Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Data-Aggregation-Aware Energy-Efficient in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Multi-Stream General Adversarial Network
- First Published: 22 January 2025
The lifetime of a wireless sensor network (WSN) can be impacted by the energy consumption of the routing protocol, because small sensor nodes are typically hard to recharge after deployment. Generally, data aggregation is employed to decrease the data redundancy and save energy at each node in a WSN. Traditional routing protocols frequently fall short of handling the complexities of data aggregation while getting energy efficient. In this paper, Optimized Multi-Stream General Adversarial Network espoused Data-Aggregation-Aware Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol for WSN (MSGAN-RPOA-DAA-EERP) is proposed. Here, Multi-Stream General Adversarial Network (MSGAN) is used for routing protocol.
Secured DDoS Attack Detection in SDN Using TS-RBDM With MDPP-Streebog Based User Authentication
- First Published: 23 January 2025
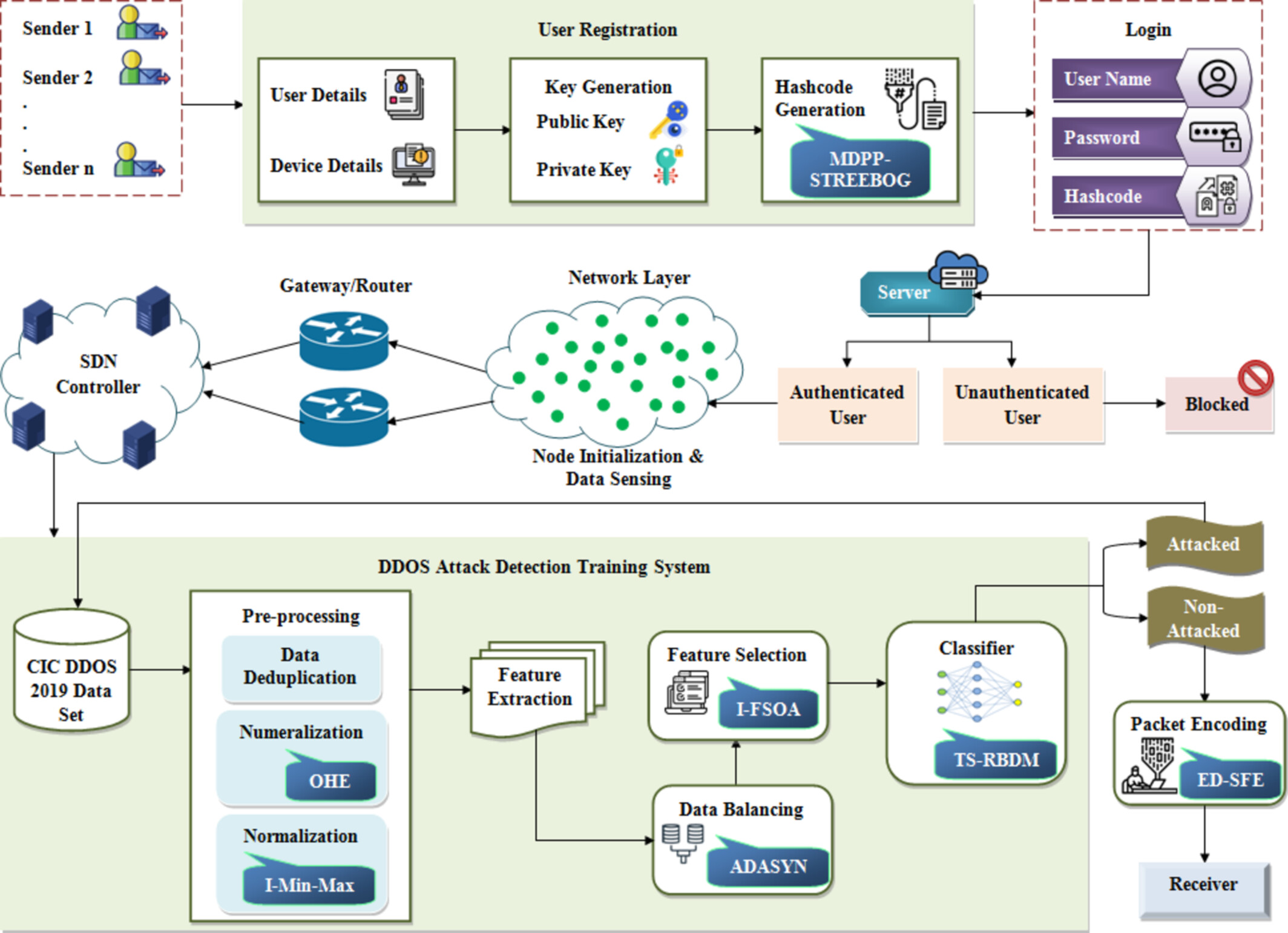
This work concentrated on detecting the DDoS attack centered on the SDN controller and classified the attack by utilizing the TS-RBDM with the user authentication process. Primarily, for user authentication, hash codes are generated. After that, the user is authenticated by the server, and these users initialize their device nodes in the network layer. Then, the network's efficacy is enhanced by the SDN controller, which sends the sensed data to the DDoS attack detection system.
Development of Heuristic Strategy With Hybrid Encryption for Energy Efficient and Secure Data Storage Scheme in Blockchain-Based Mobile Edge Computing
- First Published: 24 January 2025
In the proposed architecture, the user's data is strategically stored in the entity layer, with the optimal data storage locations determined using the innovative HBRAOA. Moving to the edge computing layer, a highly secure method of data encryption is employed. An optimal key-based homomorphic encryption algorithm, utilizing ECC. This ensures that data is encrypted using the most efficient keys, with the selection process enhanced by leveraging the same HBRAOA utilized in the entity layer. Authentication of users is facilitated through digital signatures, granting authorization within the system. These signatures are then distributed to the blockchain layer, ensuring immutable storage and providing a decentralized means of verification. Indexes of shared data are stored within the blockchain, safeguarding against faults and tampering. Lastly, the cloud layer serves as the repository for valuable encrypted data. Authenticated users possessing the necessary encrypted keys can securely access their data by decrypting it.
LoRa Meets Artificial Intelligence to Optimize Indoor Networks for Static EDs
- First Published: 30 January 2025
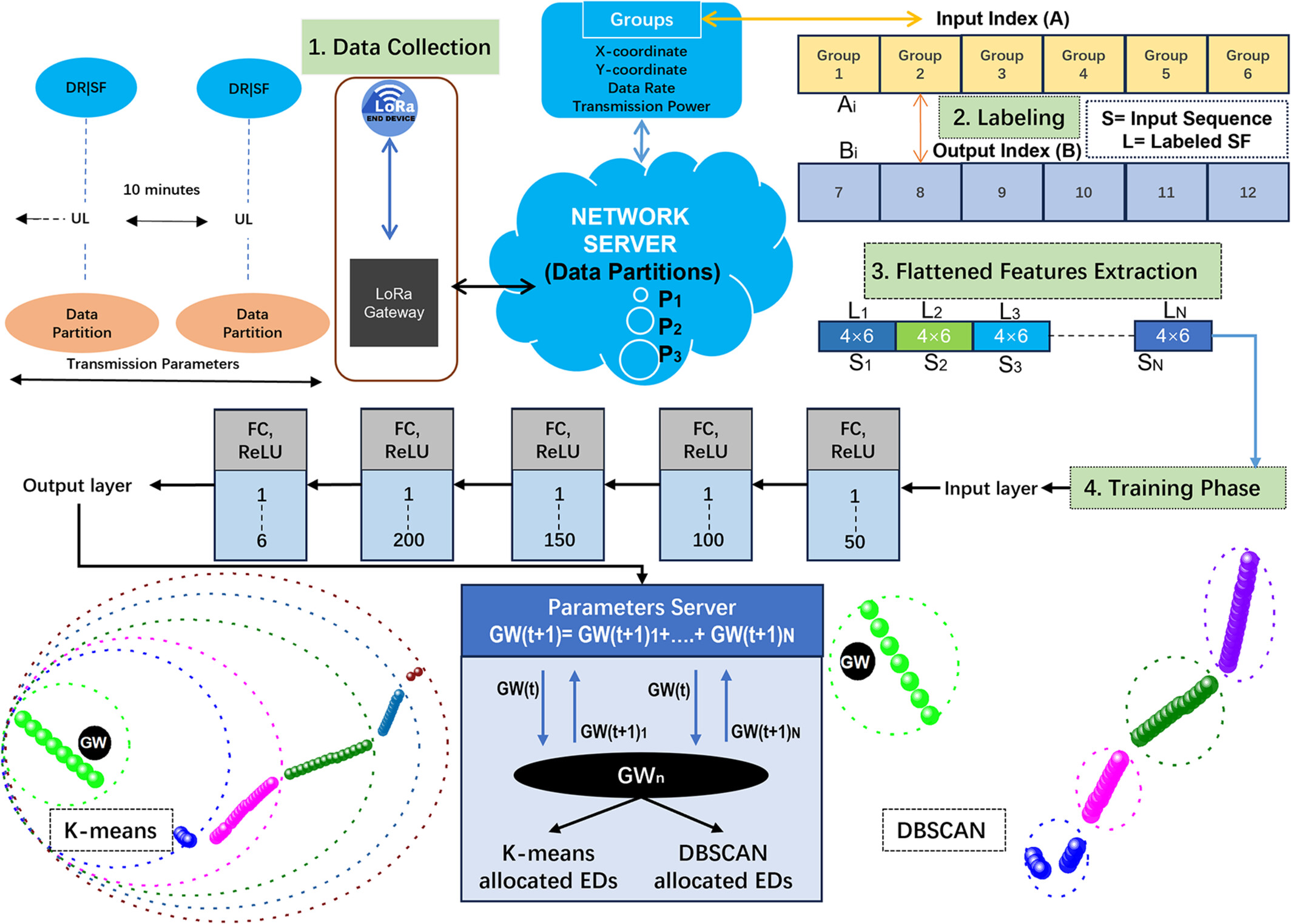
This paper meticulously allocates EDs based on K-means and DBSCAN for different GW combinations. Secondly, it introduces hybrid models tailored for LoRa-based indoor monitoring systems. These models with DNN and DML dynamically adjust transmission parameters to effectively address challenges such as interference, data throughput losses, and high-power consumption.
