Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Mitochondrial aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis: Insights and therapeutic implications
- Pages: 69-80
- First Published: 16 April 2024
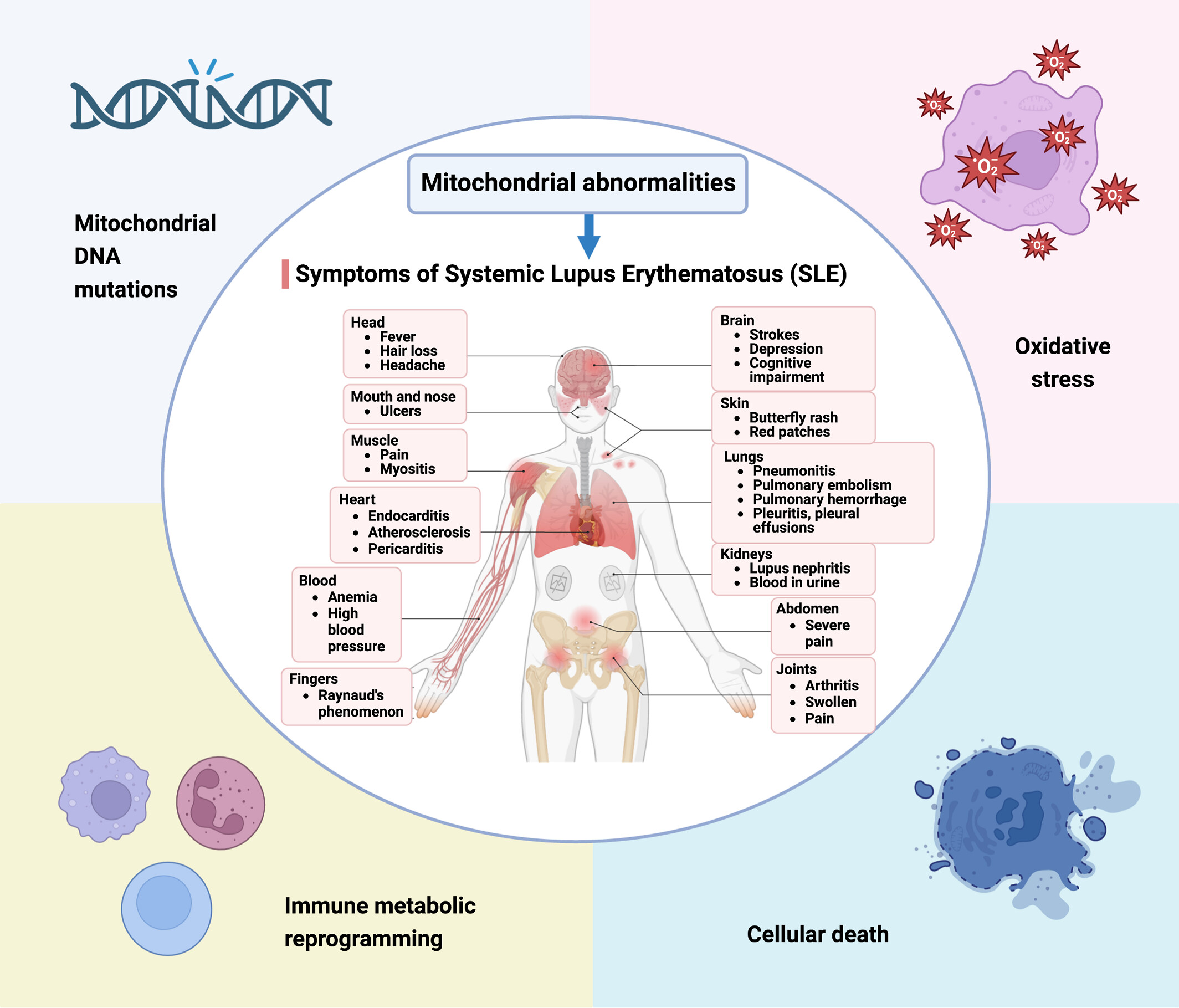
Mitochondrial abnormalities are crucial in the progression of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with key elements like mitochondrial DNA mutations, oxidative stress, and immune metabolic reprogramming leading to cellular death. These dysfunctions result in an array of SLE symptoms, pointing toward mitochondrial pathways as potential therapeutic targets for improved patient outcomes.
