Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlights from the Editors 2022
Open Access
oa
The influence of shorter red blood cell lifespan on the rate of HbA1c target achieved in type 2 diabetes patients with a HbA1c detection value lower than 7%
HbA1c检测值低于7%的2型糖尿病患者血红细胞寿命缩短对HbA1c达标率的影响
- First Published: 21 December 2022
Highlights
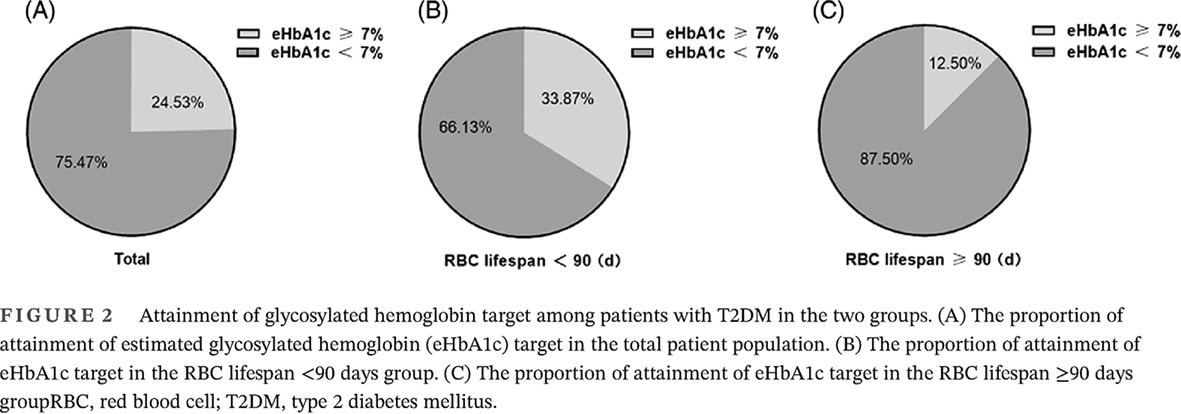
- Red blood cell (RBC) lifespan variation, is the main cause of variation in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), independent of blood glucose levels.
- This study highlighted the important impact of RBC lifespan on HbA1c test value in T2DM with HbA1c test value <7%.
- We discovered that the HbA1c test value in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) patients with RBC lifespan <90 days significantly underestimated their general blood glucose condition.
- Our results will provide more useful information to advance management of blood glucose levels for T2DM.
Open Access
oa
A novel index, Chinese visceral adiposity index is closely associated with urinary albumin-creatinine ratio in Chinese community adults, especially in hypertensive or hyperglycemic population: Results from the REACTION study
一个新的指标, 中国人内脏脂肪指数与中国社区成年人(特别是高血压或高血糖人群)尿白蛋白-肌酐比值密切相关:来自REACTION研究的结果
- First Published: 29 November 2022
Highlights
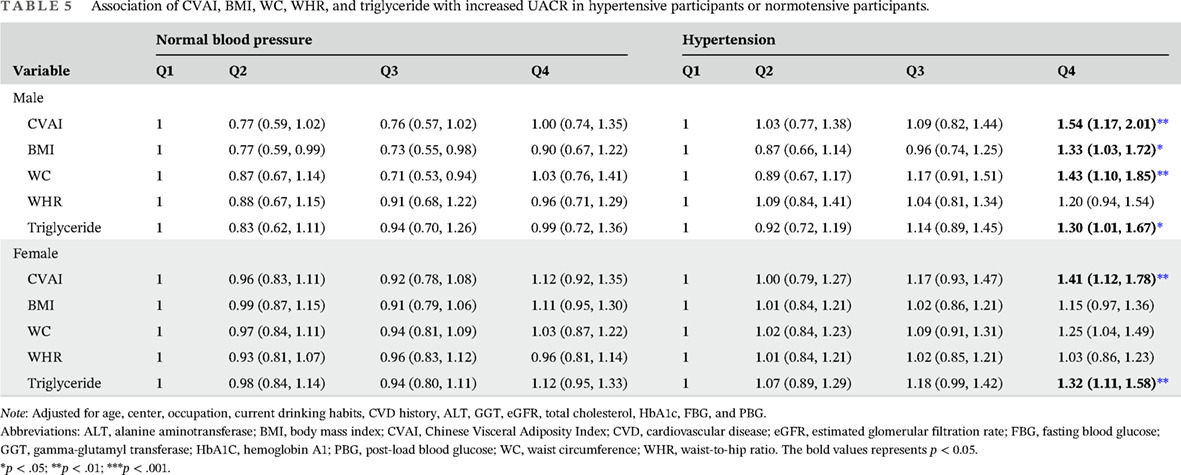
- This is the first large-sample, multicenter study of the relationship between Chinese Visceral Adiposity Index (CVAI) and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) in Chinese community adults.
- CVAI and UACR were significantly associated in both genders.
- At higher CVAI levels, the population with prediabetes, diabetes, and hypertension has a more significant correlation between CVAI and UACR.
