Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 3/2017
- Page: 241
- First Published: 22 March 2017

In this paper, adsorption of lactic acid (LA) on the outer surface, inside and in the edge of Si-doped Single Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs) with different chirality has been investigated. The results showed that the adsorption of lactic acid onto the outer surface of Si-doped carbon nanotubes is thermodynamically favored. More details will be discussed by Dr. A. N. Chermahini and his group on page 250–260 in this issue.
Contents
Contents: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 3/2017
- Pages: 242-245
- First Published: 22 March 2017
Communication
Chiral Morphology of Calcium Carbonate Mineralized in Agarose Gel
- Pages: 246-249
- First Published: 15 February 2017
Articles
Interaction of Lactic Acid and Silicon-doped Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes: A Density Functional Theory Study
- Pages: 250-260
- First Published: 28 December 2016
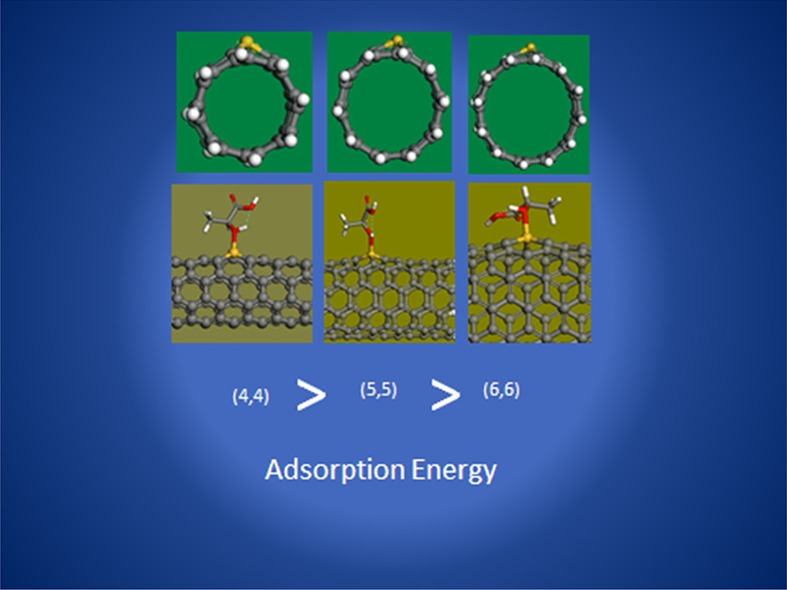
Adsorption of lactic acid (LA) on the outer surface, inside, and at the edge of Si-doped single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with different chiralities has been investigated using dispersion-corrected hybrid density functional theory. The results show that the adsorption of LA on the outer surface of Si-doped CNTs is thermodynamically favored.