A Lightweight CP-ABE Scheme for EHR Over Cloud Based on Blockchain and Secure Multi-Party Computation
- First Published: 30 January 2025
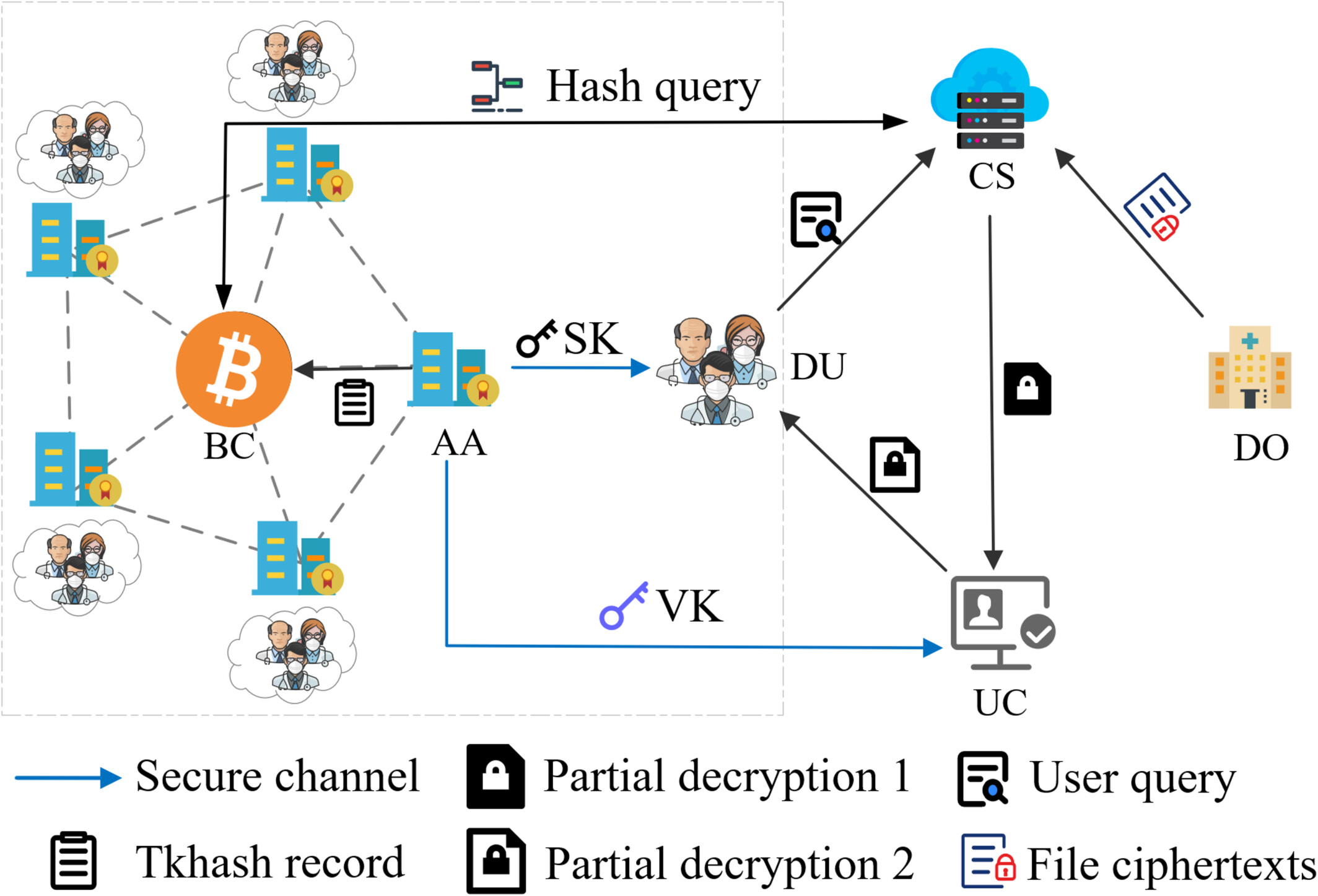
This article proposes a lightweight CP-ABE scheme for EHR over cloud based on blockchain and secure multi-party computation (LCBS). We design a blockchain suitable for EHR systems to record the users' key information, assisting multiple entities to verify the key at different stages and protecting the EHR from illegal acquisition.