Open Access
oa
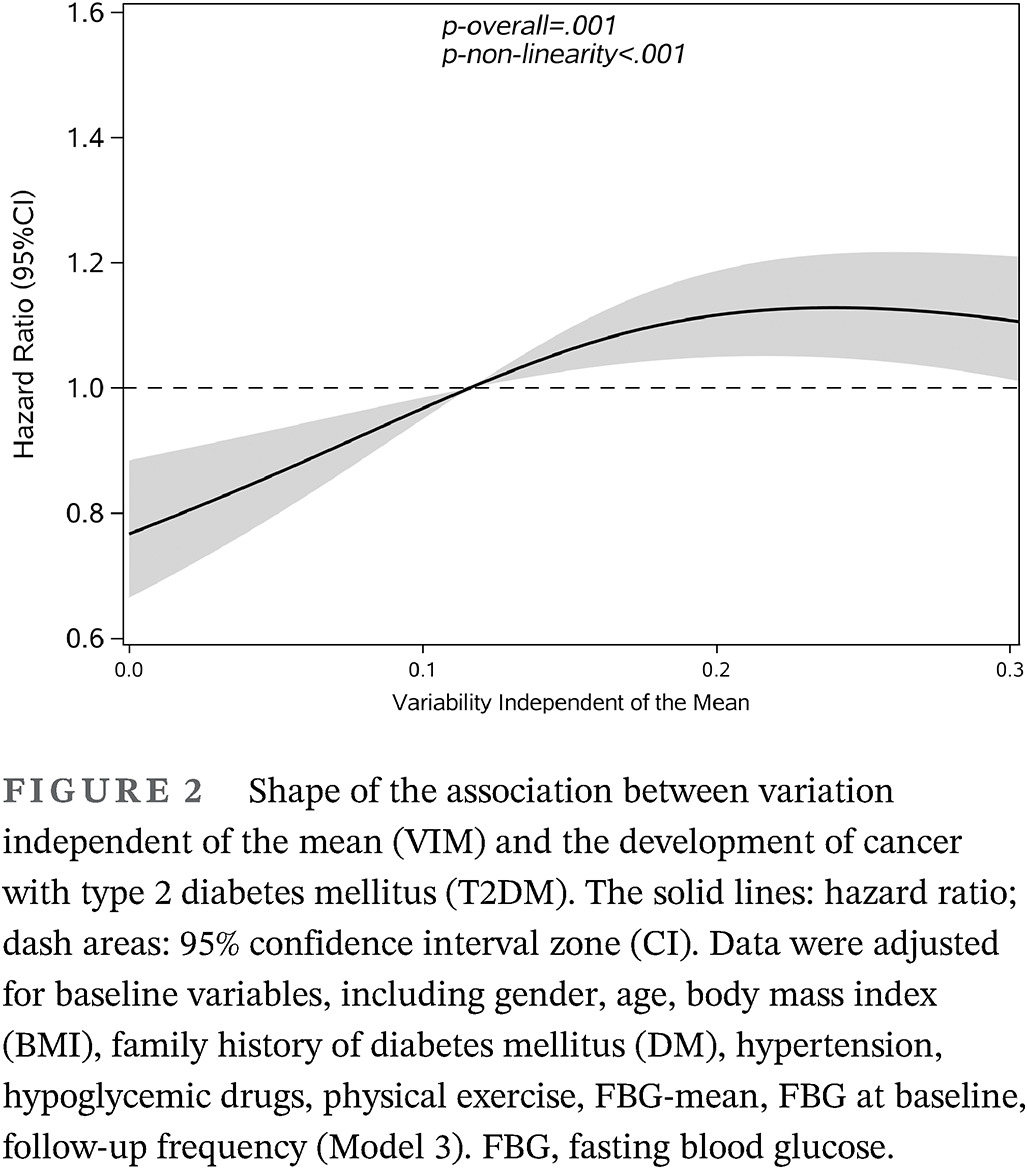
Long-term fasting glucose variability and risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective population-based cohort study in Shanghai
2型糖尿病患者的长期空腹血糖变异性与癌症风险:上海地区一项基于人群的回顾性队列研究--空腹血糖变异性对癌症的作用
- First Published: 09 November 2022
Open Access
oa
Protein pyrrole adducts are associated with elevated glucose indices and clinical features of diabetic diffuse neuropathies
蛋白质吡咯加合物与血糖指数升高和糖尿病弥漫性神经病的临床特征相关
- First Published: 04 October 2022
Highlights
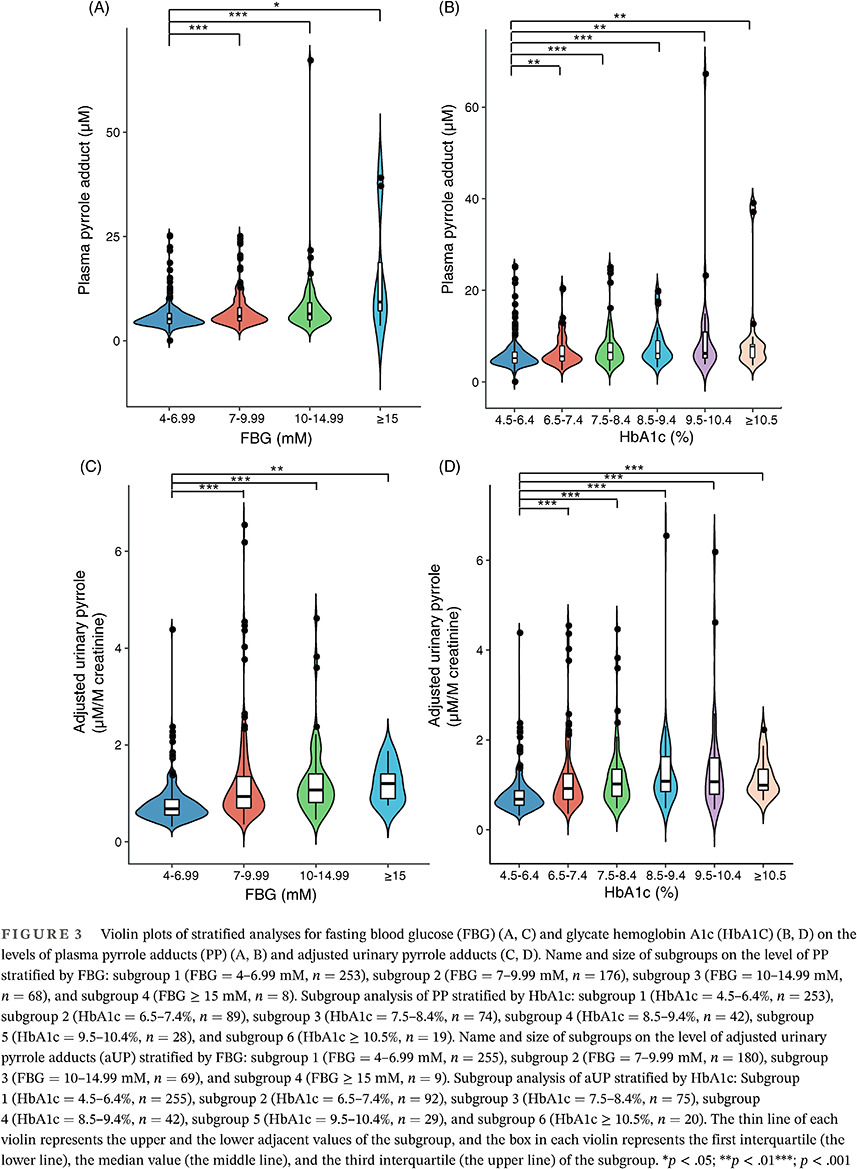
- The protein pyrrole adducts in both plasma and urine correlated well with glucose indices, namely fasting blood glucose (FBG) and glycate hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c).
- Elevated plasma pyrrole adducts was related to positive distal symmetric polyneuropathy (DSPN) symptoms and a high resting heart rate.