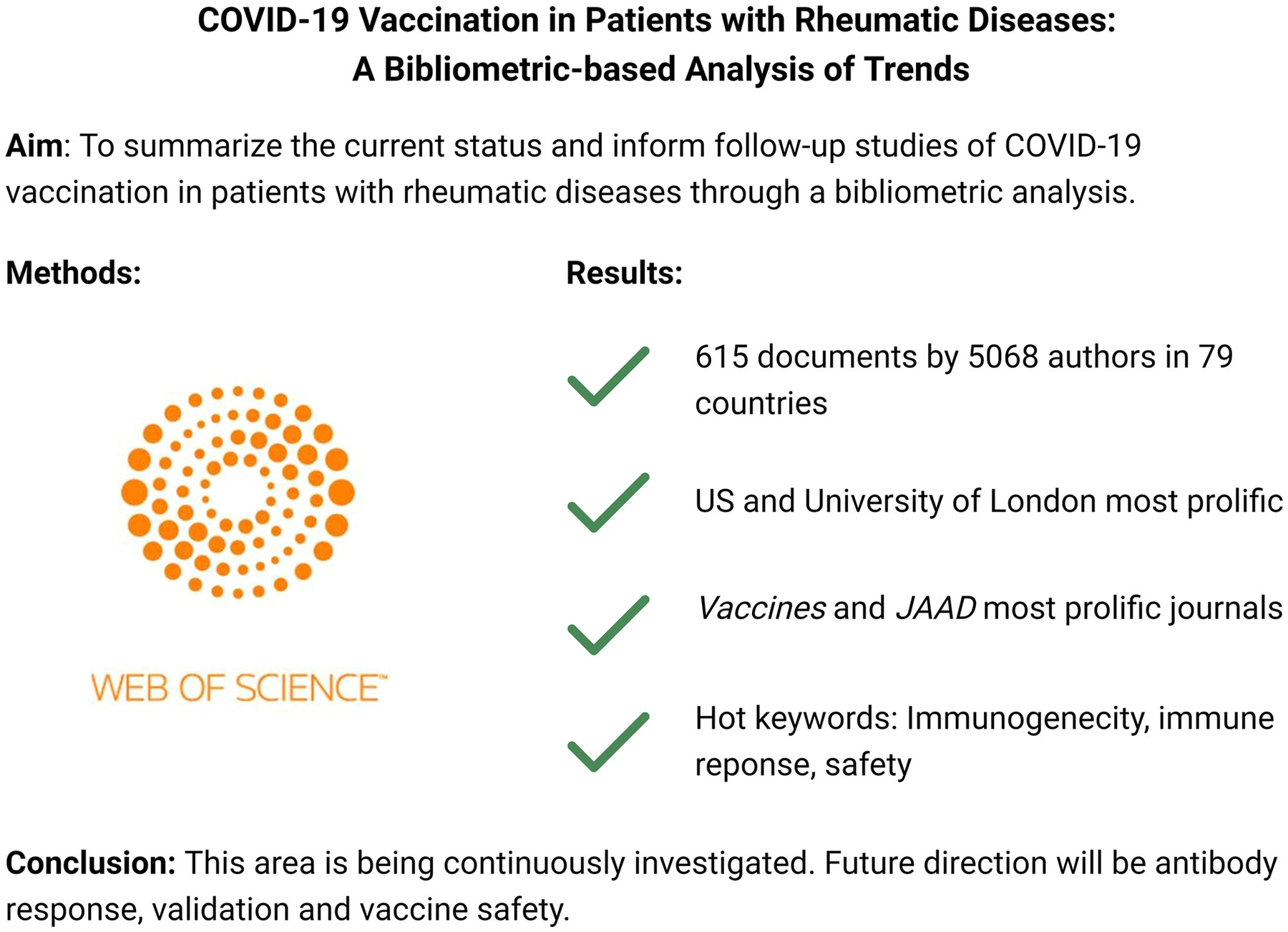
Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination in patients with rheumatic diseases: A bibliometric-based analysis of trends
- Pages: 81-89
- First Published: 04 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Enhanced therapeutic effects of apoptotic cell-conditioned mesenchymal stem cells in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice
- Pages: 90-98
