Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Original Articles
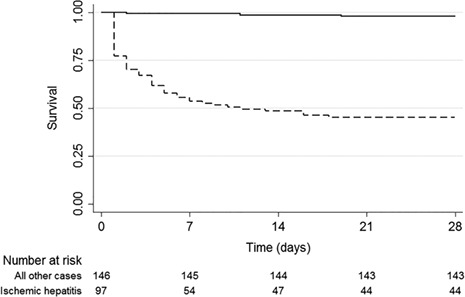
Epidemiology and outcomes of marked elevations of alanine aminotransferase >1000 IU/L in an Australian cohort
- Pages: 106-112
- First Published: 18 July 2019
Role of linear endosonography in the diagnosis of biopsy-negative malignant esophageal strictures: Exploring the unexplored
- Pages: 113-116
- First Published: 18 July 2019
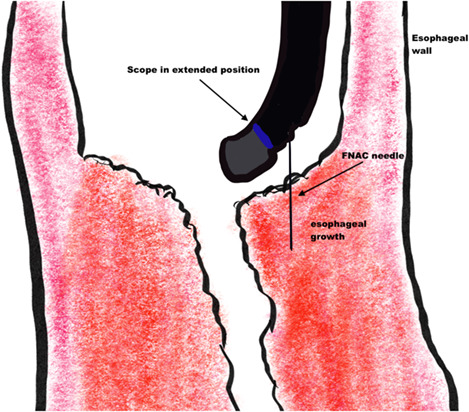
Esophageal malignancy presenting as smooth esophageal stricture with a negative biopsy for malignancy is not uncommon. We retrospectively analyzed the data of 11 such patients who appeared to have malignant esophageal stricture otherwise but had negative repetitive biopsies. Linear endosonography provided a safe and effective modality for diagnosis in such patients.
Effect of aspirin use on gastric cancer incidence and survival: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 117-125
- First Published: 19 July 2019
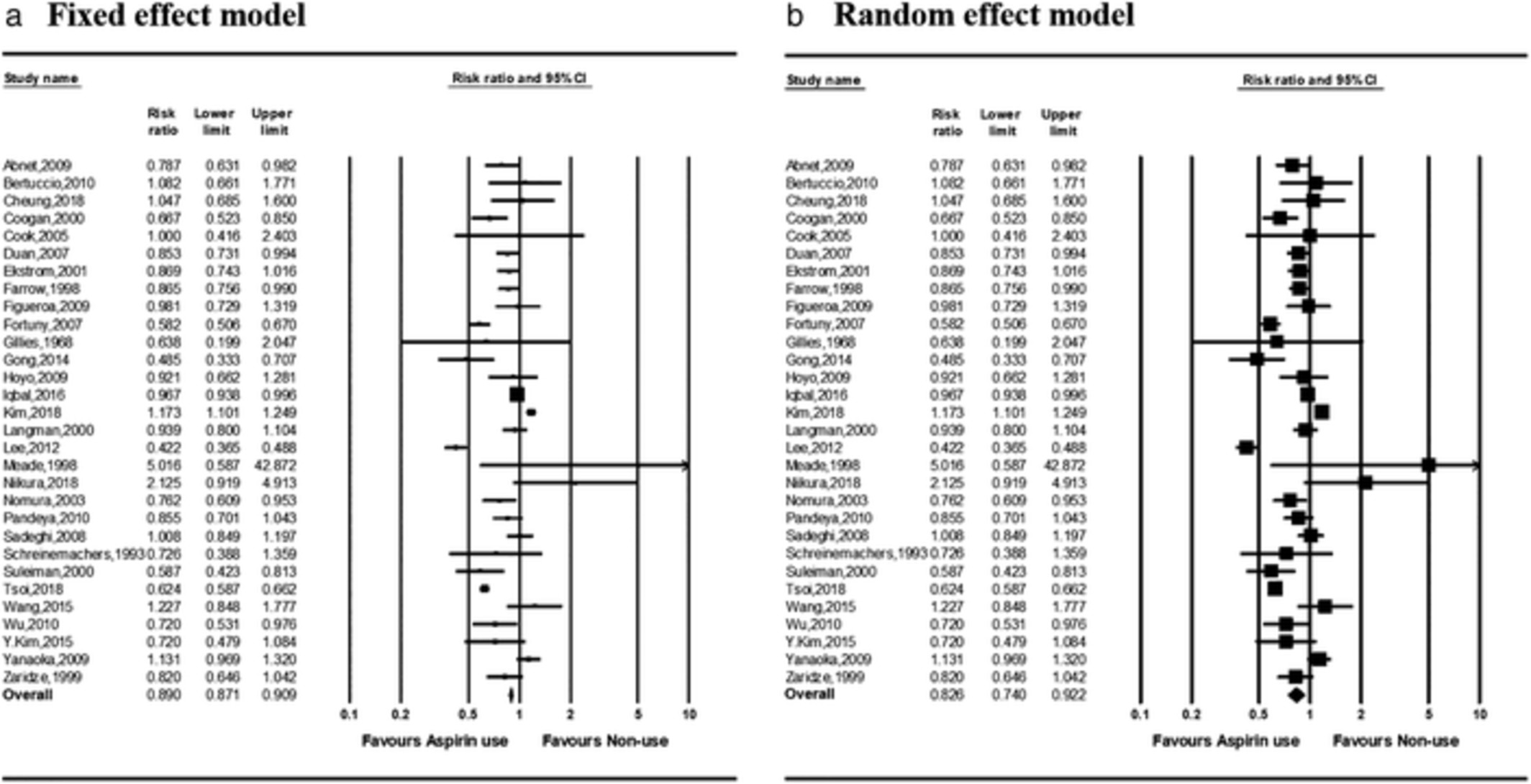
A number of recent studies have been published evaluating the chemopreventive effect of aspirin against gastric cancer, and an updated meta-analysis is required to evaluate this relationship further. Of 463 studies, we analyzed 33 studies with a total of 1 927 971 patients. The pooled risk ratios for gastric cancer incidence were 0.890 (95% confidence interval, 0.871–0.909) and 0.826 (0.740–0.922) in the fixed- and random-effects models, respectively. The pooled risk ratios for gastric cancer death in the fixed- and random-effects models were 0.798 (0.749–0.850) and 0.894 (0.780–1.024), respectively. Aspirin use may reduce the risk of gastric cancer incidence and death.
Comparison of small intestinal contrast ultrasound with magnetic resonance enterography in pediatric Crohn's disease
- Pages: 126-131
- First Published: 19 July 2019
Our findings provide preliminary evidence to suggest that small intestinal contrast ultrasonography (SICUS) offers a comparable diagnostic yield to that of magnetic resonance enterography (MRE) and ileocolonoscopy (IC) and performed better than transabdominal ultrasound (TUS) in a paediatric cohort with suspected or established Crohn's disease (CD). Our work comparing SICUS and MRE in routine clinical practice adds to the existing, albeit very limited, evidence that SICUS offers a radiation-free alternative to MRE for the evaluation of CD in children and adolescents.
Evaluation of the United Kingdom-primary biliary cholangitis and global primary biliary cholangitis group prognostic models for primary biliary cholangitis patients treated with ursodeoxycholic acid in the U.S. population
- Pages: 132-139
- First Published: 22 July 2019
In this study, we evaluated the performance of newly developed prognostic models, the United Kingdom-primary biliary cholangitis and global primary biliary cholangitis group scores, to predict long-term outcomes in patients with primary biliary cholangitis treated with ursodeoxycholic acid, adding to the expanding corpus of literature that discusses the reliability and accuracy of using those models outside Europe. Our findings suggest that advanced prognostic models are reliable and reasonably accurate to predict adverse events and can thus be generalized to the U.S. population.
Assessing the efficacy of TNF-alpha inhibitors in preventing emergency and emergent colectomies
- Pages: 140-144
- First Published: 02 August 2019
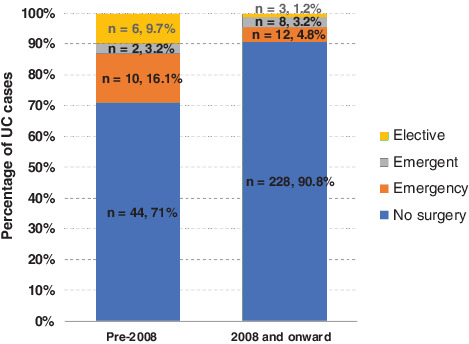
This is a retrospective cohort study that compared the rates of colectomy for severe ulcerative colitis over a 15-year period before and after the introduction of Infliximab therapy at our institution. We found a significant decrease in the rates of colectomy for severe ulcerative colitis over the study period, as well as a reduction in the rates of complications.
Assessment of tumor volume and density as a measure of the response of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib: Application of automated measurements on computed tomography scans
- Pages: 145-152
- First Published: 02 August 2019
Low FODMAP diet in children and adolescents with functional bowel disorder: A clinical case note review
- Pages: 153-159
- First Published: 02 August 2019
Functional bowel disorders (FBD) in children are becoming increasingly more common where there are data. The low FODMAP (LFD) diet is used as a successful dietary therapy for treating irritable bowel syndrome in adults; however, a paucity of data exists examining the use of this diet in children. This retrospective clinical case note review showed that the LFD is a useful dietary treatment strategy in children and adolescents with FBD and adds to the small body of evidence supporting LFD interventions in children.