- The findings of protein pyrrole adducts build a new bridge between glucose indices and the etiology of DSPN.
Open Access
oa
Association of skin autofluorescence with low bone density/osteoporosis and osteoporotic fractures in type 2 diabetes mellitus
皮肤自发荧光与2型糖尿病患者低骨密度/骨质疏松及骨质疏松性骨折的关系
- First Published: 04 September 2022
Highlights
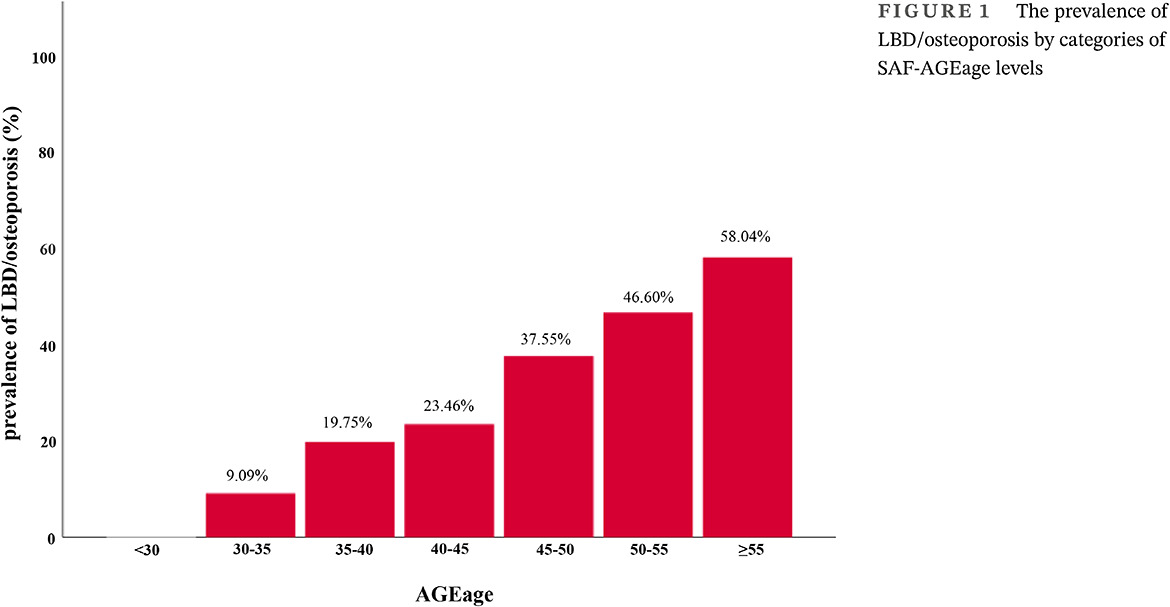
- The association between skin autofluorescence advanced glycation end products (SAF-AGEage) and low bone density/osteoporosis or major osteoporotic fractures was noteworthy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- SAF-AGEs were positively associated with the level of serum N-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen (s-PINP) and serum carboxy-terminal cross-linking peptide of type I collagen (s-CTX).
- To our knowledge, this is the first article that reports the association between SAF-AGEs and bone turnover markers in patients with T2DM.
