Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorials
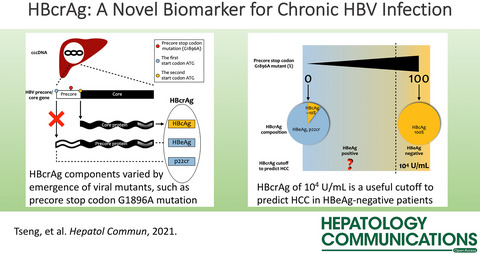
Looking Into the Crystal Ball: A Novel Biomarker for Outcomes of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection
- Pages: 5-7
- First Published: 26 December 2021
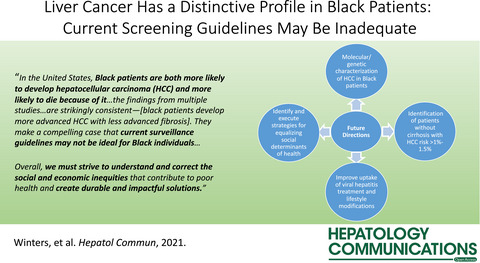
Liver Cancer Has a Distinctive Profile in Black Patients: Current Screening Guidelines May Be Inadequate
- Pages: 8-11
- First Published: 23 September 2021
Review
Role of Cholesterol-Associated Steatohepatitis in the Development of NASH
- Pages: 12-35
- First Published: 24 August 2021
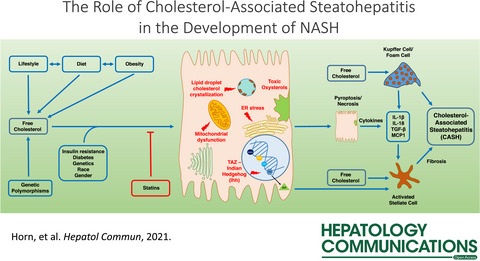
Free cholesterol accumulates in the liver in some patients with NAFLF and promotes the necroinflammation and fibrosis typical of NASH. Cholesterol-associated steatohepatitis (CASH) plays an important role in the development and progression of NASH. Randomized controlled trials are needed to demonstrate whether statins or statin/ezetimibe combination can effectively reverse steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with NASH.
Original Articles
Ultrasensitive Assay for Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidences During Entecavir
- Pages: 36-49
- First Published: 16 September 2021
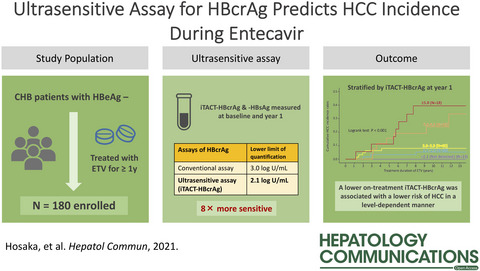
We examined the potential of HBcrAg and HBsAg measured by ultrasensitive assays for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with entecavir (ETV). The adjusted hazard ratio for HCC incidence was significantly lower in patients with HBcrAg ≤ 2.9 log U/mL at year 1 than in those in the high HBcrAg cohort. The measurement of HBcrAg via the ultrasensitive assay has a better potential for predicting HCC during antiviral treatment than the current HBcrAg assay.
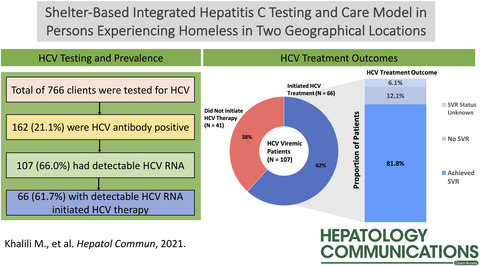
Shelter-Based Integrated Model Is Effective in Scaling Up Hepatitis C Testing and Treatment in Persons Experiencing Homelessness
- Pages: 50-64
- First Published: 10 October 2021
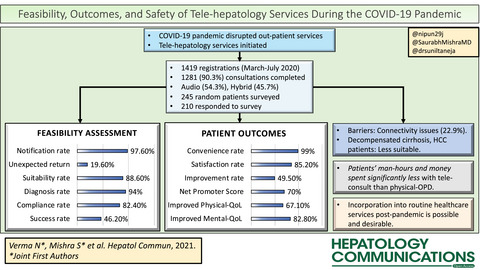
Feasibility, Outcomes, and Safety of Telehepatology Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Pages: 65-76
- First Published: 21 April 2021
Distinct Hepatic Gene-Expression Patterns of NAFLD in Patients With Obesity
- Pages: 77-89
- First Published: 11 August 2021
Dietary Risks for Liver Mortality in NAFLD: Global Burden of Disease Data
- Pages: 90-100
- First Published: 08 July 2021
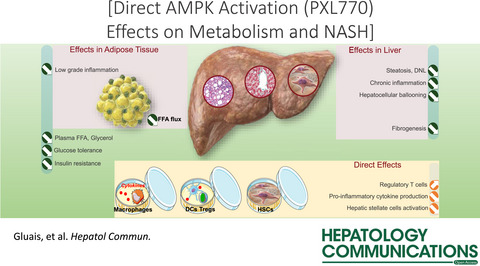
Direct AMPK Activation Corrects NASH in Rodents Through Metabolic Effects and Direct Action on Inflammation and Fibrogenesis
- Pages: 101-119
- First Published: 07 September 2021
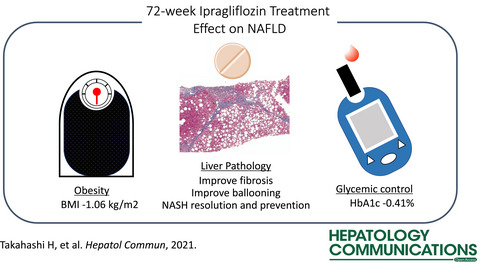
Ipragliflozin Improves the Hepatic Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes with NAFLD
- Pages: 120-132