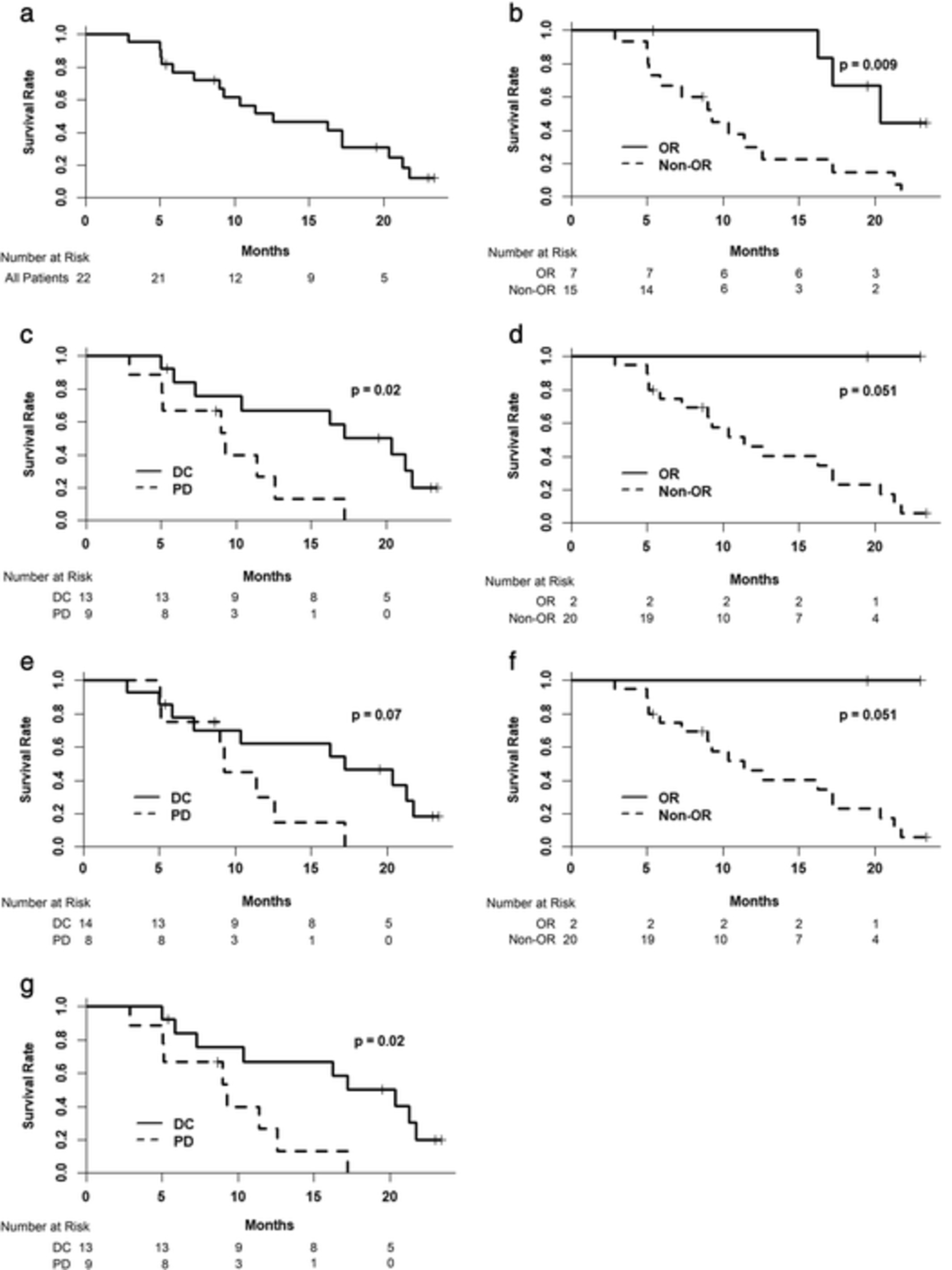
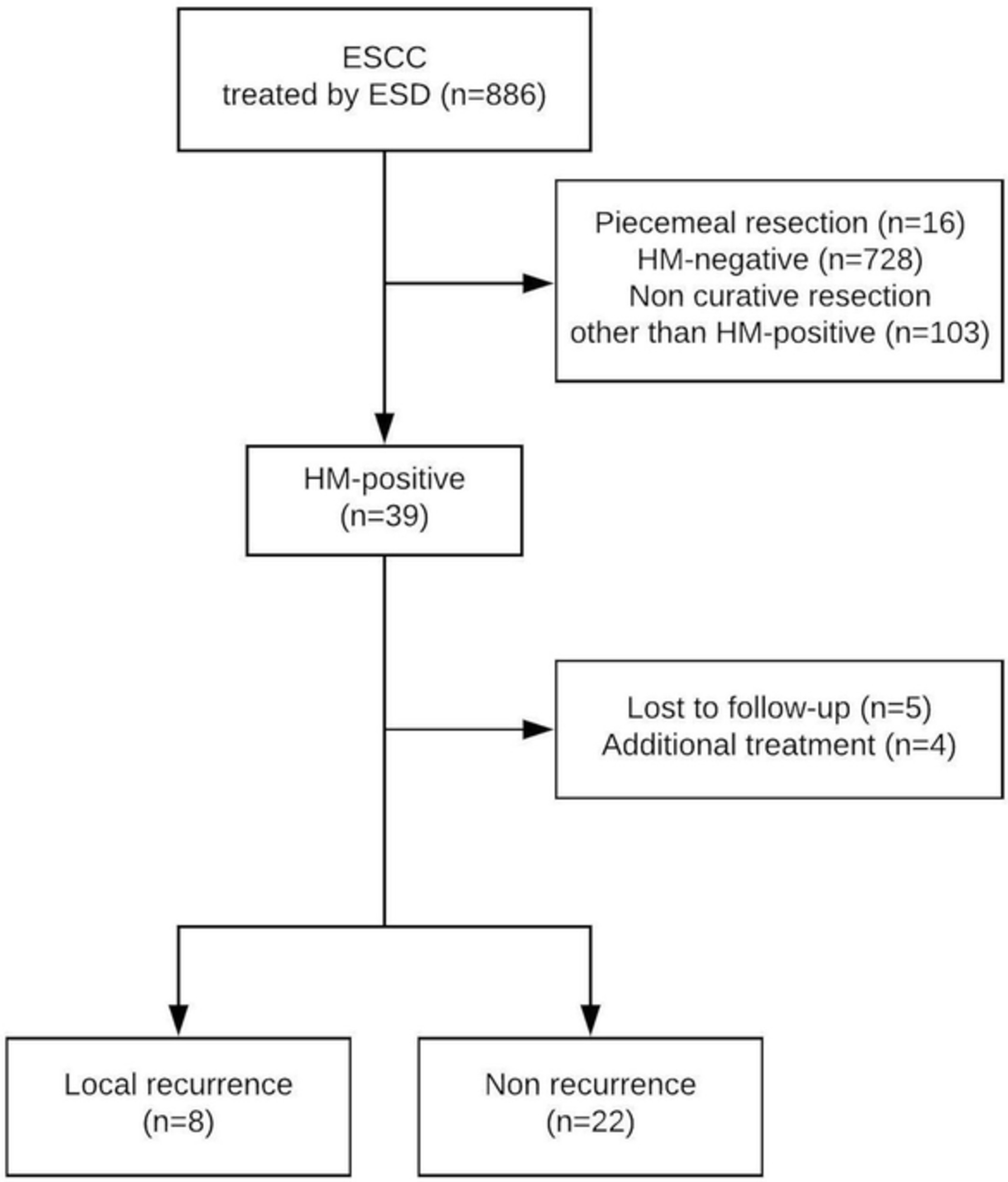
Effect of horizontal margin status and risk of local recurrence after endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal cancer
- Pages: 160-165
- First Published: 02 August 2019
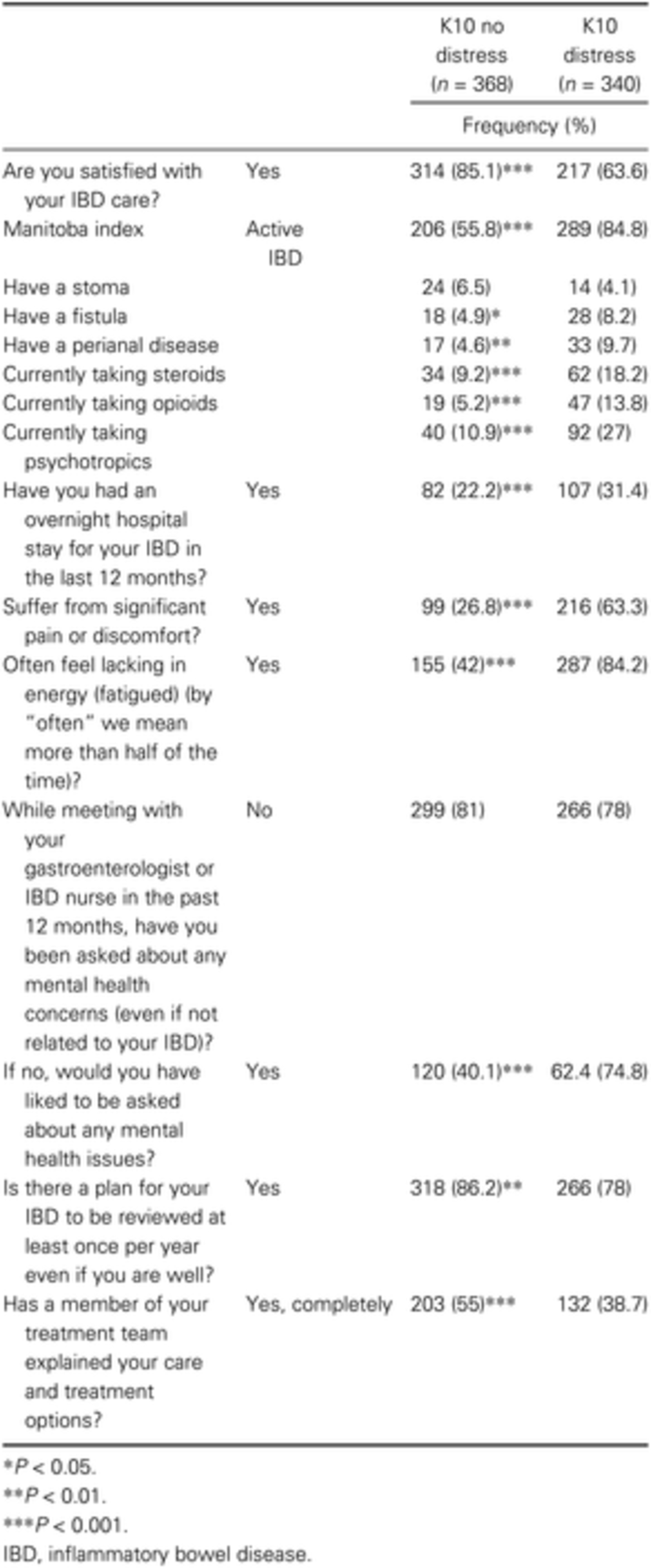
Psychological distress is highly prevalent in inflammatory bowel disease: A survey of psychological needs and attitudes
- Pages: 166-171
- First Published: 02 August 2019
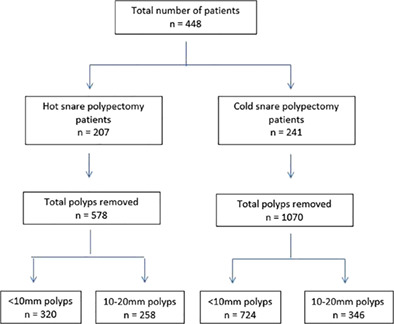
Complications of cold versus hot snare polypectomy of 10–20 mm polyps: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 172-177
- First Published: 18 August 2019
Additional effect of magnifying narrow-band imaging on estimating the invasion depth of superficial esophageal cancer
- Pages: 178-184
- First Published: 19 August 2019
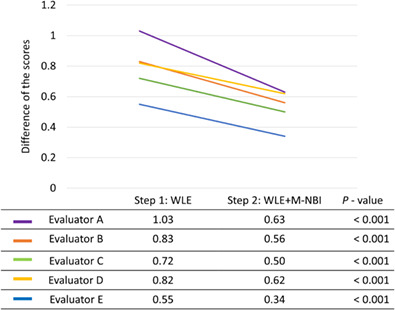
Depth estimation of 211 superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) (171 epithelial [EP] or lamina propria [LPM] cancers, 31 muscularis mucosa [MM] or shallow submucosal [SM1] cancers, and 9 deep submucosal [SM2] cancers) was performed independently by five evaluators (A, B, C, D, and E) using the numerical depth estimation scale (0 = EP/LPM, 1 = EP/LPM > MM/SM1, 2 = MM/SM1 > EP/LPM, 3 = MM/SM1, 4 = MM/SM1 > SM2, 5 = SM2 > MM/SM1, 6 = SM2), using primarily white light endoscopy (WLE) images (step 1) and, subsequently, both WLE and magnifying narrow-band imaging (M-NBI) images (step 2). The mean difference between the estimated score (from 0 to 6) and pathological score (0 for histologically proven EP/LPM, 3 for MM/SM1, and 6 for SM2) was significantly decreased in step 2 compared with that in step 1 for all five evaluators (A, 1.03 in step 1 and 0.63 in step 2, P < 0.001; B, 0.83 and 0.56, P < 0.001; C, 0.72 and 0.50, P < 0.001; D, 0.82 and 0.62, P < 0.001; E, 0.55 and 0.34, P < 0.001). This indicated that M-NBI has an additive value for estimating the invasion depth of superficial esophageal SCCs.
Efficacy and suitable indication of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection using a balloon-assisted endoscope
