Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
How to interpret the results of clinical studies: “Multicenter cutting-edge study” or “real-world big data study”?
- Pages: 344-345
- First Published: 27 April 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Essential updates 2020/2021: Recent topics in surgery and perioperative therapy for esophageal cancer
- Pages: 346-357
- First Published: 07 February 2023
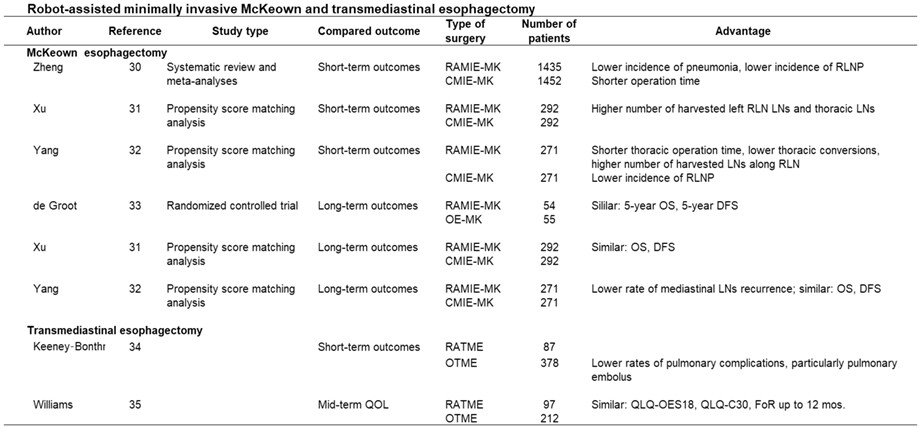
There were advantages and disadvantages in relation to the short-term outcomes of robot-assisted minimally invasive McKeown esophagectomy (RAMIE-MK) as compared with completely minimally invasive McKeown esophagectomy (CMIE-MK). However, there were no significant differences in the long-term outcomes between RAMIE-MK and CMIE-MK. The short-term and mid-term outcomes between robot-assisted minimally invasive transmediastinal esophagectomy (RATME) and open transmediastinal esophagectomy (OTME) were also compared. Although RATME has some disadvantages, such as a higher rate of pulmonary complications as compared with OTME, these are expected to be overcome in the future.
Essential updates 2021/2022: Surgical outcomes of oligometastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 358-366
- First Published: 18 January 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Annual report on National Clinical Database 2020 for gastroenterological surgery in Japan
- Pages: 367-406
- First Published: 09 February 2023
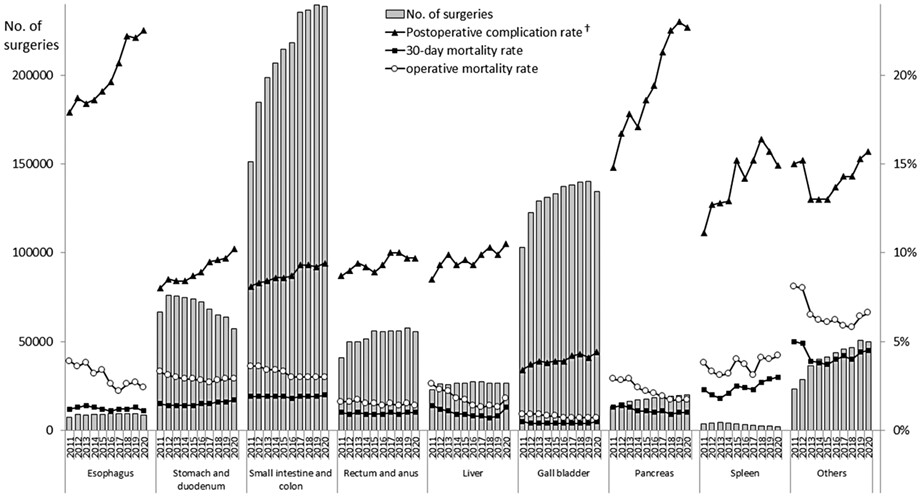
This study presents the annual report on the National Clinical Database 2020 for gastroenterological surgery in Japan. This manuscript revealed a consistent increase of the number of surgeries, especially with endoscopic surgeries, and aging of the Japanese population. Moreover, it indicated the good safety of Japanese gastroenterological surgeries, most of which have been increasingly carried out by the board-certified surgeons.
Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on gastroenterological surgeries in 2020: A study using the National Clinical Database of Japan
- Pages: 407-418
- First Published: 18 November 2022
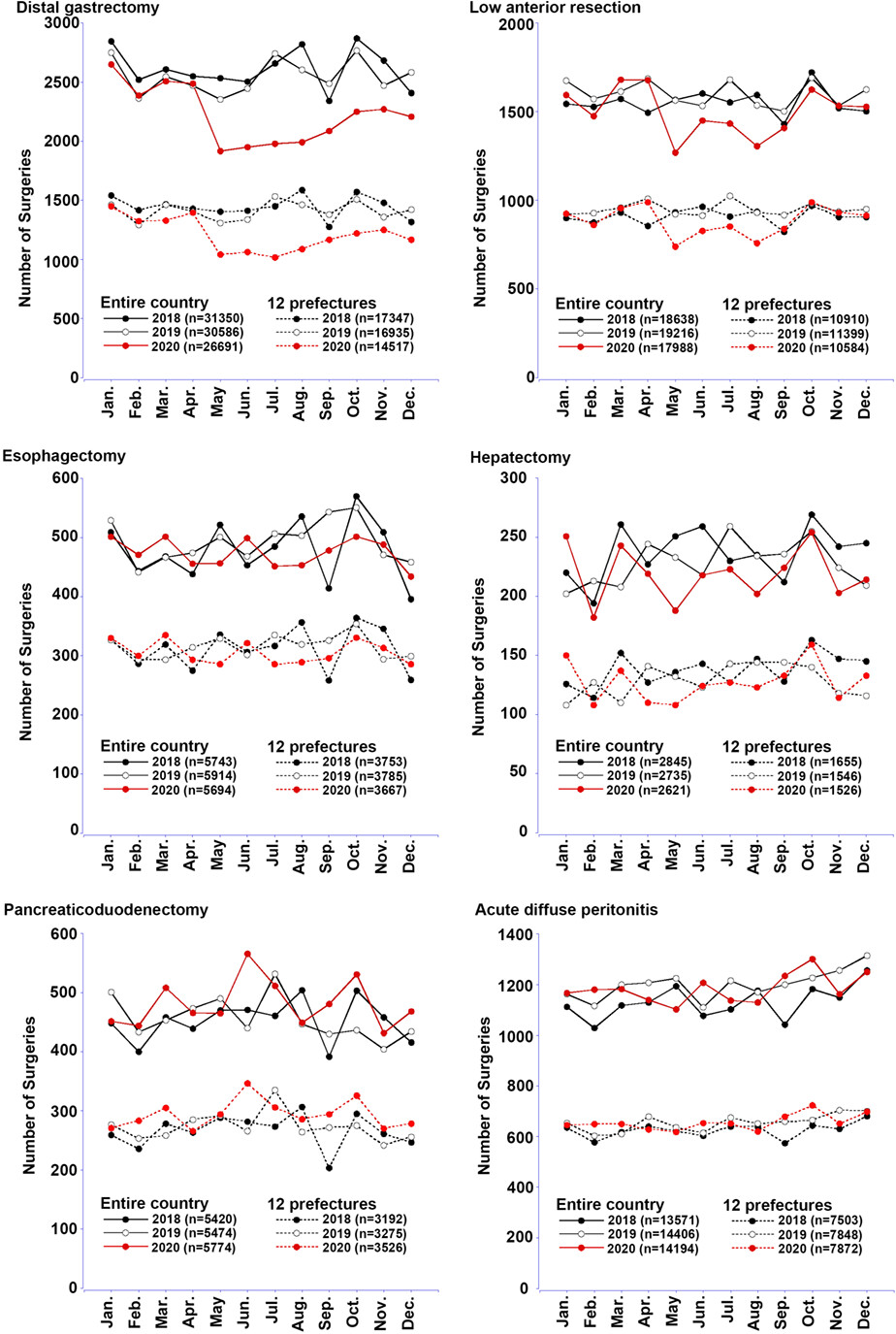
The number of surgeries for gastroenterological cancer across Japan declined soon after the state of emergency declared during the COVID-19 pandemic. The remarkable decline in T1/T2 tumors is suggestive of the prioritization or loss of the opportunity for cancer screening. The rates of severe complications and mortality were not worsened by COVID-19, even for acute diffuse peritonitis. However, the observed reduction in the cases and lack of rebound deserve further evaluation and public motivation to promote cancer screening.