Open Access
oa
Global disease burden of stroke attributable to high fasting plasma glucose in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study
204个国家和地区1990-2019年因空腹血糖升高导致的全球卒中疾病负担:全球疾病负担研究分析
- First Published: 04 August 2022
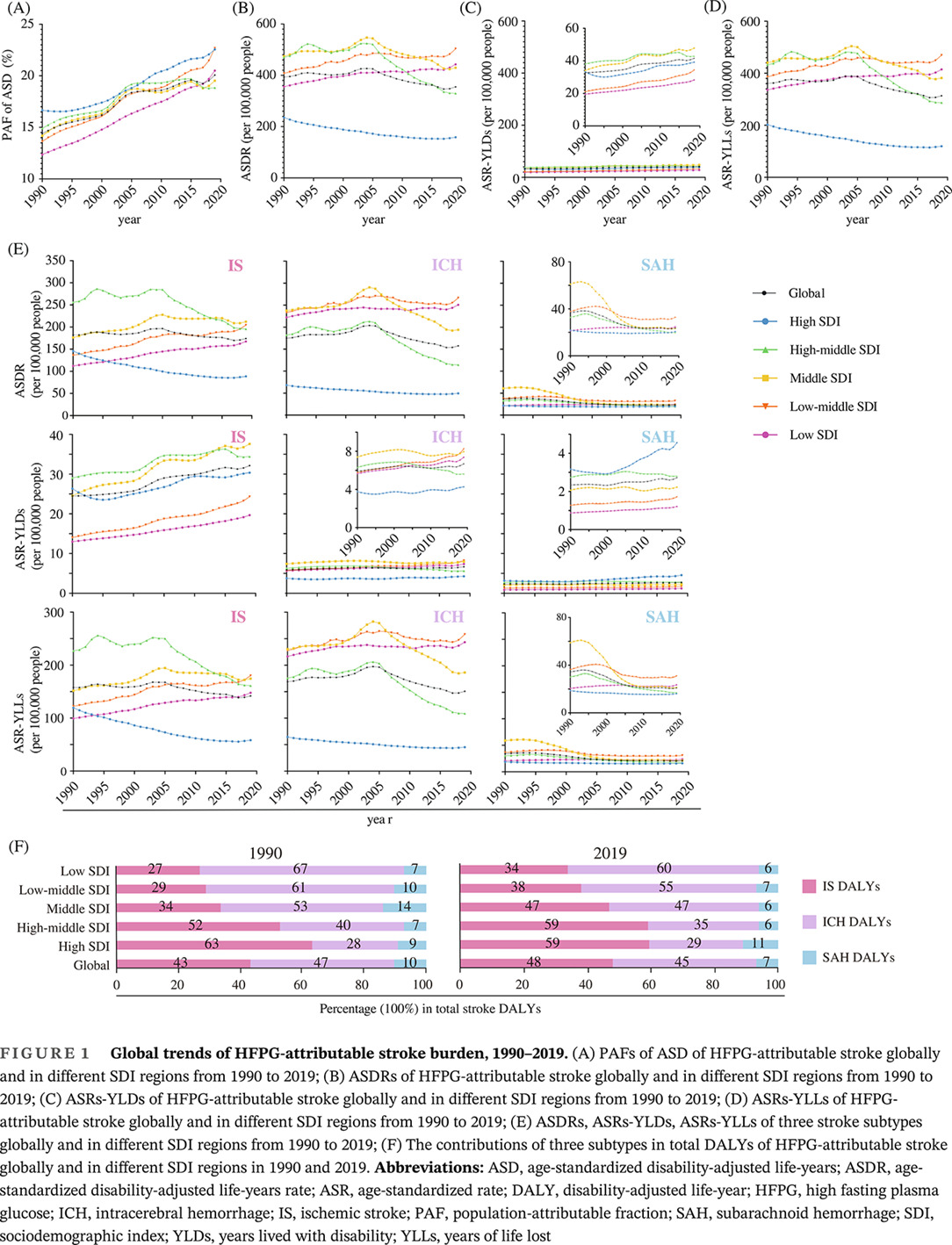
Highlights
- During the past 30 years, globally, the disease burden of stroke burden has decreased substantially; however, the disease burden of stroke attributable to high fasting plasma glucose (HFPG) failed to achieve a significant decline. The population-attributable fraction of HFPG for stroke burden has been increasing across different regions regardless of the sociodemographic index (SDI) of each region.
- The age-standardized rate of disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of HFPG-attributable stroke burden shifted from higher SDI regions to lower SDI regions.
- Older adults and males were the key populations concerning the control of HFPG-attributable stroke in all SDI regions and all stroke subtypes.
- The increase of HFPG-attributable stroke burden in females in low SDI regions and the slower decrease of DALYs of HFPG-attributable stroke rates among 25–69 years old adults in high SDI regions compared with high-middle SDI regions are worth attention as well.
