Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
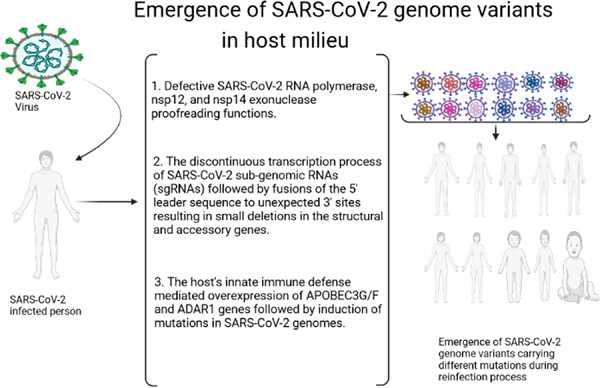
Perceptions into causes and consequences of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants
- Pages: 1-8
- First Published: 27 February 2023
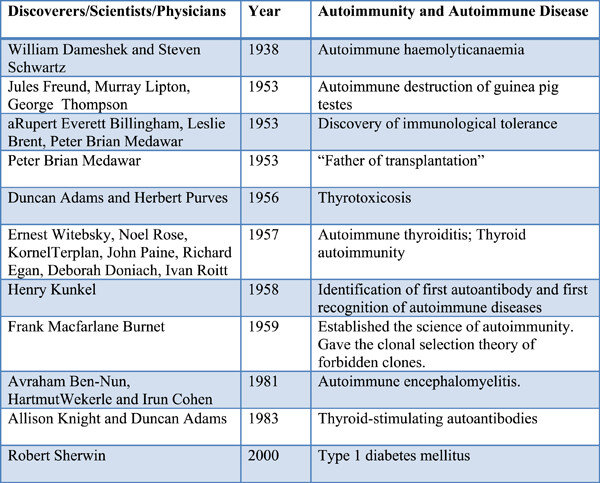
Origins and history of autoimmunity—A brief review
- Pages: 9-14
- First Published: 21 September 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
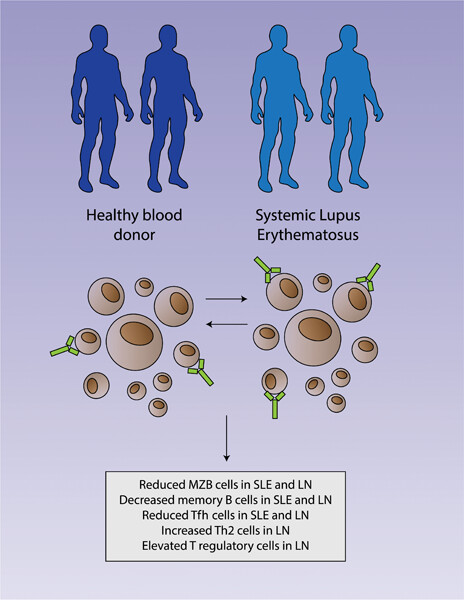
Immunophenotyping identifies distinct cellular signatures for systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis
- Pages: 15-25
- First Published: 23 November 2022
Impact of pretransplant asplenia vaccination on anti-A/B antibody titers in prospective ABO incompatible kidney transplant recipients
- Pages: 26-34
- First Published: 10 January 2023
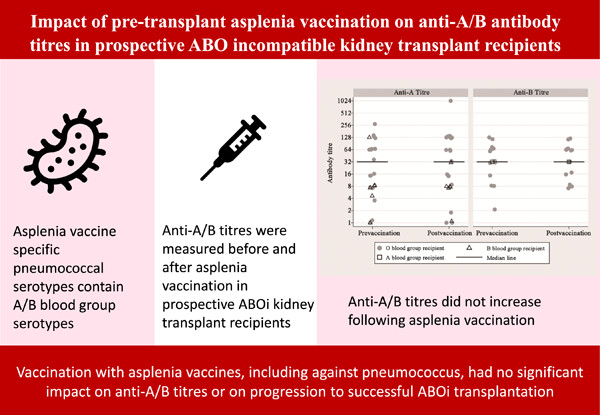
Vaccination before transplantation is recommended. Pneumococcal vaccines contain A/B blood group antigens which might increase anti-A/B titers. Potential ABO incompatible transplant recipients were assessed for a rise in anti-A/B titers following asplenia vaccination (including against pneumococcus). There was no clinically relevant rise in anti-A/B titers following vaccination. No transplant was delayed or cancelled due to a rise in titers following vaccination.
