Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
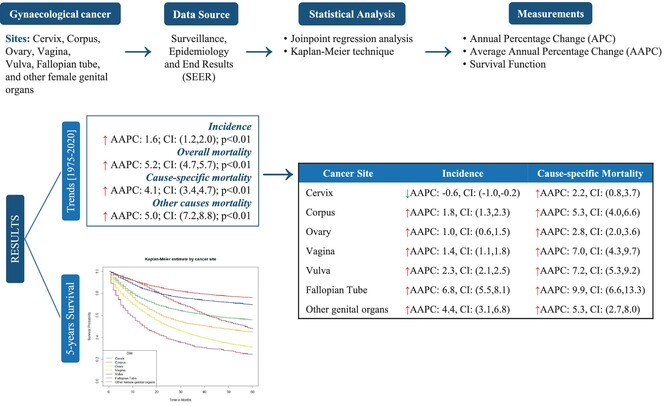
Trends in gynecological cancer incidence, mortality, and survival among elderly women: A SEER study
- First Published: 29 April 2024
Guideline for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly in China (2024 Edition)
- First Published: 29 March 2024
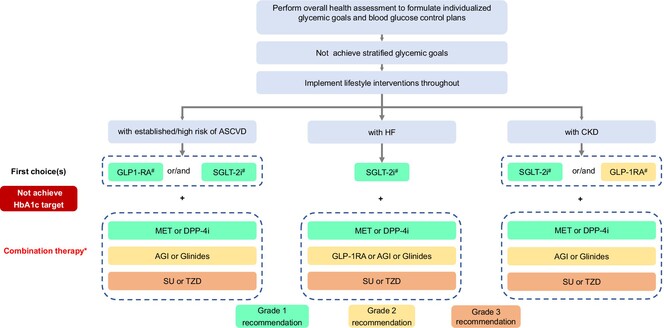
Overall health assessment should be performed to formulate individualized glycemic goals and blood glucose control plans. If individualized glycemic goals fail to be achieved, hypoglycemic drugs should be added, besides lifestyle interventions. Therapeutic drug choices should be based on the health status of elderly patients and whether established/high risk factors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), HF, or CKD are present.