Open Access
oa
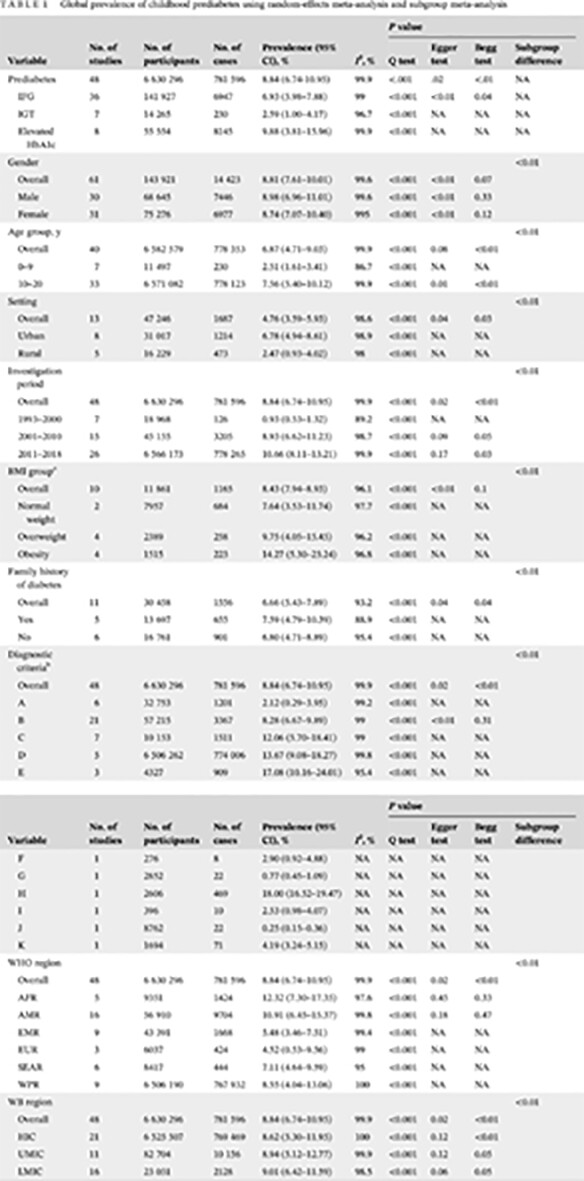
Global prevalence of prediabetes in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis
儿童和青少年中前期糖尿病的全球患病率:系统回顾和荟萃分析
- First Published: 05 July 2022
Open Access
oa
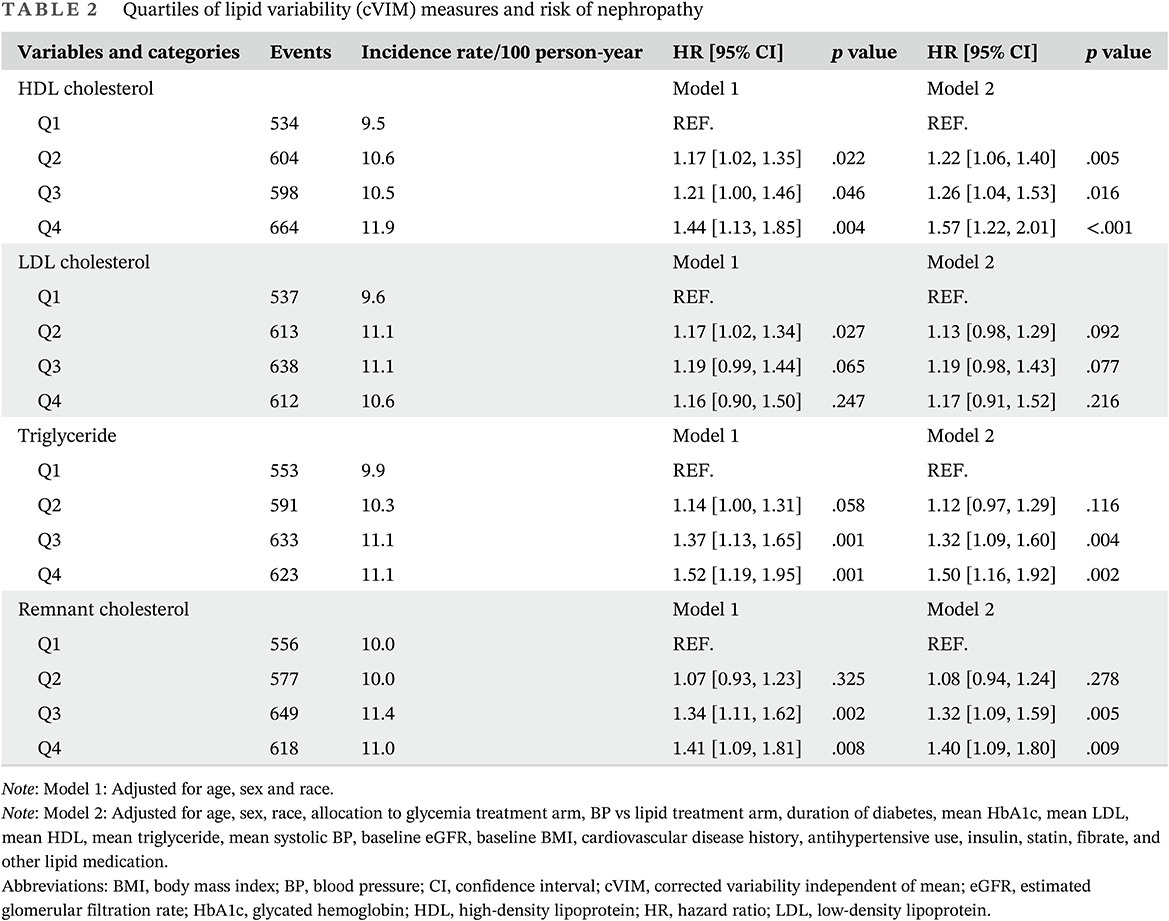
Lipid variability and risk of microvascular complications in Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial: A post hoc analysis
控制糖尿病心血管风险的行动(ACCORD)试验中的血脂变异性和微血管并发症风险:一项事后分析
- First Published: 06 June 2022
Open Access
oa
Follow-up frequency and clinical outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective analysis based on multicenter real-world data
2型糖尿病患者的随访频率和临床结局:一项基于多中心真实数据的前瞻性分析
- First Published: 25 May 2022
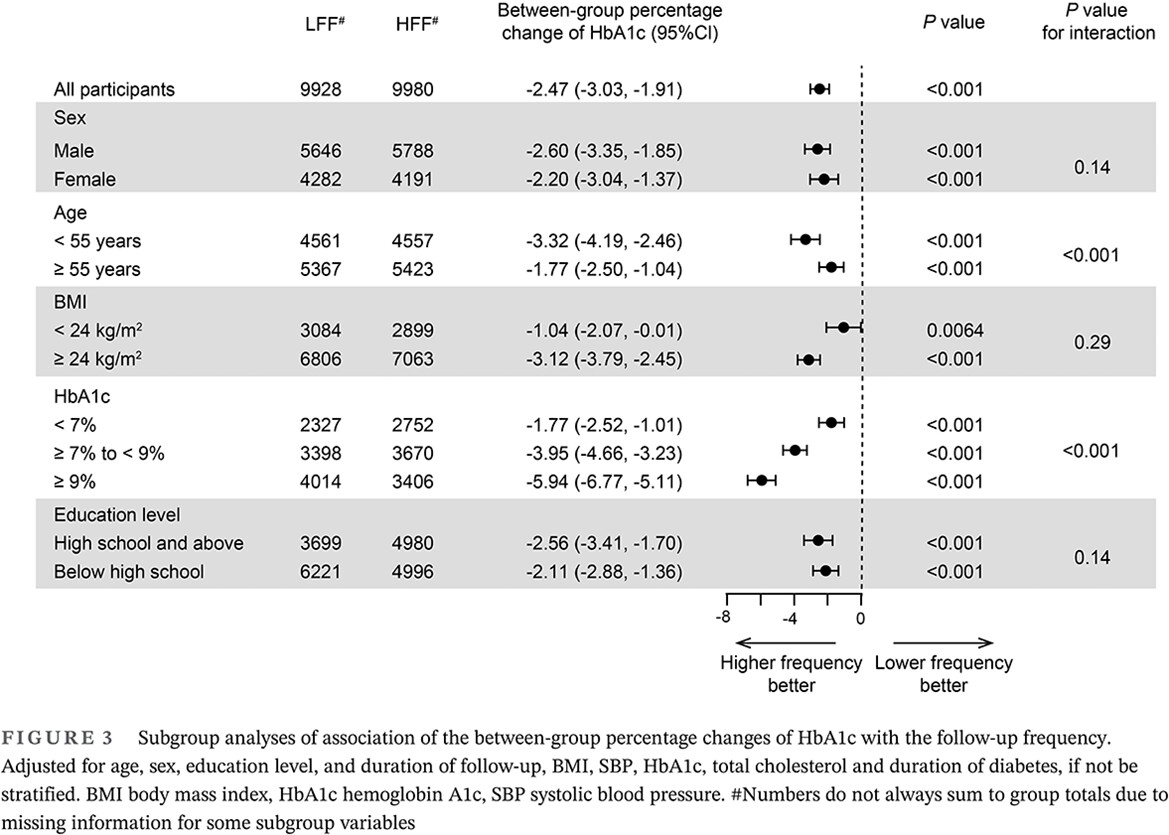
Highlights