Long-term changes in bone mineral density in postoperative patients with esophageal cancer
- Pages: 419-429
- First Published: 29 November 2022
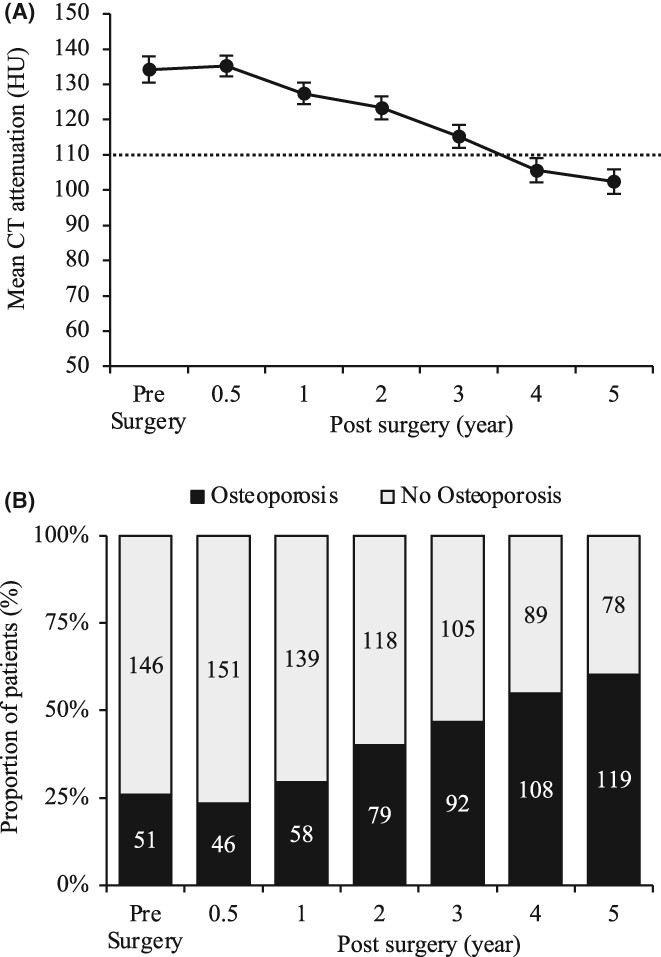
The aim of this study was to evaluate long-term changes in bone mineral density after esophagectomy and identify the risk factors for postoperative osteoporosis. Esophageal cancer survivors are more likely to develop osteoporosis after esophagectomy, with risk factors including both preoperative patient factors and postoperative factors.
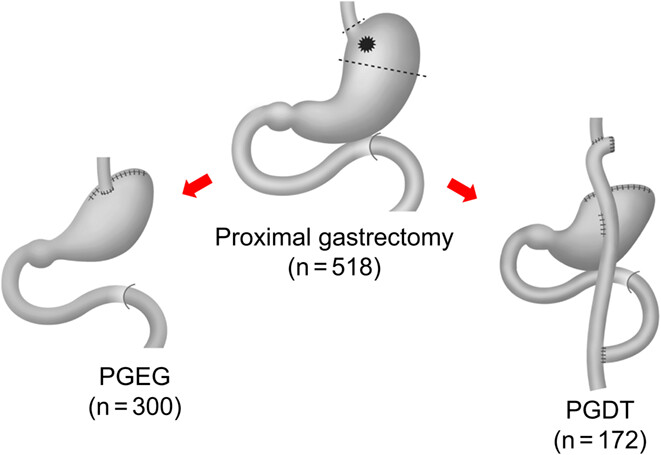
Quality of life comparison between esophagogastrostomy and double tract reconstruction for proximal gastrectomy assessed by Postgastrectomy Syndrome Assessment Scale (PGSAS)-45
- Pages: 430-440
- First Published: 15 December 2022
Prophylactic effect of negative-pressure wound therapy and delayed sutures against incisional-surgical site infection after emergency laparotomy for colorectal perforation: A multicenter retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 441-449
- First Published: 27 November 2022
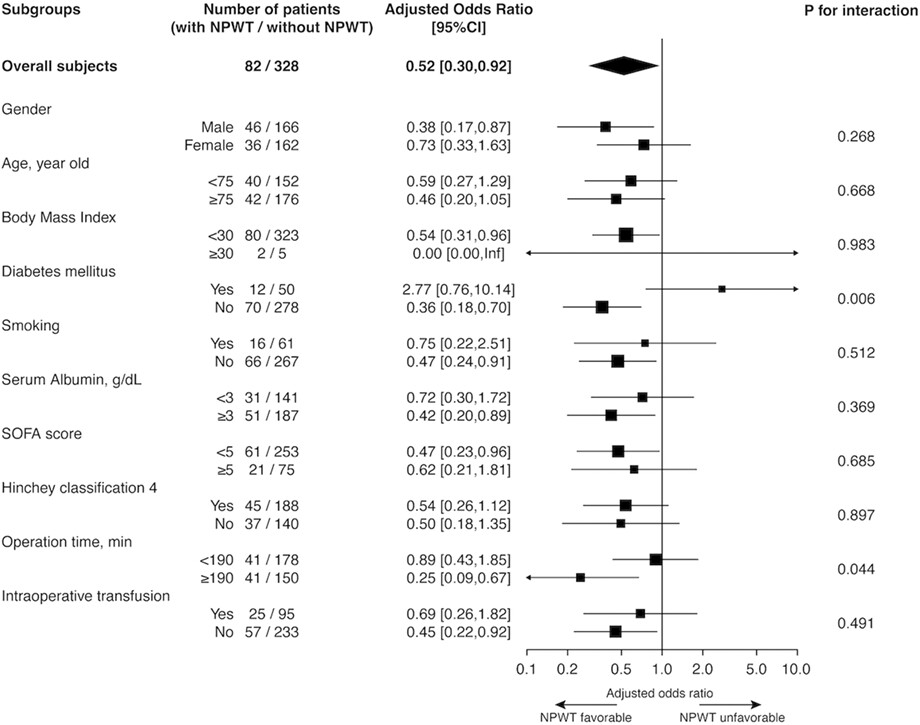
The prophylactic use of negative-pressure wound therapy was associated with a lower incidence of incisional surgical site infection after emergency surgery for colorectal perforation. Patients without diabetes mellitus or with longer operative times (≥190 min) might benefit from negative pressure wound therapy.
