Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Review Articles
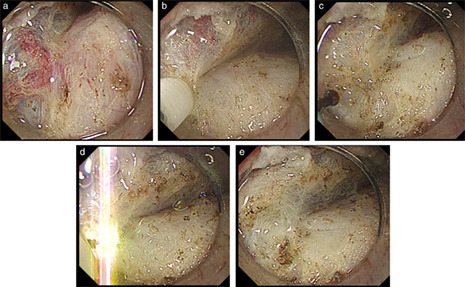
Hemorrhage control during gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: Techniques using uncovered knives
- Pages: 4-10
- First Published: 18 June 2019
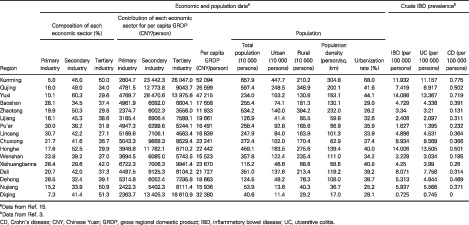
Potential influential factors on incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in mainland China
- Pages: 11-15
- First Published: 06 August 2019
Original Articles
Is complete stone removal for choledocholithiasis always necessary in extremely elderly patients?
- Pages: 16-21
- First Published: 30 May 2019
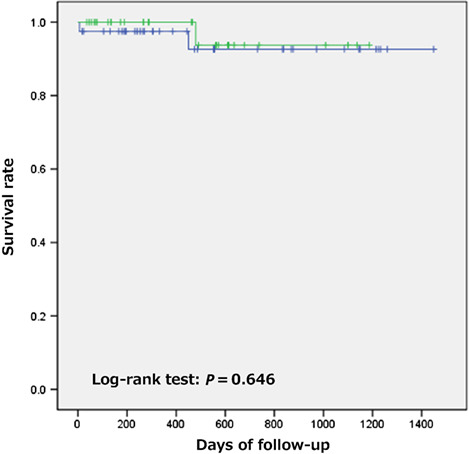
A total of 73 extremely elderly patients (>90 years) who underwent endoscopic stone removal for choledocholithiasis were retrospectively evaluated. The patients were divided into complete stone removal and incomplete stone removal (plastic stent insertion) groups. Kaplan–Meier analysis found no significant difference in overall survival (OS), and disease-specific survival (DSS) between the two groups.
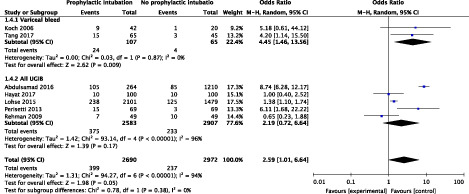
Prophylactic endotracheal intubation in critically ill patients with upper gastrointestinal bleed: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 22-28
- First Published: 24 May 2019
Prevalence of hepatitis B and C virus infections in hemodialysis patients in Vietnam: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 29-38
- First Published: 17 June 2019
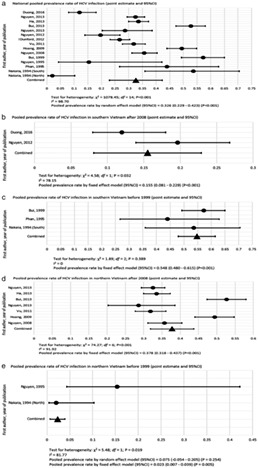
Chronic hemodialysis patients are at high risk of contracting hepatitis B (HBV) and C virus (HCV) infections. Although the chronic hemodialysis population is increasing in Vietnam, relatively little epidemiology is available for HBV and HCV infections in this population. To address this knowledge gap and to examine the implications of infection prevention of HBV and HCV in hemodialysis facilities, we reviewed the current literature on the magnitude of these infections in the hemodialysis population in Vietnam.
Explant liver evaluation decodes the mystery of cryptogenic cirrhosis!
- Pages: 39-43
- First Published: 30 May 2019
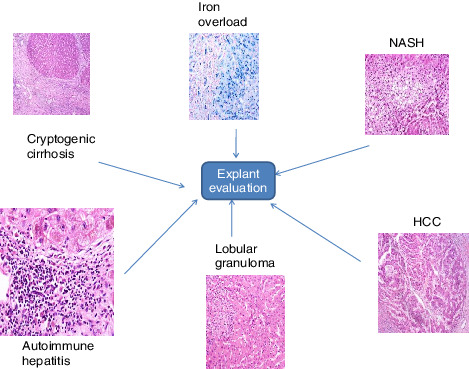
A significant concordance of explant diagnosis with pretransplant diagnosis was present in alcohol, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, autoimmune liver disease, biliary cirrhosis, and Budd–Chiari syndrome. For 37 patients with a pretransplant diagnosis of cryptogenic cirrhosis, major discordance was observed in 23 (62.1%). Cohen's Kappa for concordance of pretransplant diagnosis and explant diagnosis in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and cryptogenic cirrhosis patients was 0.75 and 0.47, respectively. An incidental hepatocellular carcinoma was observed in 16 explants, and 18 had granulomas.