Coordination Behavior of N-Donor Schiff Base Derived from 2-Benzoylpyridine Toward Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II), Pd(II), and Cr(III) Metal Ions: Synthesis, Spectroscopic and Thermal Studies, and Biological Activity
- Pages: 261-281
- First Published: 23 January 2017
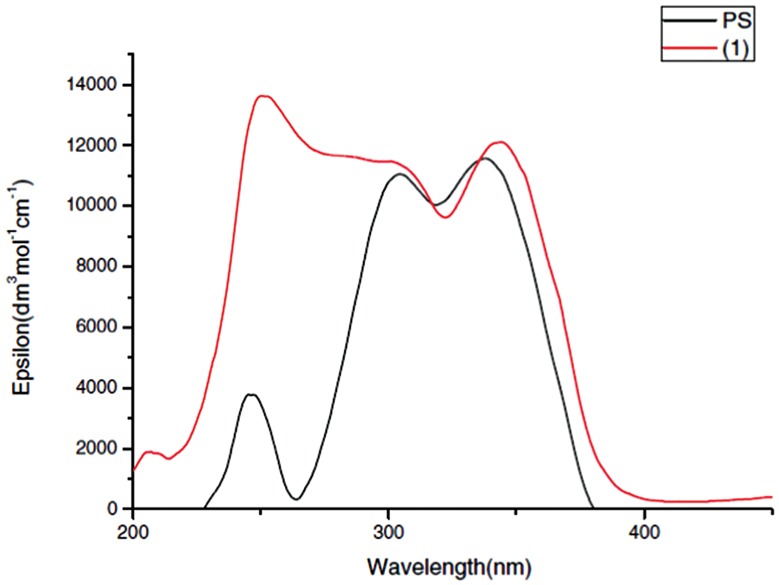
A Highly Efficient UV-C Absorber Based on Theoretical and Experimental Studies
- Pages: 282-288
- First Published: 10 February 2017
A Theoretical Approach to Model and Predict the Adsorption Coefficients of Some Small Aromatic Molecules on Carbon Nanotube
- Pages: 289-295
- First Published: 01 February 2017
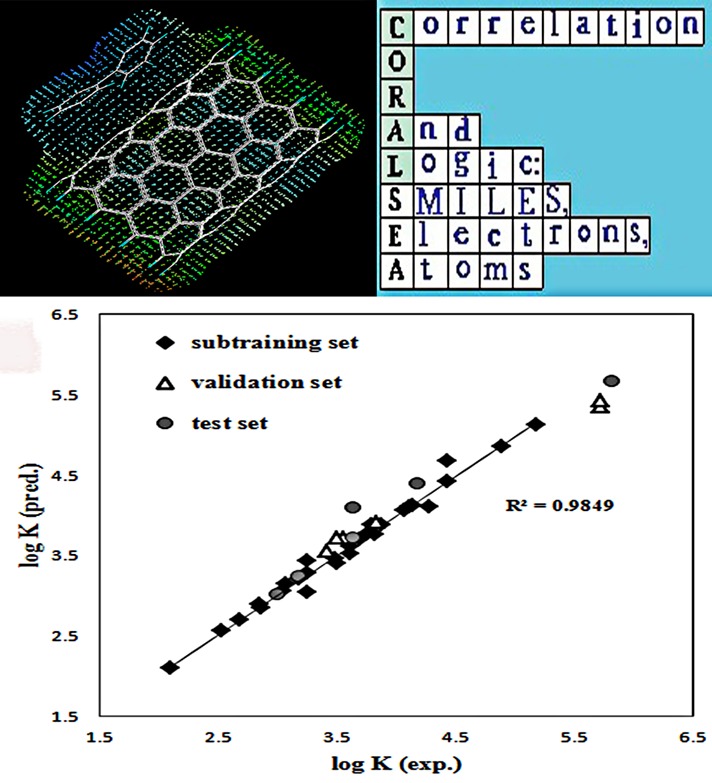
Here, for the first time, the CORAL software is used to model quantitative structure–property relationship of adsorption coefficients of chemicals on carbon nanotubes. A new method is reported for the optimization of Monte Carlo parameters in the modeling procedure. By using this method, two predictive models are obtained, which not only give satisfactory statistics for the test set but also preserves the statistical quality of subtraining and validation sets.
