Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Optimizing Energy Efficient Routing Protocol Performance in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks With Machine Learning Algorithms
- First Published: 24 February 2025
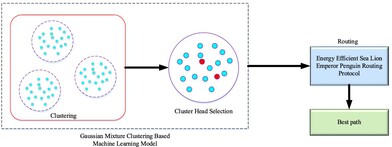
Over the last few decades, modern information and communication technology has been utilized in a variety of ways to monitor marine ecosystems. Underwater wireless sensor networks (UWSNs) can analyze soil properties, including moisture content, salinity and movement, to predict various disasters. Due to the limited capacity of the integrated batteries as well as the difficulties in replacing or charging them, energy efficiency has become a difficult problem to manage in UWSN design. Numerous approaches are presented to address these issues, but the majority of them are complicated and ineffective. In this study, the Gaussian mixture clustering-based machine learning (GMCML) model is used to compute the mean and covariance parameters for each cluster. The energy-efficient sea lion emperor penguin routing protocol (EESLEPRP) is used to determine the optimal network path. In this case, the residual energy, delay, as well as distance fitness functions of each node may be evaluated to determine the optimal path. Various methods are used to compare the proposed model in terms of throughput, number of active nodes, average end-to-end delay, death rate, packet delivery ratio, total energy consumption, packet loss ratio and packet received rate. The proposed strategy achieved a 90.56% throughput with a 2.23% PLR ratio and a 97.76% PDR. The proposed approach maintains an end-to-end latency of 1.38 ms while having the best energy usage of 97.69%. Consequently, the death rate in the proposed model is 0.0847. The results show that using the proposed model improves UWSN performance.
An Efficient Cyber Security Attack Detection With Encryption Using Capsule Convolutional Polymorphic Graph Attention
- First Published: 25 February 2025
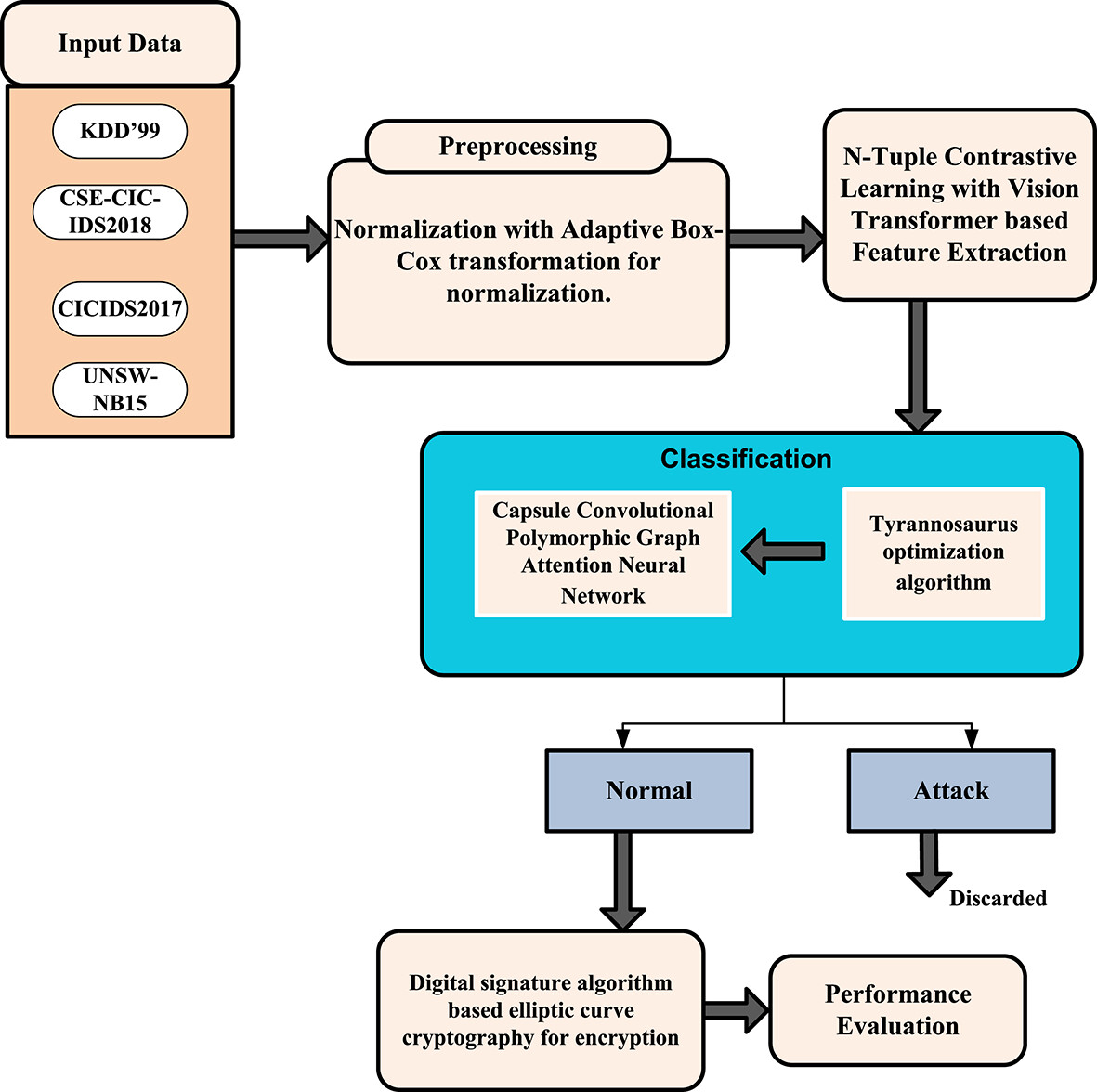
Despite advances in system security, challenges remain in the form of system vulnerabilities and evolving cyber threats. Intrusion detection using deep learning (DL), which serves as the second line of defense after firewalls, has progressed rapidly, yet still faces issues such as misclassification, false positives, and delayed or inadequate responses to attacks. These ongoing problems necessitate continuous improvement in system security screening and intrusion detection to protect networks effectively. Therefore, in this research, a novel DL framework called capsule convolutional polymorphic graph attention neural network with tyrannosaurus optimization algorithm (CCPGANN-TOA) is utilized for attack detection due to its advanced feature representation, graph attention for focusing on key data points, polymorphic graphs for adaptability, and TOA for performance optimization.