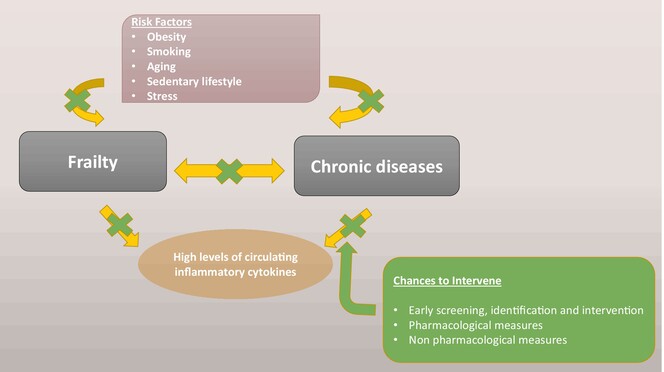
Frailty and chronic diseases: A bi-directional relationship
- First Published: 12 August 2024
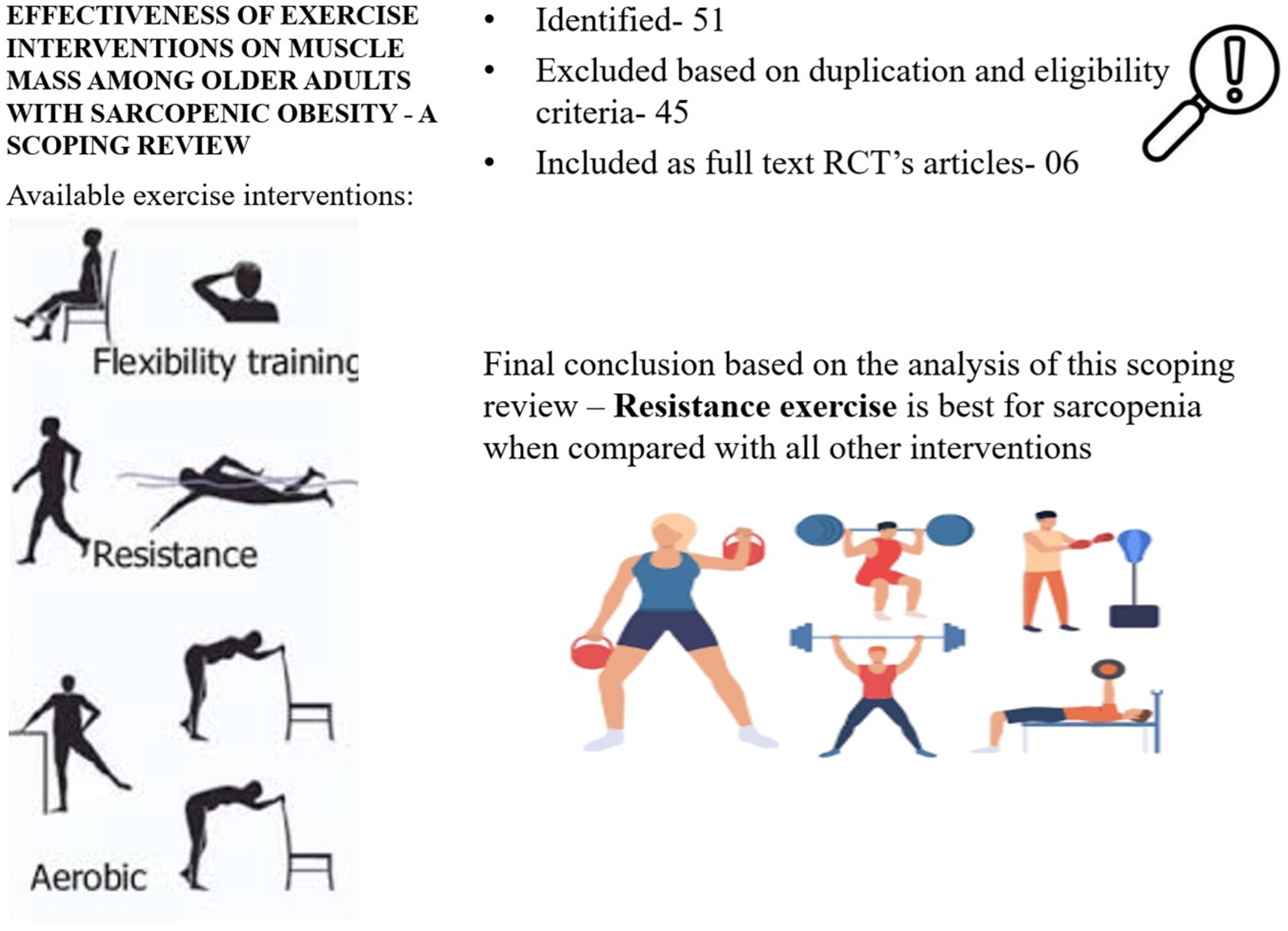
Effectiveness of exercise interventions on muscle mass among older adults with sarcopenic obesity: A scoping review
- First Published: 06 February 2024
Anti-aging effects of icariin and the underlying mechanisms: A mini-review
- First Published: 15 February 2024
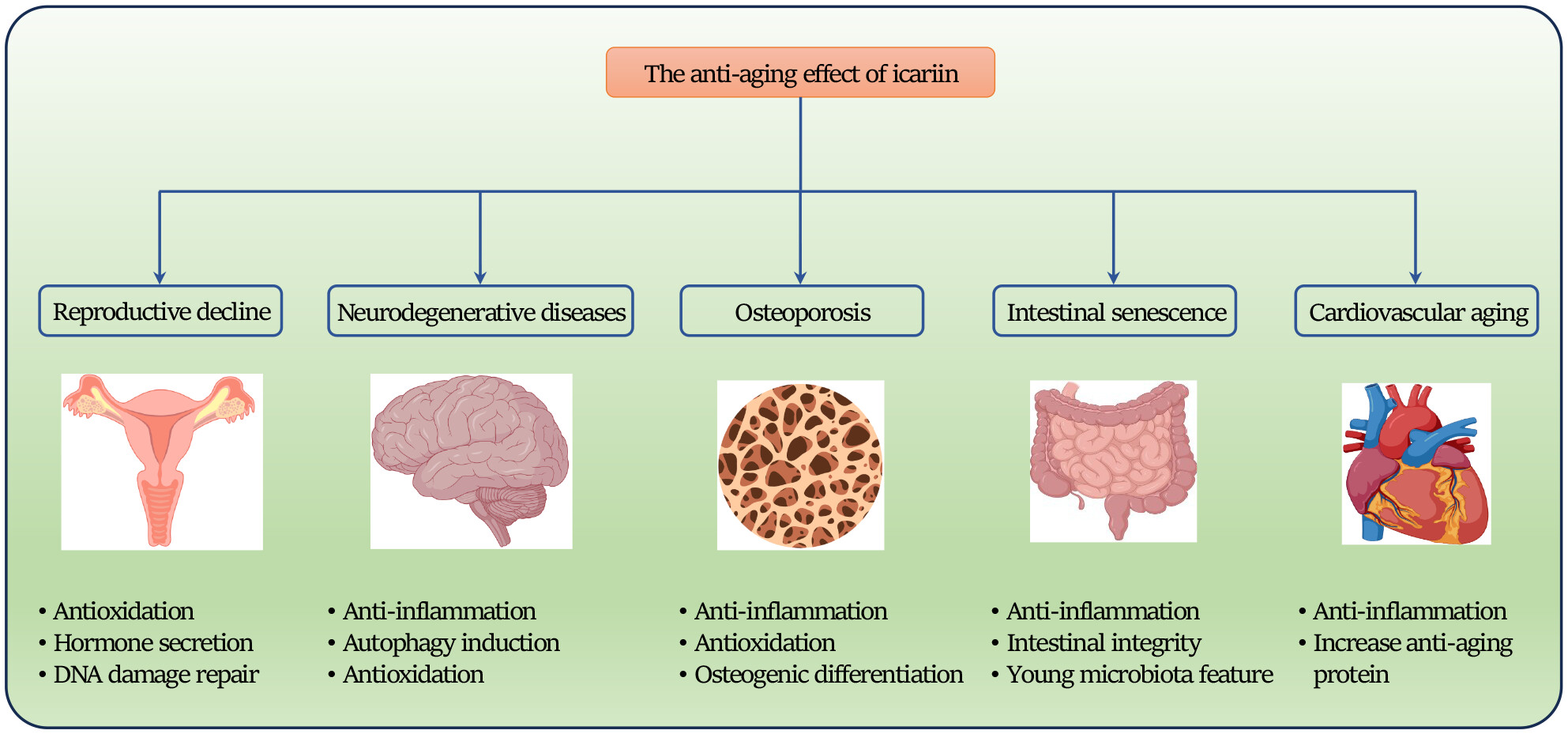
Icariin (ICA) exhibits anti-aging effects in different physiological and pathological conditions. ICA displays protective effect against reproductive function decline, neurodegenerative diseases, osteoporosis, intestinal senescence, and cardiovascular aging via anti-inflammation, autophagy induction, antioxidation, maintaining intestinal integrity, and inducing young gut microbiota features.