The weekend effect does not influence management of inflammatory bowel disease
- Pages: 44-48
- First Published: 10 June 2019
The financial and psychological toll of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) flares is quite significant; however, it is unknown whether weekend hospitalization for IBD exacerbations carry a higher hospitalization burden. Utilizing the National Inpatient Sample from 2008 to 2014, we show that there is no significant difference in mortality, cost of admission, or length of stay between weekend and weekday admissions. Given effective management on the weekends, these data can be utilized for the purposes of logistic planning, such as procedure scheduling and resource allocation.
Real-world data of Helicobacter pylori prevalence, eradication regimens, and antibiotic resistance in Thailand, 2013–2018
- Pages: 49-53
- First Published: 24 June 2019

Initial regimens (triple therapy or sequential therapy or quadruple therapy) can be an effective regimen for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection, with a success rate of > 90%. For patients who failed to respond to initial triple therapy, using a longer duration of triple therapy or changing to quadruple therapy is the best choice. The resistant rates of amoxicillin, metronidazole, levofloxacin, and tetracycline are declining, but those of clarithromycin and ciprofloxacin are increasing.
Early response and safety of lenvatinib for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in a real-world setting
- Pages: 54-60
- First Published: 10 June 2019
Lenvatinib has been recently approved for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma based on the results of the REFLECT trial, which excluded patients with a history of systemic chemotherapy, bile duct invasion, and Child-Pugh grade B. We showed the efficacy and safety of lenvatinib for those patients and also for patients who did not meet the REFLECT inclusion criteria in a real-world setting.
Endoscopic yield of chronic dyspepsia in outpatients: A single-center experience in Cambodia
- Pages: 61-68
- First Published: 24 June 2019
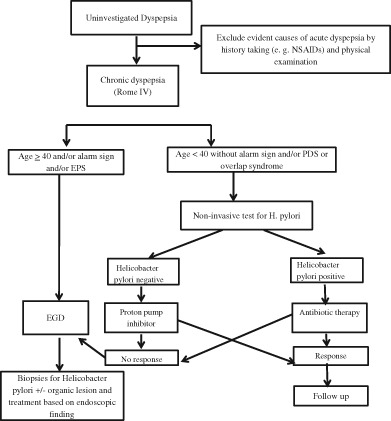
This paper is the first to describe the clinical and endoscopic correlates of patients with dyspepsia in Cambodia, including predictors for organic causes of dyspepsia such as peptic ulcer disease or gastric cancer. The results are synthesized into a proposed algorithm for the management of dyspepsia in Cambodia.
Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index and fibrosis 4 scores for hepatic fibrosis assessment compared with transient elastography in chronic hepatitis C patients
- Pages: 69-74
- First Published: 26 June 2019
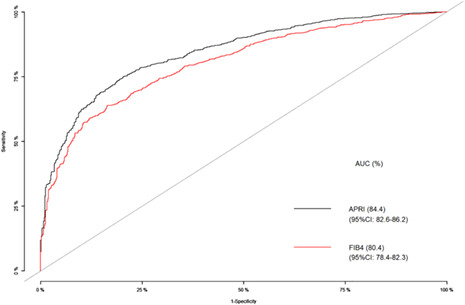
Using transient elastography as the standard reference, aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI) and fibrosis 4 (FIB-4) performed well in the prediction of cirrhotic status in chronic hepatitis C patients, but APRI was better than FIB-4 for the prediction of significant fibrosis (SF). The high cut-off values of APRI proposed by World Health Organization (WHO) for both SF and cirrhosis yielded a very high positive predictive value to determine those conditions, but at the WHO low cut-off values, the negative predictive values were not satisfactorily high enough to rule out such conditions
Genetic alterations related to endoscopic treatment of colorectal tumors
- Pages: 75-82
- First Published: 25 June 2019
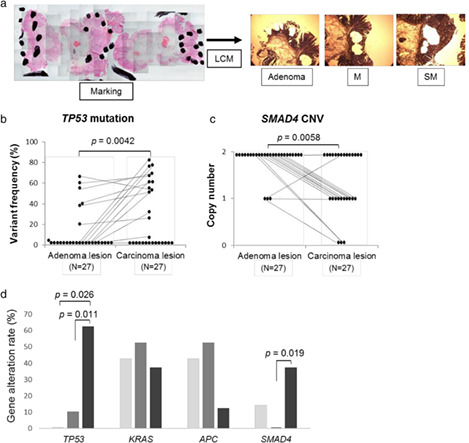
Despite recent large-scale gene analyses, genetic indicators of endoscopic resection for colorectal carcinoma remain inconclusive. Next-generation sequencing analyses of 83 colorectal tumors demonstrated that numbers of copy number variations and TP53 and SMAD4 alterations were related to colorectal tumor progression. Furthermore, TP53 alteration rates in adenoma components were high in T1b carcinomas, warranting complete treatment with en bloc resection.