SURVEY ARTICLE
TSCH in Edge IoT: A Comprehensive Survey of Research Challenges
- First Published: 25 February 2025

Time-slotted channel hopping (TSCH) revolutionizes Internet of Things (IoT) communication, offering enhanced reliability, energy efficiency, and scalability. This survey explores TSCH in IoT, delving into its advantages and applications across smart homes, industrial automation, smart grids, and healthcare. Challenges like synchronization and energy-performance trade-offs are addressed through innovative techniques. Performance metrics, including packet delivery ratio and energy consumption, are evaluated, establishing TSCH as a pivotal element in IoT communication protocols.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Fault Classification and Detection in Transmission Lines by Hybrid Algorithm Associated Support Vector Machine
- First Published: 25 February 2025
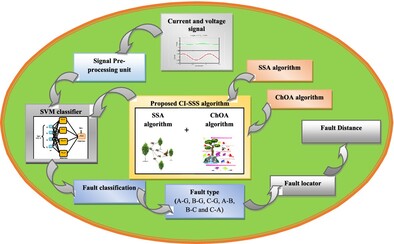
The proposed system of fault categorization and location identification comprise of preprocessing unit, fault classifier, and fault locator. The current and voltage signals acts as the input to the preprocessing unit, followed by which the classification process using SVM classifier takes place. Using the suggested CI-SSA approach, the SVM classifier's weights are precisely adjusted. Once the defect has been discovered and characterized, its location and distance are determined.
Enhancing Agricultural Supply Chain Management With Blockchain Technology and DSA-TabNet: A PBFT-Driven Approach
- First Published: 26 February 2025
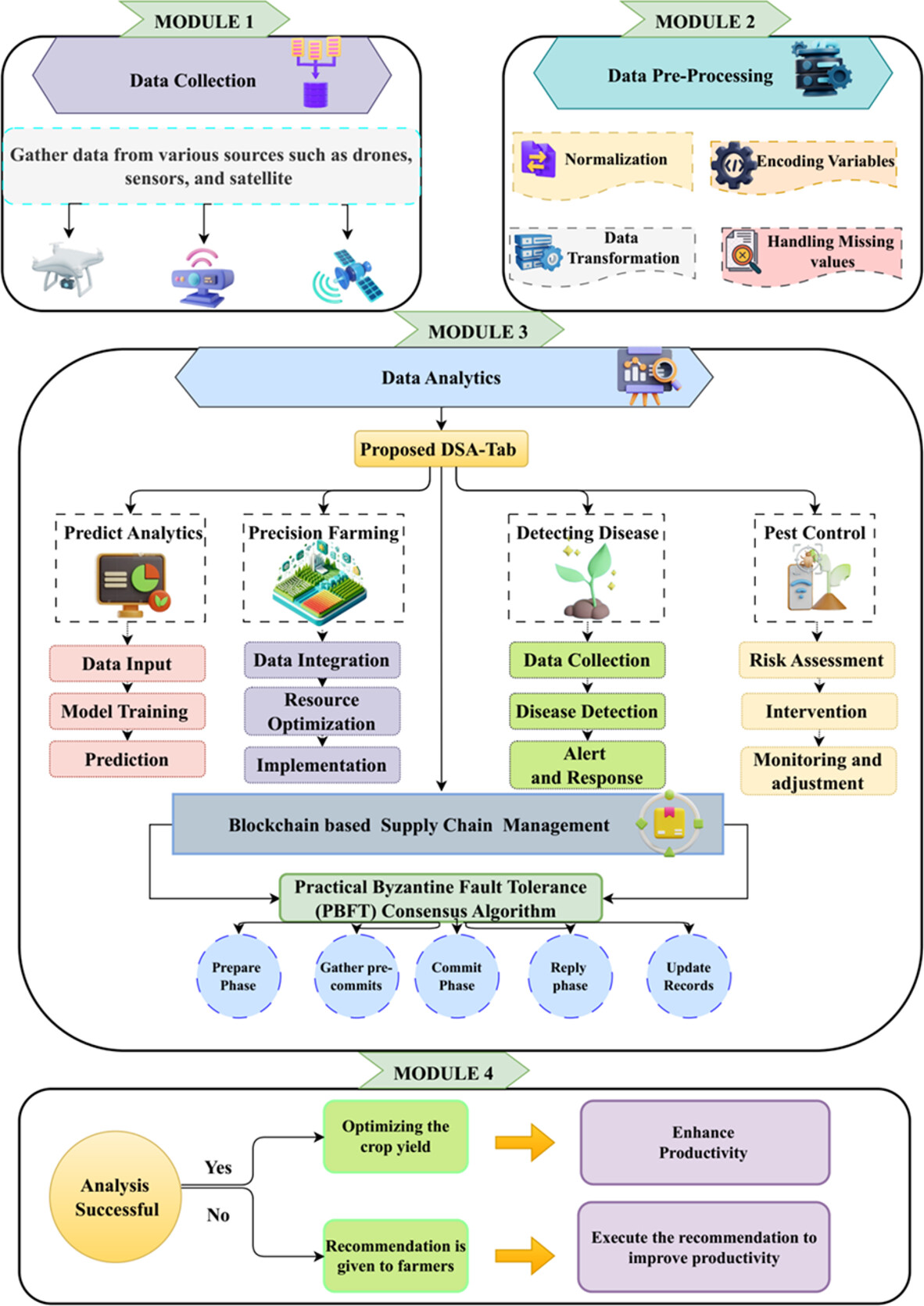
This work presents a blockchain-integrated DSA-TabNet model for agricultural supply chains, enabling transparent, tamper-proof data management and real-time quality assessment. With high accuracy and low latency, it ensures product safety, prevents fraud, and builds consumer trust while enhancing supply chain efficiency.