- First Published: 18 April 2024
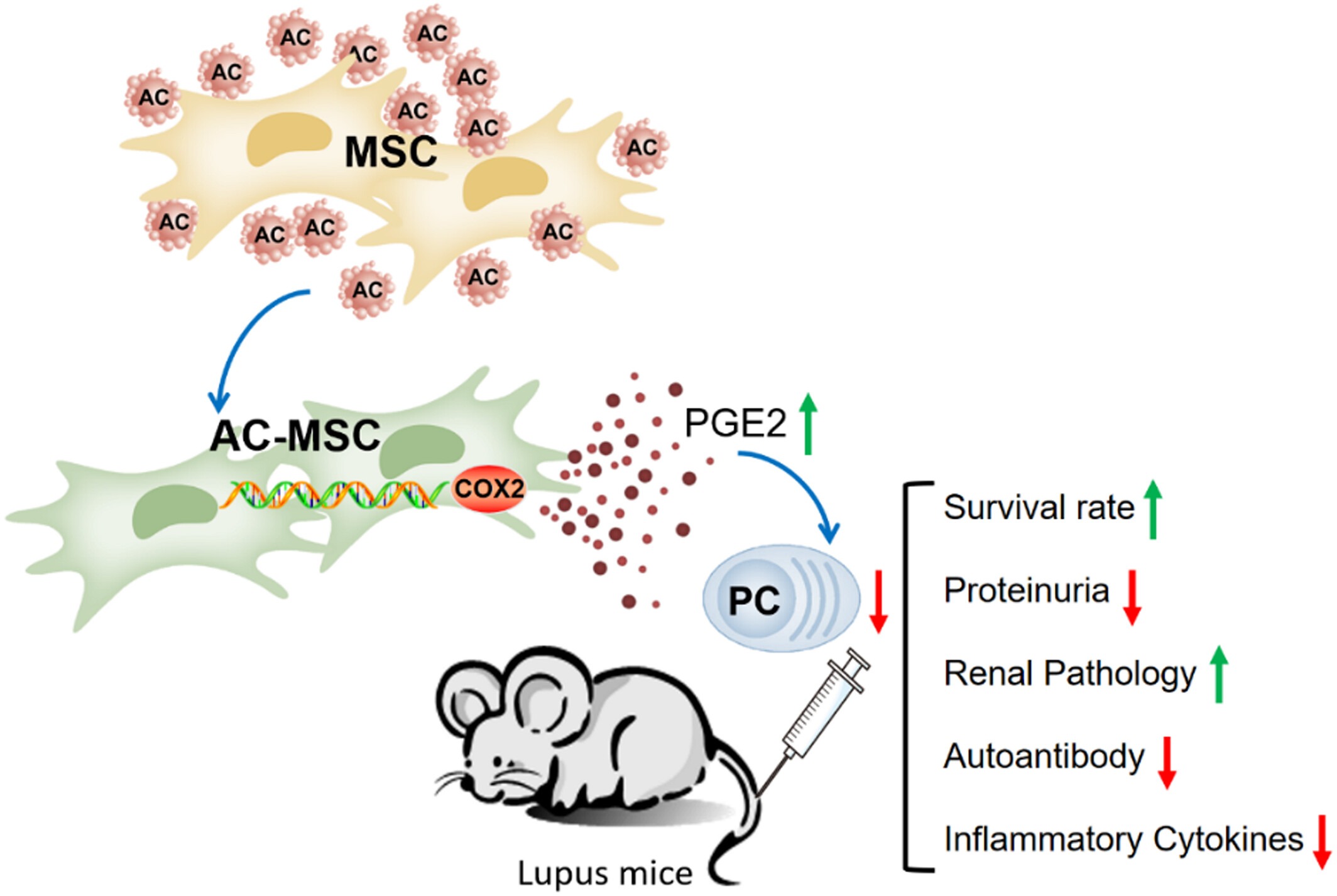
Apoptotic cell (AC)-conditioned mesenchymal stem cells exhibited enhanced therapeutic effects in lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice, partially mediated by cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2. Precondition ACs may be a new strategy for mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in treating systemic lupus erythematosus.
