Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Neurodegenerative disorders: Assessing the impact of natural vs drug-induced treatment options
- First Published: 22 February 2023
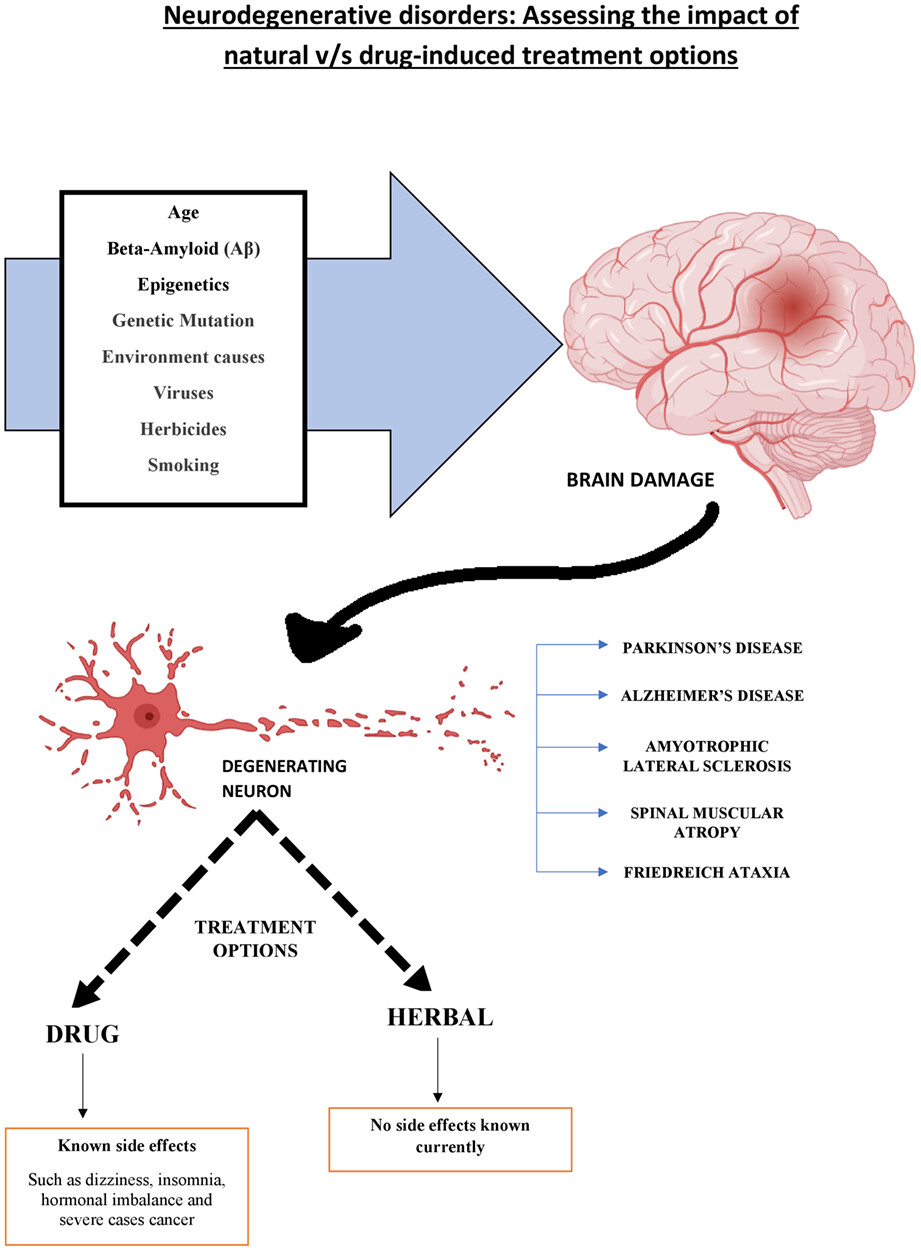
Age, Epigenetics, Beta Amyloid, Genetic Mutations, Environmental Causes, Viruses, Herbicides, and Smoking are the well-known factors that contribute to damage to the brain. These degenerative neurons are responsible for neurodegenerative diseases, ranging from commonly occurring Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Spinal Muscular Dystrophy to even rare forms such as Friedreich ataxia. However, these degenerative disorders can be treated using both drugs as well as herbal-based treatment methods. Drugs as medicines do offer relief from the symptoms but also contribute to a wide range of side effects which include dizziness, hormonal imbalance, and in serious cases, it may result in cancer. Herbal treatment on the other hand has currently not reported any side effects.