Navigating sarcopenia in COVID-19 patients and survivors: Understanding the long-term consequences, transitioning from hospital to community with mechanisms and interventions for future preparedness
- First Published: 06 February 2024
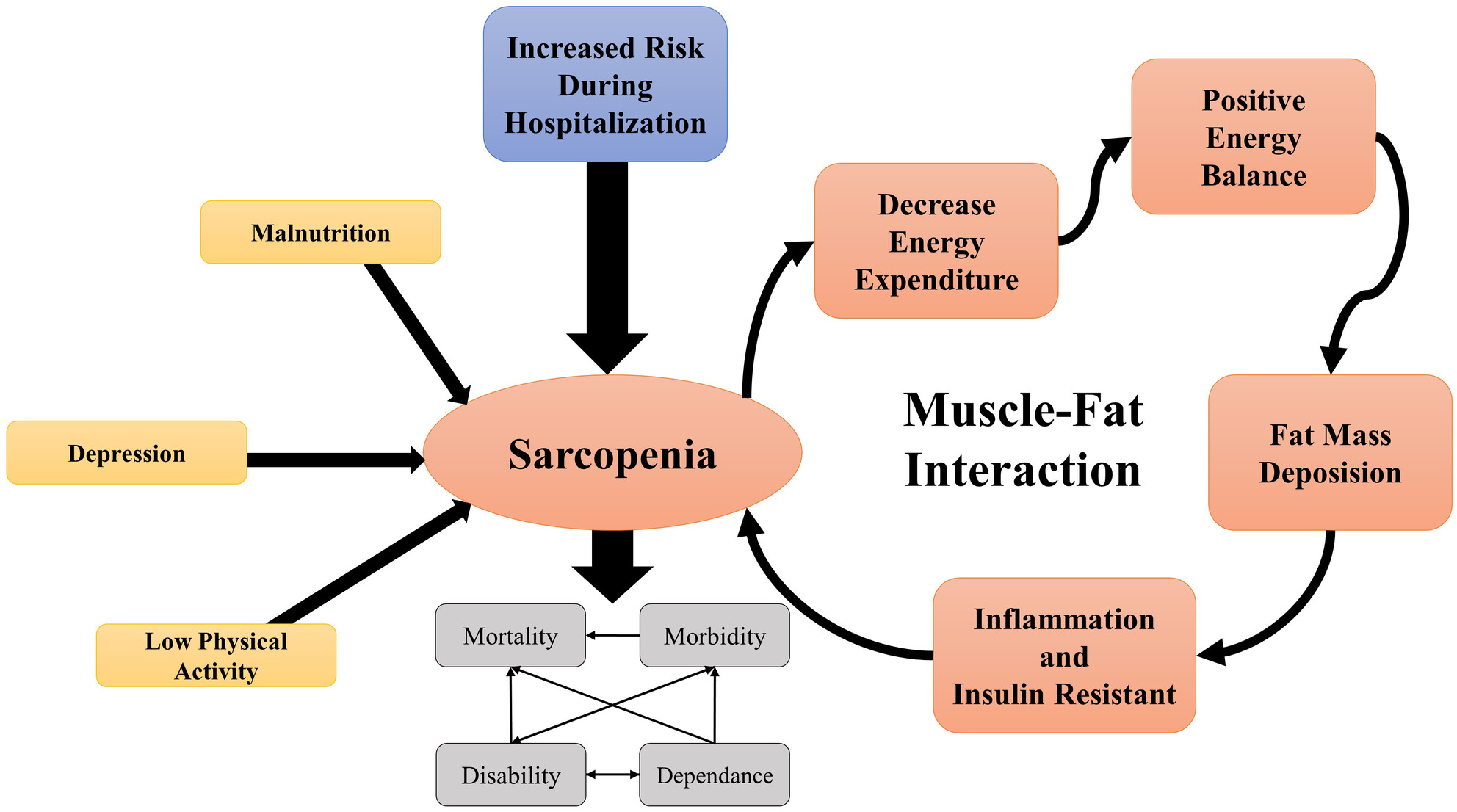
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a global impact, yet limited attention has been given to the comorbid condition of sarcopenia. This paper explores the shared underlying mechanisms between COVID-19 and sarcopenia and highlights the critical importance of addressing sarcopenia for optimal COVID-19 patient and survivor outcomes. By implementing comprehensive strategies that encompass screening, nutritional interventions, physical activity promotion, psychological support, and community-based