There is Mathematics for That!: A Formal Verification of Privacy and Simulative Analysis of Consumer-Centric Content Delivery in Iot
- First Published: 30 January 2025
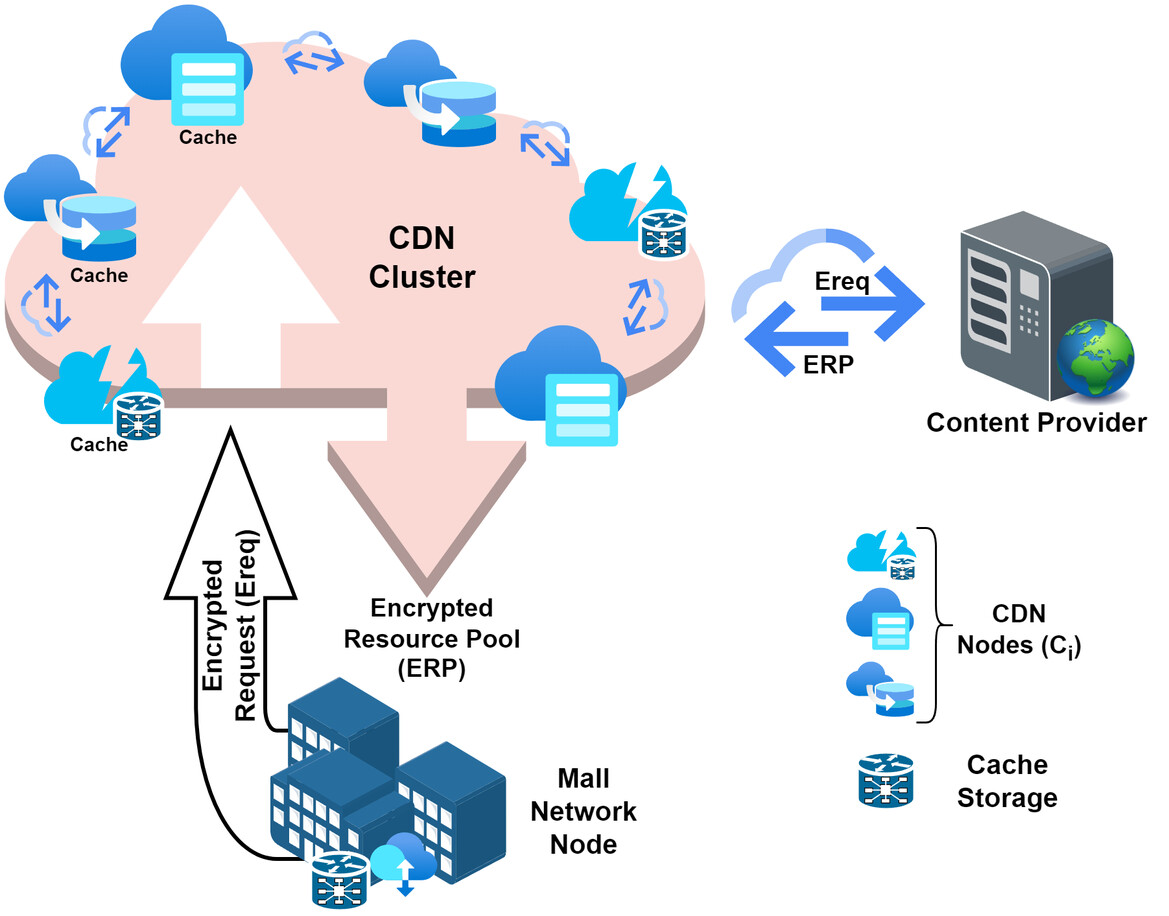
This article extends our previous research titled, ‘Towards a Software-defined Networking Model for Consumer-Centric Content Delivery Network for IoT’, by providing the formal and experimental analysis of the proposed CCDN model. The detailed contribution is given as follows: The study conducts a formal verification and analysis of privacy concerns and computational overhead associated with the data request and delivery processes. The study details the experimental setup, along with the tools and technologies leveraged in the implementation of the CCDN model. The study performs a performance evaluation of the proposed use case, measuring key metrics such as latency, throughput, and PLR. The study presents a comparative analysis between the traditional CDN and the proposed CCDN model. The study assesses the scalability of the proposed CCDN model under various scenarios.
Beyond Traditional RFID: Unveiling the Potential of Wi-Fi, 5G, Bluetooth, and Zigbee for Backscatter Systems
- First Published: 30 January 2025
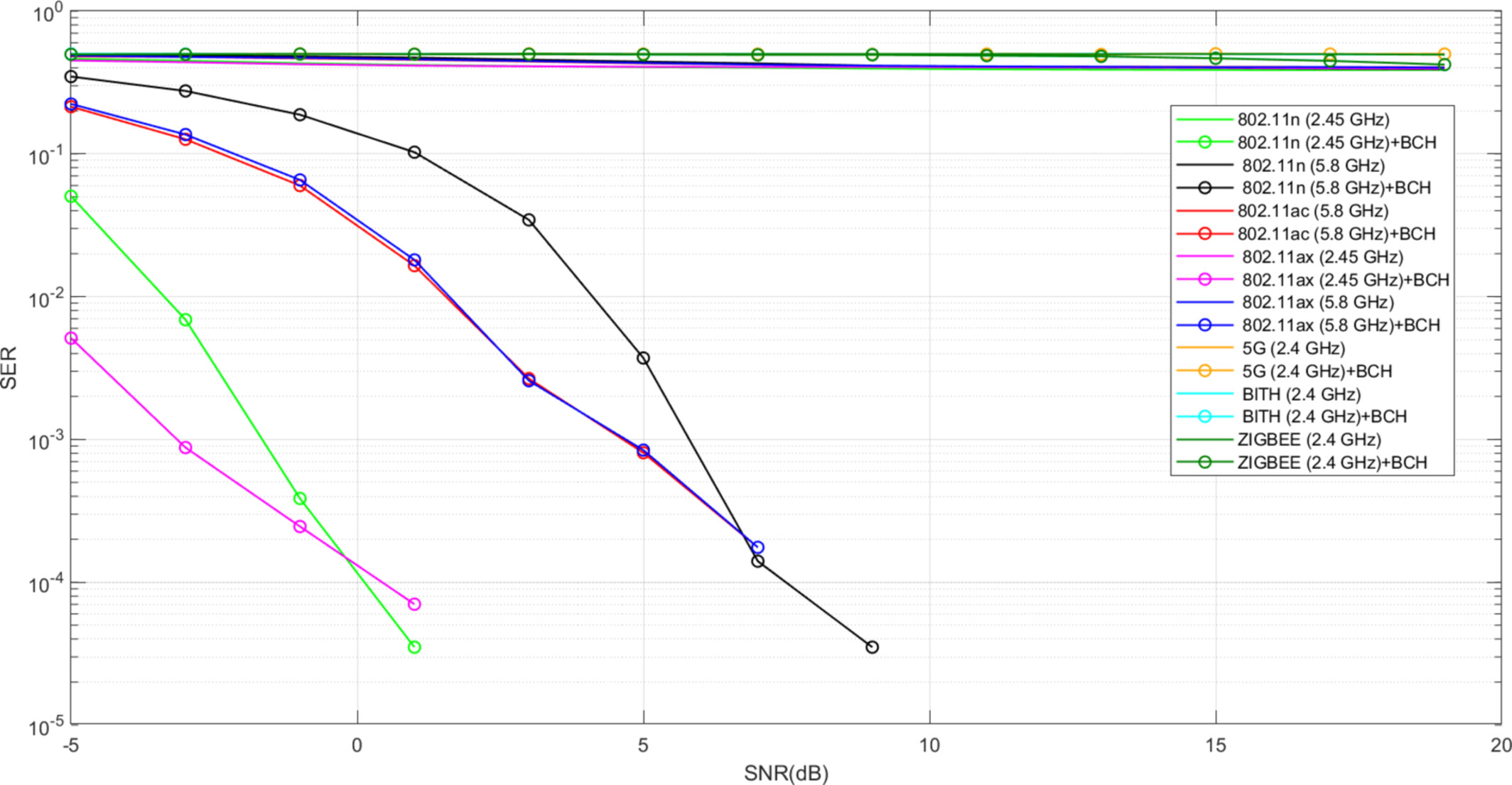
This study proposes a novel RFID system that utilizes ubiquitous radio sources, such as Wi-Fi, 5G, Bluetooth, and Zigbee, to replace expensive dedicated readers. The system achieves a communication range of up to 1 m with the help of error correction coding techniques, making it a promising alternative for RFID applications.
