Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
topical reviews
Structural dynamics: review of time-resolved cryo-EM
- Pages: 927-935
- First Published: 21 July 2022
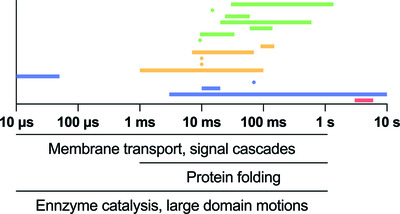
Time-resolved cryo-EM is an emerging technique in structural biology that allows the user to capture structural states which would otherwise be too transient for standard methods. There has been a resurgence in technical advancements in this field in the last five years and this review provides a summary of the technical highlights.
research papers
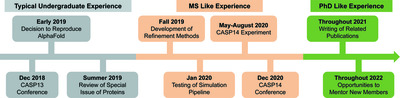
Training undergraduate research assistants with an outcome-oriented and skill-based mentoring strategy
- Pages: 936-944
- First Published: 15 July 2022
Evaluating the impact of X-ray damage on conformational heterogeneity in room-temperature (277 K) and cryo-cooled protein crystals
- Pages: 945-963
- First Published: 15 July 2022
Analysis of high-resolution data indicated that X-ray damage has little impact on conformational ensemble information from protein crystals at room temperature (277 K). In contrast, X-ray damage can alter conformational distributions obtained from cryo-cooled crystals under common experimental conditions, complicating structural interpretations in some instances. The results presented provide a strong motivation for the expanded use of room-temperature X-ray crystallography.
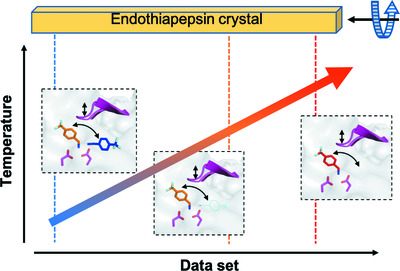
Probing ligand binding of endothiapepsin by `temperature-resolved' macromolecular crystallography
- Pages: 964-974
- First Published: 27 July 2022
Room-temperature serial synchrotron crystallography of Drosophila cryptochrome
- Pages: 975-985
- First Published: 27 July 2022
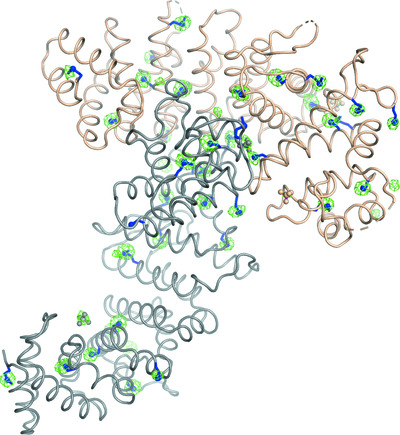
Native SAD phasing at room temperature
- Pages: 986-996
- First Published: 27 July 2022
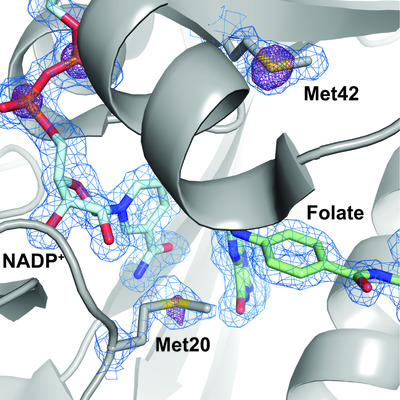
Room-temperature crystallography enables researchers to resolve the conformational heterogeneity of structures. Here, the native SAD phasing of four structures at 295 K highlights the strengths of room-temperature diffraction experiments, including detailed anomalous difference maps and alternate conformations that are well supported by the electron density.
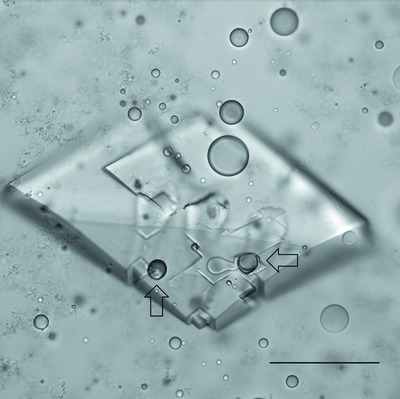
Data collection from crystals grown in microfluidic droplets
- Pages: 997-1009
- First Published: 21 July 2022
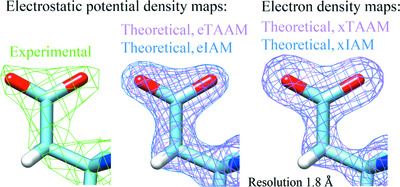
Theoretical 3D electron diffraction electrostatic potential maps of proteins modeled with a multipolar pseudoatom data bank
- Pages: 1010-1020
- First Published: 15 July 2022
Application of sulfur SAD to small crystals with a large asymmetric unit and anomalous substructure
- Pages: 1021-1031
- First Published: 15 July 2022
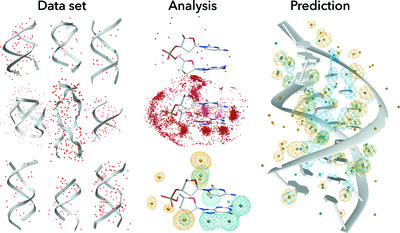
Knowledge-based prediction of DNA hydration using hydrated dinucleotides as building blocks
- Pages: 1032-1045
- First Published: 21 July 2022
α-SAS: an integrative approach for structural modeling of biological macromolecules in solution
- Pages: 1046-1063
- First Published: 27 July 2022
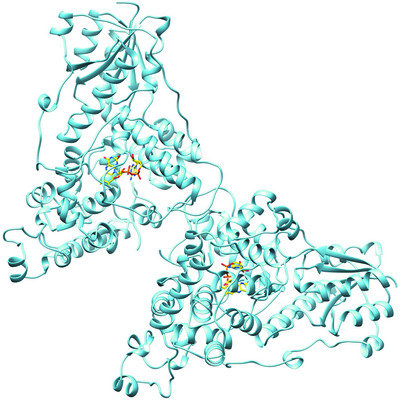
The crystal structure of CbpD clarifies substrate-specificity motifs in chitin-active lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases
- Pages: 1064-1078
- First Published: 27 July 2022
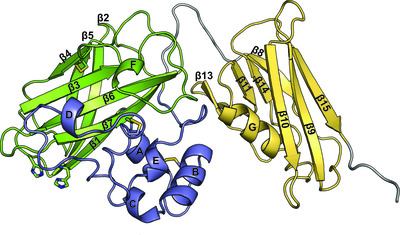
The 3 Å resolution crystal structure of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor CbpD both supports and challenges the current model of how lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases bind chitin and raises interesting possibilities about how type 2 secretion-system substrates may interact with the secretion machinery. This structure also demonstrates the utility of new, AI-powered, protein structure-prediction algorithms in making challenging structural targets tractable.