initiatives, health experts can effectively control sarcopenia and improve overall well-being in the post-COVID-19 era. Additionally, further research is imperative to deepen our understanding of the relationship between COVID-19 and sarcopenia and to develop evidence-based management approaches.
The long-term effects of childhood circumstances on older individuals: A systematic review
- First Published: 12 April 2024
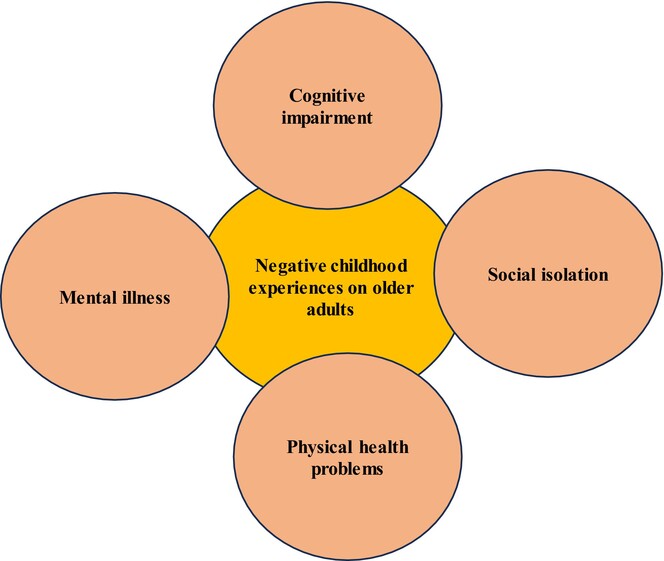
Childhood experiences profoundly shape the health, mental well-being, cognitive function, and social relationships of older individuals. From malnutrition and environmental pollutants to trauma and socioeconomic factors, early life significantly influences later-life outcomes, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive support and interventions for the older people.
