-derived data in 2409 meals recorded from 102 T1D adults, we found that basal hyperglycemia (BHG) was four times higher than that of postprandial hyperglycemia (PHG). Factors including BHG, preprandial glycemia, PHG, glycemic variability and age, body mass index, hemoprotein, and duration explained a total of 74% of the variance in HbA1c, in which fasting hyperglycemia accounted for 32.1% of variance and postprandial glycemia accounted for 24.4%.
- The relative contribution of fasting hyperglycemia increased gradually with HbA1c increasing.
Open Access
oa
Higher glucose fluctuation is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease: Insights from pooled results among patients with diabetes
较高的血糖波动与较高的心血管疾病风险相关:来自糖尿病患者汇总分析的观点
- First Published: 18 April 2023
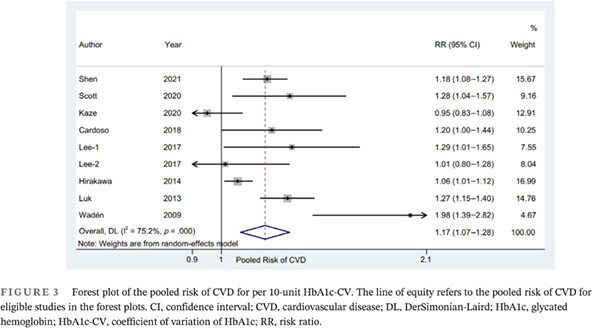
Highlights
- This study is the first registered meta-analysis with three different insights to explore the relationship between the glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) variability and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- Our study suggests that the higher glucose fluctuation is significantly associated with the higher CVD risk in diabetes patients based on HbA1c variability.
- The CVD risk associated with per HbA1c-SD might be higher among patients type 1 diabetes than patients with type 2 diabetes.
Open Access
oa
Association of alcohol consumption with all-cause mortality, new-onset stroke, and coronary heart disease in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism—Findings from a 10-year follow-up of the REACTION study
糖代谢异常患者饮酒与全因死亡率、新发卒中以及冠心病的关系——来自REACTION研究10年随访的发现
- First Published: 11 April 2023
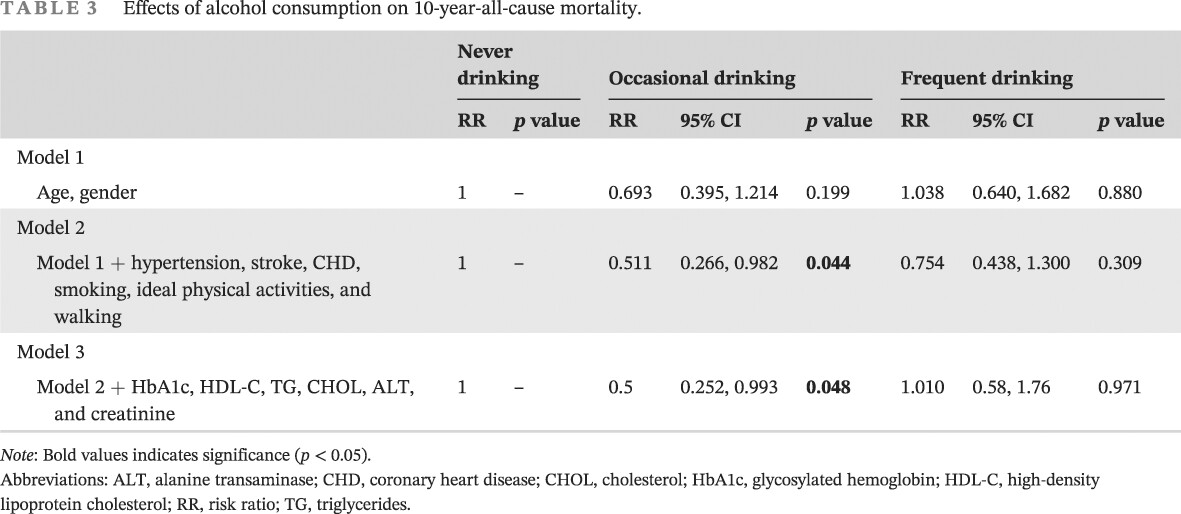
Highlights
- This long-term longitudinal study demonstrates the association between alcohol consumption and health outcomes in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism including type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes.
- Occasional drinking (less than once a week) reduces the risk of all-cause mortality, while heavy alcohol consumption (≥30 g/day for men and ≥15 g/day for women) significantly increases the risk of new-onset stroke.
- Patients with abnormal glucose metabolism should avoid heavy alcohol intake, but light alcohol consumption or occasional drinking is acceptable.