Blockchain Empowered Quantum Safe Batch Aggregate Signature Algorithm for Authenticated Data Trading in Internet of Vehicles
- First Published: 02 February 2025
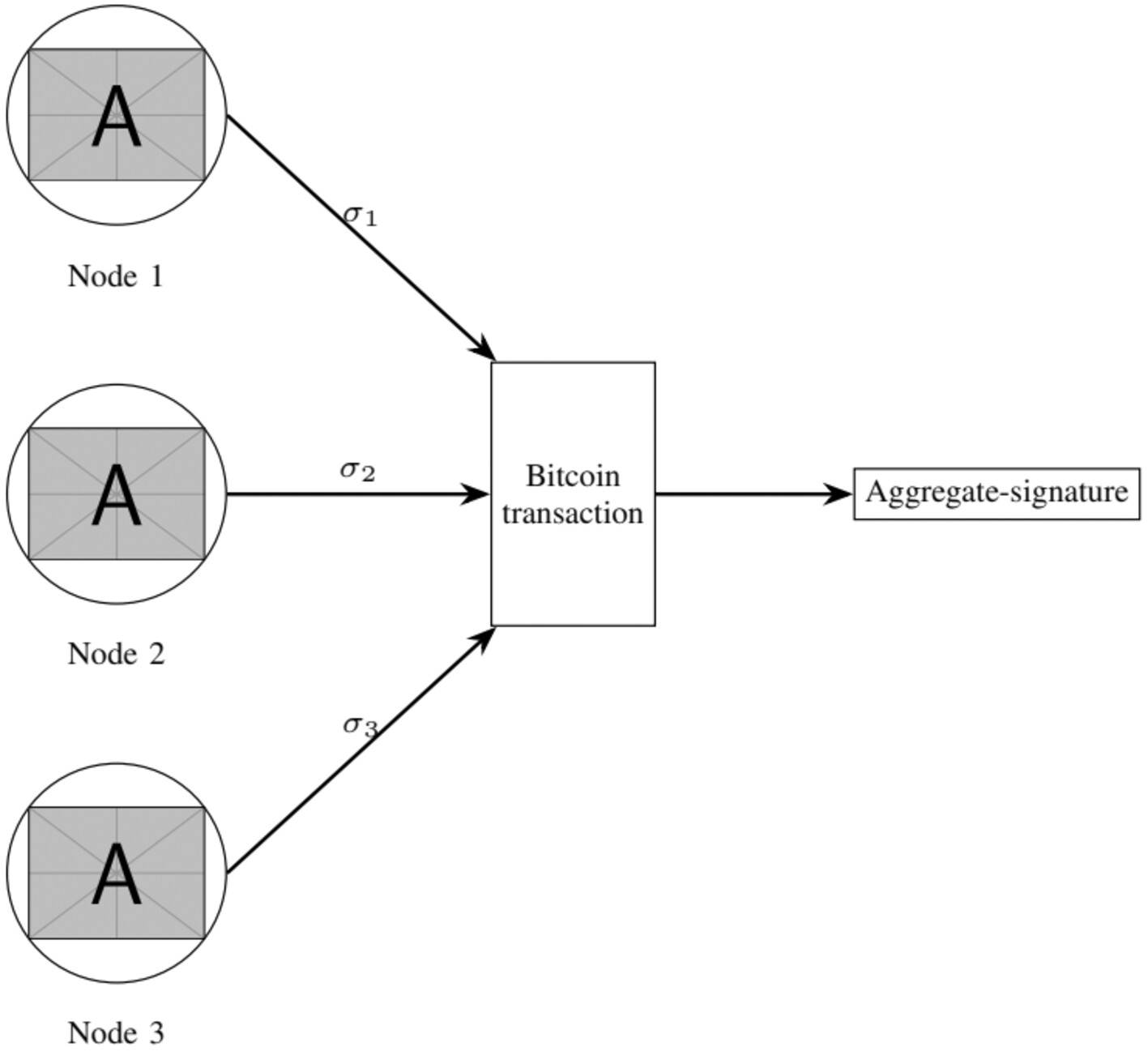
In this paper, an authorized node performs local aggregation, gathering data, trading information, and enabling the verification of transactions in a distributed environment. The practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance consensus mechanism supporting multi-signature is also secure against future quantum attacks, and it is established based on local aggregators, audits, and verifies transaction records among data traders. The goal is to provide an authenticity and truthful method for data trading in IoV. The proposed algorithm is secure against quantum attacks, and it uses MLWE, and MSIS assumptions based on ring, which make it efficient.
An Enhanced IOMT and Blockchain-Based Heart Disease Monitoring System Using BS-THA and OA-CNN
- First Published: 03 February 2025
- Data Security and Integrity: Patient and doctor data is secured through blockchain and IPFS, ensuring that the data is both encrypted and tamper-proof.
- Advanced Heart Disease Classification: The system uses advanced techniques like PV-EMD, wavelet components extraction, and OA-CNN to analyze ECG, PCG, and arrhythmia data, leading to accurate heart disease classification.
- High Accuracy: The proposed system achieves a high classification accuracy of 98.32%, outperforming existing models in detecting heart disease.
Optimal Beamforming for Covert Communication in MIMO Relay Systems
- First Published: 04 February 2025
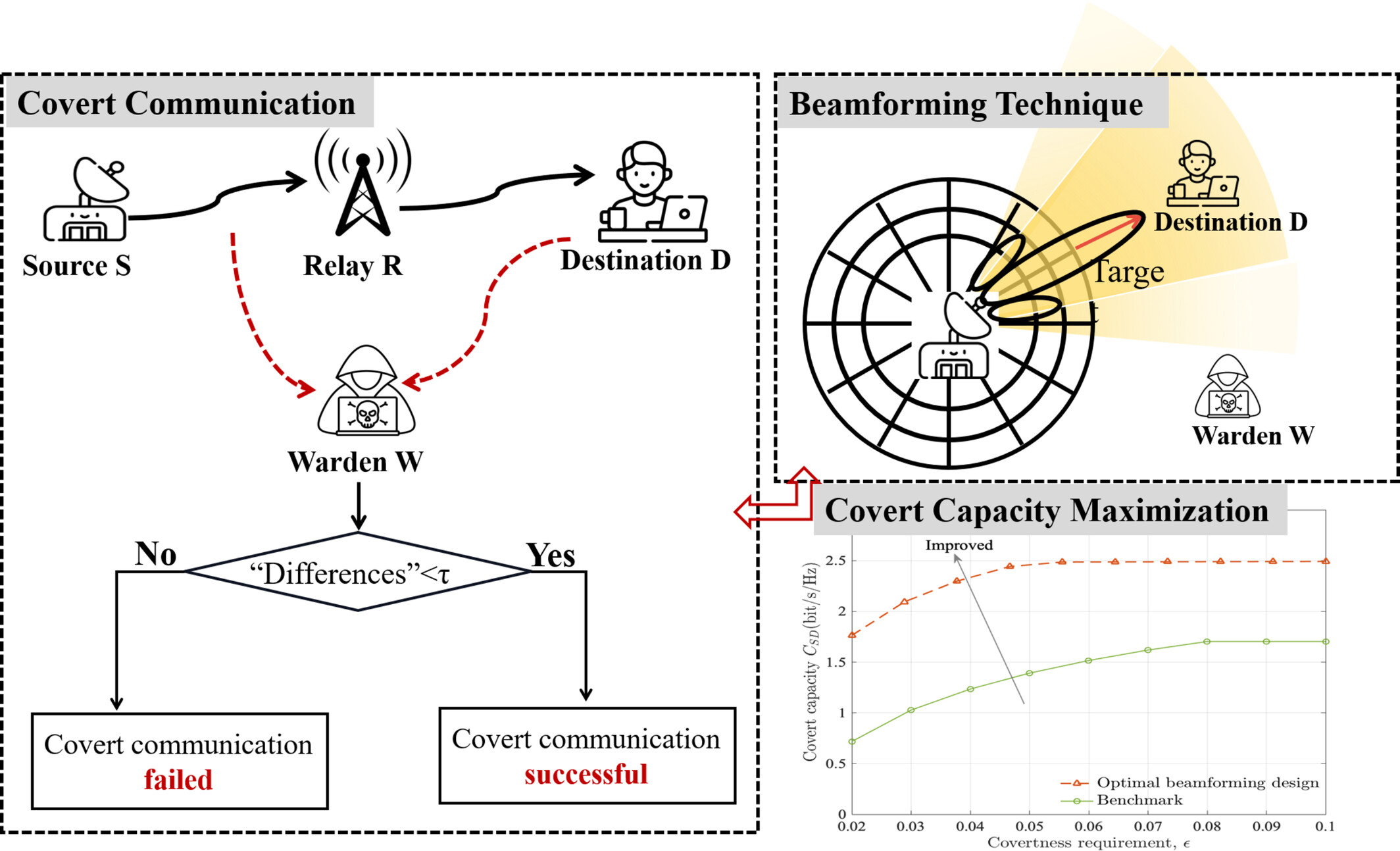
This paper presents an analysis of optimal beamforming design for covert communication in a MIMO relay system, where a multi-antenna source covertly communicates with a multi-antenna destination via a multi-antenna DF relay, avoiding detection by a single-antenna warden. We develop corresponding theoretical models for performance analysis in terms of DEP and covert capacity and explore the optimization of beamforming matrices at source and relay for covert capacity maximization.This work demonstrates significant performance enhancements in covert communication through MIMO relay systems.
