Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Heterogeneity in the immune microenvironment of bone metastasis in driver-positive non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 17 April 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
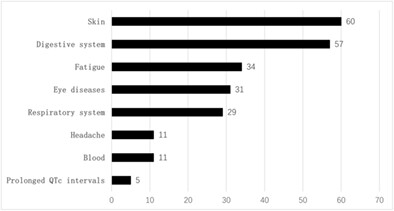
Analysis of adverse drug reactions of Osimertinib in the 2nd-line treatment of EGFR mutant advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer
- First Published: 10 August 2022
The effect of Acapella trainer on respiratory function of patients after thoracoscopic lung cancer surgery
- First Published: 14 March 2021
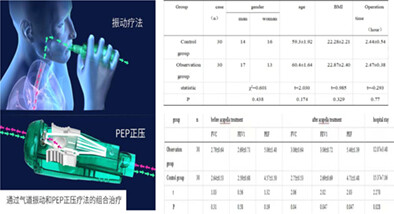
We selected 60 patients who underwent full video-assisted thoracoscopic lung cancer surgery in our thoracic surgery. The control group adopted conventional respiratory function training methods, and the experimental group used Acapella training equipment for respiratory function training. By observing the respiratory function of the two groups of patients before and 30 days after the operation, and the postoperative hospital stay, we concluded that the Acapelle training device can improve the patient's respiratory function, shorten the postoperative hospital stay, and reduce medical expenses.
REVIEWS
Carbon ion radiotherapy in the management of non-small cell lung cancer
- First Published: 22 March 2022

Carbon ion radiotherapy is a form of high-linear energy transfer radiation therapy that may have several theoretical advantages over traditional low-linear energy transfer therapies in the treatment of both early-stage and locally advanced non-small cell cancer. These potential advantages include the ability to achieve high intratumoral radiation doses while sparing adjacent critical structures of the mediastinum, delivering adequate radiation doses in fewer fractions, limiting/eliminating the use of concurrent cytotoxic chemotherapy, and increasing the response to immunotherapy, thereby reducing eventual metastatic spread.
REVIEW
Application of radiomics in lung immuno-oncology
- First Published: 04 April 2023
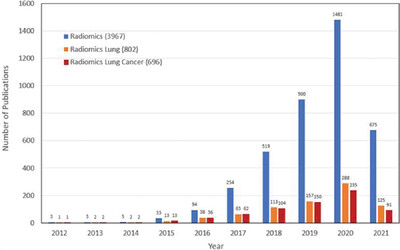
Radiomics is a rapidly evolving field of research that extracts and analyzes quantitative features within medical images. Those features are termed as radiomic features that can characterize a tumor in a comprehensive and quantitative manner with regard to its internal structure and heterogeneity. Radiomic features can be used, alone or in combination with demographic, histological, genomic, or proteomic data, for predicting prognosis or treatment response. Immunotherapy, or immune-oncology, is the study of cancer treatment by taking advantage of the body's immune system to prevent, control, and eliminate cancer. In this review, we first provide a brief introduction to both radiomics and immune-oncology in lung cancer. Then, we discuss the need in developing immune-oncology biomarkers, and the advantages of radiomics in identifying biomarkers related to immunotherapy. We also discuss potential areas in and out of tumors, such as intra-tumoral hypoxic region and tumor microenvironment, where radiomic markers might be extracted, as well as potential application of radiomic biomarkers in clinical lung cancer management. Finally, we present radiation and immune modulation in non-small cell lung cancer, clinical trials, and their design to incorporate radiomic biomarkers, and radiomics-guided precision radiation therapy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Environmental and Occupational Lung Disease
Lung cancer screening an asbestos exposed population: Existing lung cancer risk criteria are not sufficient
- First Published: 08 March 2023

This prospective cohort study of 1743 asbestos exposed individuals demonstrates that the population is at high risk for lung cancer regardless of smoking status, low dose CT screening is effective at identifying early-stage lung cancer in this population and existing lung cancer risk criteria do not capture this population adequately.