SLAMF8 as a potential biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis identified by comparing peripheral blood mononuclear cells, fibroblast-like synoviocytes, and synovial tissue using bioinformatics analysis
- Pages: 99-108
- First Published: 08 May 2024
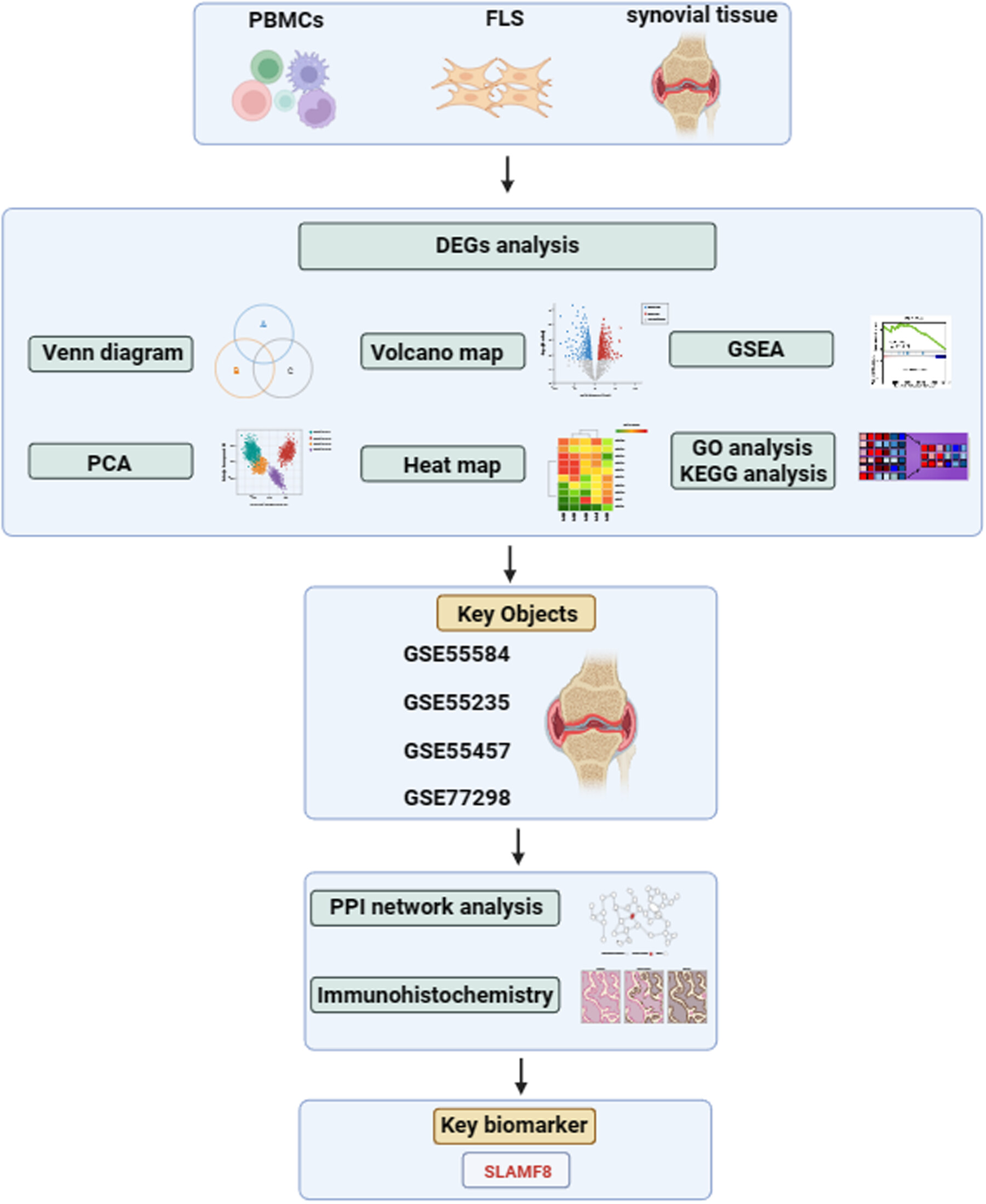
Microarray datasets of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis, and healthy control were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. Venn diagram, principal component analysis, heat map, volcano map, gene set enrichment analysis, gene ontology, and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes were used to analyze the data. Synovial tissue was identified as the key research objects. Further by protein–protein interaction network analysis of the four synovial tissue datasets and validation with immunohistochemistry of patients with RA and collagen-induced arthritis mice models, we identified that SLAMF8 may be a key biomarker for RA.