SURVEY ARTICLE
An Extensive Review of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques on Network Intrusion Detection for IoT
- First Published: 05 February 2025
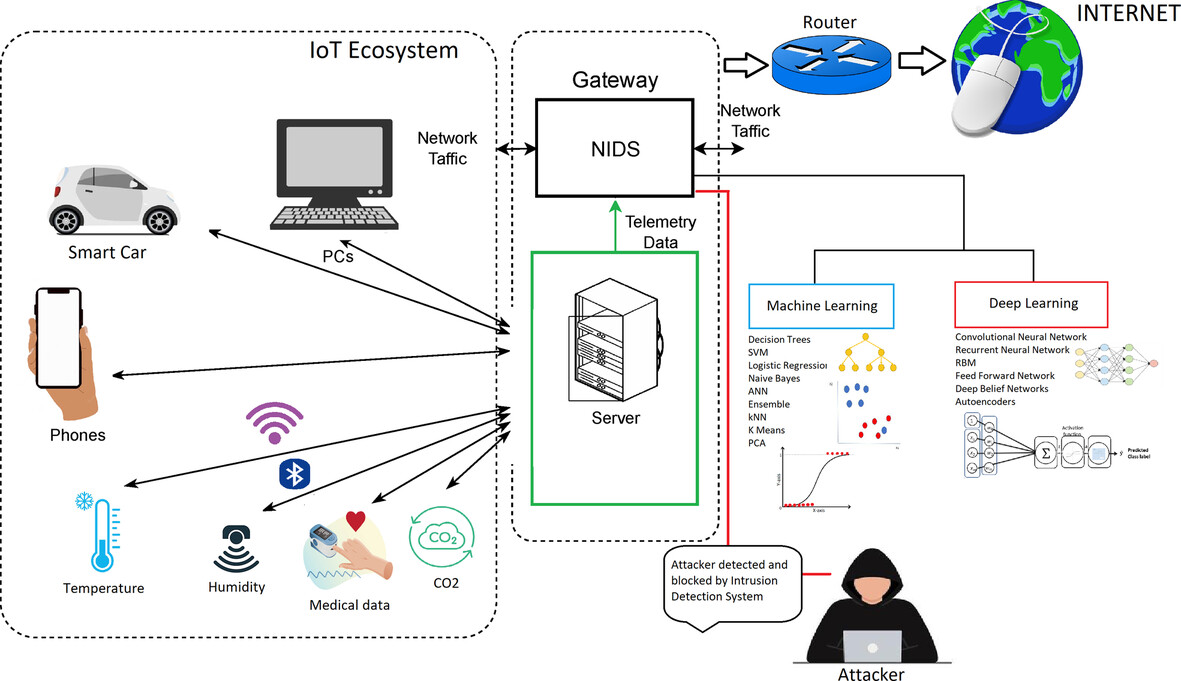
In this paper, we present a comprehensive analysis of IoT intrusion detection system (IDS) methods, deployment strategies, evaluation approaches, datasets, and technologies, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. We extensively discuss different machine learning and deep learning techniques and explore various algorithms, citing recent studies conducted by researchers. We also highlight the current state of IDS and identify the challenges and potential avenues for further research.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Distributed Cooperative Spectrum Optimization Method Based on Coalition Formation Game for Ocean and Traffic Iot
- First Published: 06 February 2025

To enhance spectrum utilization for maritime users and shore-side traffic, we propose a distributed anti-jamming cooperative spectrum decision-making method based on a coalition formation game. It achieves stable coalition grouping by optimizing coalition formation strategies and power control, thereby increasing the transmission rate and reducing the loss.
Channel Estimation Based Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces for Massive MIMO System Considering Spatially Correlated Channels
- First Published: 09 February 2025
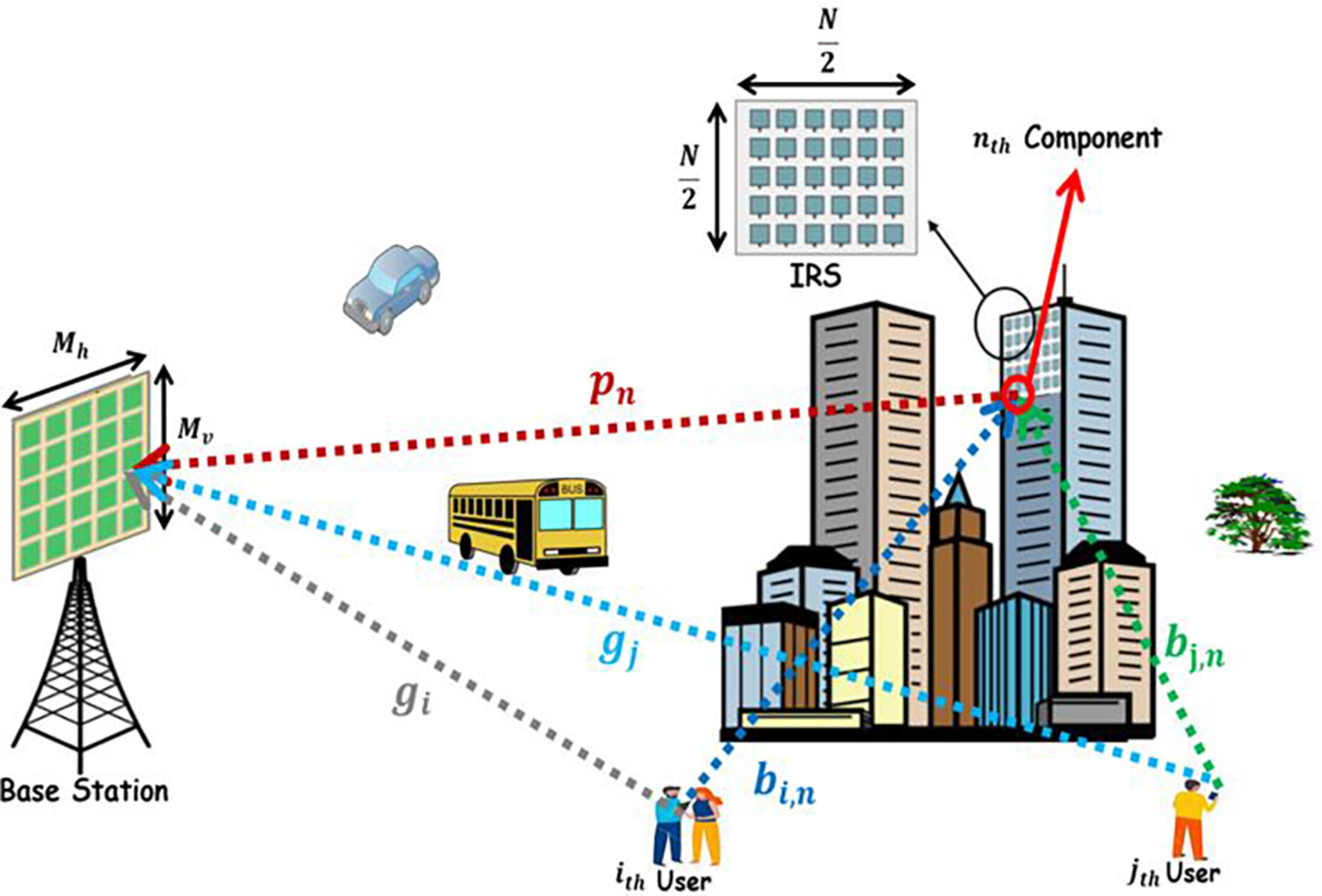
This work investigates a three-stage Massive multiple-input multiple-output (M-MIMO) channel estimation assisted by an IRS in a more practical propagation environment, that is, spatially correlated channels. In this framework, this work proposes a local multiple scattering (LMS) model that describes the spatial correlation (SC) over the proposed uniform rectangular array (URA) by relying on the LMS model that describes the SC over a ULA configuration. In other words, using the Kronecker product (KP) of the correlation matrix constructed through a ULA, we built the correlation matrix that describes the SC over the proposed URA.