- Pages: 185-190
- First Published: 19 August 2019
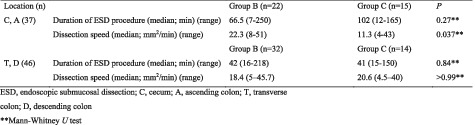
In cases of colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection with poor maneuverability, the use of balloon-assisted endoscopy (BAE) contributed to improvement in the R0 resection rate. In addition, BAE contributed to quicker dissection speed for lesions located in the cecum/ascending colon. This is an important point for deciding which to select, BAE or conventional endoscopy.
Clinical validation of the chronic liver disease questionnaire for the Chinese population in Singapore
- Pages: 191-197
- First Published: 20 August 2019
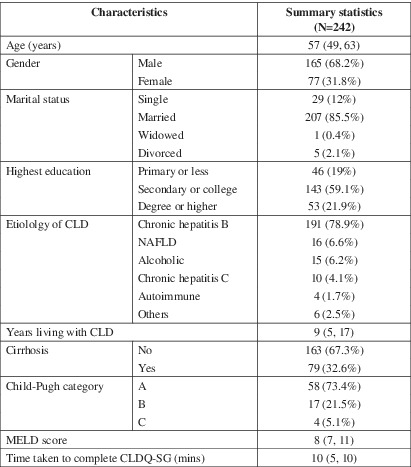
Assessment of health-related quality of life is an essential component of chronic disease management, yet this is not routinely performed in clinical practice. To meet this need, we previously performed a translation and adaptation of the Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire for the Mandarin-speaking Chinese population in Singapore. This study aims to validate this Chronic Liver Disease Questionnaire (Singapore version) by demonstrating its internal consistency and validity in a population of chronic liver disease patients. By sharing the results of our validation study, we hope to encourage physicians to use this health-related quality of life tool in routine clinical practice in the management of patients with chronic liver disease.
Evaluation of lactulose, lactose, and fructose breath testing in clinical practice: A focus on methane
- Pages: 198-205
- First Published: 20 August 2019
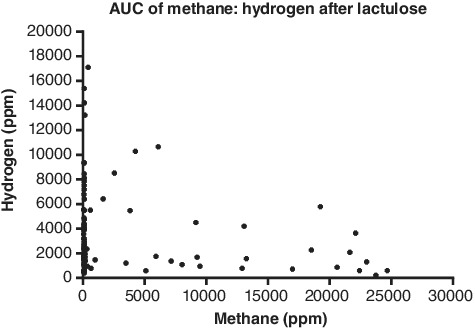
Breath testing is used to identify carbohydrate malabsorption and small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Measuring methane alongside hydrogen is advocated to reduce false-negative studies, but the variability of methane production is unknown. The validity of including an increase of ≥20 ppm methane to identify carbohydrate malabsorption or small intestine bacterial overgrowth should be questioned due to the variability of readings during testing.