Mechanical and oral antibiotics bowel preparation for elective rectal cancer surgery: A propensity score matching analysis using a nationwide inpatient database in Japan
- Pages: 450-457
- First Published: 29 November 2022

Using the Japanese National Database, we showed that mechanical and oral antibiotics bowel preparation for rectal cancer surgery is associated with a decreased incidence of postoperative complications without increasing the incidence of CD colitis or MRSA colitis. In fact, mechanical bowel preparation alone is still the most major bowel preparation for rectal cancer surgery in the real world.
Long noncoding RNA 01534 maintains cancer stemness by downregulating endoplasmic reticulum stress response in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 458-470
- First Published: 29 December 2022
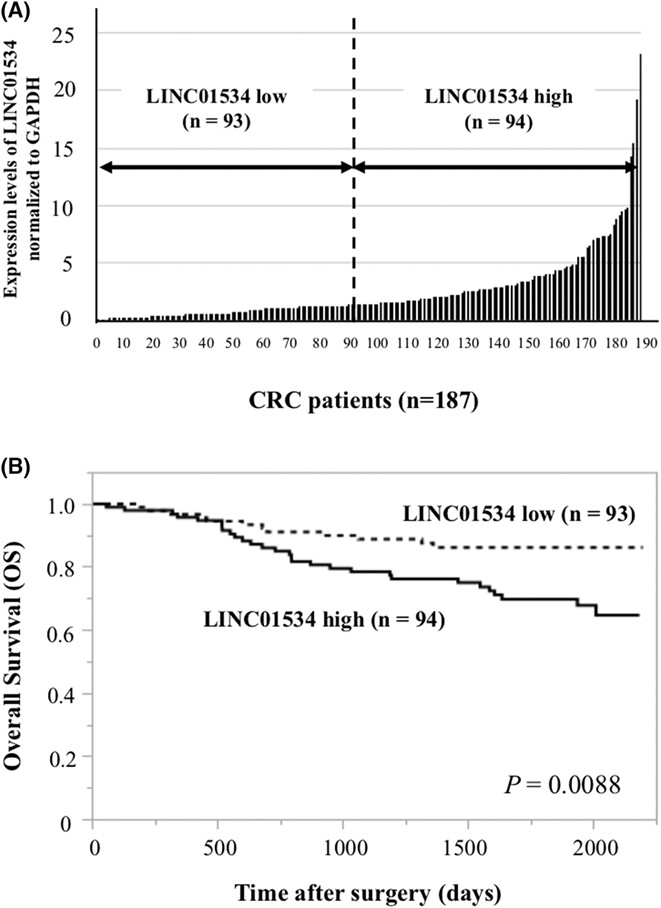
Long noncoding RNA 01534 (LINC01534) had a function in maintenance of cancer stemness and coordinated suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Moreover, we found that high expression of LINC01534 was associated with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. This study suggested that targeting LINC01534 is a potential therapeutic option against CRC that may improve outcome in CRC patients.
