Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
REVIEW ARTICLE
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome and functional abdominal pain disorders in children with inflammatory bowel disease in remission
- Pages: 818-823
- First Published: 03 November 2022
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Bowel cleansing efficacy of 1 L NER1006 versus macrogol and 3 L polyethylene glycol using split-dose administration
- Pages: 824-832
- First Published: 05 November 2022
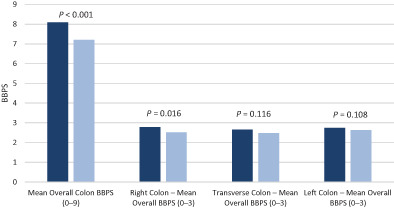
In Australia, high-volume polyethylene glycol based bowel preparations is our gold standard to achieve acceptable levels of colon cleansing for a colonoscopy. Yet, the rebooking rates and subsequent costs to the health service warranted further investigation to determine whether other bowel preparation options were more effective, while maintaining a safety profile. The results from our study demonstrated that NER1006, a novel 1 L low-volume polyethylene-based bowel preparation produced significant results compared with its counterpart of macrogol and 3 L polyethylene glycol (P < 0.001). The results from this study will provide more confidence when prescribing NER1006, especially in patients who are intolerant to high-volume preparations.
Clinicopathological characteristics of advanced gastric cancer after Helicobacter pylori eradication
- Pages: 833-838
- First Published: 02 November 2022
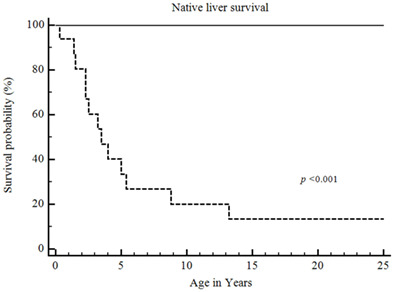
Different clinical and genetic features of Alagille patients with progressive disease versus a jaundice-free course
- Pages: 839-845
- First Published: 31 October 2022
Inflammatory bowel disease type influences development of elevated liver enzymes
- Pages: 846-853
- First Published: 03 November 2022
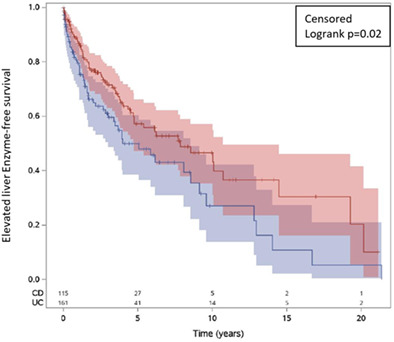
We evaluated the incidence, predictors, and outcomes associated with elevated liver enzymes (ELE) in a diverse and vulnerable inflammatory bowel disease cohort. In multivariate Cox regression, ulcerative colitis (vs Crohn's disease) had a 34% lower risk of developing new ELE during follow-up (hazard ratio 0.66, 95% confidence interval: 0.46–0.95, P = 0.02). Mortality rate was higher for patients with ELE (0% normal vs 2.3% transient ELE vs 6.5% persistent ELE, P < 0.001).
Persistent epigenetic alterations in transcription factors after a sustained virological response in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 854-863
- First Published: 30 October 2022
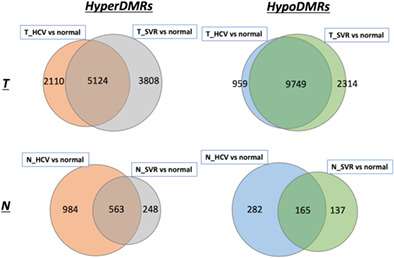
This study aimed to reveal that abnormalities present in the epigenome play a role in hepatocellular carcinogenesis upon resolution of an hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. We performed genome-wide comprehensive epigenome and transcriptome analyses using surgically resected clinical samples and cultured cells. This study demonstrated that DNA methylation abnormalities, retained after HCV eradication, affect the expression of transcription factors and their target genes, and suggested that DNA methylation in sustained viral response patients may be functionally important in carcinogenesis.
Evaluation of the circumferential location of mild reflux esophagitis (Grade A and B) in the lower esophagus
- Pages: 864-868
- First Published: 07 November 2022
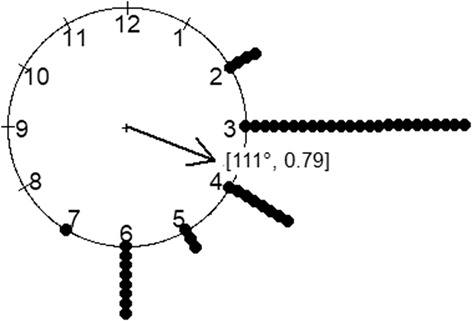
In the single lesion group, mild mucosal breaks were exclusively distributed between 2 and 7 o'clock, with 50% in the 3 o'clock direction (right lateral wall). In the multiple lesion group, mild mucosal breaks were distributed circumferentially, not uniformly; however, at least one lesion was located between 2 and 7 o'clock in 91% of subjects. These two distributions significantly differed.
