Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
editorial
Foreword to the special virtual issue dedicated to the proceedings of the PhotonDiag2018 workshop on FEL Photon Diagnostics, Instrumentation, and Beamlines Design
- Pages: 250-253
- First Published: 10 March 2020
research papers
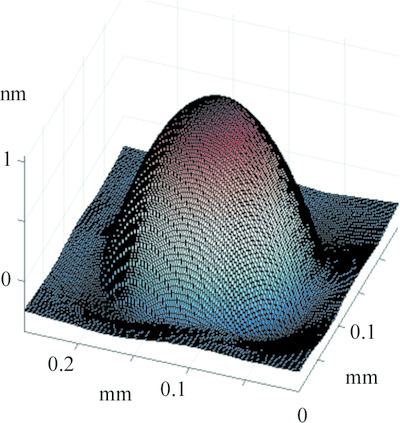
X-ray free-electron laser wavefront sensing using the fractional Talbot effect
- Pages: 254-261
- First Published: 12 February 2020
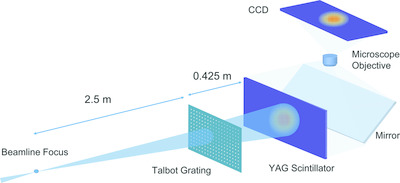
A wavefront sensor for an X-ray free-electron laser has been developed using the fractional Talbot effect. This wavefront sensor enables measurements over a wide range of energies, as is common on X-ray instruments, and is compatible with the high average power pulses expected in upcoming X-ray free-electron laser upgrades.
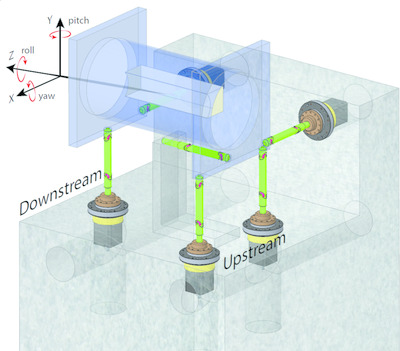
A five-axis parallel kinematic mirror unit for soft X-ray beamlines at MAX IV
- Pages: 262-271
- First Published: 29 January 2020
Understanding the mechanical limitations of the performance of soft X-ray monochromators at MAX IV laboratory
- Pages: 272-283
- First Published: 19 February 2020

At MAX IV, a fourth-generation, or diffraction-limited, synchrotron light source, six soft X-ray monochromators (Bloch, Veritas, HIPPIE, SPECIES, FinEstBeAMS and SoftiMAX beamlines) are examined with a focus on their resolving power, energy range and the time required to change measurement range. When measuring the mechanical resolution defined by angular vibrations, FinEstBeAMS shows a resolving power R of better than 30000 for all studied cff values, while, for HIPPIE, the resolving power for cff = 2.25 and higher and for energies lower than 1 keV is better than 100000.
X-ray optics and beam characterization using random modulation: theory
- Pages: 284-292
- First Published: 20 February 2020
X-ray optics and beam characterization using random modulation: experiments
- Pages: 293-304
- First Published: 20 February 2020
Modelling phase imperfections in compound refractive lenses
- Pages: 305-318
- First Published: 11 February 2020
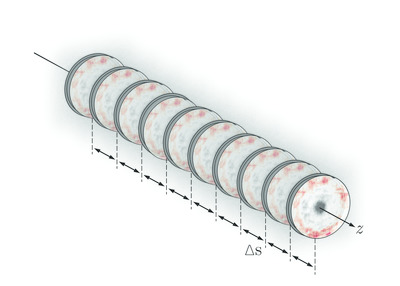
Coherent and partially coherent accurate wavefront propagation simulations using Synchrotron Radiation Workshop (SRW) through thick two-dimensional Be compound refractive lenses are presented, taking into account the effects of phase errors obtained by X-ray speckle vectorial tracking at the BM05 Instrumentation Beamline at the ESRF.
Room-temperature X-ray response of cadmium–zinc–telluride pixel detectors grown by the vertical Bridgman technique
- Pages: 319-328
- First Published: 27 January 2020
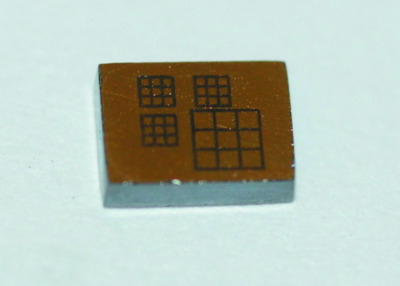
Sub-millimetre arrays with pixel pitch less than 500 mm, based on boron oxide encapsulated vertical Bridgman grown cadmium–zinc–telluride crystals, were fabricated. Excellent room-temperature performance characterizes the detectors even at high-bias-voltage operation (9000 V cm−1) with energy resolution of 1 keV FWHM at 60 keV.
