Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
scientific commentaries
AlphaFold, small-angle X-ray scattering and ensemble modelling: a winning combination for intrinsically disordered proteins
- Pages: 1313-1314
- First Published: 27 September 2023
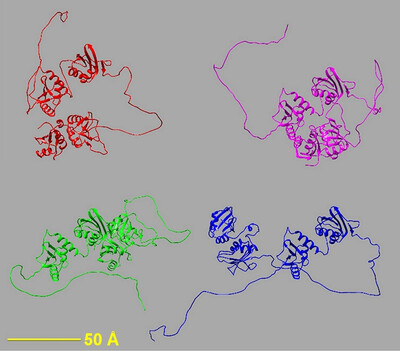
A recent article by Brookes, Rocco, Vachette & Trewhella [J. Appl. Cryst. (2023), 56, 910–926] on improving the accuracy of AlphaFold structural predictions for disordered proteins is discussed.
research papers
Indium Kα radiation from a MetalJet X-ray source: the long way to a successful charge-density investigation
- Pages: 1315-1321
- First Published: 05 September 2023
Indium Kα radiation from a MetalJet X-ray source: comparison of the Eiger2 CdTe and Photon III detectors
- Pages: 1322-1329
- First Published: 05 September 2023
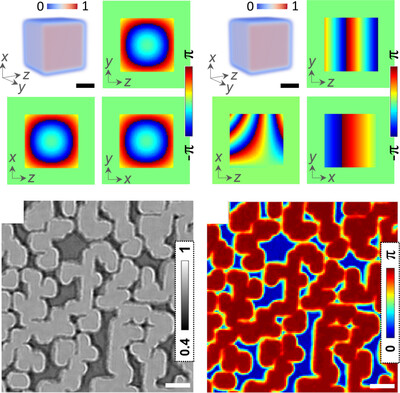
Strategy to simulate and fit 2D grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering patterns of nanostructured thin films
- Pages: 1330-1347
- First Published: 16 August 2023
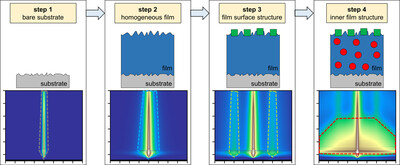
A strategy to simulate and fit 2D grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering patterns of supported, nanostructured soft-matter thin films using the distorted-wave Born approximation is introduced. The different scattering contributions of the nanostructure, surface roughness and background scattering are treated separately and are adjusted step by step. To minimize calculation efforts, 1D line cuts are chosen, in which the scattering is predominantly attributed to one of the contributions, and the parameters found are used in the subsequent steps. Hence, separate measurements of the bare substrate are beneficial.
Small-angle scattering from flat bilayers containing correlated scattering length density inhomogeneities
- Pages: 1348-1360
- First Published: 16 August 2023
A versatile approach to high-density microcrystals in lipidic cubic phase for room-temperature serial crystallography
- Pages: 1361-1370
- First Published: 18 August 2023
Shear influence on colloidal cluster growth: a SANS and USANS study
- Pages: 1371-1380
- First Published: 25 August 2023
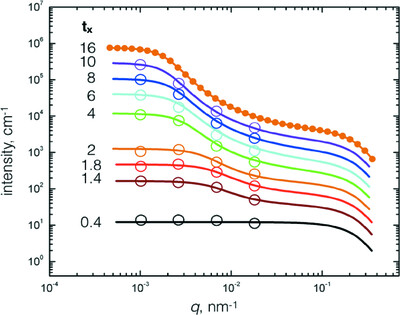
This study examines the time evolution of microscopic structure in a model industrial process, a sol of gel-initiated silica particles in a simple Couette shear field, using small-angle neutron scattering SANS) and ultra-small-angle neutron scattering (USANS) over a large range of scattering vector magnitudes/length scales. Comparison of the experimentally derived parameters with a simple theoretical model provides additional insight.