See related Editorial
Interstitial Lung Disease
Lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective multicentre study in Europe
- First Published: 18 September 2022
This is the largest study in Caucasian population showing that lung cancer is prevalent and exerts a dramatic impact on patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Incidence of lung cancer increases over time in patients with IPF. Early identification and surgical resection might confer survival benefit. There remains substantial heterogeneity in disease management.
CASE REPORTS
A case of disseminated intravascular coagulation following tumour lysis syndrome due to small cell carcinoma of the lung
- First Published: 06 February 2023
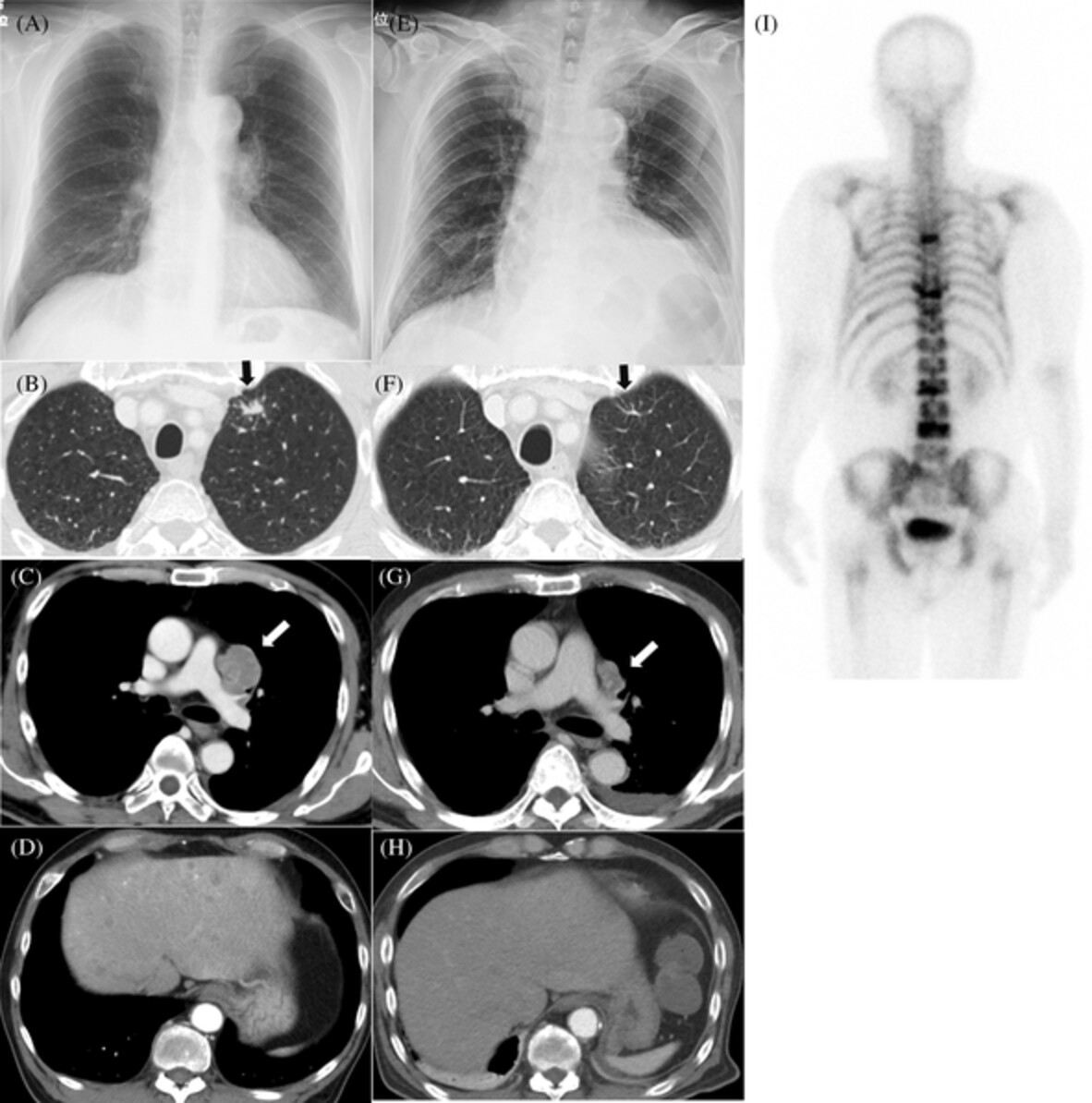
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) following tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) is a rare but serious life-threatening complication that clinicians need to be aware of when treating patients with advanced small cell lung cancer (SCLC). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of DIC following TLS in a case of SCLC.
