Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Masthead
Contents
Table of Contents: ChemBioEng Reviews 4/2015
- Pages: 229-230
- First Published: 14 August 2015
Reviews
Mineralization of Carbon Dioxide: A Literature Review
- Pages: 231-256
- First Published: 11 May 2015
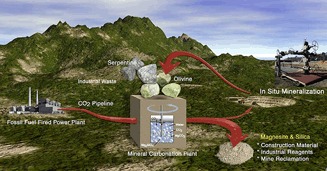
Due to the rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, carbon capture and storage methods are being researched. Carbon mineralization is reviewed as an alternative to conventional geologic storage. In situ mineralization is a component of underground geologic sequestration, while in ex situ mineralization, the carbonation reaction occurs in a separate reactor or industrial process.
Dissolution and Separation of Wood Biopolymers Using Ionic Liquids
- Pages: 257-278
- First Published: 08 July 2015
Wood is a promising renewable alternative for petroleum-based bio-fuels and useful biomaterials such as cellulose and lignin. However, processing of wood biomass has so far been expensive and time consuming. A green approach is the dissolution in ionic liquids. Here, the dissolution process and its influences as well as the economic impacts are discussed.
The Development of Stirring Technology from an Empirical Art to Science†
- Pages: 279-289
- First Published: 23 June 2015
A Review on Gas Separation Applications of Supported Ionic Liquid Membranes
- Pages: 290-302
- First Published: 17 July 2015
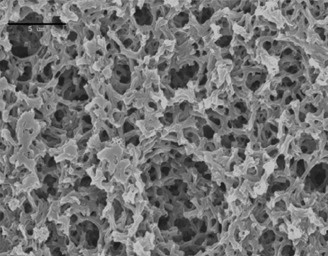
Ionic liquids are organic salts remaining liquids even under ambient temperatures. They normally consist of an organic cation and a polyatomic inorganic or organic anion. Due to their advantages, such as near-zero vapor pressure and good chemical and thermal stabilities, they are good replacements for conventional solvents in supported ionic liquid membranes. Here, the focus lies on gas separation applications.
Molecular Modeling and Simulation in Fluid Process Engineering†
- Pages: 303-310
- First Published: 08 July 2015
Molecular simulation has become very versatile due to the advance of high performance computing. It is possible to predict thermodynamic properties through physically realistic molecular models. Transport processes and heterogeneous systems can also be simulated reliably.