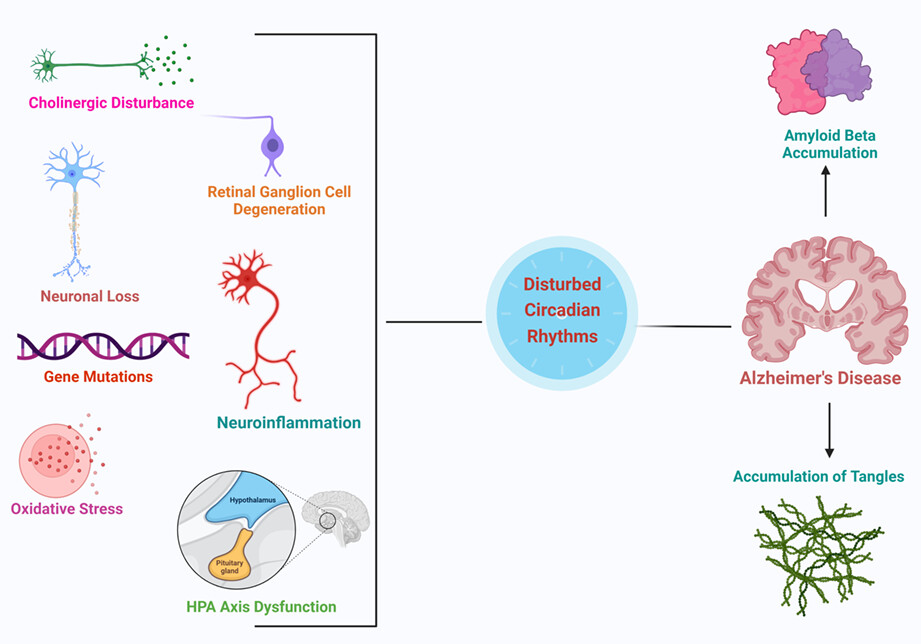
Circadian dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease – An updated review
- First Published: 15 August 2022
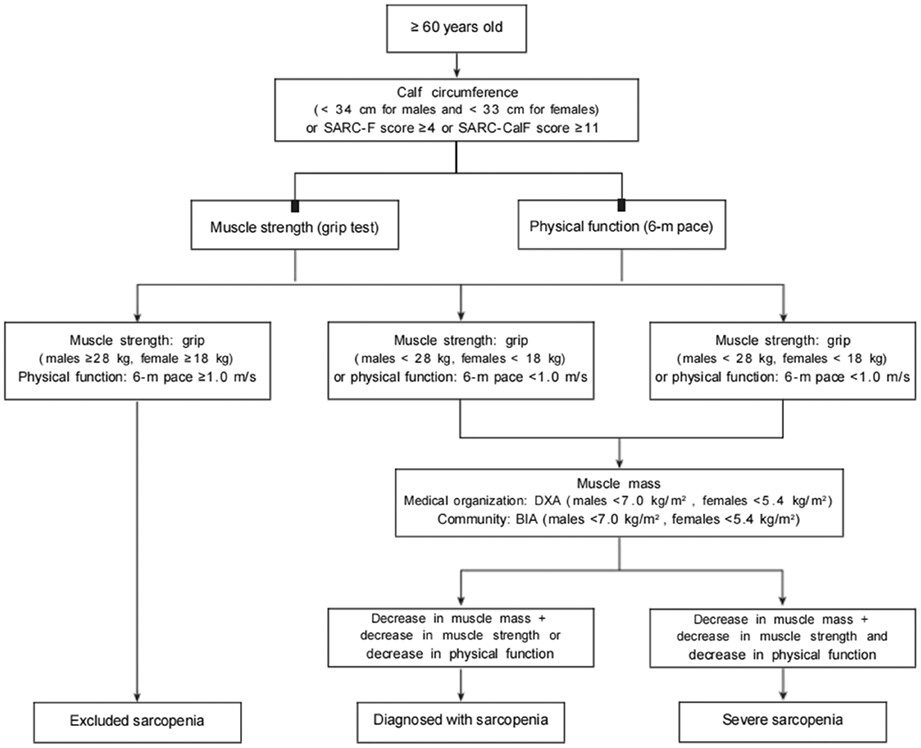
Chinese expert consensus on prevention and intervention for elderly with sarcopenia (2023)
- First Published: 26 April 2023
Polypharmacy and cumulative anticholinergic burden in older adults hospitalized with fall
- First Published: 05 April 2023
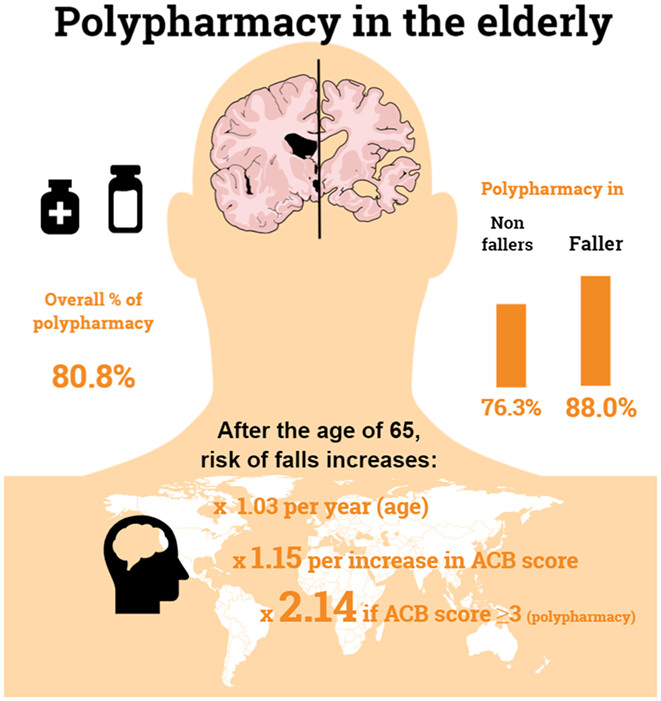
Polypharmacy (the use of ≥ 5 regular oral medication) is very common in adults over 65 and its prevalence is increasing. Polypharmacy and its cumulative effect on Acetylcholine Burden (ACB) both are significantly associated with increased falls risk and hospitalisation in older adults ≥ 65 years. The presence of polypharmacy and each unit rise in ACB score have a stronger effect of increasing falls risk compared to age and comorbidities.
A pathological convergence theory for non-communicable diseases
- First Published: 05 November 2023
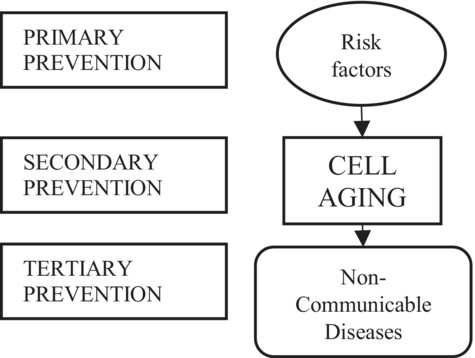
Aggressions from main risk factors converge in limited pathophysiological pathways (eventually inflammation/oxidative stress). Genetic, pathophysiologic, and epidemiologic evidences suggest that most non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are different facets of cell aging. Cell aging as common convergence mechanism that exponentially increases mortality by most NCDs in older ages.