Energy-Efficient Long Range Repair Connectivity Policy for Maritime Wireless Sensor Networks
- First Published: 26 February 2025
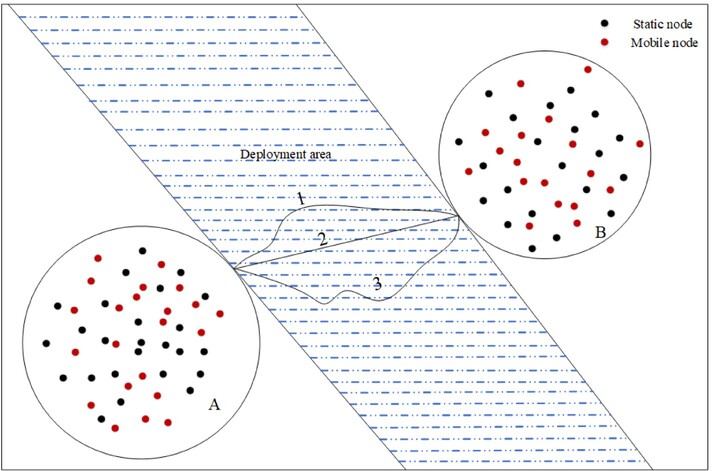
The proposed algorithm efficiently achieves connectivity repair with optimal energy consumption through three key steps. Initially, it locates drifting nodes based on the Lagrangian tracking approach. Subsequently, according to the location information, the length of the connectivity repair path is determined for preparing link establishment. Lastly, an optimal deployment distance with a closed-form solution is utilized to achieve the minimum energy consumption during the deployment of mobile nodes for connectivity repair.
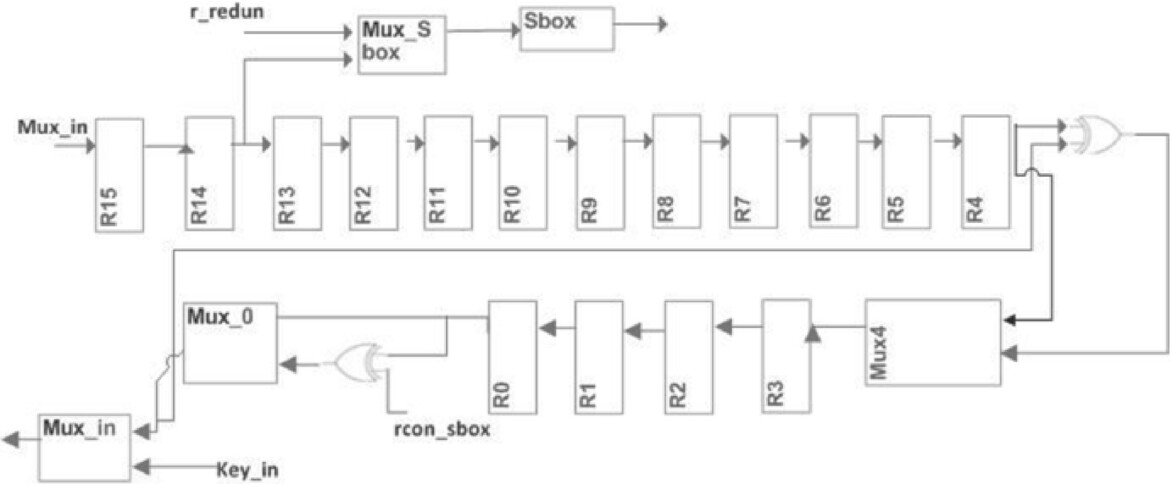
A Comparison of 163-Bit Hybrid Karatsuba Multiplier and Word-Serial Multipliers for ECC Processors
- First Published: 28 February 2025
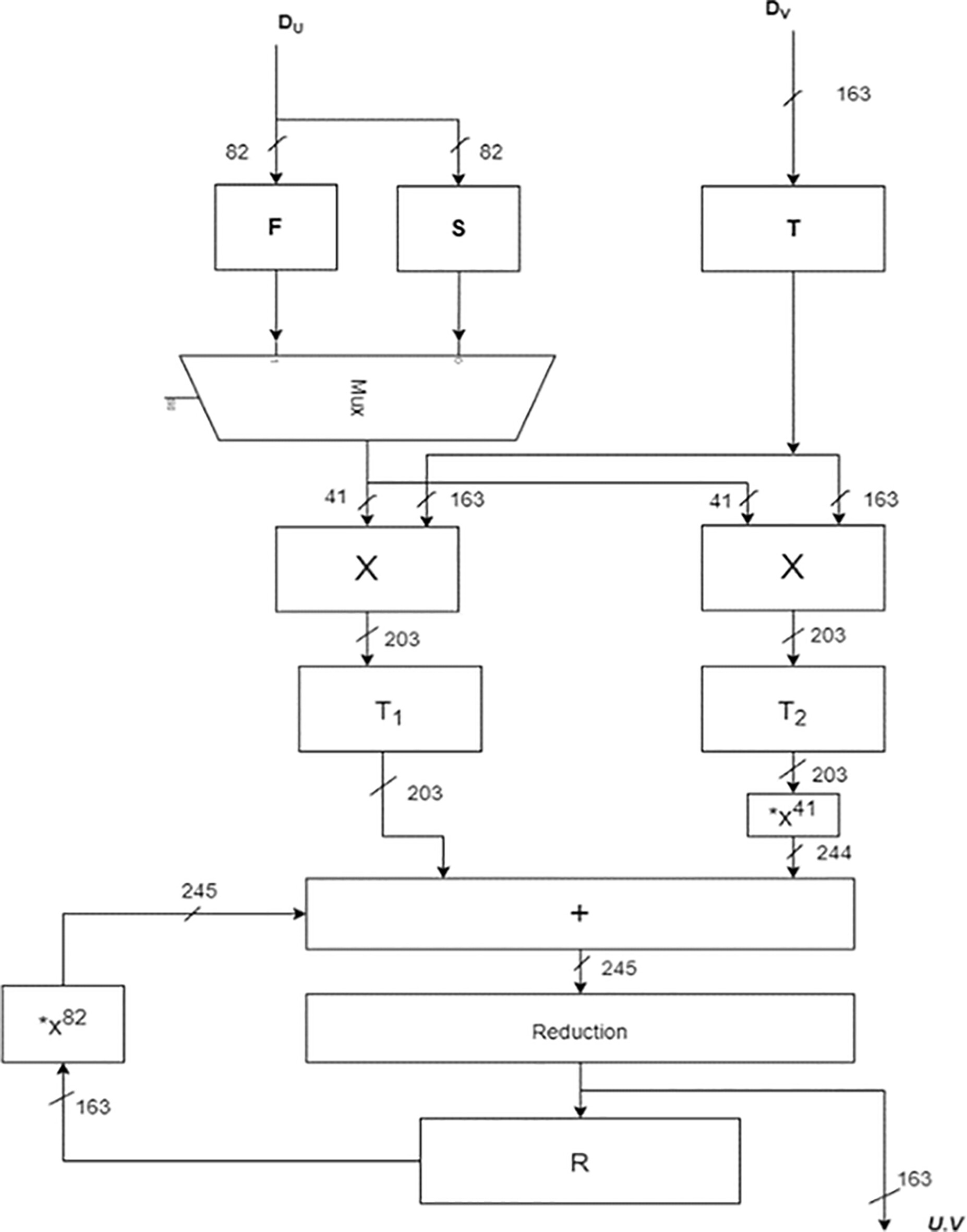
The resource-constrained IoT devices employed in real-time applications demand the design of a compact yet fast multiplier. In this paper, we have proposed a Hybrid Karatsuba Multiplier (HKMul) for GF (2163) for use in Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). It is a sub-quadratic multiplier. A Word-Serial Multiplier (WSMul) for the same ECP is also reimplemented in this work.