Predictors of invasive cancer of large laterally spreading colorectal tumors: A multicenter study in Japan
- Pages: 83-89
- First Published: 16 July 2019
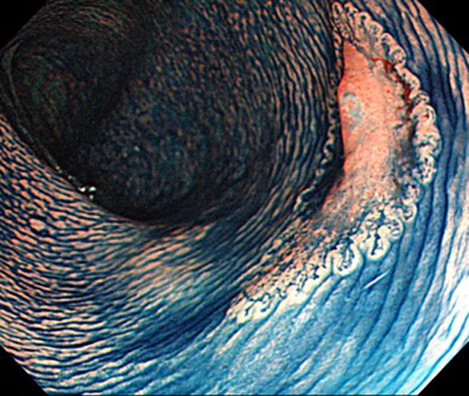
We performed a logistic regression analysis to determine whether the risk of invasive cancer of large colorectal laterally spreading tumors (LSTs) measuring 20 mm or greater and treated endoscopically can be predicted based on factors such as endoscopic findings in a large group of patients enrolled in a multicenter study in Japan. The locations and tumor diameters of the LSTs were found to differ significantly according to the LST subclassification. The risk of pathological T1 cancer was significantly associated with LST subclassification and tumor diameter.
Case Reports
Invasive aspergillosis causing gastric necrosis and perforation: A case report
- Pages: 90-93
- First Published: 27 February 2019
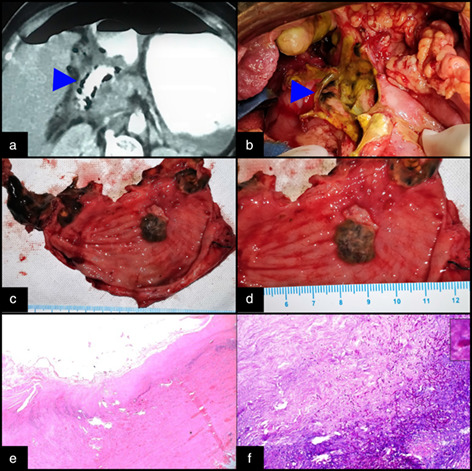
Primary gastric aspergillosis is extremely rare. We report a rare case of primary invasive gastric aspergillosis in a 60-year-old diabetic and cirrhotic woman, with a large gastric perforation. Large confluent areas of gastric ulceration and necrosis with blackish exudates in an appropriate setting should evoke suspicion for invasive fungal infection and these patients should be started on prophylactic antifungal therapy immediately.