A Novel Approach to Driver Negligence Detection: EAXB-EVS Algorithm With IoT Integration
- First Published: 09 February 2025
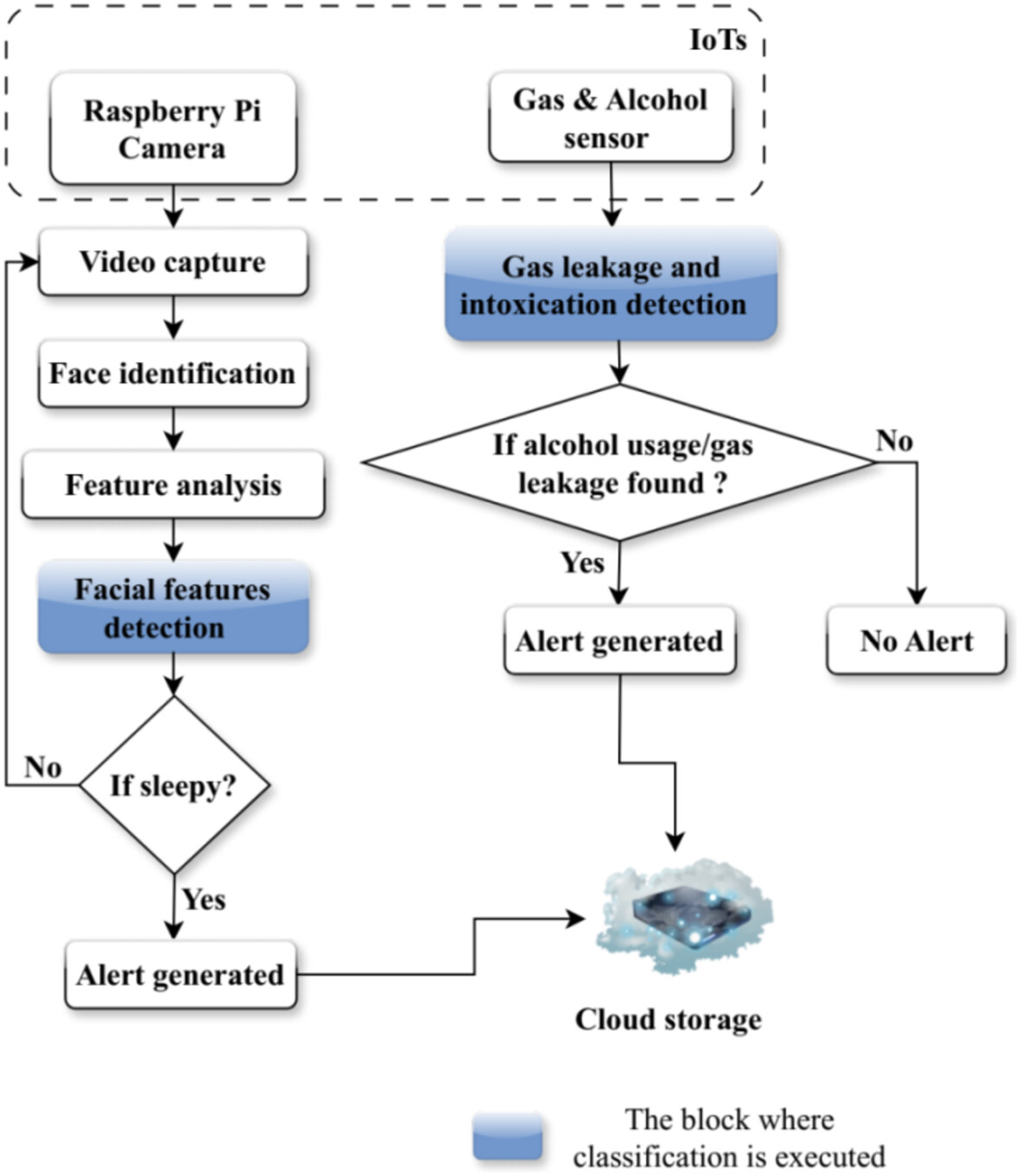
A novel Ensemble-voting Adaptive extreme-based Energy Valley Search (EAXB-EVS) algorithm is proposed for driver's negligence detection within the VANET environment. The adaptive extreme boost algorithm's hyperparameter is fine-tuned using the Energy Valley Search optimization (EVS) algorithm to offer the most accurate response to alert generation. Ensemble voting methodology merges multiple weak models, forming a robust model to determine the driver's state of carelessness including intoxication, gas leakage, and drowsiness. The experimental results validate the model's ability to detect the motorist's status of driving and the network's ability.
A Secure and Efficient Framework for Intelligent Transportation: Leveraging ISDF and Augmented Iot Algorithms
- First Published: 13 February 2025
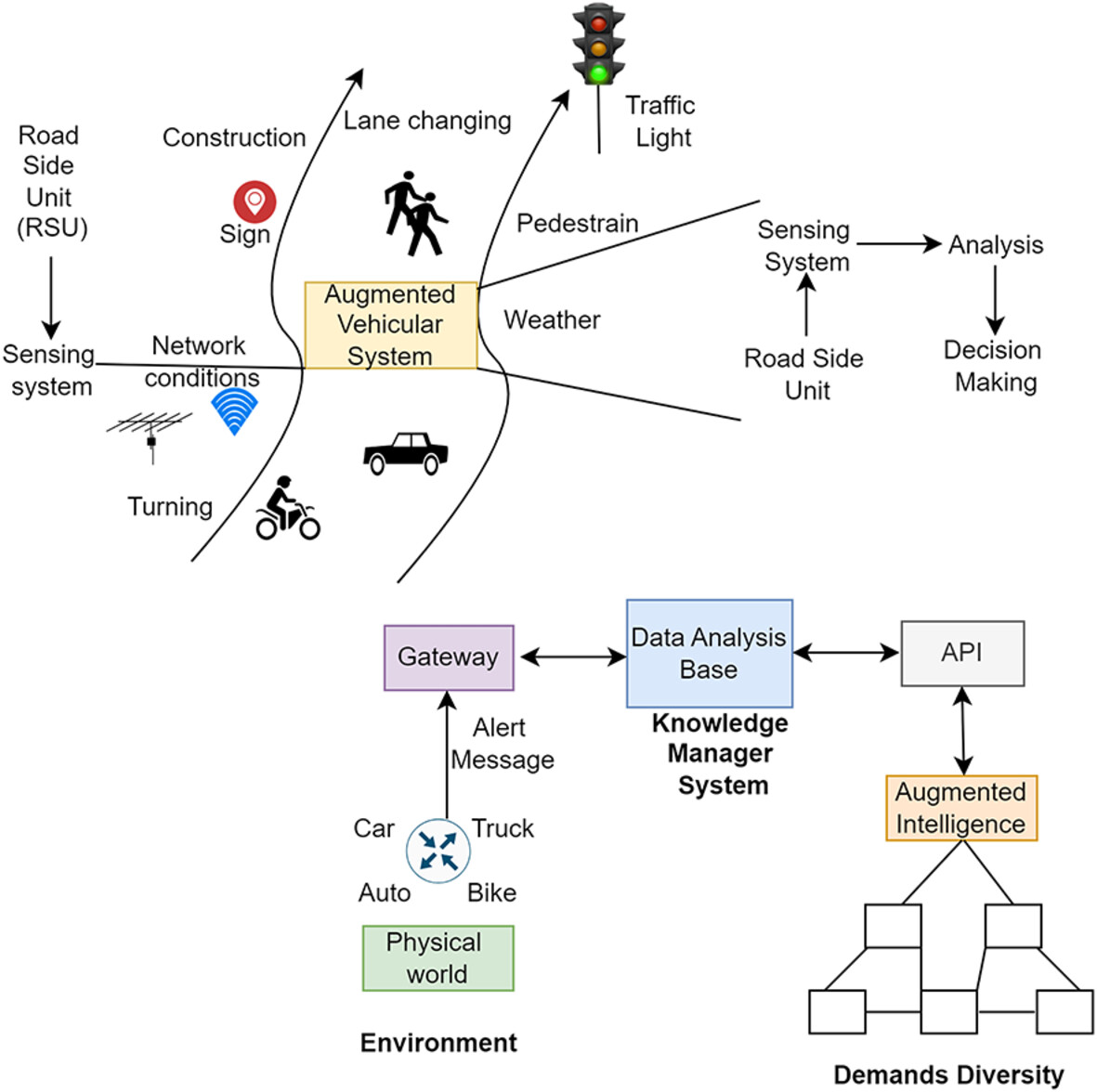
This article proposes an efficient decision-making framework for the Integrated Sensing Digital Framework (ISDF) in intelligent transportation. Using augmented algorithms and bootstrapping learning, the framework improves real-time vehicular communication and security in IoT networks. Simulations validate its performance against delivery ratio, accuracy, and resilience to DoS attacks.