Changes in operative trends and short-term outcomes of surgery for congenital biliary dilatation in adults using real-world data: A multilevel analysis based on a nationwide administrative database in Japan
- Pages: 471-478
- First Published: 18 October 2022
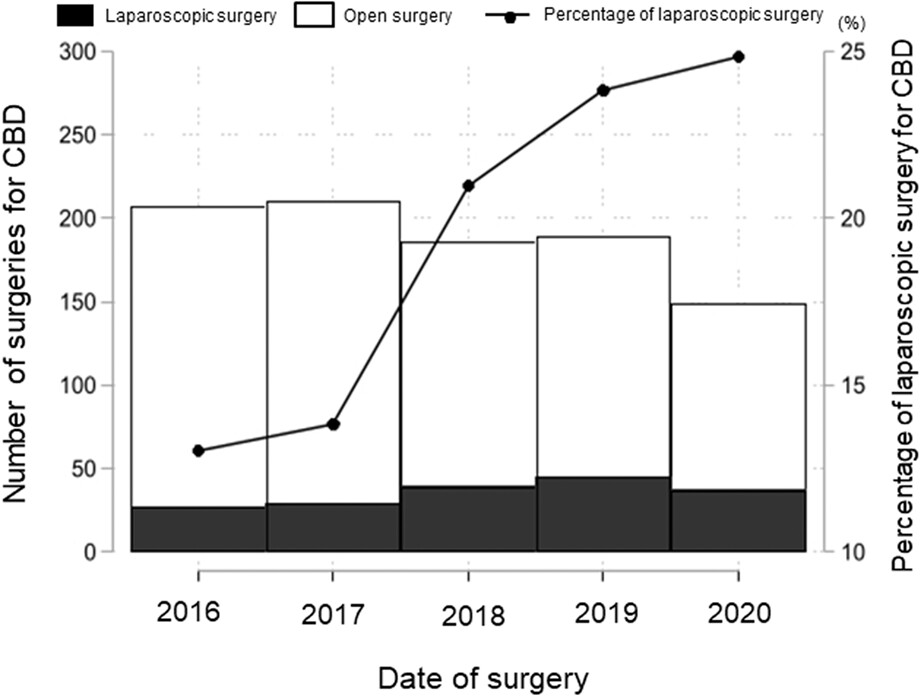
Our real-world data highlight that laparoscopic surgery for CBD had short-term results comparable to those of open surgery. The rate of laparoscopic surgery has been increasing every year; however, the number of cases is still low, and the high cost of laparoscopic surgery is an issue that requires further research to resolve. More high-quality studies are needed to further validate our conclusions and long-term outcomes.