CASE SERIES
Real-time visualization of lung malignancy with needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy during shape-sensing robotic-assisted bronchoscopy
- First Published: 02 February 2023
REVIEWS
CAR-T cell therapy for lung cancer: Potential and perspective
- First Published: 15 March 2022
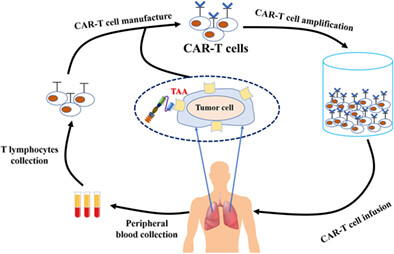
The clinical application process of CAR-T cell immunotherapy. The clinical process of CAR T is as listed: T lymphocyte collection; CAR T-cell manufacturing; CAR T-cell amplification and screening in vitro; CAR-T cells are infused back into patients; CAR-T cells are transported to the tumor site and perform their function in the tumor microenvironment.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Efficacy of first-line immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with advanced NSCLC with KRAS, MET, FGFR, RET, BRAF, and HER2 alterations
- First Published: 02 May 2022
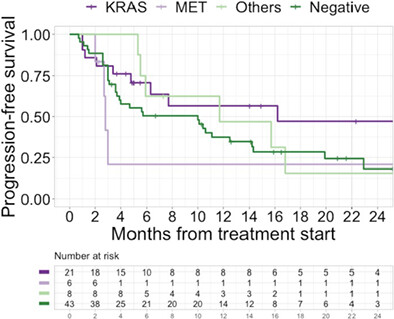
The benefit of the first-line ICI was similar in advanced NSCLC regardless of the drivers, except for MET drivers. The median PFS according to the driver subgroup was 16.2 months (95% CI: 6.3–NR) for KRAS alterations, 2.8 months (95% CI: 2.7–NR) for MET alterations, 11.7 months (95% CI: 5.9–NR) for other alterations (FGFR, RET, BRAF, and HER2), 10.0 months (95% CI: 3.7–14.3) for driver-negative.
REVIEWS
Recent advances in immunotherapy for lung cancer
- First Published: 24 February 2023
In recent years, immunotherapy has gradually moved from the back line to the front line, from advanced to early patients. This article focuses on the latest developments in perioperative and advanced lung cancer immunotherapy, discusses the problems and challenges at the current stage, and explores new directions for future development.
Adjuvant and neo-adjuvant immunotherapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Current status and perspectives
- First Published: 19 February 2023
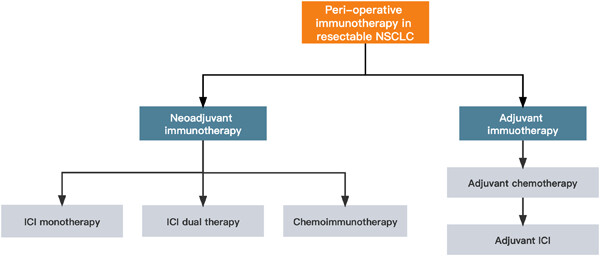
At present, immunotherapy represented by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), either by monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy, has shown benefit in promoting pathological responses and prolonging survival for patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) without oncogenic mutations. Investigation on predictive biomarkers of responses to adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapies is also continuously ongoing. This review focuses on the existing data of current clinical trials of adjuvant and neoadjuvant strategies with ICIs in resectable NSCLC, the exploration of predictive biomarkers, and the perspectives and urgent challenges in the future.