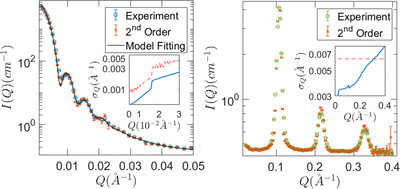
Retrieving the size distribution of SBA-15 mesopores from small-angle X-ray scattering data using a Monte Carlo method
- Pages: 1381-1391
- First Published: 01 September 2023
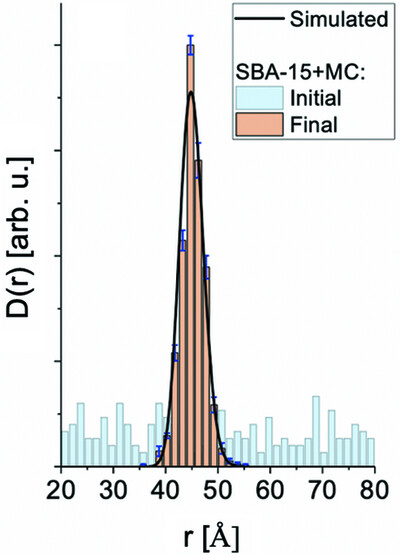
The new model proposed in this work allows retrieval of the mesopore size distribution of SBA-15 (and similar ordered mesoporous materials) from small-angle X-ray scattering data using a free modelling approach. According to the obtained results, even more complex size distributions can be recovered, such as the case of SBA-15 with expanded mesopores.
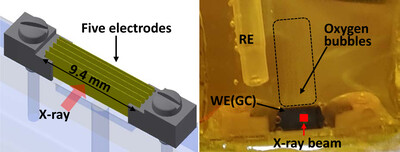
Multielectrode electrochemical cell for in situ structural characterization of amorphous thin-film catalysts using high-energy X-ray scattering
- Pages: 1392-1402
- First Published: 18 August 2023
Microstructure and texture analysis of 304 austenitic stainless steel using Bragg edge transmission imaging
- Pages: 1403-1415
- First Published: 25 August 2023
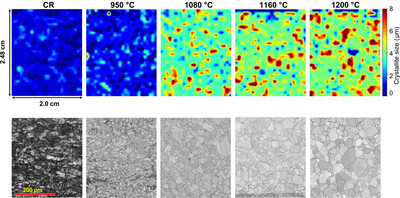
In this work, the crystallite size, texture and phase volume fraction of type 304 stainless steel samples were measured using Bragg edge imaging and were validated by the electron backscatter diffraction method. The Bragg edge imaging results were obtained using a compact accelerator neutron source.
High-resolution 3D grain orientation mapping by inclined scanning 3D X-ray diffraction microscopy
- Pages: 1416-1425
- First Published: 25 August 2023
Strain generated by the stacking faults in epitaxial SrO(SrTiO3)N Ruddlesden–Popper structures
- Pages: 1426-1434
- First Published: 01 September 2023
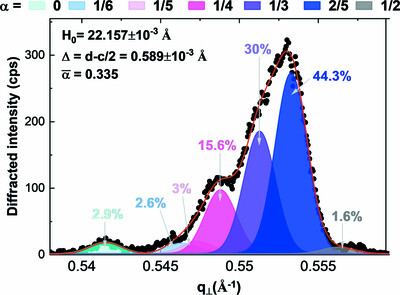
The residual mismatch related to stacking faults in SrTiO3-based Ruddlesden–Popper (RP) structures is shown to be accommodated by a delocalized mechanism of lateral strain transfer from the disturbed regions to the RP structure, generating a distribution of compressive strain in the latter. The methodology used to show this mechanism, based on X-ray diffraction experiments, also allows the assessment of the stacking fault spatial distribution and the accurate determination of the interplanar distance separating the two SrO planes forming the defects.