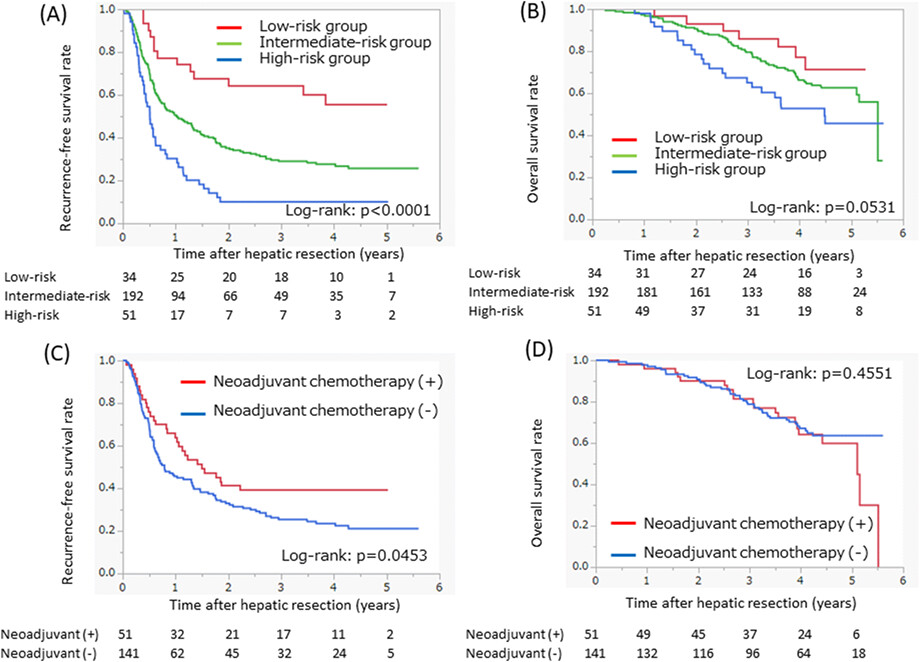
Clinical outcomes of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for resectable colorectal liver metastasis with intermediate risk of postoperative recurrence: A multi-institutional retrospective study
- Pages: 479-490
- First Published: 21 October 2022
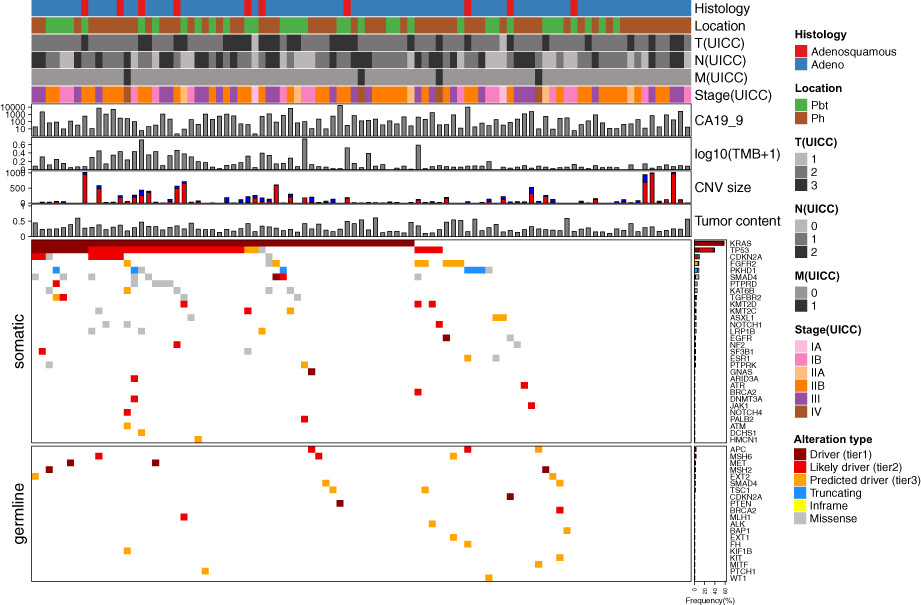
Genomic landscape of pancreatic cancer in the Japanese version of the Cancer Genome Atlas
- Pages: 491-502
- First Published: 27 November 2022
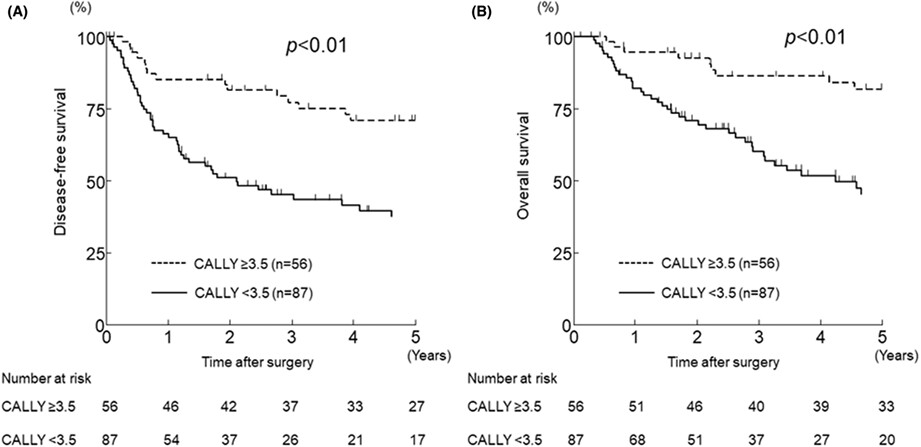
The impact of C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte (CALLY) index on the prognosis of patients with distal cholangiocarcinoma following pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Pages: 503-511
- First Published: 18 November 2022
Clinical implications and optimal extent of lymphadenectomy for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A multicenter analysis of the therapeutic index
- Pages: 512-522
- First Published: 27 November 2022
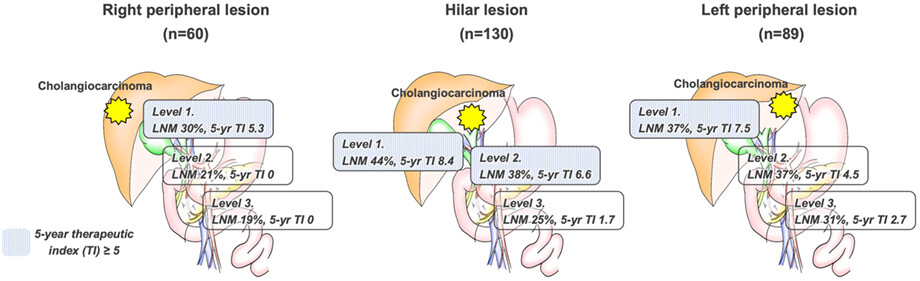
Lymph node metastases are lethal prognostic factors in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC). Lymphadenectomy is crucial for accurate staging and hoped-for as possible oncological