Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The role of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the antinociceptive and reparative actions of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with peripheral neuropathic pain
- Pages: 245-257
- First Published: 24 August 2023
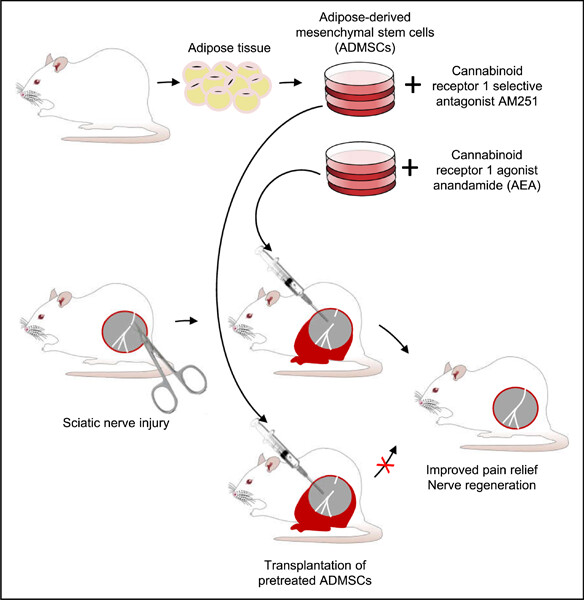
The study aimed to evaluate the antinociceptive and reparative effects of adipose-derived MSCs (ADMSCs) upon pharmacological modulation of cannabinoid CB1 receptor in peripheral tissues or on ADMSCs membranes in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy. The impact of the CB1 receptor state was evaluated by nociceptive responses, gait parameters, and histology. Obtained results indicate the predominant role of CB1 receptors on ADMSCs in their antinociceptive and reparative effects.
CCA repair or ECA ligation—Which middle cerebral artery occlusion is better in the reperfusion mouse model?
- Pages: 258-269
- First Published: 18 August 2023
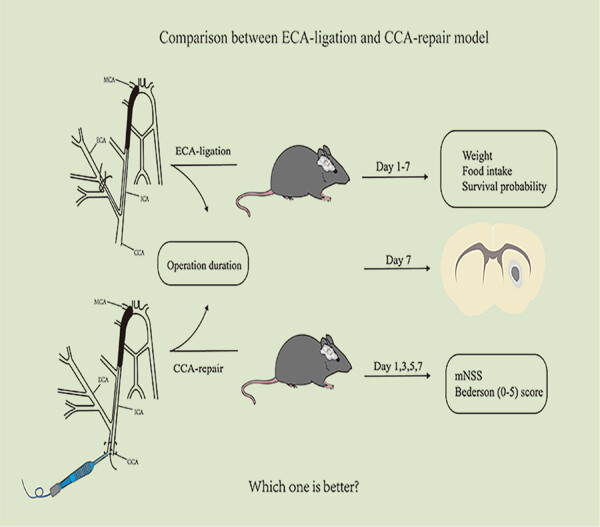
Two models were established: the common carotid artery-repair model and the external carotid artery-ligation model. The operation duration, postoperative body weight, and food intake within 7 days, neurological function deficits (modified neurological severity scores and Bederson [0–5] score) on Day 1/3/5/7 after operation, the number of intraoperative and postoperative deaths within 7 days and lesion volume on Day 7 were recorded in the two models. Which model is better for focal cerebral ischemia?
Study of the method of spinal cord neuron culture in Sprague–Dawley rats
- Pages: 270-280
- First Published: 25 December 2022
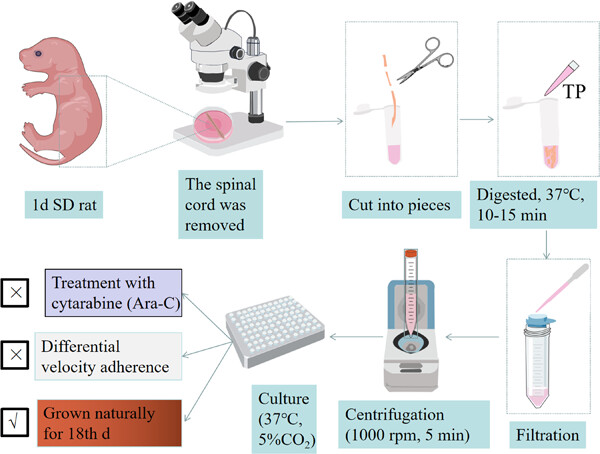
In this study, the separation and purification methods of spinal cord neuron (SPN) culture, that is, the cytarabine (Ara-C) inhibition method, the differential velocity adherent method, and natural growth medium for neurons, were compared. The neuron-specific medium can be grown naturally and cultivated to obtain SPNs of higher purity. Let them grow naturally, the heterogeneous cells appear aggregated and floated on the 11th day, and individual neurons can be clearly seen. On the 18th day, a large number of heterogeneous cells aggregated and died. This was especially obvious on the 20th day. Compared with the SPNs on the 18th day, the cell viability on the 18th day was better.