- In this prospective analysis based on multicenter real-world data, higher-frequency follow-up achieved better glycemic control compared with lower-frequency follow-up in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- Furthermore, stratification analysis indicated that metabolic benefits with higher-frequency follow-up were predominant in patients with younger age or worse glycosylated hemoglobin. This study provides evidence-based recommendations for more efficient follow-up policies for targeted T2DM patients with different baseline characteristics.
Open Access
oa
Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on patients with diabetic kidney disease: A preliminary study on the basis of podocyturia
SGLT2抑制剂对糖尿病肾病患者的影响:基于尿足细胞的初步研究
- First Published: 28 February 2022
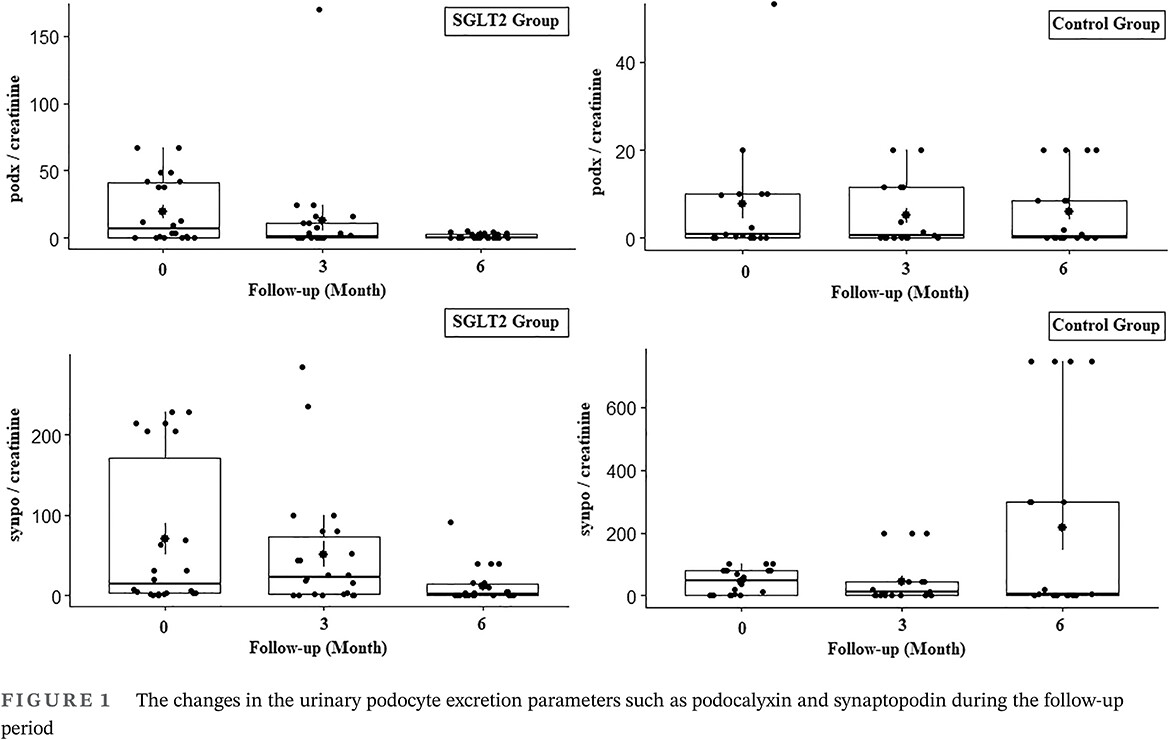
Highlights
- Diabetic kidney disease is a progressive disease with the pathology of glomerular damage and loss of podocytes.
- Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) can be expected to decrease the amount of podocyte excretion.
- Male patients receiving SGLT2i have better diabetic kidney disease-related parameters and podocyturia levels.
Open Access
oa
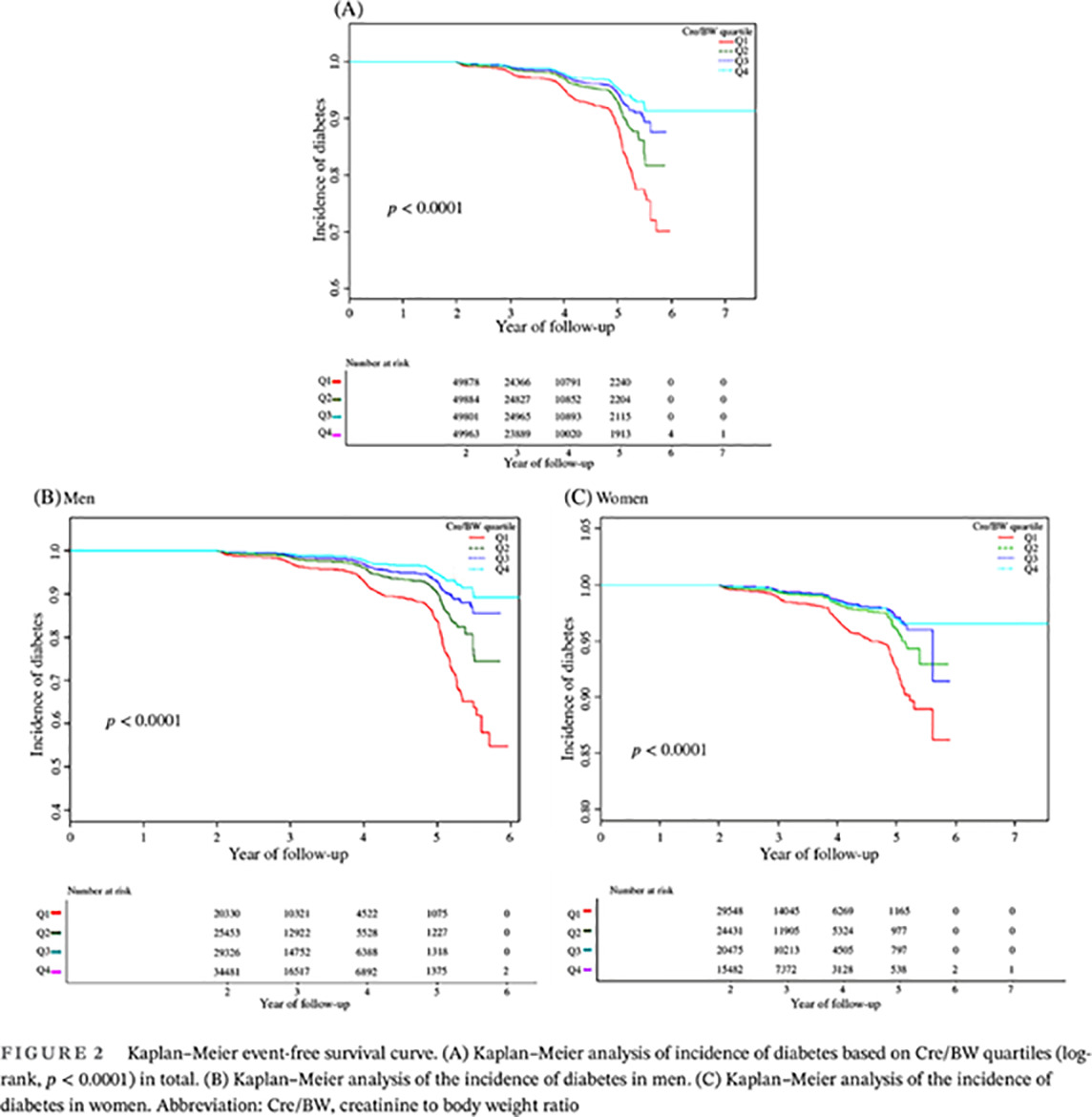
Relationship between creatinine to body weight ratios and diabetes mellitus: A Chinese cohort study
肌酐体重比与糖尿病的关系:一项中国队列研究
- First Published: 10 January 2022
Open Access
oa
Vitamin D receptor methylation attenuates the association between physical activity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study
维生素D受体甲基化减弱体力活动和2型糖尿病之间的联系:一项病例对照研究
- First Published: 08 November 2021
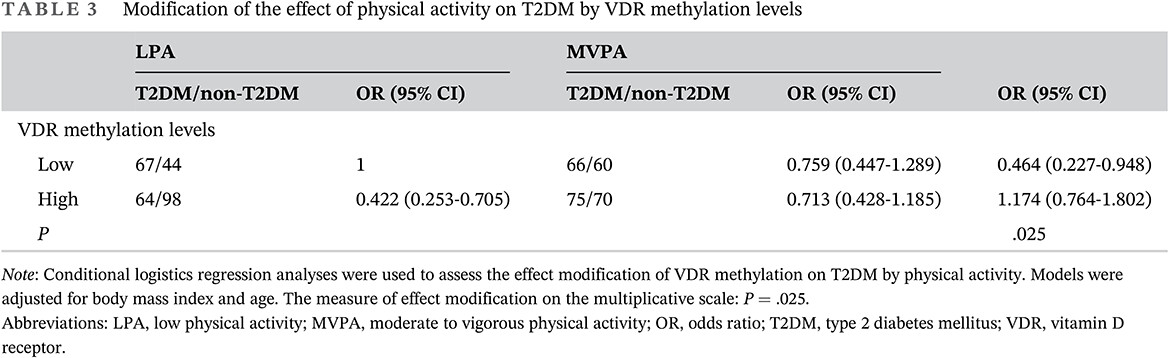
Highlights
- Vitamin D receptor (VDR) methylation attenuates the association between physical activity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- The methylation status of the VDR promoter is associated with the secretion and sensitivity of insulin.