Long-term prognosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis treated with therapeutic low-density lipoprotein-apheresis in patients with severe kidney dysfunction and proteinuria
- Pages: 35-42
- First Published: 27 March 2023
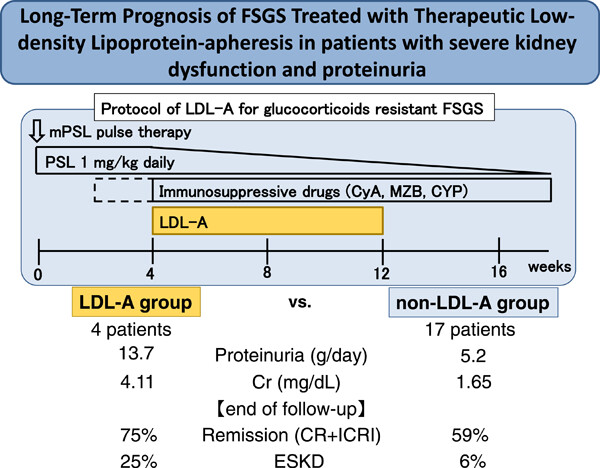
The prognosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) patients with nephrotic syndrome is poor. We investigated the effectiveness of treatment in 50 patients with primary FSGS. Low-density lipoprotein-apheresis (LDL-A) was performed in 4 patients who presented with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome. In comparison with 17 patients who did not receive LDL-A after 1989, the LDL-A group had higher urinary protein excretion (13.7 vs. 5.2 g/day, P = 0.053) and serum creatinine (4.11 vs. 1.65 mg/dL) levels at onset. Nevertheless, the LDL-A group showed a numerically higher remission rate (75% vs. 59%) compared with the nonlipoprotein-apheresis group.
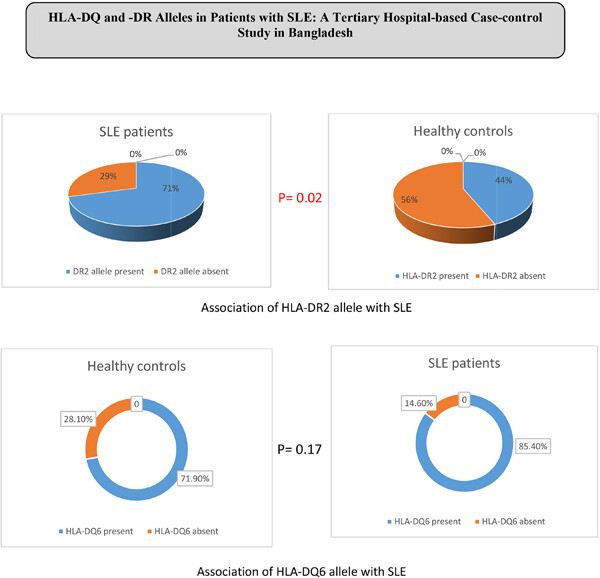
HLA-DQ and -DR alleles in patients with SLE: A tertiary hospital-based case–control study in Bangladesh
- Pages: 43-49
- First Published: 24 February 2023
CASE REPORTS
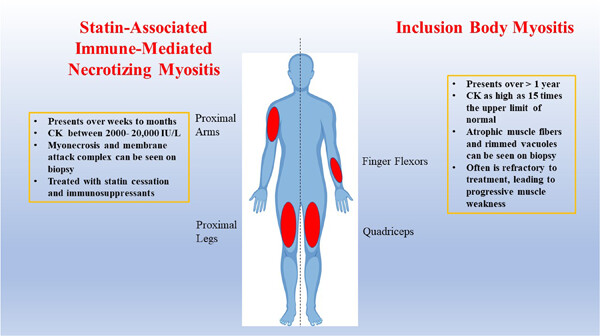
Phenotypical statin-associated immune-mediated necrotizing myositis with histological features of inclusion body myositis
- Pages: 50-55
- First Published: 24 November 2022
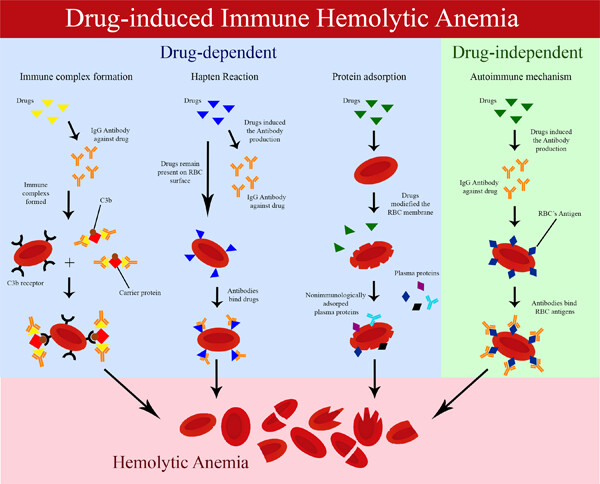
Acute kidney injury following autoimmune hemolytic anemia due to simultaneous use of ciprofloxacin and hydrochlorothiazide: A case report and review of the literature
- Pages: 56-62
- First Published: 27 February 2023
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Peripheral smear reckons the nature of IgM cold agglutinins: A case-based study asserting the role of thermal amplitude and clonality
- Pages: 63-65
- First Published: 04 November 2022