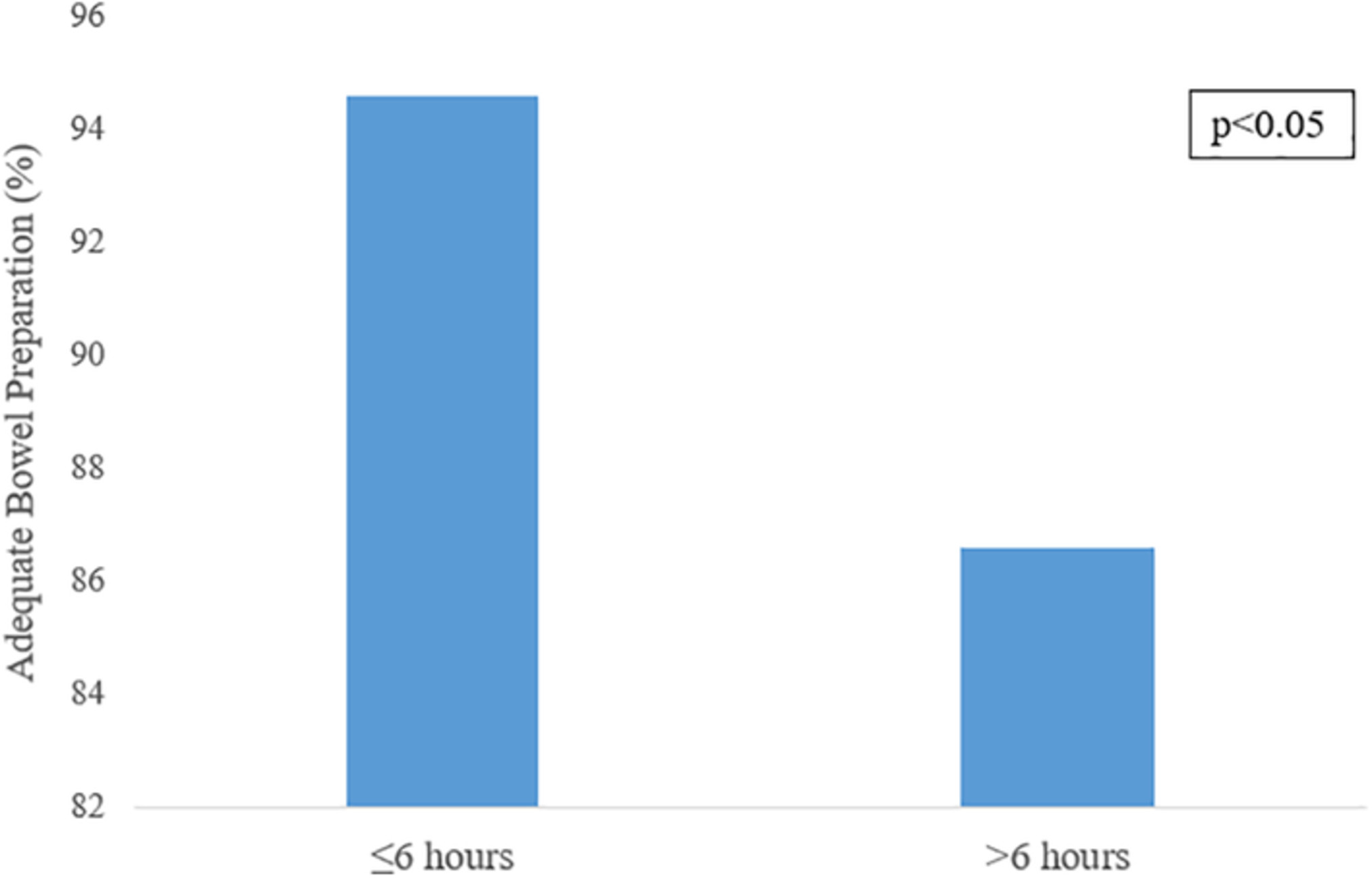
Factors affecting bowel preparation adequacy and procedural time
- Pages: 206-214
- First Published: 20 August 2019
Abdominal tuberculosis in children: A real-world experience of 218 cases from an endemic region
- Pages: 215-220
- First Published: 20 August 2019
Roles of healthcare professionals in the management of chronic gastrointestinal diseases with a focus on primary care: A systematic review
- Pages: 221-229
- First Published: 27 August 2019
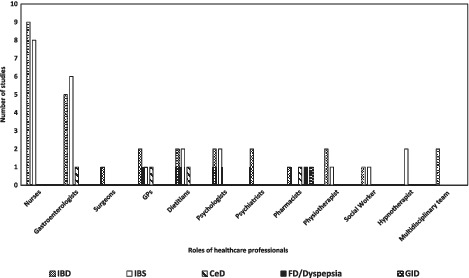
Although the review showed the roles of general practitioners (GPs), pharmacists, dietitians, and psychologists in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) management, nurses and gastroenterologists were the key drivers delivering specialized care to IBD patients. Many key services are accessible only for hospital inpatients (tertiary care) or through outpatient clinics (secondary care) with an absence of a multidisciplinary approach including GPs and pharmacists. The available evidence shows opportunities for primary care providers to play a more active role in the management of IBD patients.
Introduction of gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection and skill acquisition in a regional hospital
- Pages: 230-235
- First Published: 27 August 2019
Postoperative complications are main reason for noncompliance with enhanced recovery after surgery program in patients undergoing hepatectomy and pancreatectomy
- Pages: 236-240
- First Published: 27 August 2019
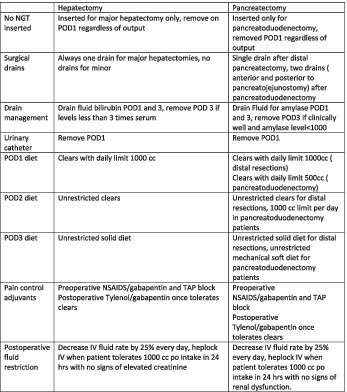
Enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) programs are used to improve postoperative outcomes such as lengths of stay and complications after hepatobiliopancreatic surgery. Logistic barriers in program implementation, as well as postoperative complications, are cited as the main reasons for noncompliance with ERAS. In our study, only postoperative complications were the main reason for noncompliance with the ERAS protocol.
Safety of wireless capsule endoscopy in patients with implantable cardiac devices
- Pages: 241-244
- First Published: 04 September 2019
Screening for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in community setting: A cohort study using controlled attenuation parameter-transient elastography
- Pages: 245-250
- First Published: 04 September 2019
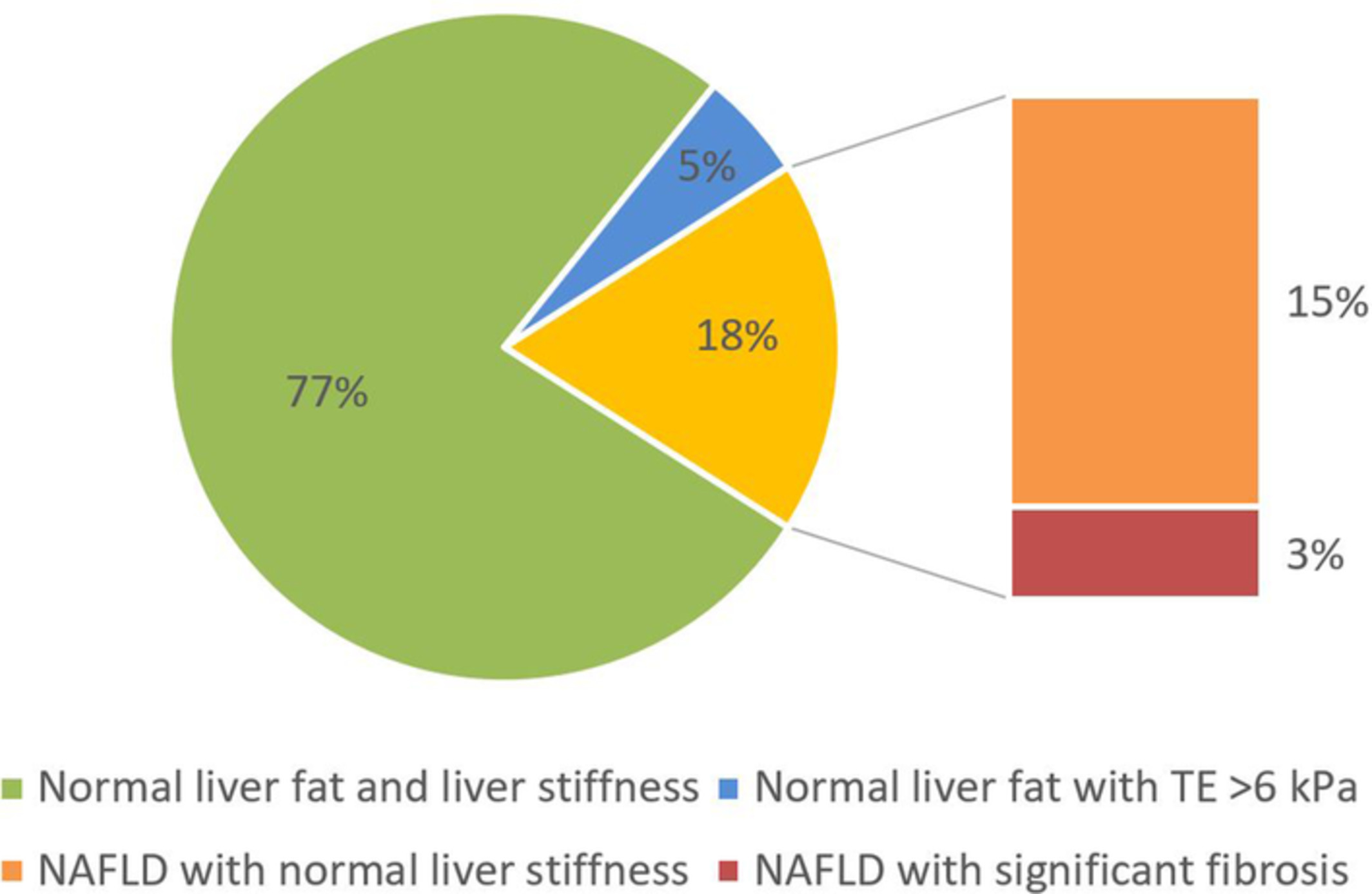
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with significant fibrosis (transient elastography > 8 kPa) is prevalent in asymptomatic populations. The predictors of significant fibrosis in NAFLD were male gender and history of dyslipidemia. Screening for NAFLD using CAP/TE in asymptomatic population should be considered in hospitals with available facilities.