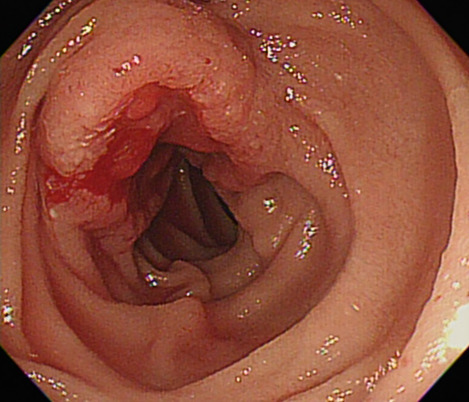
Obscure gastrointestinal bleeding with negative abdominal computed tomography study: The importance of enteroscopy for early diagnosis of small bowel malignancy
- Pages: 94-96
- First Published: 22 February 2019
Endoscopic retrieval of two proximally migrated plastic pancreatic duct stents
- Pages: 97-98
- First Published: 12 March 2019
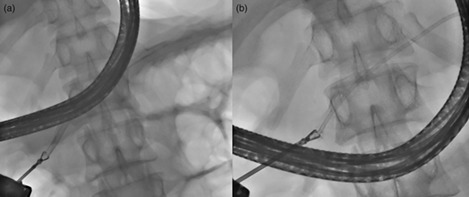
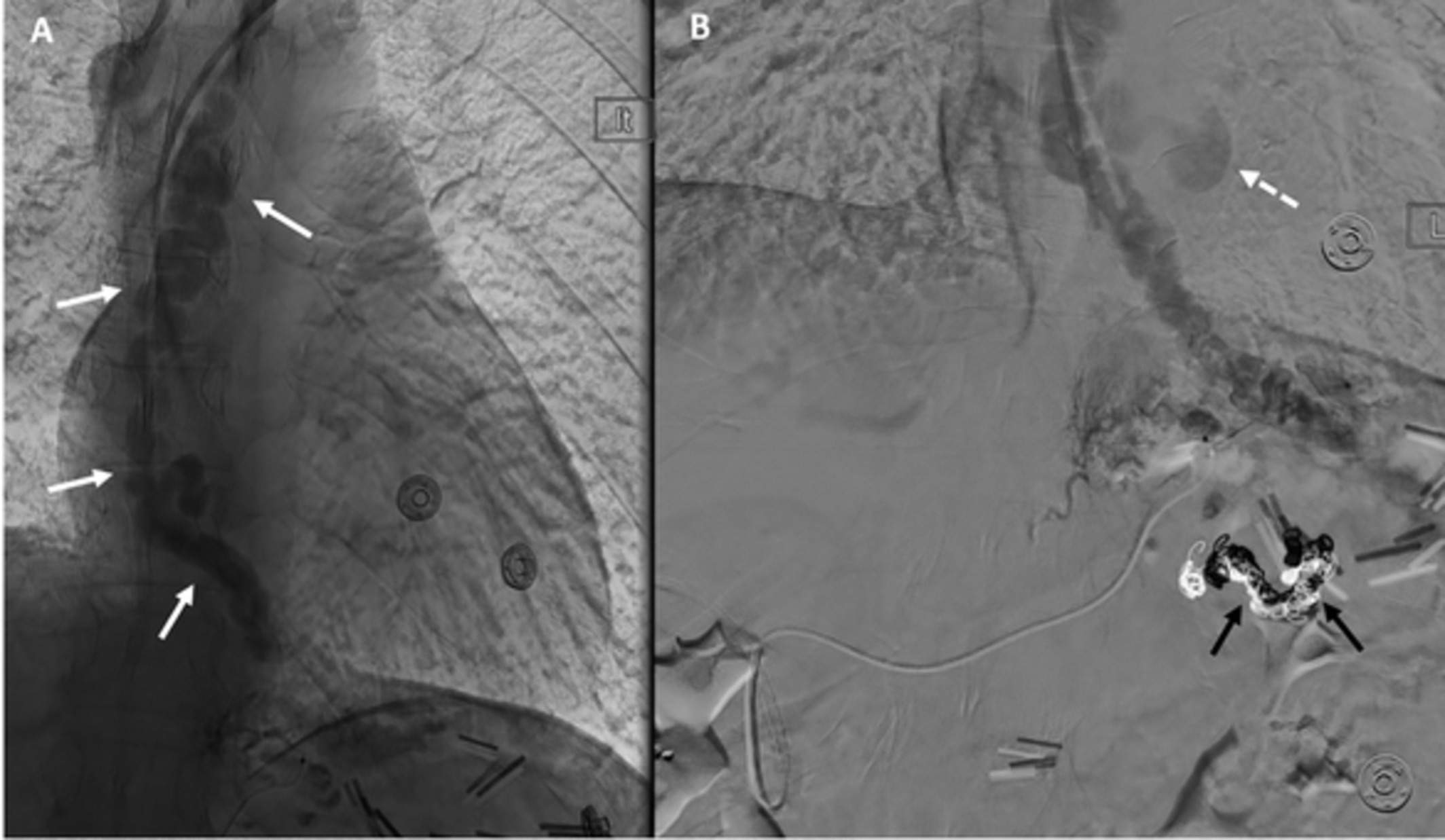
Plastic stent migration is an important complication of pancreatic duct (PD) stenting. Proximal stent migration can cause serious complications, including obstructive pancreatitis. The endoscopic removal of proximally migrated stents is difficult because of the small diameter of PD, the bended and sometimes tortuous course of PD, the presence of strictures, and a lack of dedicated endoscopic accessories. We report a rare case of endoscopic retrieval of two proximally migrated plastic stents from PD.
Portopulmonary venous anastomosis as a rare cause of embolic stroke following endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection for gastric variceal hemorrhage: A case report and review of the literature
- Pages: 99-102
- First Published: 11 April 2019