Grazing-emission X-ray fluorescence as a multiprobe tool for thin-film metrology
- Pages: 1435-1445
- First Published: 01 September 2023
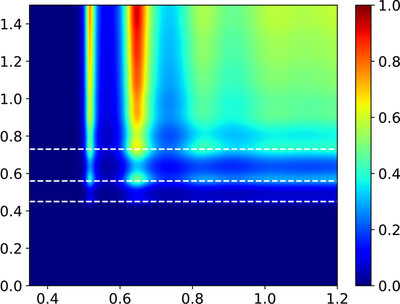
The multiprobe nature of the grazing-emission X-ray fluorescence approach in contrast to the conventional grazing-incidence X-ray fluorescence or X-ray standing-wave technique is investigated. A semi-analytic solution taking into account both grazing-incidence and grazing-emission geometries is derived. This solution is used to study the anomalous Kossel effect.
The dependence of X-ray elastic constants with respect to the penetration depth
- Pages: 1446-1455
- First Published: 01 September 2023
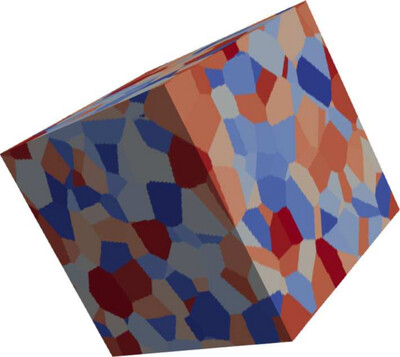
A numerical method that provides the surface and bulk X-ray elastic constants of non-textured polycrystalline materials is proposed. The results obtained for engineering materials with such a method indicate that, for crystalline materials with significant elastic anisotropy, the X-ray elastic constants depend on the penetration-depth-to-grain-size ratio.
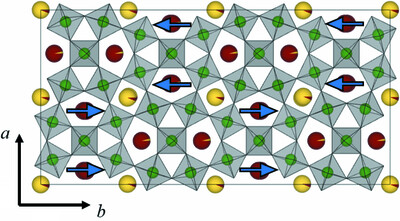
Revisiting the structures and phase transitions of Ba2NaNb5O15
- Pages: 1456-1465
- First Published: 05 September 2023
Significance of diffraction peak shapes in determining crystallite size distribution: a peak shape analysis procedure for pseudo-Voigt profiles and its application
- Pages: 1466-1479
- First Published: 05 September 2023
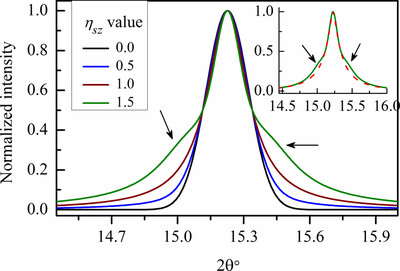
An unequivocal relationship between diffraction peak shape and crystallite size distribution has been derived. A procedure to separate the diffraction peak shape contribution arising from the effect of crystallite size is described. Application of this approach is established using several worked examples of practical situations from the literature.
Remote and automated high-throughput powder diffraction measurements enabled by a robotic sample changer at SSRL beamline 2-1
- Pages: 1480-1484
- First Published: 20 September 2023
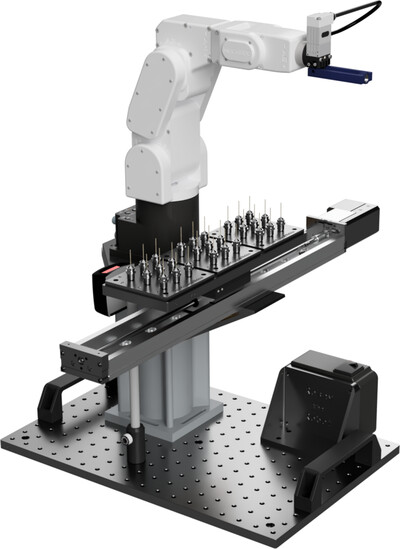

The general-purpose powder diffraction beamline at Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource (SSRL) is described. The latest developments at the beamline, including the implementation of a robotic sample changer for mail-in operations, are discussed and several datasets measured from this setup are included for reference.