Frailty and oral anticoagulant prescription in adults with atrial fibrillation: A systematic review
- First Published: 01 June 2022
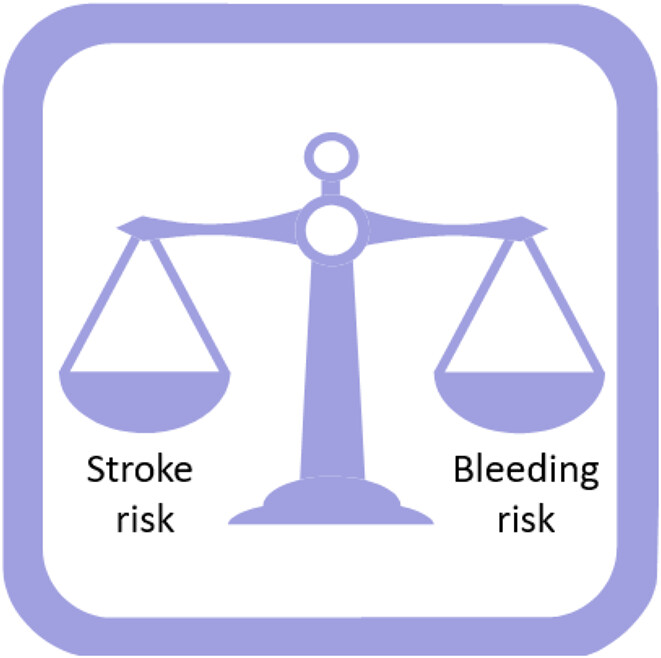
Frailty is an important consideration in anticoagulation decision making for stroke prevention in patients with AF. There is scope to improve frailty screening and treatment in patients with AF. Frailty status is an important risk marker that should be considered when evaluating stroke risk alongside tools such as the CHA2DS2VASc and HAS-BLED.
Identification of potential neuroprotective compound from Ganoderma lucidum extract targeting microtubule affinity regulation kinase 4 involved in Alzheimer's disease through molecular dynamics simulation and MMGBSA
- First Published: 12 December 2022
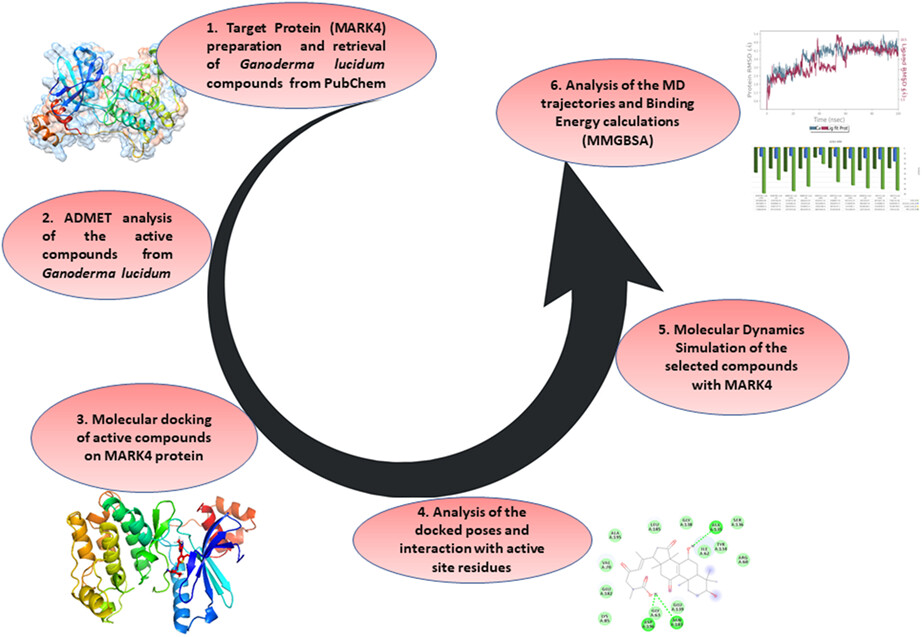
Alzheimer's disease is the world's most common neurological disorder. Microtubule affinity regulation kinase 4 (MARK4) is currently one of the most promising drug targets for Alzheimer's disease. Ganoderma lucidum, which is also known as “Reishi mushroom,” from which five potential compounds were selected. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (ADMET) analysis followed by molecular docking and molecular dynamics for each complex was performed. Based on molecular dynamics simulation and molecular mechanics generalized born surface area (MMGBSA) results, this study revealed that ganoderic acid A and ganoderenic acid B are the most promising compounds against Alzheimer's disease.
