Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
“Closing the chasm” – guidelines bridge the gap from evidence to implementation
- Pages: 163-166
- First Published: 22 September 2021
GUIDELINES
Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of childhood obstructive sleep apnea (2020)
- Pages: 167-187
- First Published: 05 August 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Clinical characteristics and effectiveness of antiviral agents in hospitalized children with infectious mononucleosis in China: A multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 188-194
- First Published: 22 September 2021
FAM89A and IFI44L for distinguishing between viral and bacterial infections in children with febrile illness
- Pages: 195-202
- First Published: 22 September 2021
Epidemiological characteristics and clinical manifestations of pediatric patients with COVID-19 in China: A multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 203-210
- First Published: 12 August 2021
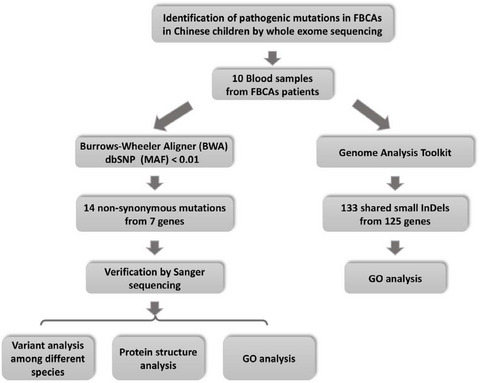
Identification of potential pathogenic mutations in Chinese children with first branchial cleft anomalies detected by whole-exome sequencing
- Pages: 211-216
- First Published: 23 June 2021
REVIEW
Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 in children: A review of the current knowledge
- Pages: 217-228
- First Published: 17 August 2021
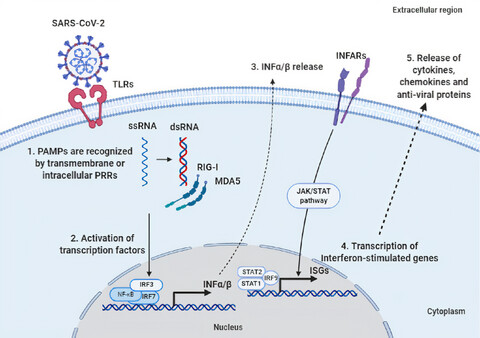
Despite the limited immunological studies from children with COVID-19, this review compares data between adults and children in terms of innate and adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2, discusses the possible reasons why children are mostly asymptomatic, and highlights unanswered or unclear immunological issues.
Antimicrobial stewardship program in pediatric medicine
- Pages: 229-238
- First Published: 22 September 2021
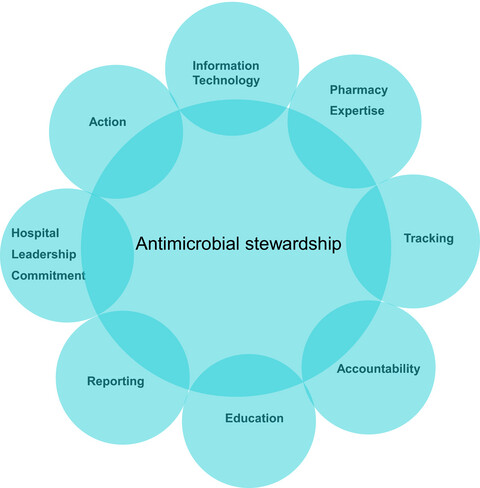
The rising threats from antimicrobial resistance due to inappropriate utilization of antimicrobial agents in health care including the pediatric population have been a topic of concern at the global level for the last several decades. The antimicrobial stewardship program (ASP) is a multidisciplinary institutional initiative focusing primarily on the improvement of antimicrobial prescribing practices and limiting inappropriate use. ASPs play an important role in the implementation of healthcare strategies in pediatrics worldwide to reduce antimicrobial resistance. Many published reports demonstrate how adapted ASPs in pediatrics result in improvement of unnecessary antimicrobial utilization, decreasing drug resistance and treatment failure, minimization of adverse clinical outcomes, decreasing healthcare costs and hospital length of stay, and optimization of diagnostic strategies. However, some barriers in pediatric ASP still exist. This narrative review describes core elements of ASP, the impact of implemented ASPs in pediatric healthcare, and the challenges of pediatric ASP as seen by the authors.
CASE REPORT
Toxoplasma gondii infection in children after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 239-243
- First Published: 22 September 2021
An infrequent cause of neonatal upper airway obstruction: Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis presenting to a remote facility
- Pages: 244-246
- First Published: 21 June 2021
SHORT COMMUNICATION
A brief introduction to the FUTang Updating medical REcords (FUTURE) database
- Pages: 247-248
- First Published: 22 September 2021







.png)