The interaction between instrumental activities of daily living and dual sensory function on cognition among the elderly in China: A cross-sectional survey
- Pages: 281-289
- First Published: 09 August 2023
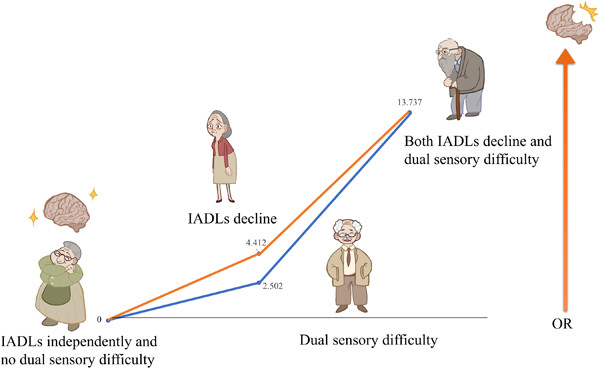
The aim of this study was to explore the interaction between instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) and dual sensory function in the elderly and its correlation with cognition. Logistic regression was conducted, and the relative excess risk ratio, attribution ratio, and interaction index (S) were calculated to examine the effects of IADLs, sensory function, and their interaction on cognition among the elderly. Results indicated that there was no multiplicative interaction between IADL decline and dual sensory difficulty on the risk of cognitive decline in the elderly, but there was additive interaction.
The effective doses of remimazolam besylate in the procedural sedation of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- Pages: 290-297
- First Published: 09 November 2022
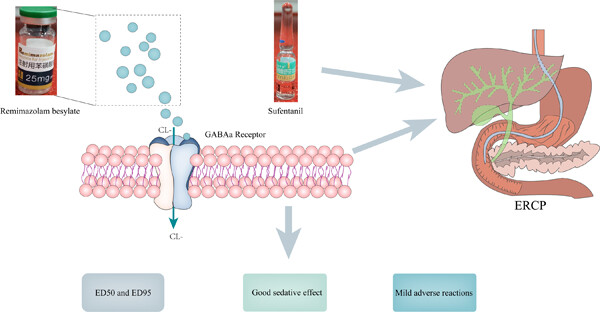
The combination of remimazolam besylate and sufentanil in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography yields a good sedative effect and only mild adverse reactions; importantly, we calculated a half-effective dose and 95% effective dose values for remimazolam besylate. The mechanism may be related to the action of remimazolam besylate on γ-aminobutyric acid type-A receptors, affecting the inward flow of chloride ions.
REVIEWS
Gold and silver nanoparticles in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diagnostics and treatments
- Pages: 298-315
- First Published: 14 August 2023
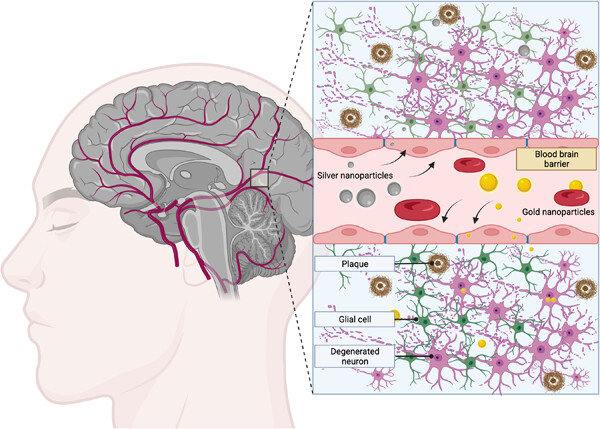
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are emerging as promising tools in the application for treating neurodegenerative diseases. Thanks to their unique properties, these nanoparticles (NPs) can be used for various purposes in this field of medicine. In the last years, more efforts are involved in the application of NPs as new agents both for early diagnosis and therapy of neurodegenerative diseases, thanks to their ability to overcome the Blood–Brain Barrier. Their unique physicochemical properties make them powerful tools for the development of a new nanoplatform to contrast Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Wnt signaling in synaptogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
- Pages: 316-325
- First Published: 06 September 2023
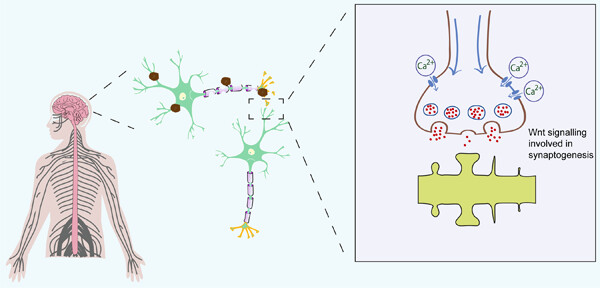
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the leading etiological factor in the development of dementia. A prominent causative factor for its onset is the aggregation of amyloid β-protein (Aβ). The presence of Aβ aggregates contributes to abnormal axonal and presynaptic terminal functioning, ultimately resulting in the formation of immature synapses connecting presynaptic terminals with a variety of dendritic spines. This process is potentially modulated by regulatory mechanisms orchestrated by the Wnt signaling pathway.
