Edited By: Please see editorial board information
Structural Biology - Acta Crystallographica Section D journal covers all aspects of structural biology, with a particular emphasis on biological macromolecules and the software and methods used to determine them. We focus on new structures from the smallest macromolecules to the largest complex molecular machines, and any structural biology technique including crystallography, cryoEM, SAXS, computational prediction, NMR and integrative approaches.
Journal Metrics
- 5.8CiteScore
- 3.8Journal Impact Factor
Featured Articles
Articles
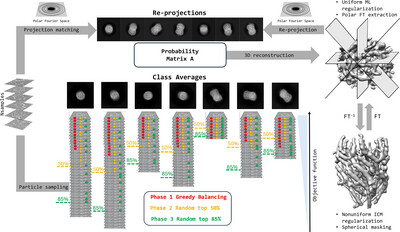
Probabilistic single-particle cryo-EM ab initio 3D reconstruction in SIMPLE
- 14 July 2025
Q-score as a reliability measure for protein, nucleic acid and small-molecule atomic coordinate models derived from 3DEM maps
- 14 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
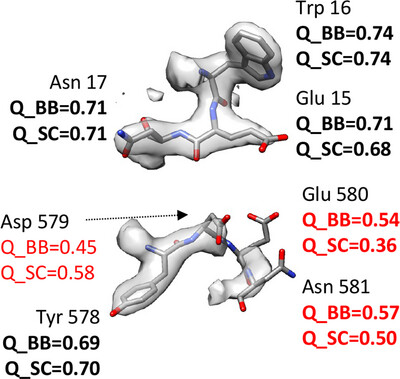
Q-scores are calculated for atomic models derived from 3D electron microscopy maps, measure how well the model fits the map and reflect the quality of the map itself. Here, we develop a statistical model for Q-scores applied to many maps and models in the EMDB and PDB, respectively, and show how it can be used to assess the reliability of entire models as well as their subcomponents.
Efficient high‐resolution refinement in cryo‐EM with stochastic gradient descent
- 327-343
- 2 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
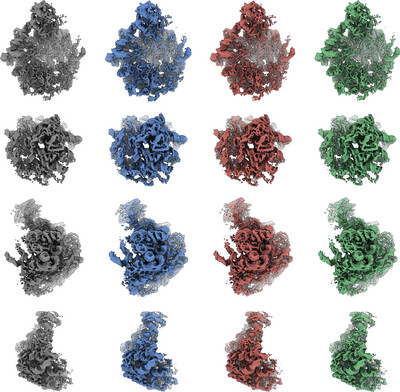
In the context of cryo-EM reconstruction, we provide a theoretical analysis showing that the condition number of the optimization problem is particularly large at high resolution, leading to slow convergence of gradient-based methods such as stochastic gradient descent. We then propose a method to overcome this issue by computing a preconditioner using Hutchinson's estimator, which results in improved convergence speed, as evidenced by numerical experiments.
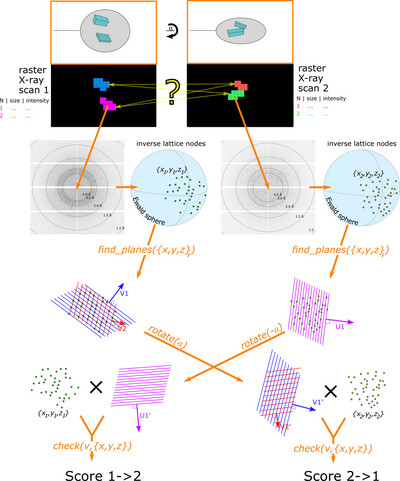
Enhanced capabilities for multi‐crystal data collection based on double mesh scans
- 344-356
- 2 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
Crystal structure of coagulation factor XII N‐terminal domains 1–5
- 380-393
- 2 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
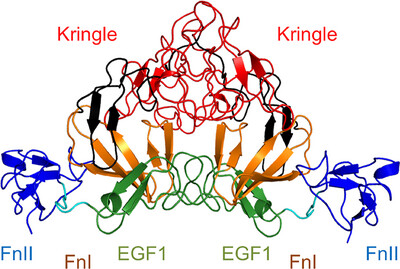
Factor XII (FXII) is a plasma serine protease which becomes activated by interactions with polyanions such as polyphosphates from bacteria, with Zn2+ as a critical cofactor. The crystal structure of FXII domains 1–5, coupled with a second crystal structure of the isolated FnII domain in complex with Zn2+ ions, advances our understanding of FXII structure and ligand recognition.
The following is a list of the most cited articles based on citations published in the last three years, according to CrossRef.
PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution
- 213-221
- 5 February 2010