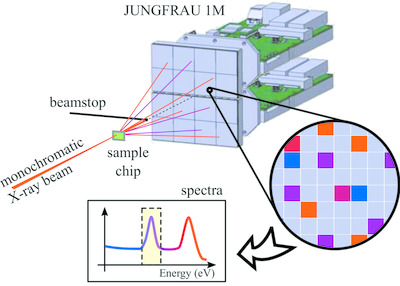
X-ray fluorescence detection for serial macromolecular crystallography using a JUNGFRAU pixel detector
- Pages: 329-339
- First Published: 11 February 2020
First pump–probe–probe hard X-ray diffraction experiments with a 2D hybrid pixel detector developed at the SOLEIL synchrotron
- Pages: 340-350
- First Published: 19 February 2020
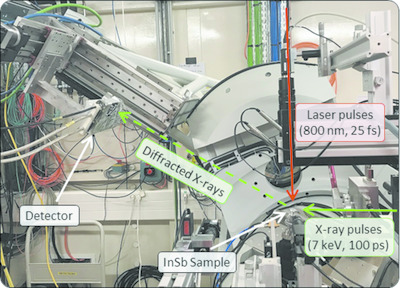
A new photon-counting camera based on hybrid pixel technology has been developed at the SOLEIL synchrotron; it allows the implementation of pump–probe–probe hard X-ray diffraction experiments for the first time. A benchmark experiment was successfully performed, showing the advantages of the pump–probe–probe scheme.
High-pressure developments for resonant X-ray scattering experiments at I16
- Pages: 351-359
- First Published: 27 February 2020
The HARE chip for efficient time-resolved serial synchrotron crystallography
- Pages: 360-370
- First Published: 27 February 2020
Development of shock-dynamics study with synchrotron-based time-resolved X-ray diffraction using an Nd:glass laser system
- Pages: 371-377
- First Published: 27 January 2020
Synchrotron radiation diffraction in a single crystal of paratellurite investigated with a new experimental scheme
- Pages: 378-385
- First Published: 11 February 2020
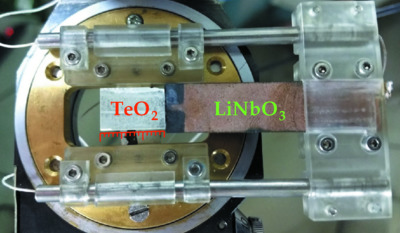
First results are presented for synchrotron radiation diffraction in a paratellurite (TeO2) single crystal investigated with a new experimental scheme consisting of a standard monochromator and a relatively narrow slit. A new method of measuring the angular position of the crystal by means of an adaptive piezoactuator is applied for the first time. The experimental curves are compared with the theoretical diffraction rocking curves of the paratellurite crystal, both theoretical and calculated taking into account the instrumental function.
A semi-analytical approach for the characterization of ordered 3D nanostructures using grazing-incidence X-ray fluorescence
- Pages: 386-395
- First Published: 11 February 2020
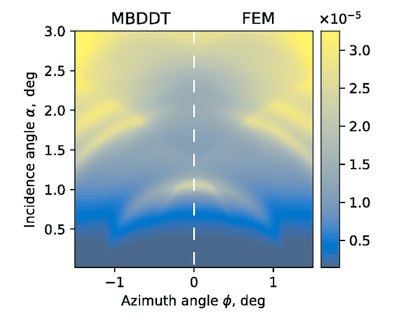
Following the recent demonstration of the sensitivity of grazing-incidence X-ray fluorescence to the lateral structure of periodic nano-patterned devices, a computational scheme for the simulation of experimental data is presented. This can be used for the element-selective analysis of 3D atomic distributions in nano-patterned structures.