Feasibility of the lidocaine injection method during esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection
- Pages: 251-255
- First Published: 06 September 2019
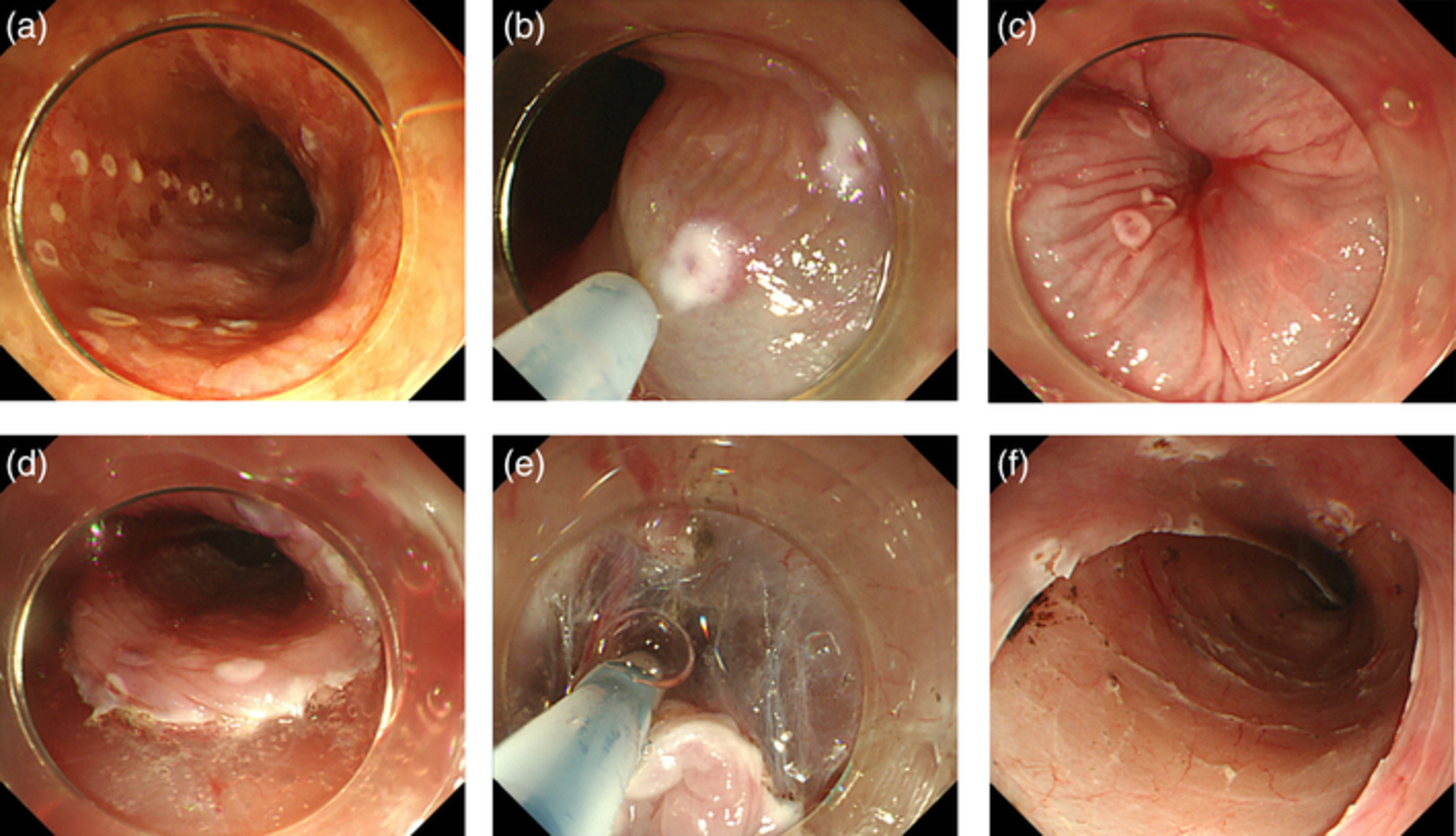
Esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is often technically difficult due to intraoperative body movements. Esophageal ESD using the lidocaine injection method (LIM) did not cause body movements that disturbed the procedure in our study. LIM may help create a stable conscious sedation method for esophageal ESD.
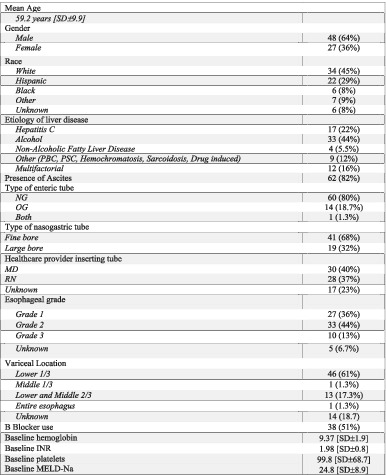
Enteric tube placement in patients with esophageal varices: Risks and predictors of postinsertion gastrointestinal bleeding
- Pages: 256-259
- First Published: 10 September 2019
Exclusive enteral nutrition: An optimal care pathway for use in adult patients with active Crohn's disease
- Pages: 260-266
- First Published: 10 September 2019
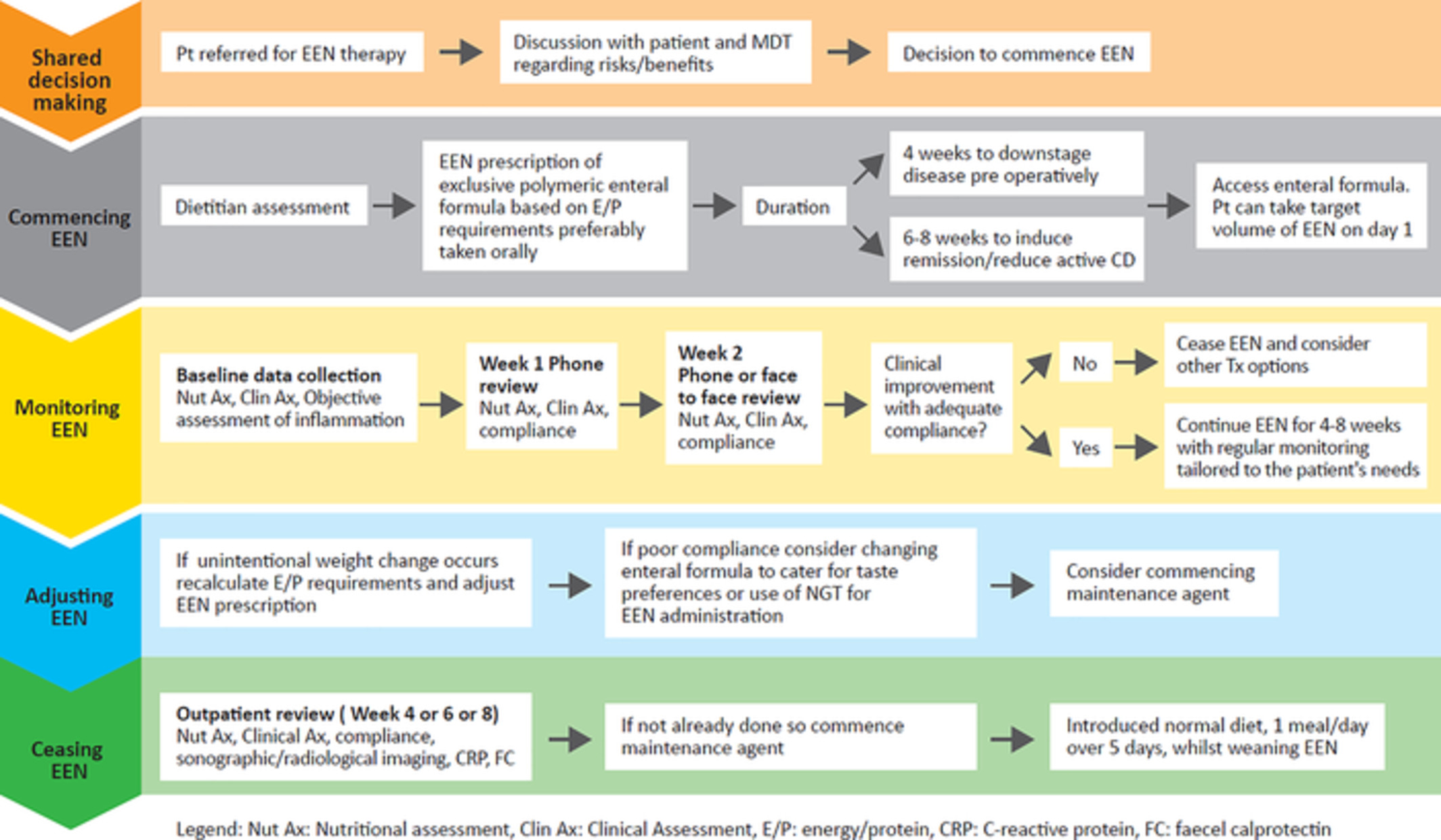
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) is an alternative therapeutic option to corticosteroids for patients with Crohn's disease (CD). This study aimed to develop an optimal care pathway for using EEN in adults with active CD. Six key consensus statements regarding the practical application of EEN in adults with active CD were developed based on available evidence and expert opinion to assist clinicians in delivering this therapy.
Gastrointestinal ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease care: Patient perceptions and impact on disease-related knowledge
- Pages: 267-272
- First Published: 09 October 2019
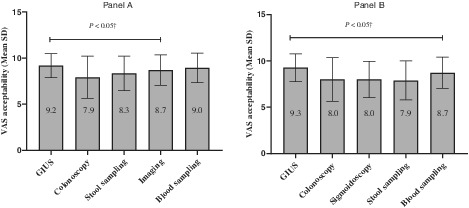
Gastrointestinal ultrasound (GIUS) is being increasingly used for disease monitoring in inflammatory bowel disease; however, patient perceptions of the different modalities available are sparse. This article evaluates patient perceptions, finding that GIUS was preferred to other modalities, and it was also found to have an impact on disease-related knowledge.