- A high physical activity level is associated with a decreased risk of T2DM compared to a low physical activity level.
Open Access
oa
Pregnancy outcomes in women with type 1 diabetes in China during 2004 to 2014: A retrospective study (the CARNATION Study)
2004 - 2014年中国1型糖尿病妇女妊娠结局:回顾性研究(CARNATION研究)
- First Published: 07 October 2021
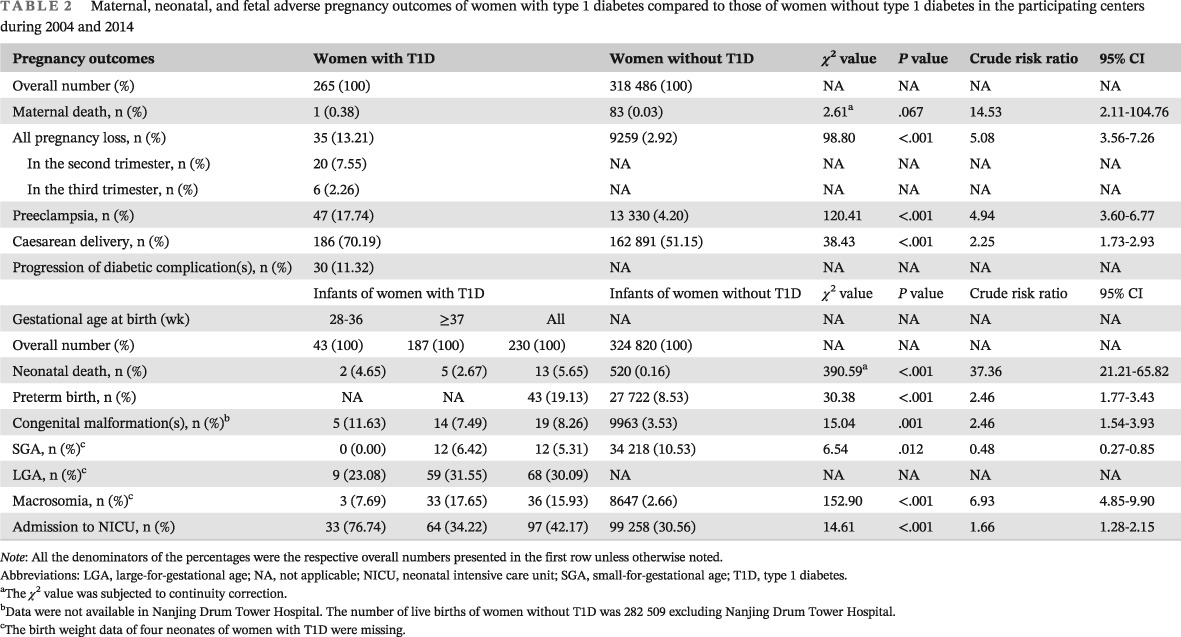
Highlights
- This retrospective study is the first to report pregnancy outcomes among Chinese women with type 1 diabetes during 2004 to 2014.
- We found that the pregnancy outcomes were poor among this population, despite dramatic improvement in the outcomes of the maternal care system for the general population, scientific progress, and release of guidelines.
- Our findings implicate a great burden of women with type 1 diabetes and that there is an urgent need to take measures to reduce adverse pregnancy outcomes.