Assessing the causality of interferon-γ and its receptor 1/2 with systemic lupus erythematosus risk using genetic data
- Pages: 109-118
- First Published: 13 May 2024
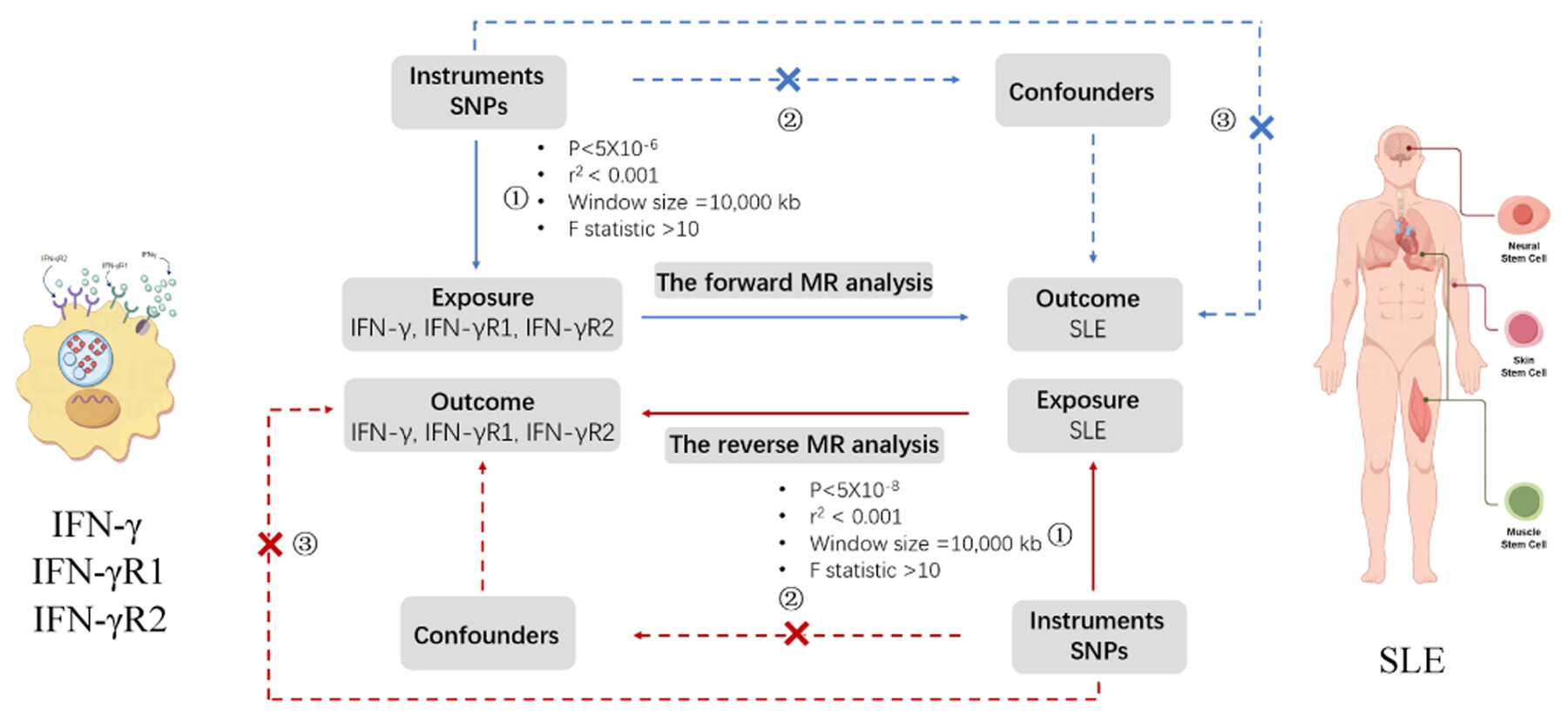
This study aims to assess the causal association between Interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IFN-γ receiver α (IFN-γR1), IFN-γ receiver β (IFN-γR2) and Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) within a bidirectional Mendelian-randomization design. Bidirectional two-sample MR was performed using inverse variance weighting (IVW), MR-Egger regression, and weighted median methods. A series of sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the robustness of the results. Our study provides new insights into the role of IFN-γ, IFN-γR1, and IFN-γR2 in the treatment of SLE.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Integrated analysis of lncRNAs expression profiling in systemic lupus erythematosus
- Pages: 119-121
- First Published: 06 March 2024
Combination therapy with methylprednisolone, rituximab, and tofacitinib in antimelanoma differentiation-associated 5 gene dermatomyositis with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease
- Pages: 122-125
- First Published: 12 March 2024
Advancements in therapeutic paradigm: Harnessing IL-17A inhibitor secukinumab to ameliorate psoriasis vulgaris in the presence of resistant pericardial effusion
- Pages: 126-128
- First Published: 24 January 2024
Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with homonymous hemianopia
- Pages: 129-130
- First Published: 02 February 2024
RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS
Fibroblast diversity and clinical associations in systemic sclerosis
- Page: 131
- First Published: 25 April 2024
CORRIGENDUM
Correction to “Molecular insights into onset of autoimmunity in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients”
- Page: 132
- First Published: 07 May 2024