Adaptive Entropy Lightweight Encryption Estimate for Software Defined Network to Mitigate Data Security Threats in Smart Cities
- First Published: 17 February 2025
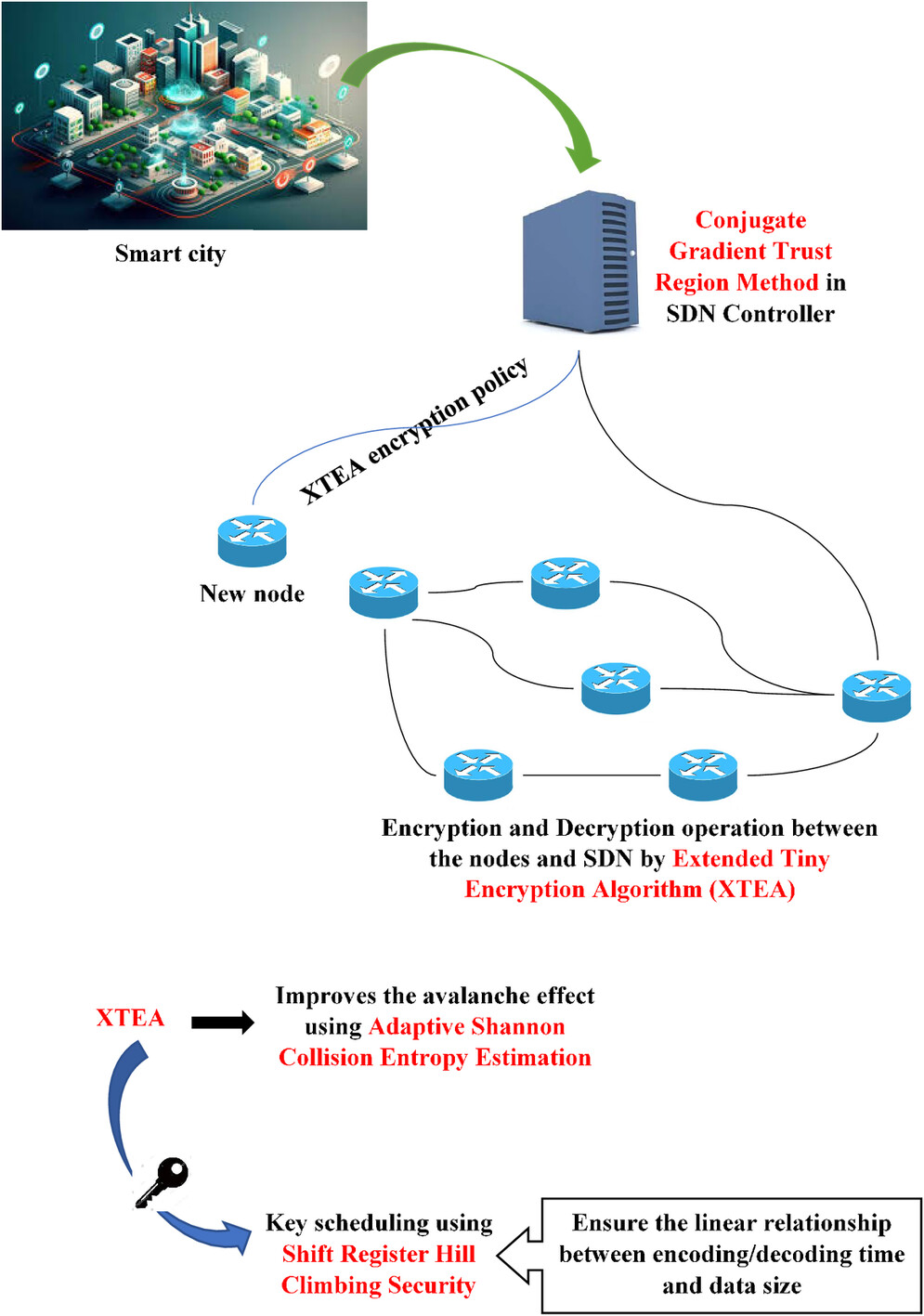
Traditional networking environments typically configure encryption policies statically on individual devices, but a fast and space-efficient system for data security is needed. Hence, a novel Adaptive Entropy Lightweight Encryption Estimate for the Software Define Network is introduced to mitigate data security threats. Large-scale SDN deployments necessitate complex encryption policies, with lightweight algorithms posing limitations due to their lack of high avalanche effects. Thus, a novel Adaptive Entropy Lightweight Encryption Algorithm is proposed that uses Extended Tiny Encryption Algorithm (XTEA) for efficient encryption and decryption and Adaptive Shannon Collision Entropy Estimation to improve the avalanche effect. Moreover, the Conjugate Gradient Trust Region Method within SDN allows controllers to adjust XTEA encryption parameters. Further, maintaining a linear relationship between encoding/decoding time and data size is crucial for efficient resource allocation and processing time estimation in lightweight encryption algorithms. Hence, a novel Shift Register Hill Climbing Security is introduced, which uses Shifted Feedback Register (SFR) to generate pseudo-random bits, and Beta-Adapt Hill Climbing algorithm (BAHC) to dynamically adjust SFR parameters. The findings indicate that the suggested model has less execution time, delay, packet loss, and high throughput, compared to other existing models.
Wireless mmWave Communication in 5G Network Slicing With Routing Model Based on IoT and Deep Learning Model
- First Published: 14 February 2025
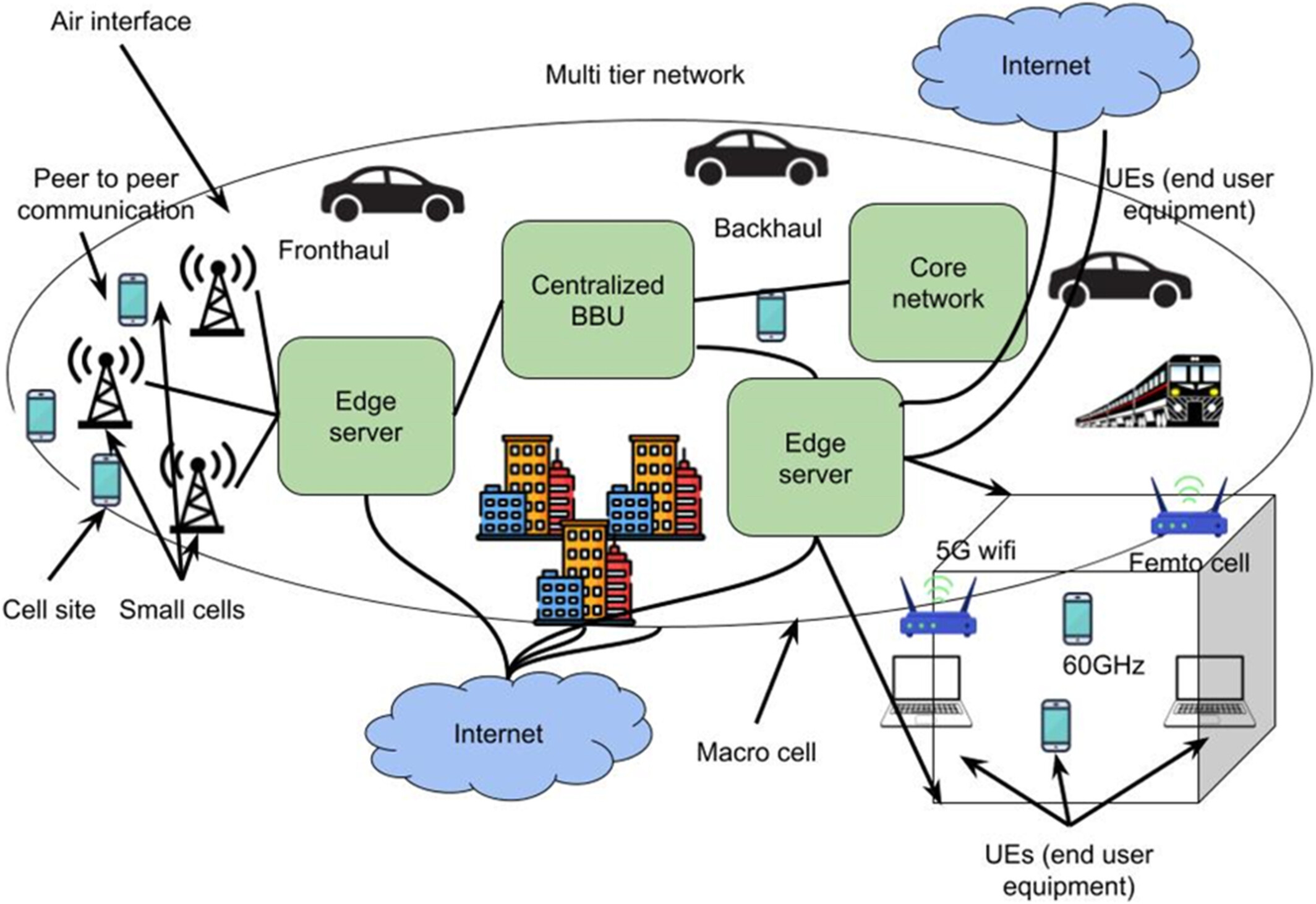
With the service-based architecture, network functions can be deployed as micro-services in a scalable, flexible, and economical manner. Additionally, it makes the CN more programmable, which makes it possible to automate and coordinate network operations, making the network more flexible and able to deliver real-time services. The data plane function UPF which is in charge of forwarding and processing network traffic between user equipment (UEs) and the network; AMF (Access and Mobility Function), which controls UE mobility within the network; and SMF (Session Management Function), which initiates, maintains and terminates sessions between UEs and the network, are some of the crucial components of the service-based 5G network. Based on the network standards and additional QoS requirements of each UE, the Network Slice Selection Function, or NSSF, chooses, distributes, and manages the appropriate number of network slices. Channel model: Each scattering path in mm-wave channels should be compatible with the channel characteristics because there are a limited number of scattering paths and a large number of geometric channel methods.