Concentrated protein solutions investigated using acoustic levitation and small-angle X-ray scattering
- Pages: 396-404
- First Published: 12 February 2020
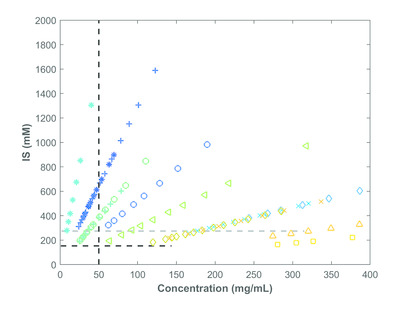
An acoustically levitated droplet has been used to collect synchrotron small-angle X-ray scattering at very high protein concentrations (>200 mg ml−1) – difficult to measure in standard flow-through cells. The data can be collected with minimal sample consumption. Details of the methodology and data treatment are shown thoroughly.
Seed-skewness algorithm for X-ray diffraction signal detection in time-resolved synchrotron Laue photocrystallography
- Pages: 405-413
- First Published: 11 February 2020
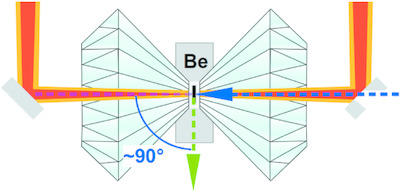
A portable on-axis laser-heating system for near-90° X-ray spectroscopy: application to ferropericlase and iron silicide
- Pages: 414-424
- First Published: 13 February 2020
X-ray absorption linear dichroism at the Ti K-edge of rutile (001) TiO2 single crystal
- Pages: 425-435
- First Published: 14 February 2020
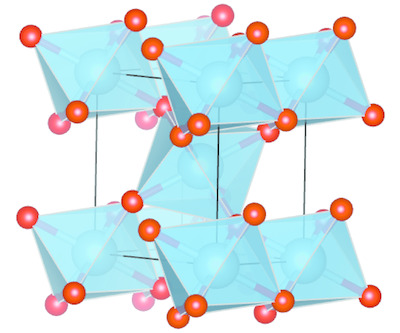
Linear dichroism at the Ti K-edge is investigated in rutile TiO2 single crystal. A complete assignment of the pre-edge is provided based on finite difference method calculations and spherical tensor analysis. The origin of weak peak A2 similar to anatase TiO2 is discussed from the presence of oxygen vacancies or from an intrinsic quadrupolar transition.
Theoretical development and experimental validation on the measurement of temperature by extended X-ray absorption fine structure
- Pages: 436-445
- First Published: 14 February 2020
Resonant inelastic X-ray scattering using a miniature dispersive Rowland refocusing spectrometer
- Pages: 446-454
- First Published: 20 February 2020
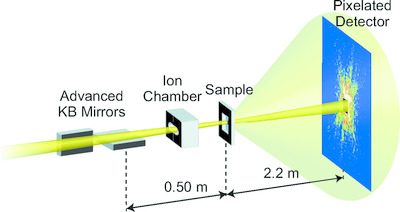
Nanoscale determination of interatomic distance by ptychography-EXAFS method using advanced Kirkpatrick–Baez mirror focusing optics
- Pages: 455-461
- First Published: 29 January 2020
Computer simulations of X-ray phase-contrast images and microtomographic observation of tubules in dentin
- Pages: 462-467
- First Published: 27 January 2020
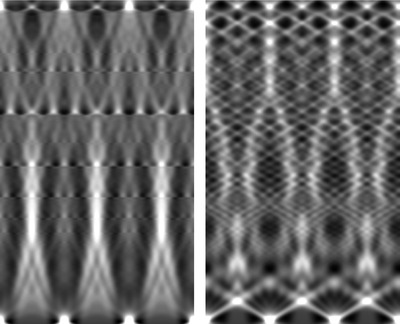
Problems of imaging dentinal tubules using synchrotron radiation (SR) are addressed. In computer modeling of a phantom material similar to dentin, it was assumed that the radiation was coherent and that the tubules were parallel to each other. Real millimetre-sized dentin specimens have been investigated by SR microtomography when the incident radiation is not fully coherent. Tomograms were reconstructed from experimental projections using an algorithm for incoherent radiation. The directions of the tubules in a volume of the specimens were generated. However, the tubule cross-section structure cannot be restored.