Synthesis and Characterization of Thiazepine/Benzothiazepine Derivatives Through Intramolecular C-2 Ring Expansion Pathway
- Pages: 296-302
- First Published: 01 February 2017
Solvent- and Metal-free Oxidative Esterification of Aromatic Aldehydes Using Urea-2,2-dihydroperoxypropane as a New Solid Oxidant
- Pages: 303-309
- First Published: 01 February 2017
Comprehensive Interactions of ACE Inhibitors With Their Receptor by a Support Vector Machine Model and Molecular Docking
- Pages: 310-320
- First Published: 01 February 2017
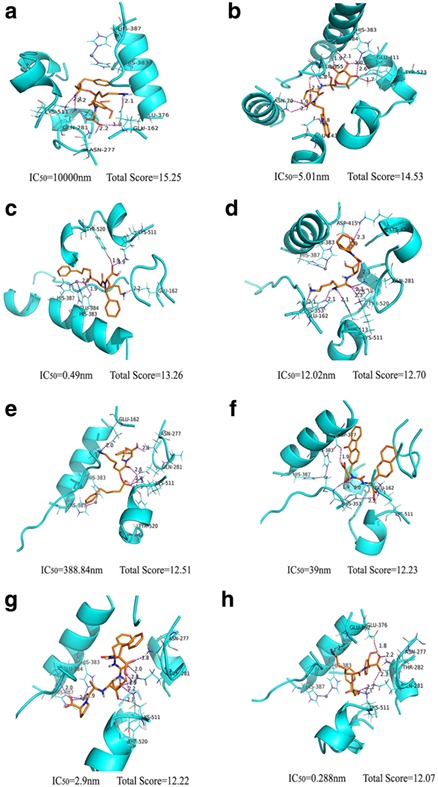
We use quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) model and molecular docking to characterize the interaction of inhibitors with angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE). The model is simple, accurate, and robust. Structure-based molecular docking studies reveal the hydrogen bond is an important force for the binding affinity. This work is useful in understanding the interaction mechanisms of inhibitors with ACE, as well as designing new ACE inhibitors.
Design and Synthesis of Novel Thioureas Derived from 4-(4-Fluorophenoxy)aniline as Anticancer Agents
- Pages: 321-330
- First Published: 01 February 2017
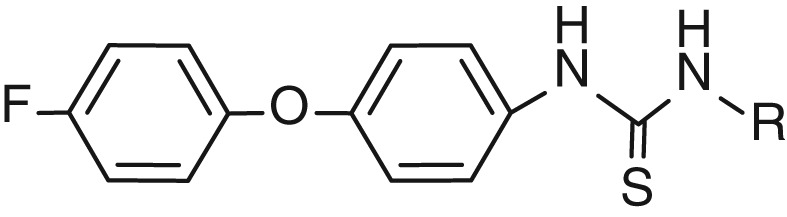
In this work, a new series of thiourea derivatives were obtained by the reaction of 4-(4-flourophenoxy)aniline with different isothiocyanates. The compounds 3, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 15, and 17 showed excellent activity compared to reference drugs on MCF-7 and SKBR3 cell lines. Especially, compound 3 did not show any cytotoxic effect on the normal breast cell line.
Sulfamic Acid-functionalized Nano-titanium dioxide as a Novel and Highly Efficient Heterogeneous Nanocatalyst for One-pot and Solvent-free Synthesis of Hexahydroquinolines
- Pages: 331-336
- First Published: 18 January 2017
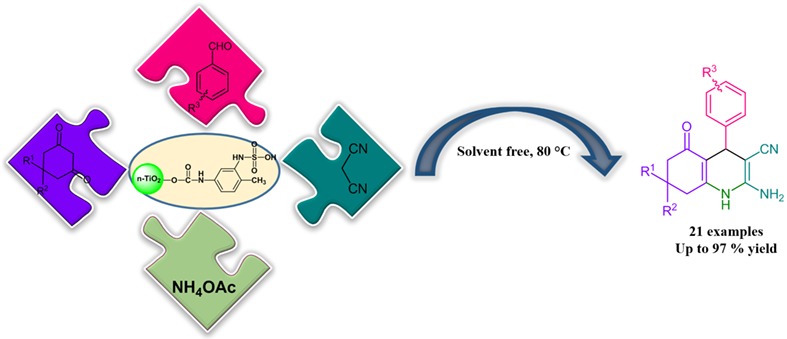
Hexahydroquinolines are synthesized via one-pot, four-component condensation of 1,3-cyclic diketones, aromatic aldehydes, malononitrile, and ammonium acetate in the presence of sulfamic acid-functionalized nano-titanium dioxide as a novel type of heterogeneous nanocatalyst. The reaction condition is optimized using the response surface method (Box–Behnken design [BBD]). The nanocatalyst can be recovered easily by centrifugation and reused for at least seven consecutive runs.