Routes and methods of neural stem cells injection in cerebral ischemia
- Pages: 326-339
- First Published: 06 August 2023
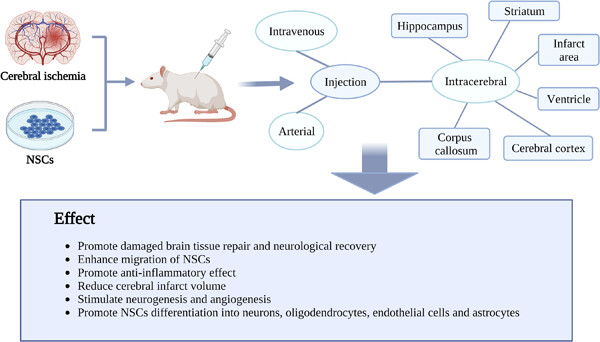
Cerebral ischemia is a serious cerebrovascular disease with the characteristics of high morbidity, disability, and mortality. Neural stem cells (NSCs) transplantation therapy is a very promising treatment method, which not only has anti-inflammatory, antiapoptotic, promoting angiogenesis, and neurogenesis effects, but also can improve some side effects related to thrombolytic therapy. At the same time, NSCs treatment could exert protective effects in alleviating cerebral ischemia-induced brain damage and neurological dysfunctions. However, the different injection routes and doses of NSCs determine diverse therapeutic efficacy. We summarized the injection routes of NSCs, which mainly include intravenous, arterial, as well as intracerebral injection via ventricles, striatum, corpus callosum, cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and infarct area. Moreover, the injection methods and doses of transplanted NSCs in cerebral ischemia were also introduced.
Basic information about memantine and its treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other clinical applications
- Pages: 340-348
- First Published: 06 June 2023
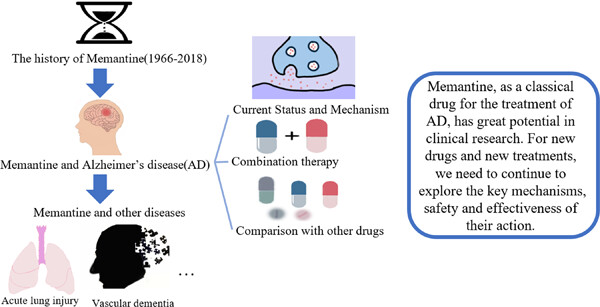
This article reviews the use of memantine in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Memantine and other drugs have limited efficacy and side effects in the treatment of AD. Combined therapy is one possible way to improve the efficacy of memantine therapy, which needs to be explored further. It is challenging to produce an entirely new drug, and it is important to examine the usefulness of memantine in other diseases.
CASE REPORT
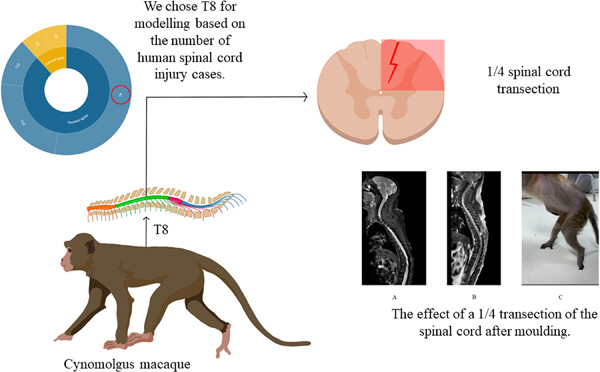
Development of an innovative minimally invasive primate spinal cord injury model: A case report
- Pages: 349-356
- First Published: 10 July 2023