Fast diffraction-enhanced imaging using continuous sample rotation and analyzer crystal scanning
- Pages: 468-471
- First Published: 28 January 2020
A lathe system for micrometre-sized cylindrical sample preparation at room and cryogenic temperatures
- Pages: 472-476
- First Published: 29 January 2020
Limited angle tomography for transmission X-ray microscopy using deep learning
- Pages: 477-485
- First Published: 13 February 2020
Tomographic reconstruction with a generative adversarial network
- Pages: 486-493
- First Published: 19 February 2020
Transmission, refraction and dark-field retrieval in hard X-ray grating interferometry
- Pages: 494-502
- First Published: 26 February 2020
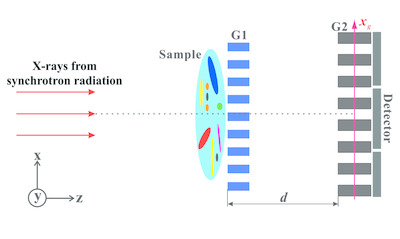
A three-image algorithm is proposed for quantitative transmission, refraction and dark-field retrieval in hard X-ray grating interferometry. The novel algorithm is theoretically derived, and validated by proof-of-principle synchrotron radiation experiments. Furthermore, the noise properties of the three retrieved signals are investigated in terms of the standard deviations.
short communications
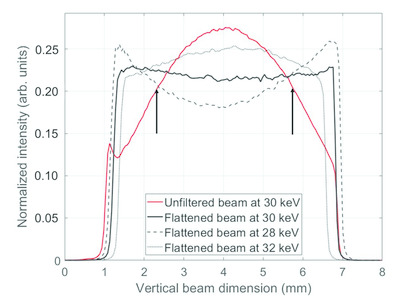
Flattening filter for Gaussian-shaped monochromatic X-ray beams: an application to breast computed tomography
- Pages: 503-506
- First Published: 27 January 2020
beamlines
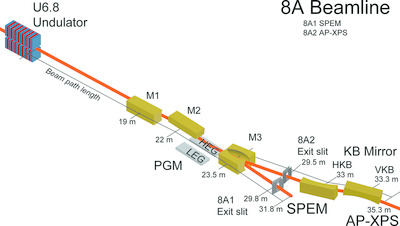
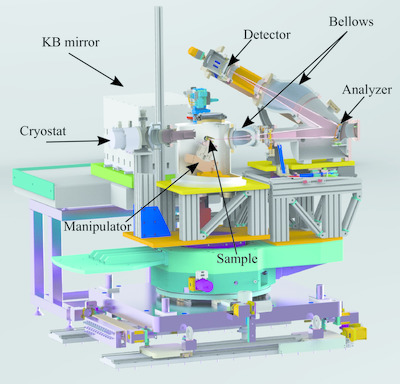
AP-XPS beamline, a platform for operando science at Pohang Accelerator Laboratory
- Pages: 507-514
- First Published: 28 January 2020
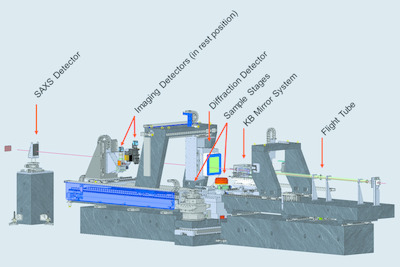
ID15A at the ESRF – a beamline for high speed operando X-ray diffraction, diffraction tomography and total scattering
- Pages: 515-528
- First Published: 28 January 2020
The HXD95: a modified Bassett-type hydrothermal diamond-anvil cell for in situ XRD experiments up to 5 GPa and 1300 K
- Pages: 529-537
- First Published: 29 January 2020
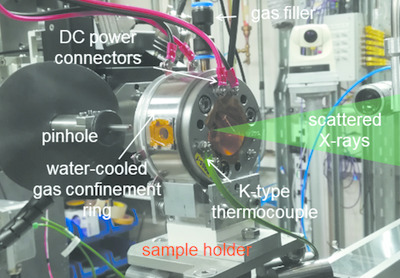
A Bassett-type hydrothermal diamond-anvil cell has been modified to enable in situ X-ray diffraction measurements on liquid samples up to 5 GPa and 1300 K at the Diamond Light Source. The new experimental setup provides a maximum accessible scattering vector Qmax of 18 Å−1 (at 56 keV) for improved resolution in G(r).
IRIXS: a resonant inelastic X-ray scattering instrument dedicated to X-rays in the intermediate energy range
- Pages: 538-544
- First Published: 26 February 2020
Development of XANES nanoscopy on BL7C at PLS-II
- Pages: 545-550
- First Published: 20 February 2020
computer programs
ProQEXAFS: a highly optimized parallelized rapid processing software for QEXAFS data
- Pages: 551-557
- First Published: 11 February 2020
New tools for calibrating diffraction setups
- Pages: 558-566
- First Published: 20 February 2020
PyXAS – an open-source package for 2D X-ray near-edge spectroscopy analysis
- Pages: 567-575
- First Published: 20 February 2020