A macro analytic method for coal tar derived from pyrolysis at different temperatures
- Pages: 337-345
- First Published: 19 January 2017
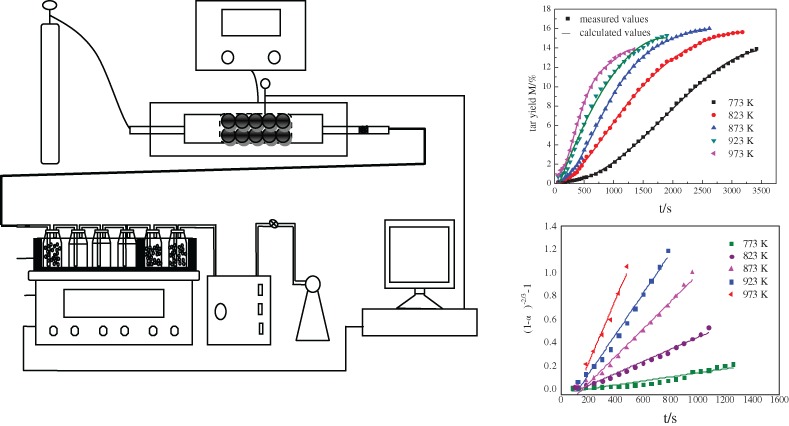
An experimental investigation aimed at studying kinetics of tar evolution during coal pyrolysis was reported. Pyrolysis tests were conducted on a specially designed laboratory-scale apparatus which allowed continuous monitoring and recording the tar yield. The fitting result illustrates that the established hybrid dynamic model was effective for the prediction of tar yield. Furthermore, shrinking core model, multi-particle's first order reaction and Anti-Jander diffusion equation were respectively built to elucidate the macro releasing mechanisms of coal tar.
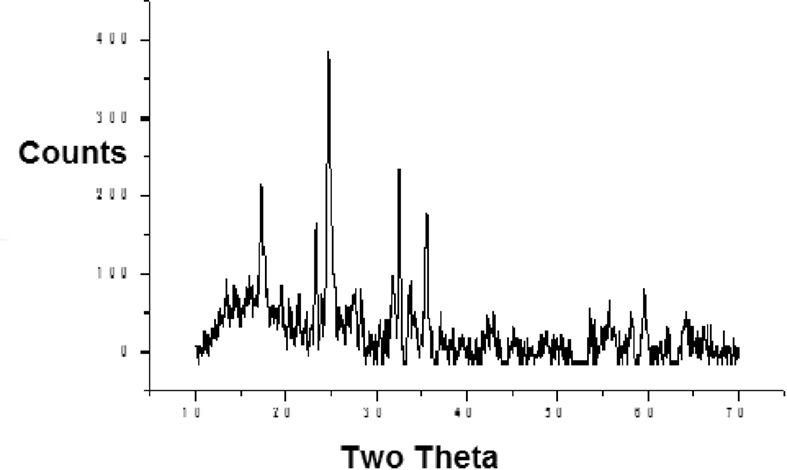
Synthesis and Characterization of [Zn-Al] Layered Double Hydroxides: Effect of the Operating Parameters
- Pages: 346-353
- First Published: 06 February 2017
![Synthesis and Characterization of [Zn-Al] Layered Double Hydroxides: Effect of the Operating Parameters](/cms/asset/80428863-c211-41e3-b532-17e2252a2750/jccs201600258-toc-0001-m.jpg)
[Zn-Al] layered double hydroxides were synthesized by the coprecipitation method at constant pH. The different synthesis parameters, including the aging time, the initial concentration of the cationic solution, the synthesis pH, the molar cationic ratio Zn/Al, and the nature of the alkali, were varied. The obtained products were characterized by different techniques and the optimal synthesis conditions were determined.
Preview
Preview: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 4/2017
- Page: 354
- First Published: 22 March 2017