treatment in ICC. A prognostic value of lymphadenectomy could be proven by analysis of the therapeutic index, especially in the hilar type. Lymphadenectomy should be a minimal requirement for the multimodal treatment of ICC. The implication and extent of lymphadenectomy for ICC should rely on tumor location.
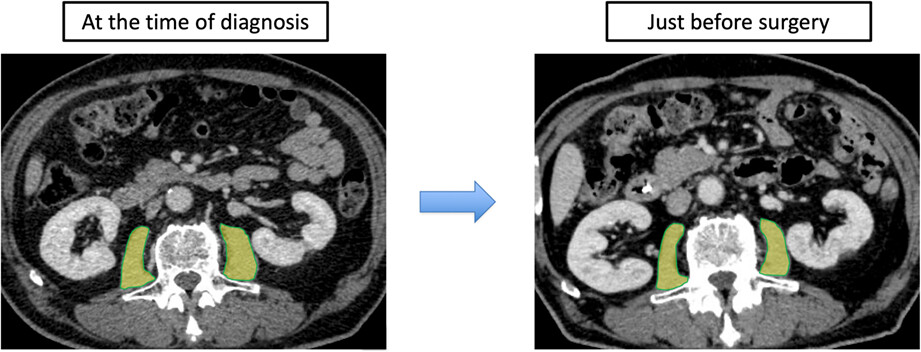
Prognostic impact of preoperative skeletal muscle change from diagnosis to surgery in patients with perihilar cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 523-532
- First Published: 11 December 2022
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Letter to the Editor Re: Yamamoto R, Sugiura T, Ashida R, Ohgi K, Yamada M, Otsuka S, and Uesaka K. Prognostic value of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and the surgical margin in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2022; 6:307–315
- Pages: 533-534
- First Published: 12 January 2023
The authors reply: Re: Yamamoto R, Sugiura T, Ashida R, Ohgi K, Yamada M, Otsuka S, and Uesaka K. Prognostic value of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and the surgical margin in extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2022;6:307–315
- Pages: 535-536
- First Published: 21 February 2023