Blockchain-Integrated Secure Healthcare Information Sharing via Advanced Blowfish Encryption Standard With Optimal Key Generation
- First Published: 27 February 2025
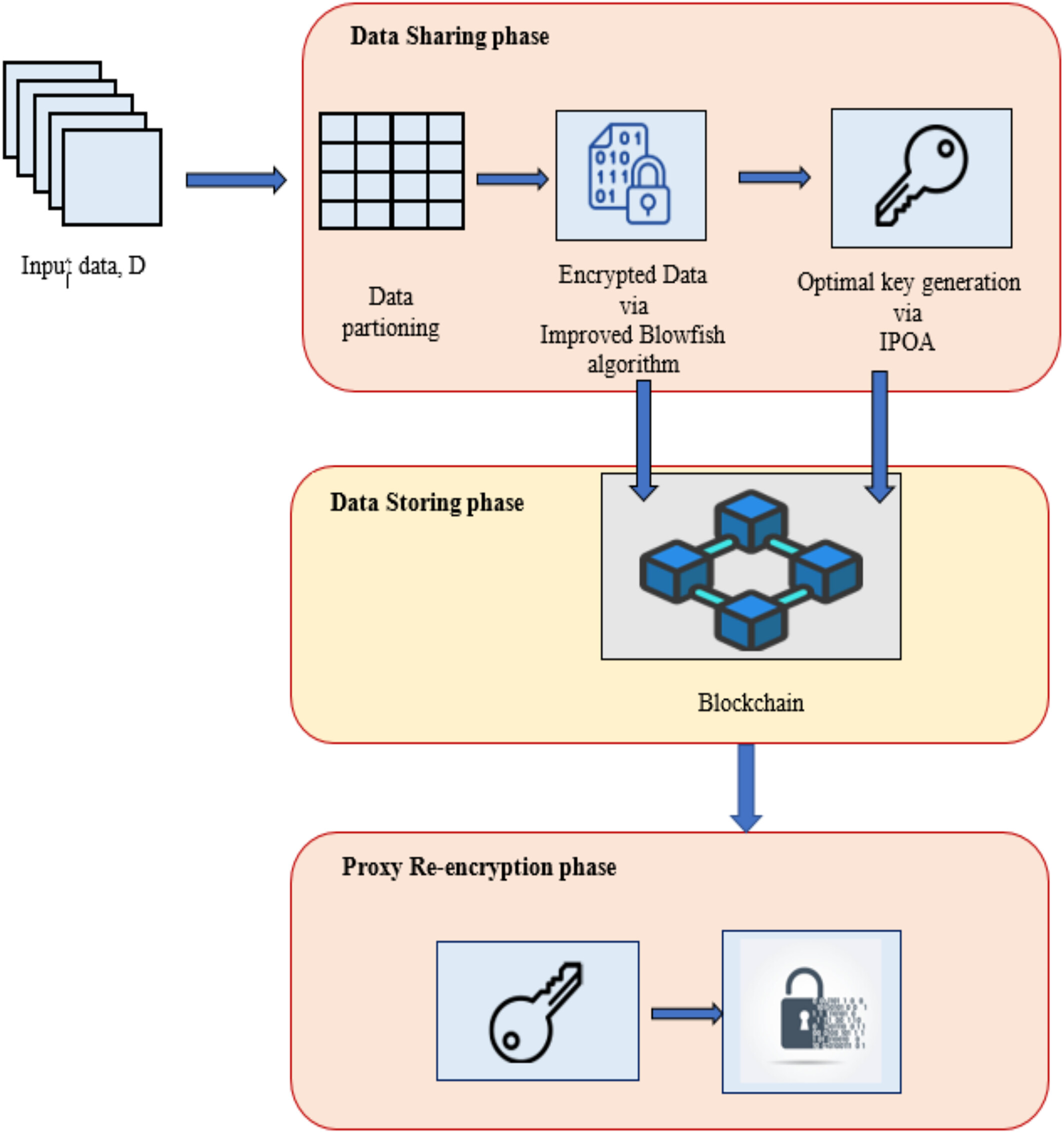
In this research, blockchain-integrated technology with enhanced encryption and optimal key generation is proposed. The data sharing initiates with partitioning the healthcare data into manageable blocks, followed by encryption using an enhanced version of the Blowfish algorithm. The Improved Blowfish algorithm incorporates bitwise operations and conditional transformations to strengthen data security and flexibility in handling encrypted data. Also, the proposed work implements the Improved Pelican Optimization Algorithm (IPOA) for optimal key generation. IPOA optimizes encryption keys based on the minimizing correlation between original and encrypted data, thereby ensuring robust data protection. A blockchain is used to store encrypted data and keys, taking use of its decentralized and unchangeable structure to guard against manipulation and unwanted changes. Furthermore, the proxy re-encryption technique is employed to securely manage and distribute decryption capabilities without exposing sensitive information.