Artificial intelligence based on falling in older people: A bibliometric analysis
- First Published: 09 April 2024

The English-articles based on artificial intelligence and falls in the older people are both few in number. The number of publications has increased in recent years according to technological developments. In future research, relevant analyzes should be conducted in scientific databases, such as Scopus and PubMed.
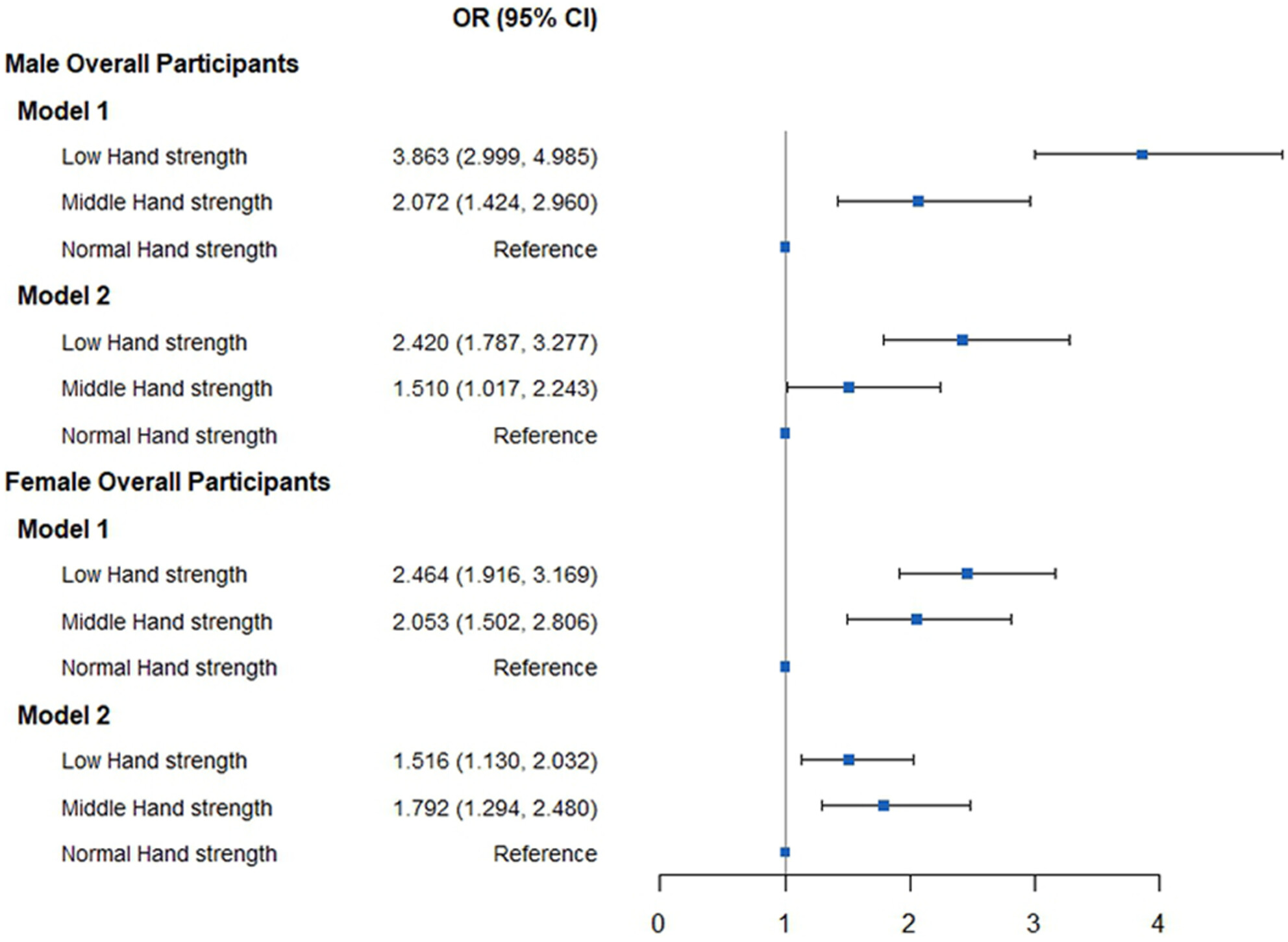
Association between low handgrip strength and incontinence among Chinese middle-aged and older people: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 25 April 2024