Design and performance of the high-resolution stress and texture neutron diffractometer HETU
- Pages: 1485-1493
- First Published: 20 September 2023
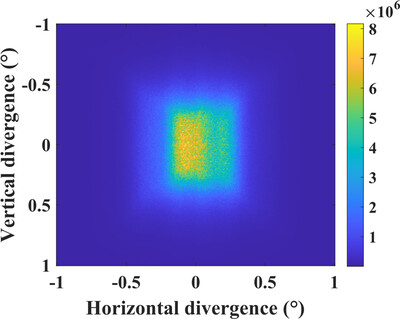
The HETU neutron diffractometer has been developed to enable a high instrument resolution measurement mode or a high neutron flux mode, with use of a double-focusing perfect single-crystal silicon monochromator or a highly oriented pyrolytic graphite monochromator, for investigations of residual stress and texture of engineering materials and components.
Explainable machine learning for diffraction patterns
- Pages: 1494-1504
- First Published: 20 September 2023

This article describes a qualitative study to unpack the internal workings of convolutional neural networks with the aim of visualizing information in the fundamental blocks of a standard network with serial crystallography data. Moreover, the study highlights region(s) or part(s) of an image that mostly contribute to a hit or miss prediction.
Optimizing the slicing pattern of stress-relief crystal analyzers for X-ray Raman scattering
- Pages: 1505-1511
- First Published: 20 September 2023

The batch production and performance evaluation of the spherically bent crystal analyzers fabricated for the `Qian Kun' X-ray Raman spectrometer at the High Energy Photon Source in China are reported. Radially dicing thin silicon wafers was found to be more effective in relieving stress than conventional strip cuts in the case that the total number of divided blocks is roughly the same.
Time-of-flight spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering applied to biological cell nuclei
- Pages: 1512-1521
- First Published: 27 September 2023
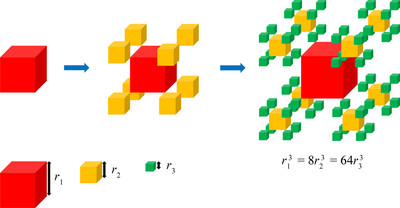
The applicability of time-of-flight spin-echo small-angle neutron scattering to the study of the inner fractal structure of the nuclei of biological cells is demonstrated. The method is used to show the logarithmic fractal structure of the large-scale organization of chromatin in rat lymphocyte nuclei.
Simultaneous SANS/FTIR measurement system incorporating the ATR sampling method
- Pages: 1522-1527
- First Published: 27 September 2023
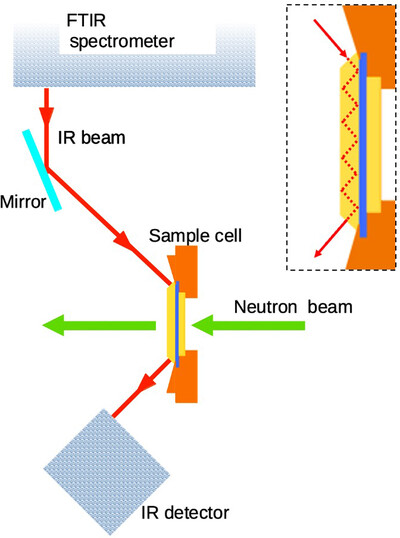
A simultaneous small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and infrared absorption measurement system using the attenuated total reflection (ATF) sampling method for Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy has been developed to handle samples with large infrared absorption. This system allows each measurement to be performed under appropriate conditions.
Bragg coherent modulation imaging for highly strained nanocrystals: a numerical study
- Pages: 1528-1536
- First Published: 27 September 2023
Desmearing small-angle scattering data by central moment expansions
- Pages: 1537-1543
- First Published: 27 September 2023
teaching and education
Escape our Lab: creating an escape room game in the field of materials science and crystallography
- Pages: 1544-1556
- First Published: 18 August 2023

A variable educational exit game is presented to stimulate interest of young people in STEM-related fields. The game addresses scientific content from crystallography, materials science and related fields and is suitable for a wide range of player groups, such as secondary school pupils, undergraduate students and teachers.