Hybrid AI-Driven Bio-Inspired Wearable Sensors With Aquasense AI Technology for Multimodal Health Monitoring and Rehabilitation in Dynamic Environments
- First Published: 28 February 2025
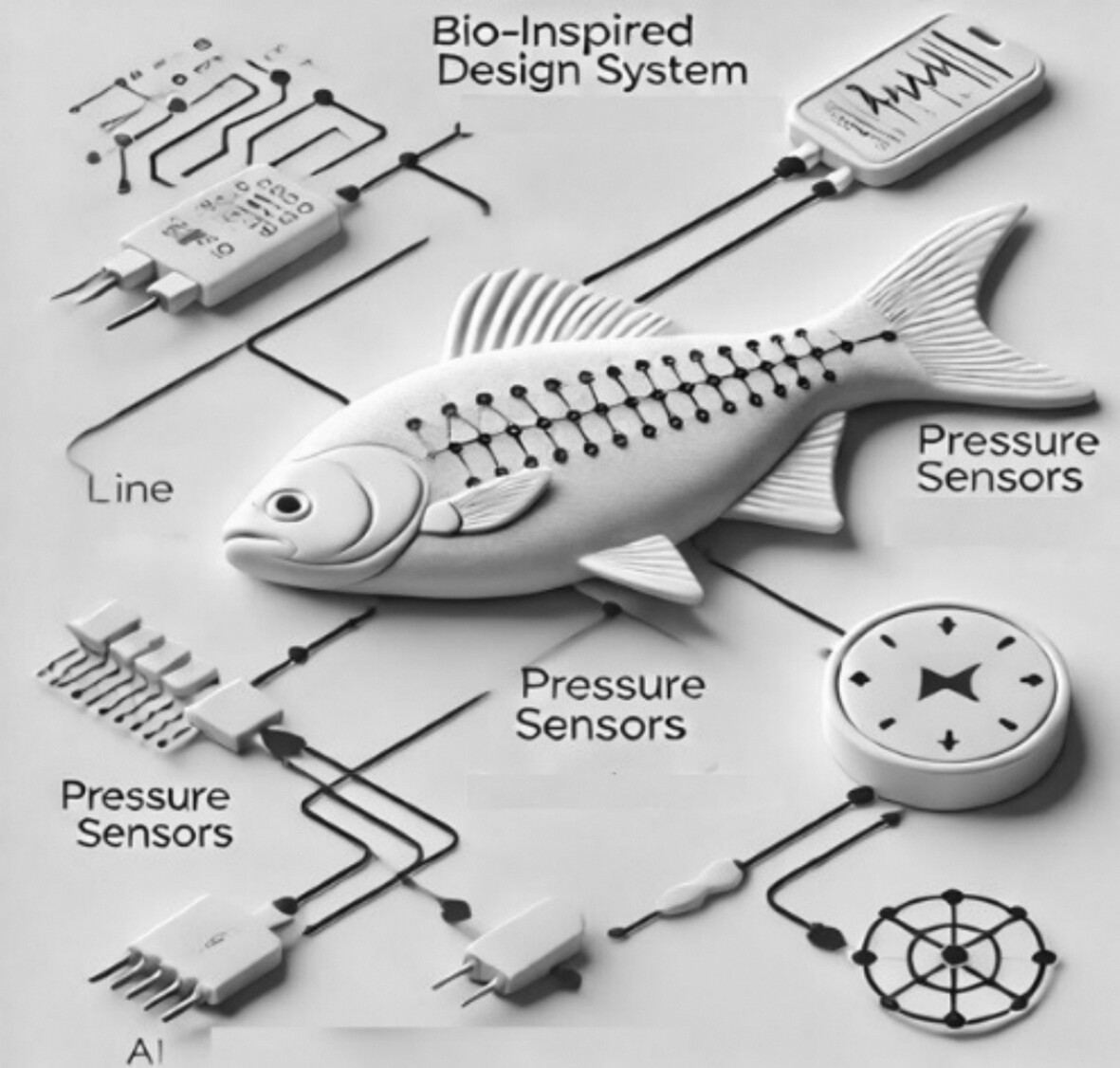
AquaSense AI is a bio-inspired, wearable sensor system that enables a paradigmatic shift in healthcare and physiotherapy, emulating nature's sensory capabilities of aquatic animals. The use of flexible, waterproof sensors is used to detect human motion, balance, and posture on land and in water. AquaSense AI is perfect for application in swimming pools and hydrotherapy sessions. AquaSense AI delivers real-time, high-precision feedback to enable effective rehabilitation, fall prevention, and fitness monitoring. In underwater, these sensors follow the posture of a person and the coordination of their limbs through the detection of pressure changes, while on land it monitors gait, posture, and balance. The sophisticated AI algorithms within the system, including Hierarchical Adaptive Neural Network (HANN) and Multimodal Self-Learning Framework, adjust sensor sensitivity to the environment and provide personalized feedback over time, continuously adapting to the movements and rehabilitation progress of the user. The bio-inspired design, adaptive AI, and real-time predictive analytics are capable of dual functionality in clinical and fitness applications, improving safety, rehabilitation outcomes, and general health monitoring in diverse environments.