Point-of-care gastrointestinal ultrasound in inflammatory bowel disease: An accurate alternative for disease monitoring
- Pages: 273-279
- First Published: 09 October 2019
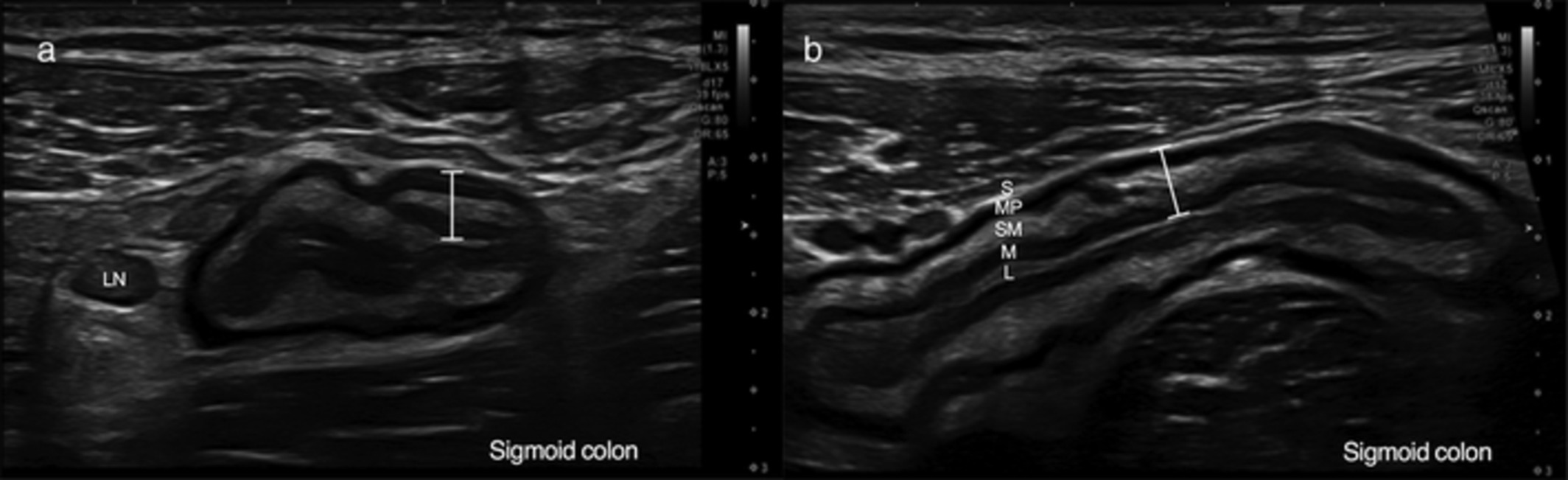
Point of care ultrasound is incorporated into routine IBD assessment in many European centers, however uptake in Australia has been slow. This article evaluates the accuracy of point of care ultrasound in monitoring disease activity in a local cohort of IBD patients. Point of care ultrasound was found to be accurate for monitoring disease activity and extent in IBD compared to the gold standard, ileocolonoscopy.
Case Reports
Huge bilharzial polyp mimicking colon cancer
- Pages: 280-283
- First Published: 12 April 2019
Endoscopic diagnosis of Fasciolopsis buski: Revisited (with video)
- Pages: 284-286
- First Published: 22 April 2019
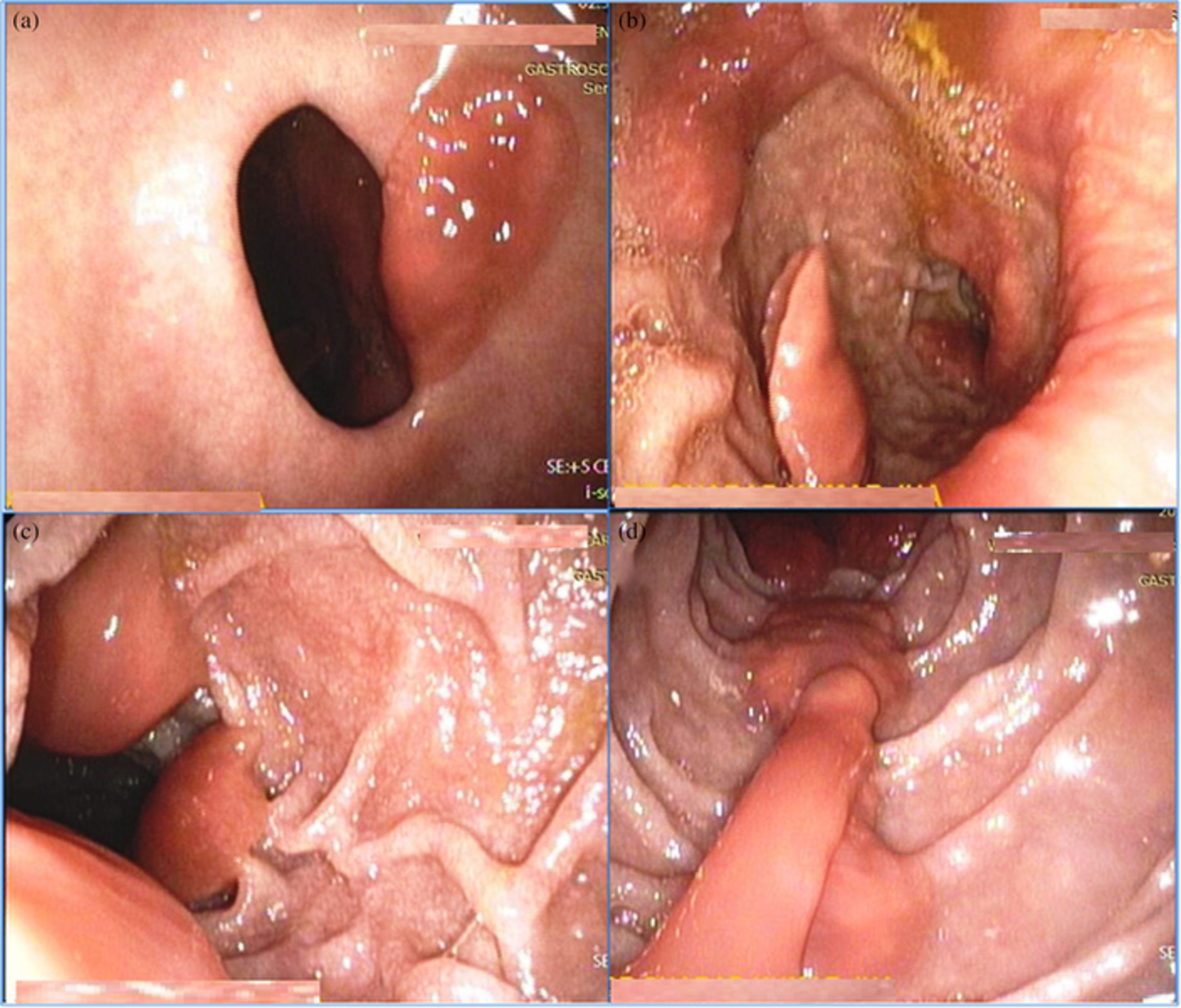
Endoscopic diagnoses of human Fasciolopsis buski mostly come as a surprise, especially in the absence of intense peripheral eosinophilia. Although F. buski infections are not uncommon in Southeast Asia, endoscopic diagnosis of parasite has been described in a few case reports. Here, we describe and illustrate the endoscopic removal of F. buski from the stomach and duodenum.