Remote laboratory training for high school students: grocery store based hands-on project in protein crystallography
- Pages: 1557-1568
- First Published: 18 August 2023

This paper describes a hands-on crystallization laboratory exercise that can be carried out remotely at home with safe household products. The project meets some of the US Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) goals for K-12 education, including teaching scientific practices that reflect those used by professional scientists.
short communications
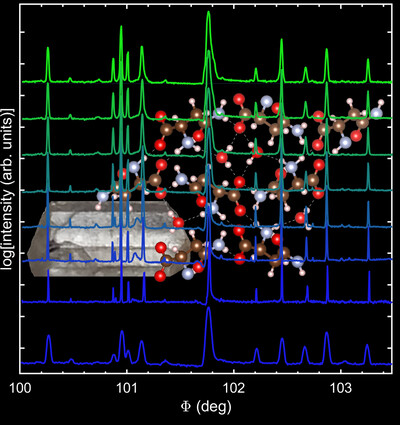
A novel energetic cocrystal of DATNBI/TNT with low sensitivity and an unexpected polymorphic transition
- Pages: 1569-1573
- First Published: 01 September 2023
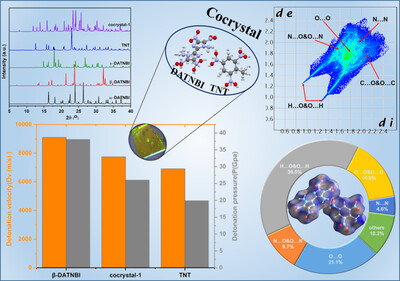
A cocrystal of 4,4′,5,5′-tetranitro-1H,1′H-(2,2′-biimidazole)-1,1′-diamine (DATNBI) and TNT with a molar ratio of 1:2 was synthesized for the first time. The thermal decomposition temperature and mechanical sensitivity of the cocrystal have been greatly improved compared with DATNBI, which provides a certain basic support for the subsequent cocrystal design of DATNBI.
computer programs
Introduction to Python Dynamic Diffraction Toolkit (PyDDT): structural refinement of single crystals via X-ray phase measurements
- Pages: 1574-1584
- First Published: 16 August 2023
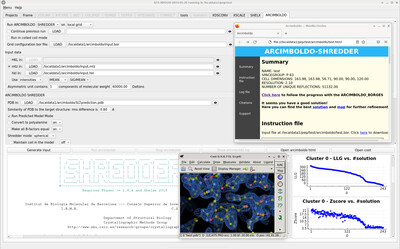
XDSGUI: a graphical user interface for XDS, SHELX and ARCIMBOLDO
- Pages: 1585-1594
- First Published: 05 September 2023
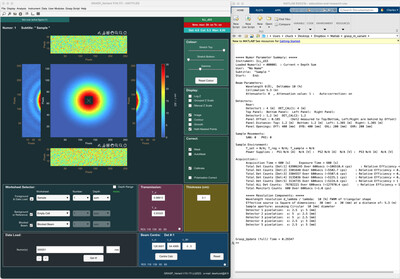
Graphical reduction and analysis small-angle neutron scattering program: GRASP
- Pages: 1595-1609
- First Published: 20 September 2023
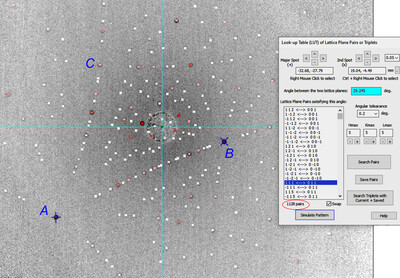
Upgraded LauePt4 for rapid recognition and fitting of Laue patterns from crystals with unknown orientations
- Pages: 1610-1615
- First Published: 27 September 2023