Eye Blinking Feature Processing Using Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network for Deep Fake Video Detection
- First Published: 05 March 2025
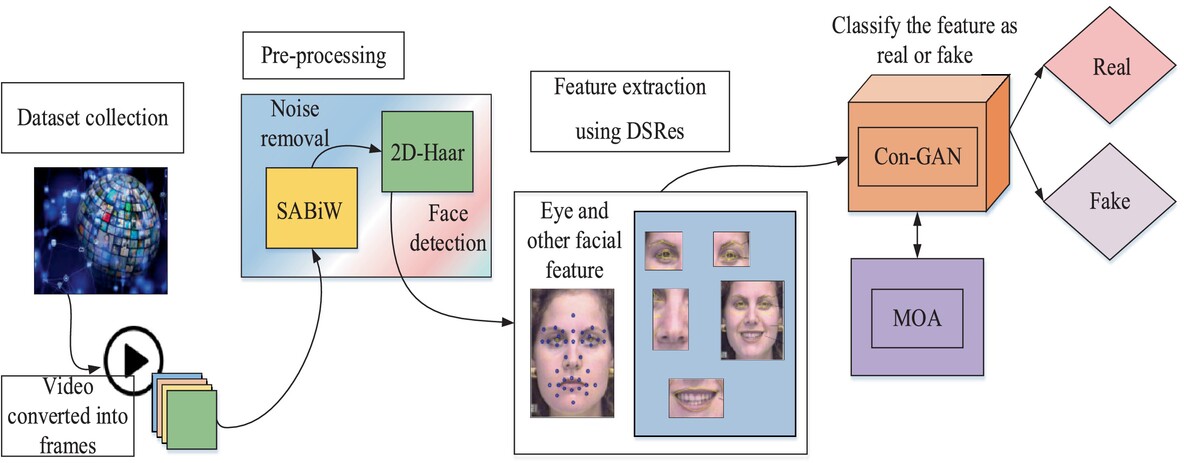
To convert the video into images collected from the dataset, the images are pre-processed using SABiW and 2D Haar for noise removal and face detection. To identify the eye region feature and extract the features using the depthwise separable residual network model. To classify the video as real or fake using the extracted feature of eye blinking with the convolutional attention advanced generative adversarial network. Optimize the network model's weight coefficient using the mud ring optimization algorithm.
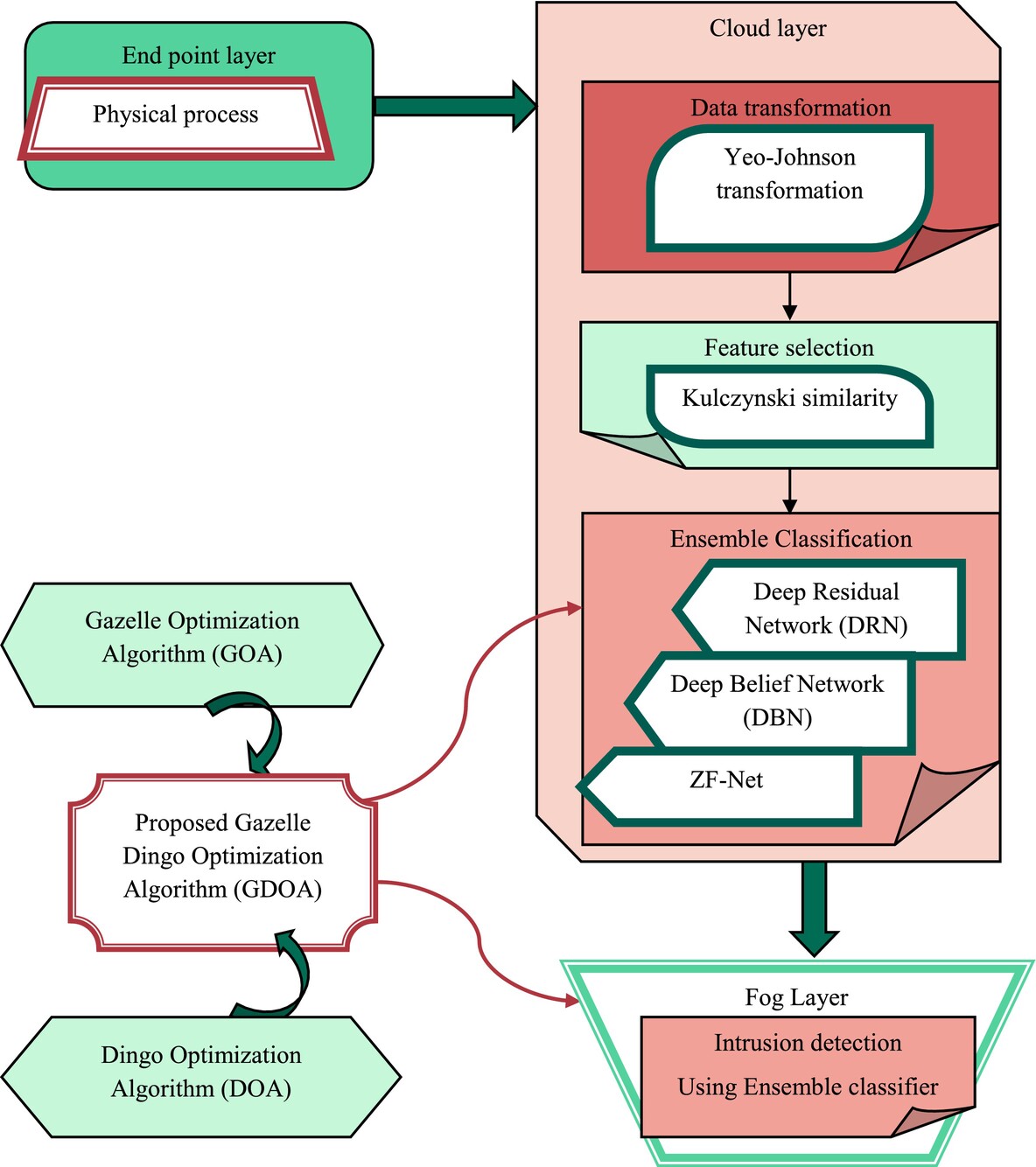
Gazelle-Dingo Optimization and Ensemble Classification: A Hybrid Approach for Intrusion Detection in Fog Computing
- First Published: 05 March 2025
SURVEY ARTICLE
Exploring the Transformative Impact of Blockchain Technology on Healthcare: Security, Challenges, Benefits, and Future Outlook
- First Published: 05 March 2025
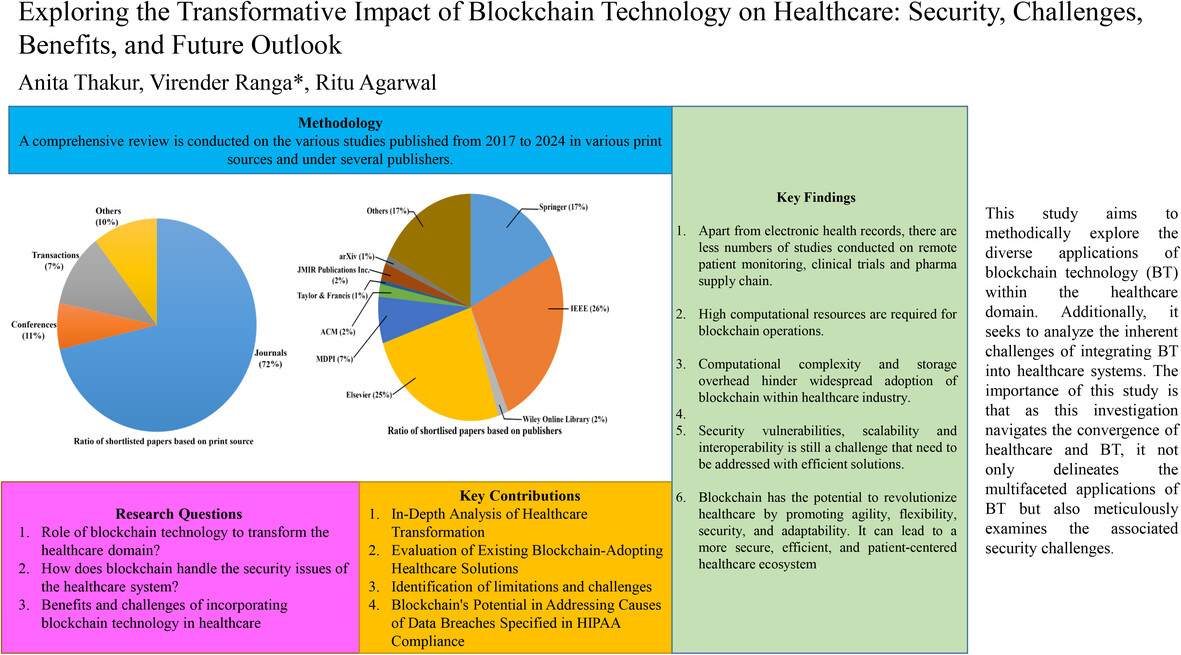