Prevalence of constipation on an internal medicine ward
- First Published: 22 February 2023
The prevalence of frailty and its relationship with sociodemographic factors, regional healthcare disparities, and healthcare utilization in the aging population across India
- First Published: 07 August 2023
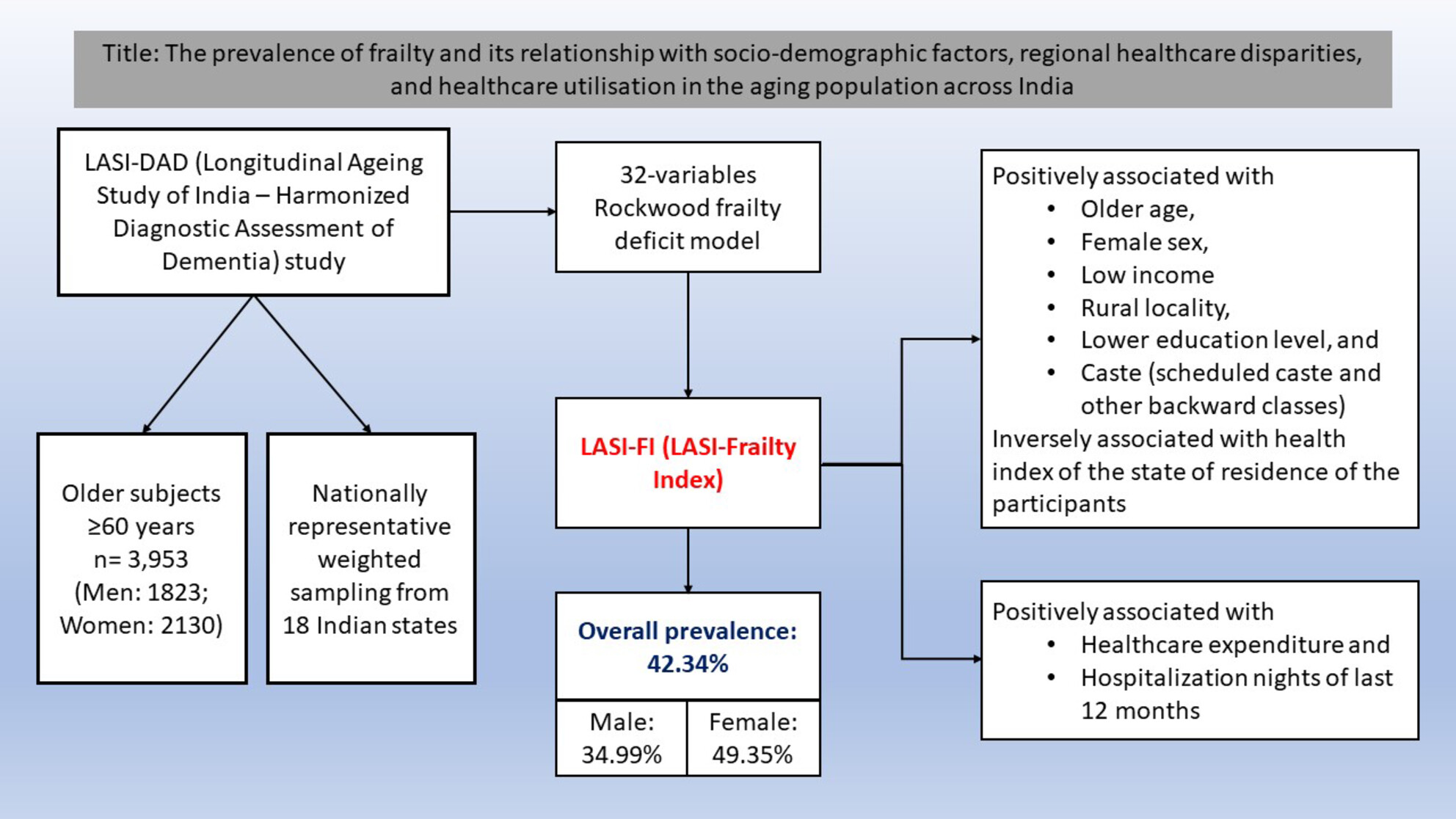
Using nationally representative weighted sampling, the prevalence of frailty in the Indian population aged ≥ 60 years was found to be 42.34%. Frailty was positively associated with older age, female sex, low income, less education, living in a state with poor health index or rural areas, and belonging to the scheduled caste or other backward class (marginalized community). We also found that older adults with a higher degree of frailty experienced higher health expenditures and hospitalization rates in the previous year.