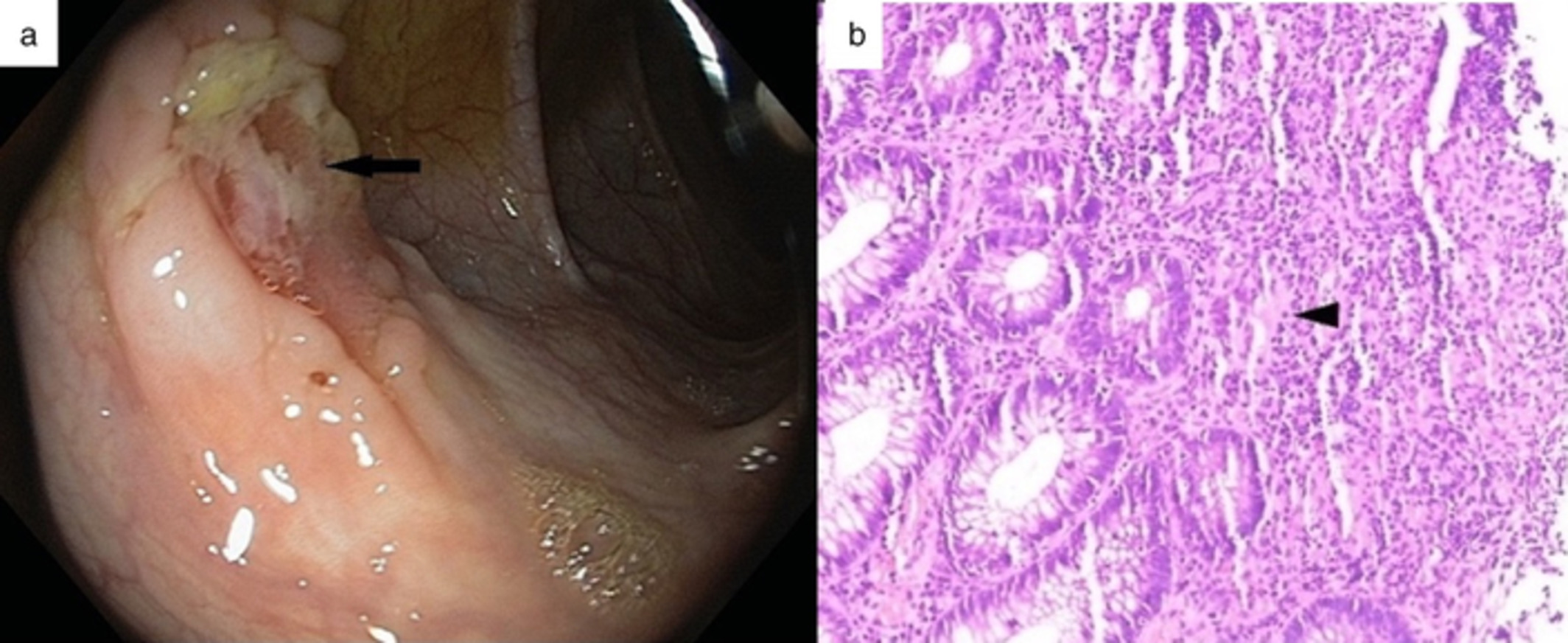
An unusual case of hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis and ulcerative colitis in a young Indian girl
- Pages: 289-291
- First Published: 10 June 2019
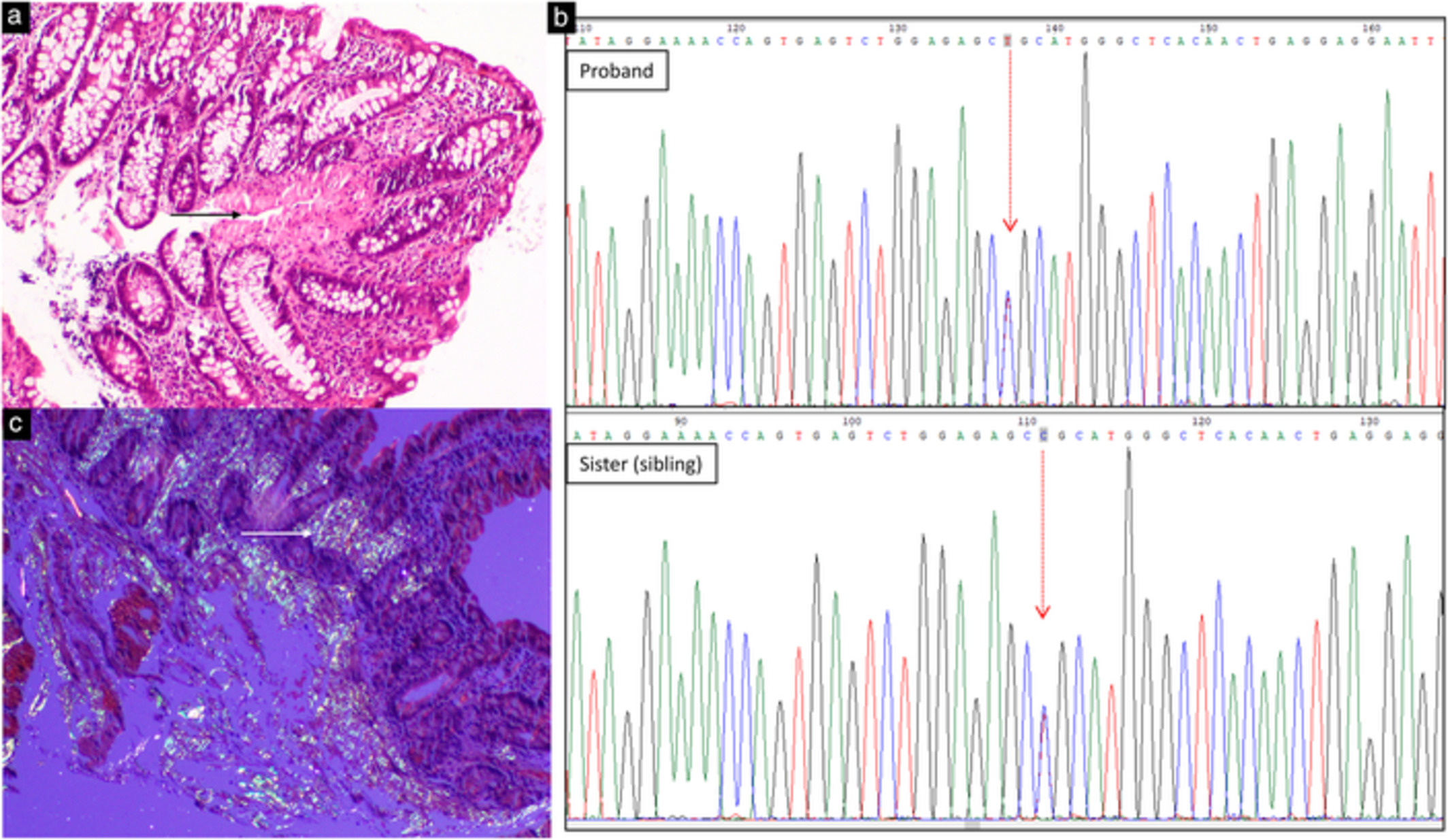
Amyloidosis can occur as a consequence of inflammatory bowel disease or can mimic inflammatory bowel disease. Hereditary transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis is hardly ever recognised in the Indian subcontinent. We report a case of TTR amyloidosis occurring in a young Indian girl who also had ulcerative colitis.
Jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, and portal lymphadenopathy in a middle-aged female: Is it lymphoma?
- Pages: 292-293
- First Published: 24 June 2019
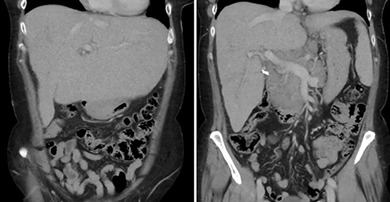
We describe the case of a 56-year-old female who presented with a 2-month history of painless jaundice and constitutional symptoms. Computed tomography scan showed massive hepatosplenomegaly with abdominal lymphadenopathy. Liver biopsy and a strongly positive antimitochondrial antibody titer confirmed the diagnosis of primary biliary cholangitis.
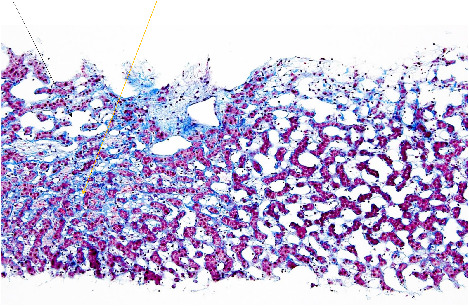
Fecaloma presenting as huge abdominal mass
- Pages: 294-295
- First Published: 25 June 2019
Novel technique using pancreatic duct stent facilitates difficult biliary cannulation in patients with Roux-en-Y anatomy (with video)
- Pages: 296-298
- First Published: 19 July 2019
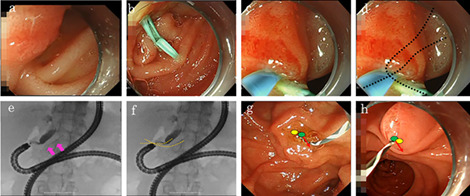
This study presents the case of a 70-year-old man who underwent total gastrectomy with Roux-en-Y anatomy. It was difficult to adjust the catheter in the direction of the bile duct despite using double-guidewire technique. We placed a 5Fr-5cm pancreatic duct (PD) stent to assist biliary cannulation. We inserted a catheter crossing the PD stent. By doing so, selective biliary cannulation was successful.