This study aims to methodically explore diverse applications of the blockchain technology (BT) within the healthcare domain. Additionally, it seeks to analyze the inherent challenges of integrating BT into healthcare systems. The importance of this study is that as this investigation navigates the convergence of healthcare and BT, it not only delineates the multifaceted applications of BT but also meticulously examines the associated security challenges.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Cluster Based Lion Optimization Routing Protocol for Internet of Vehicles (CLORP)
- First Published: 04 March 2025
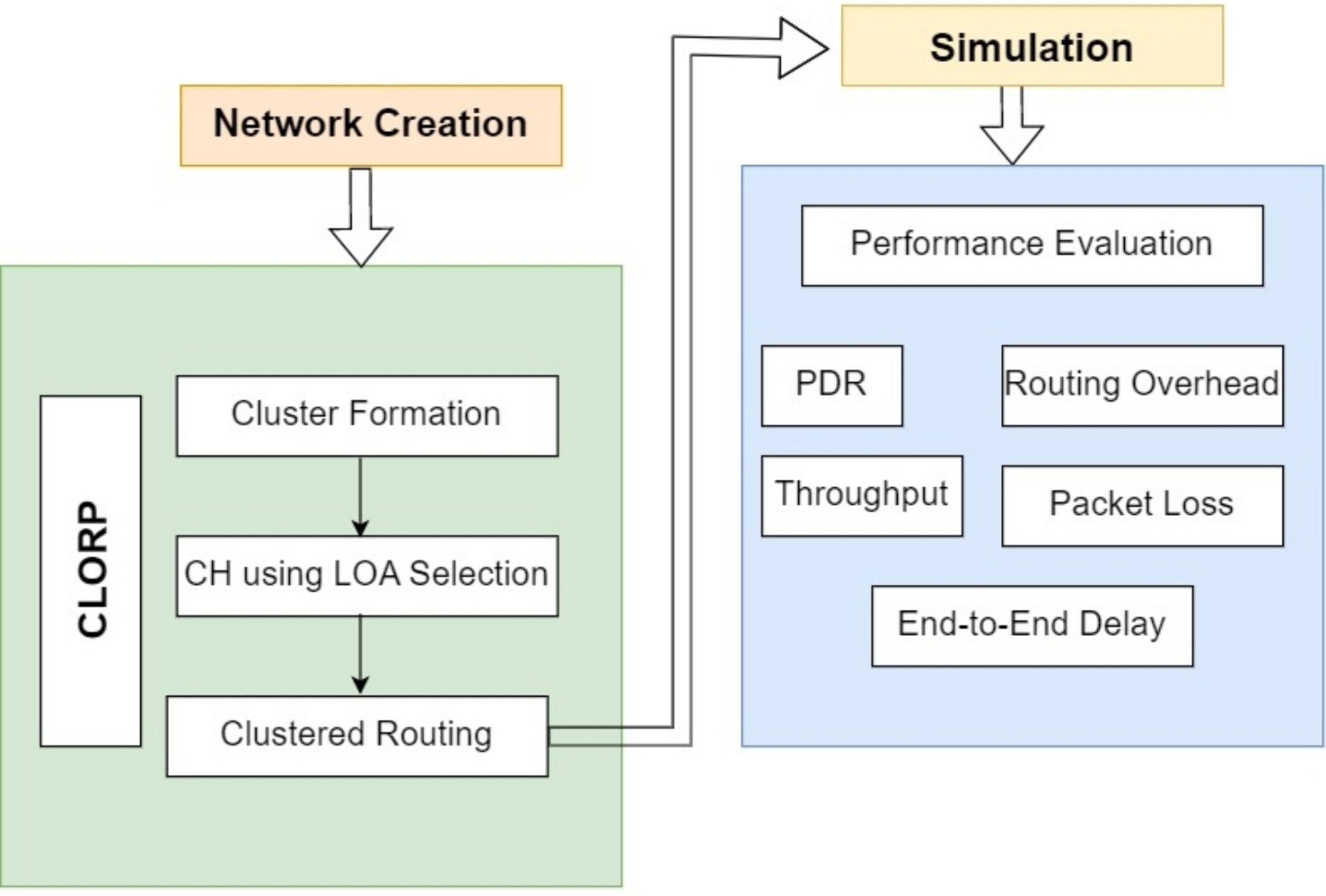
Because of its dynamic network, the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) has routing issues that impact packet delivery, throughput, latency, and routing overhead. By employing stable clusters and maximizing cluster head selection using the Lion optimization algorithm, the suggested protocol, CLORP, improves upon the AODV routing protocol with the goal of lowering control message burden and enhancing network performance. The effectiveness of CLORP is assessed by comparing its performance against a variety of protocols, such as AODV versions and other optimized protocols.