SURVEY ARTICLE
Towards Secure and Efficient Data Aggregation in Blockchain-Driven IoT Environments: A Comprehensive and Systematic Study
- First Published: 14 February 2025
Conducting a systematic and analytical investigation of data aggregation methods in blockchain-based IoT. Providing a comparative analysis of selected articles, offering a detailed overview of their techniques. Identifying crucial areas for future research, where advancements in data aggregation methods for blockchain-based IoT can be made.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
An Optimized Dual Generative Hyperbolic Graph Adversarial Network With Multi-Factor Random Permutation Pseudo Algorithm Based Encryption for Secured Industrial Healthcare Data Transferring
- First Published: 17 February 2025
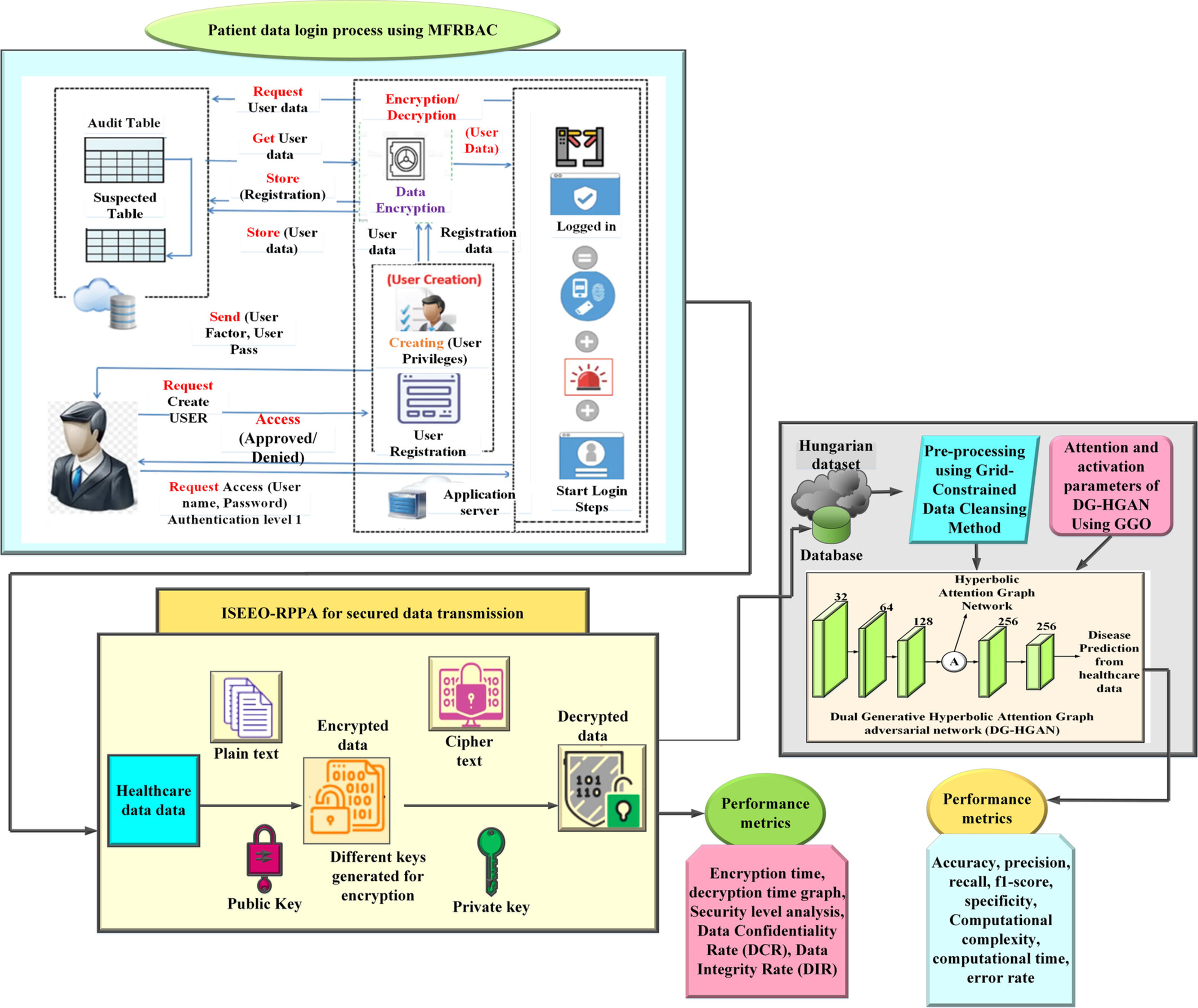
This work is proposed. In this, manuscript, an optimized dual generative Hyperbolic Attention Graph adversarial network with Multi-factor Random Permutation Pseudo Algorithm based encryption (Deep Greylag-GHGAN) for secured Industrial healthcare data transferring is proposed. In this, the initial patient data are authenticated using combines Multi-Factor Role-Based Access Control (MFRBAC). To further enhance security, an Improved Secure Encryption with Energy Optimization using a Random Permutation Pseudo Algorithm (ISEEO-RPPA) is employed. Subsequently, the secured medical data undergoes a thorough pre-processing phase using the Grid-Constrained Data Cleansing Method, which includes steps for instance data emetic, data decrease, normalization, and noise lessening. The pre-processed data is then classified using a dual generative Hyperbolic Attention Graph adversarial network (DG-HGAN). Finally, the classification process is optimized using the Greylag Goose Optimization (GGO) algorithm. This multi-faceted approach ensures not only the security and integrity of medical data but also its efficient and accurate classification, making it suitable for real-world industrial healthcare applications. The suggested Deep Greylag-GHGAN technique is realized in python Platform. The observed quantitative outcomes reveal that the proposed Deep Greylag-GHGAN method attains an improved security by 93%, and accuracy by 99.9% than the other conventional methods. This indicates the approach's superior efficiency and potential for further development in the field.
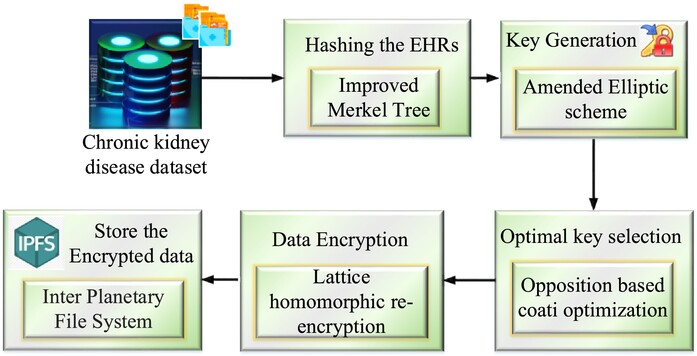
Lattice Homomorphic Assisted Privacy Preserving Electronic Health Records Data Transmission in Internet of Medical Things Using Blockchain
- First Published: 17 February 2025
ERRATUM
Correction to “Energy Efficient Resource Allocation in Cache-Enabled Fog Networks”
- First Published: 10 February 2025