- First Published: 17 June 2021
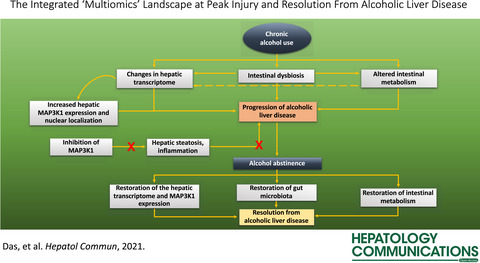
The Integrated “Multiomics” Landscape at Peak Injury and Resolution From Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease
- Pages: 133-160
- First Published: 28 August 2021
Transcriptomic Cross-Species Analysis of Chronic Liver Disease Reveals Consistent Regulation Between Humans and Mice
- Pages: 161-177
- First Published: 28 August 2021
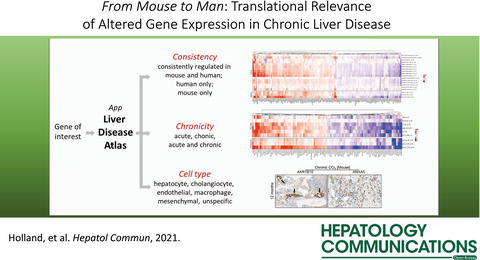
In the present study, we observed that – although major interspecies differences remain – improved mouse models show up to 40% of the gene expression changes seen in liver tissue of human NAFLD or NASH, which is much higher than previously reported. Moreover, we identified gene sets consistently regulated in human and mouse chronic liver disease. Based on single-cell RNA-sequencing data set we mapped liver cell types to those genes and validated them by immunostaining.
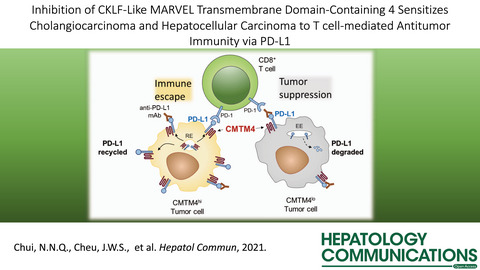
Inhibition of CMTM4 Sensitizes Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatocellular Carcinoma to T Cell–Mediated Antitumor Immunity Through PD-L1
- Pages: 178-193
- First Published: 21 July 2021
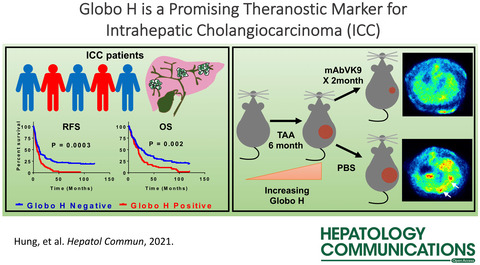
Globo H Is a Promising Theranostic Marker for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
- Pages: 194-208
- First Published: 24 August 2021
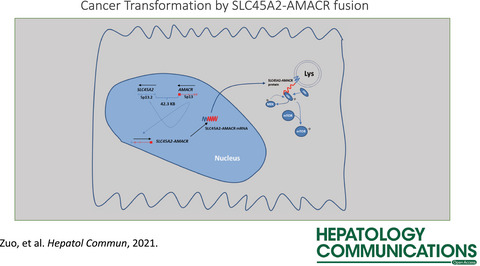
Oncogenic Activity of Solute Carrier Family 45 Member 2 and Alpha-Methylacyl-Coenzyme A Racemase Gene Fusion Is Mediated by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
- Pages: 209-222
- First Published: 10 September 2021
Therapeutic Underuse and Delay in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Prevalence, Associated Factors, and Clinical Impact
- Pages: 223-236
- First Published: 25 August 2021

One-fourth of HCC patients receive no therapy and one-fifth of treated patients experience treatment delays. Both were associated with demographic, socioeconomic, clinical characteristics of patients, facility type, and regions. The association between therapeutic delay and survival was stage- and treatment-dependent. Therapeutic delay was associated with worse OS in patients who had early-stage HCC or received curative treatment.
Cognitive Impairment and Physical Frailty in Patients With Cirrhosis
- Pages: 237-246
- First Published: 24 August 2021
Correspondence
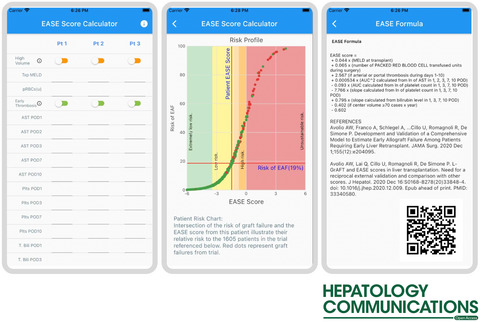
Availability of a Web and Smartphone Application to Stratify the Risk of of Early Allograft Failure Requiring Liver Retransplantation
- Pages: 247-248
- First Published: 22 June 2021
Smartphone Apps to Stratify the Risk of Early Allograft Failure Are Just the Beginning for Next-Generation Outcome Prediction in Transplantation Medicine
- Page: 249
- First Published: 21 June 2021