Endoscopy training in Australia during COVID-19: Efficacy and knowledge assessment of gastroenterology and general surgery trainees
- Pages: 869-875
- First Published: 08 November 2022
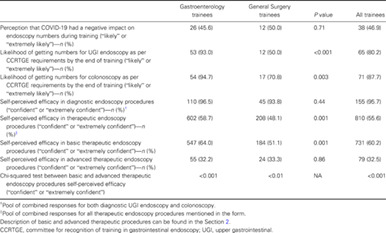
During COVID-19, restrictions to elective procedures were introduced worldwide. Our study aimed to assess Australian advanced Gastroenterology and General Surgery trainees' self-perceived efficacy and knowledge in endoscopy during the pandemic. We have found that although self-efficacy in endoscopic diagnostic procedures was achieved for most trainees, differences in self-perceived efficacy and knowledge were shown between gastroenterology and surgical trainees and may be reflective of the different opportunities for learning between the two groups.
Depression is associated with increased disease activity in patients with ulcerative colitis: A propensity score-matched analysis using a nationwide database in Japan
- Pages: 876-885
- First Published: 15 November 2022
Comparison of the effects of individual symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease co-existing functional dyspepsia on patients' daily lives: A prospective, observational study
- Pages: 886-893
- First Published: 05 November 2022
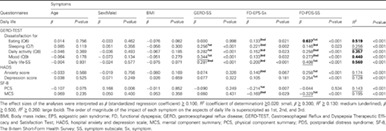
Patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) frequently also have co-existing symptoms of functional dyspepsia (FD). The authors aimed to investigate the effects of each symptom of typical GERD, co-existing FD epigastric pain syndrome (EPS), and postprandial distress syndrome (PDS) on patients’ level of satisfaction in daily life, the presence of psychiatric disorders, and quality of life using multiple regression analysis. Of the three symptoms, FD-PDS symptom had the most prominent effect on the various aspects of daily life, whereas the impact of GERD symptom on daily life was rather modest.
Treatment outcomes and costs of a simplified antiretroviral treatment strategy for hepatitis C among Hepatitis C Virus and Human Immuno deficiency Virus co-infected patients in Ukraine
- Pages: 894-903
- First Published: 17 November 2022
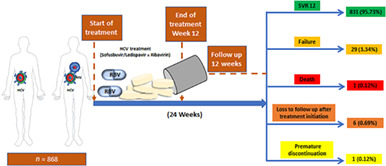
We assessed treatment and cost outcomes for integrated HIV and viral hepatitis testing with ledipasvir/sofosbuvir ± weight-based ribavirin for 12 weeks in Kyiv, Ukraine. Overall, a sustained virological response (SVR) was achieved in 831 of 868 patients (95.7%). The SVR in patients with hepatitis C alone and hepatitis C/HIV co-infection was 98.4% and 93.6%, respectively. Using generic medication, costs per patient 44 were estimated at US$680.
Obliterative portal venopathy: A neglected and probably misdiagnosed disease with peculiar etiology in South America
- Pages: 904-909
- First Published: 16 November 2022
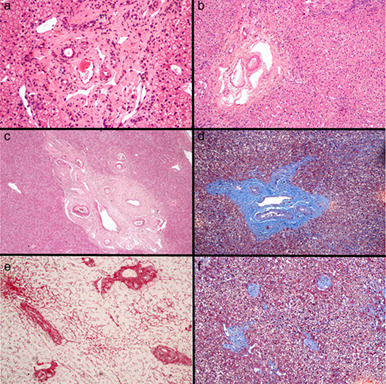
Classically described in the group of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension, obliterative portal venopathy (OPV) causes are still unknown. Our aim is to describe the characteristics of 43 OPV patients and potential risk factors. Clinically significant portal hypertension was found in 28% of cases. The most frequent indication for liver biopsy was elevation of liver enzymes, mostly γ-glutamyl transferase increase in 76% of patients. One third of our patients have exposure to medications, especially herbal medicines at the time of enzymatic changes.
Chronic steroid use: An overlooked impact on patients with inflammatory bowel disease
- Pages: 910-914
- First Published: 10 November 2022
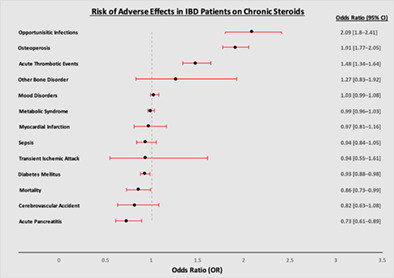
Steroids have long been used in inducing remission of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but there is controversy about whether IBD patients should be on chronic steroids for maintenance therapy. In this retrospective study, we aim to identify the complications of chronic steroid use in patients with IBD. Our results highlight the importance of monitoring patients on steroids and avoiding chronic use as patients on chronic steroid use had higher odds of developing adverse effects, such as osteoporosis, opportunistic infections, and acute thromboembolic events.
CASE REPORT
A rare cause of jejunal perforation: Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 915-917
- First Published: 16 November 2022
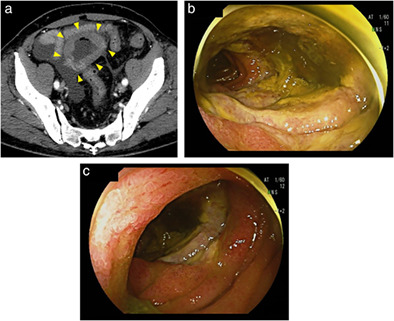
Monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T-cell lymphoma (MEITL) is a very rare intestinal T-cell lymphoma which is observed most frequently in the jejunum. MEITL is prone to cause intestinal perforation and the prognosis is very poor when it occurs. Here we report a fatal case of MEITL causing jejunal perforation at the time of diagnosis in a 79-year-old man.