- This study provided evidence of lifestyle instructions for patients with abnormal glucose metabolism.
Open Access
oa
Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
糖尿病合并COVID-19患者的非胰岛素类降糖药物治疗:一项系统综述和荟萃分析
- First Published: 23 January 2023
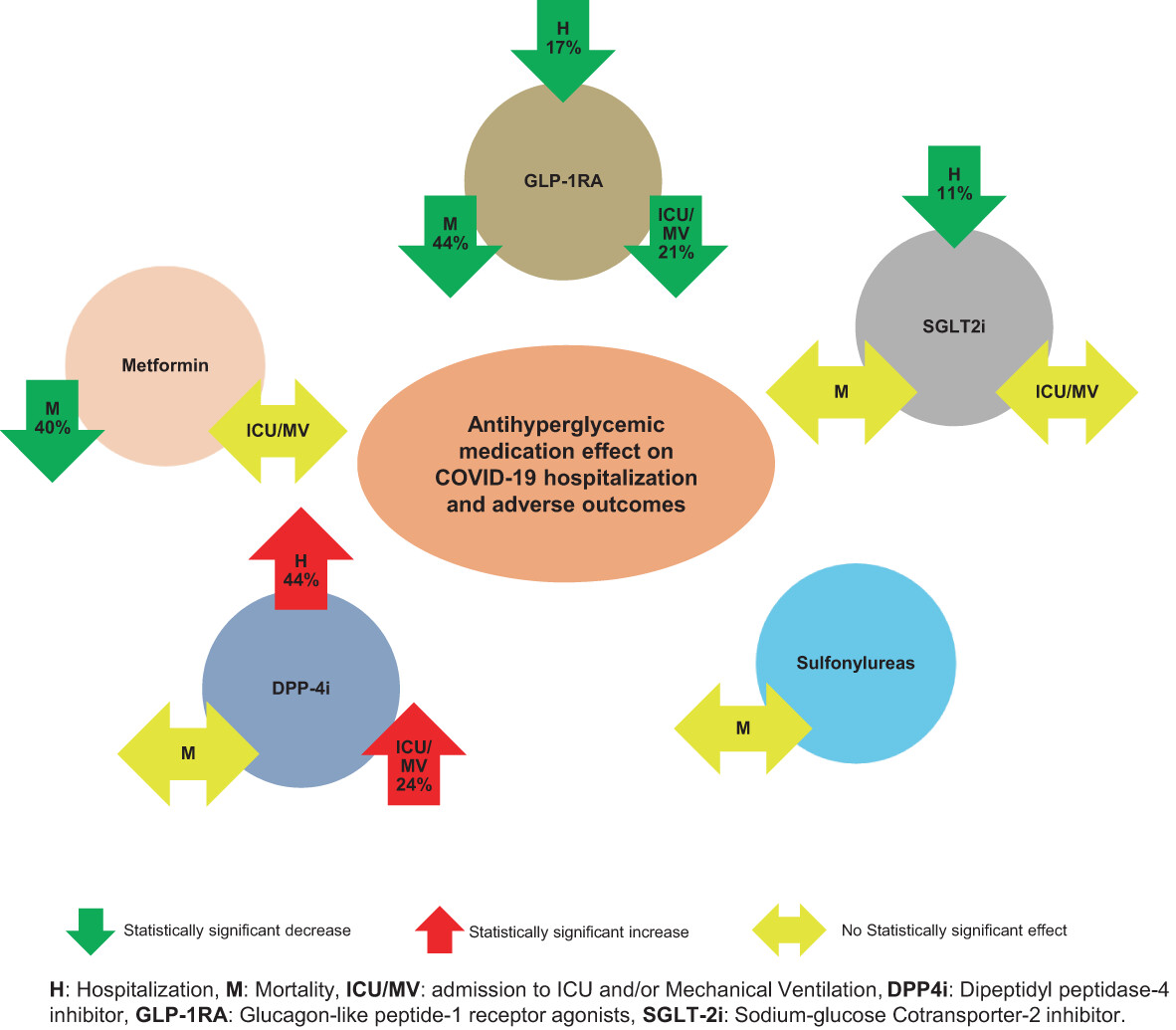
Highlights
- Metformin was associated with statistically significantly lower overall mortality for inpatients and outpatients.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use was associated with statistically significant higher hospitalization risk and higher risk of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and/or mechanical ventilation.
- There was a statistically significant decrease in hospitalization for sodium glucose transporter 2 inhibitor) users vs. nonusers.
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use was associated with a statistically significant decrease in mortality, ICU admission and/or mechanical ventilation, and hospitalization.