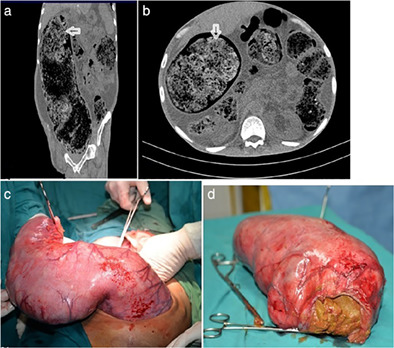
Clue to the cause of portal hypertension: Look at the raindrops
- Pages: 299-300
- First Published: 01 August 2019
An unusual cause of granulomatous colitis: Behcet's disease
- Pages: 303-305
- First Published: 15 August 2019
An incidental finding of low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm during cesarean section: A case report
- Pages: 306-308
- First Published: 17 August 2019
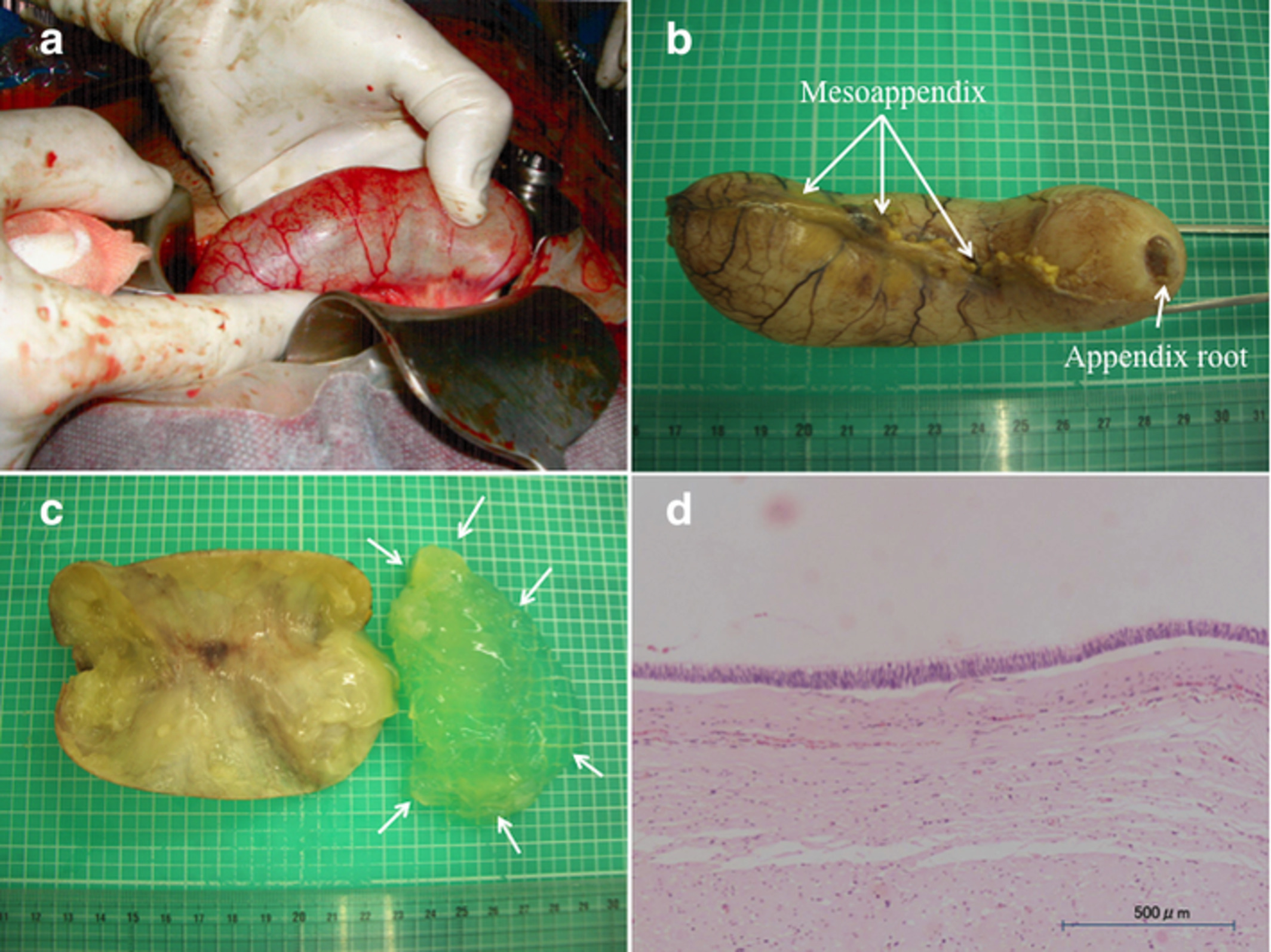
Here, we report the case of a 24-year-old pregnant women with incidentally discovered low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm (AMN) during cesarean section. To the best of our knowledge, there is a preoperatively diagnosed AMN complicating pregnancy. Previous reports suggested that AMN is detected during an operation performed for incidental reasons, such as acute abdomen, in all cases.
The number and size of Lugol-voiding areas were reduced by pneumatic dilation in a patient with achalasia and esophageal cancer
- Pages: 309-311
- First Published: 18 August 2019
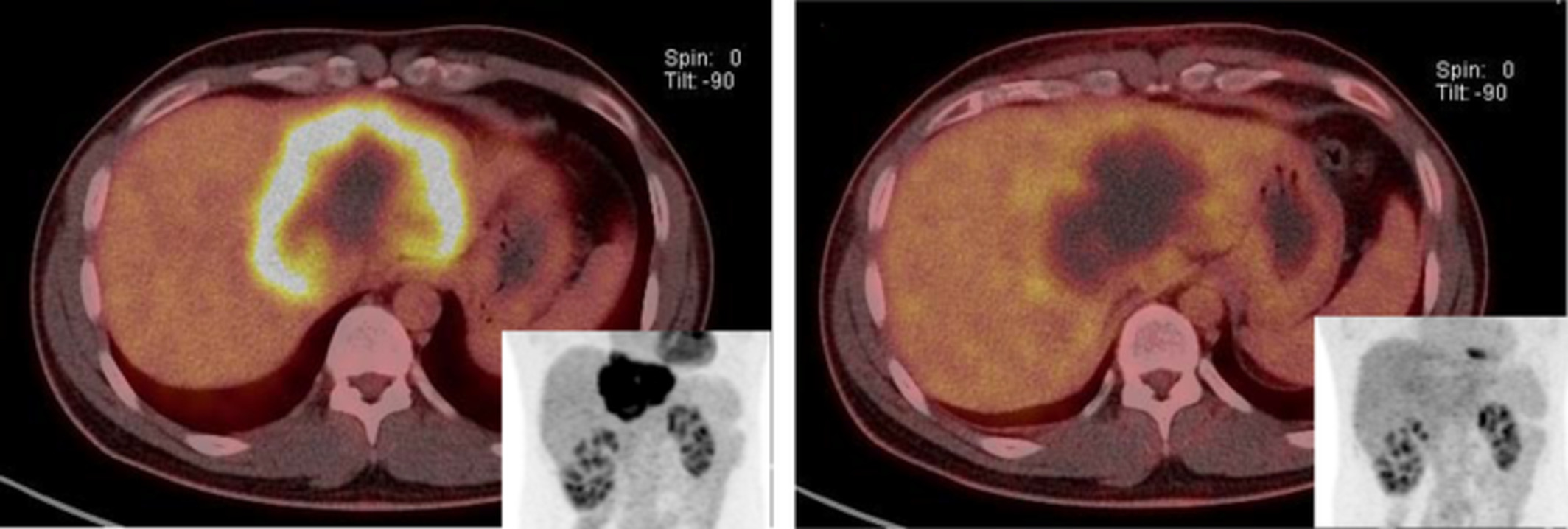
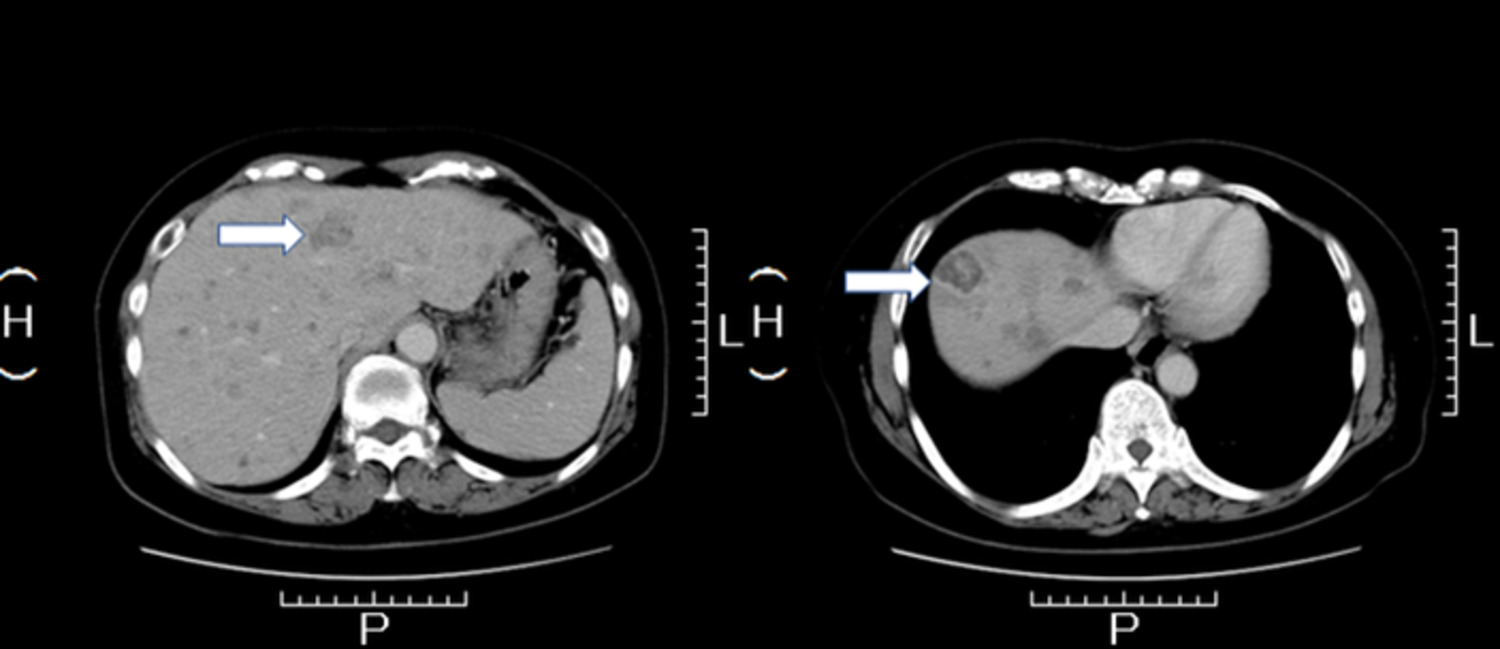
Hypereosinophilia-related liver pseudotumor with elevated interleukin-5 levels preceding T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 312-314
- First Published: 06 September 2019