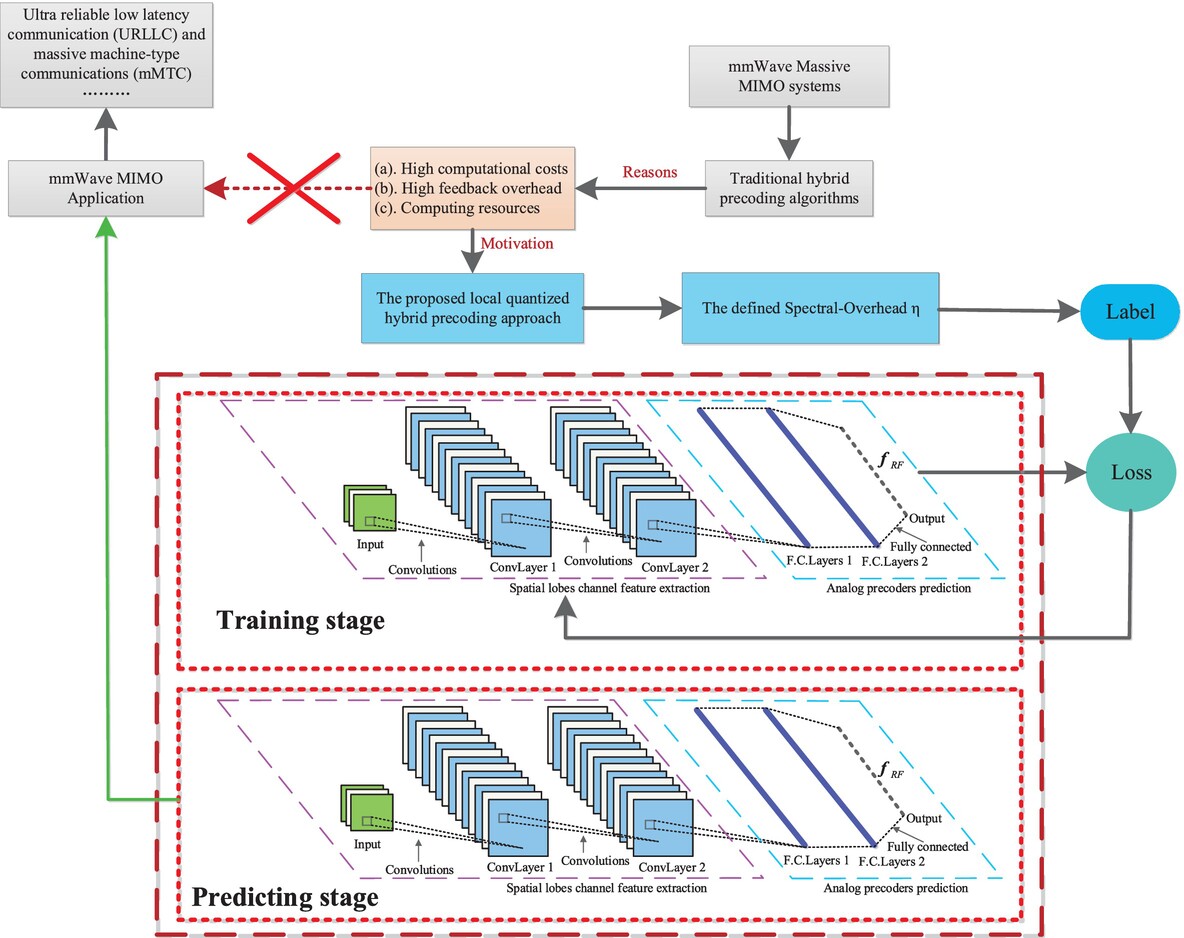
CNN-Based Local Quantized Hybrid Precoding for Low Complexity and Overhead
- First Published: 05 March 2025
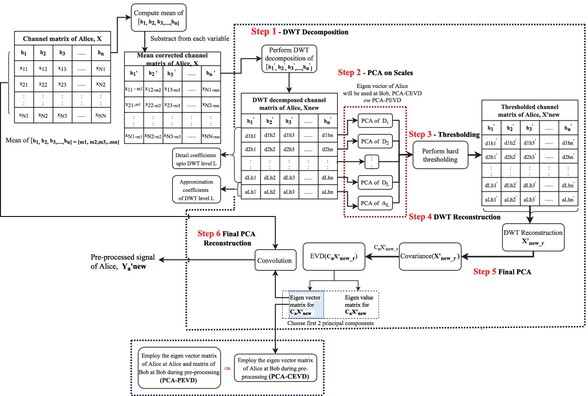
A Multiscale Principal Component Analysis Approach to Physical Layer Secret Key Generation in Indoor Environments
- First Published: 05 March 2025
Feasibility Analysis for Deployment of Free Space Optical Links in Urban Coastal Environments
- First Published: 05 March 2025
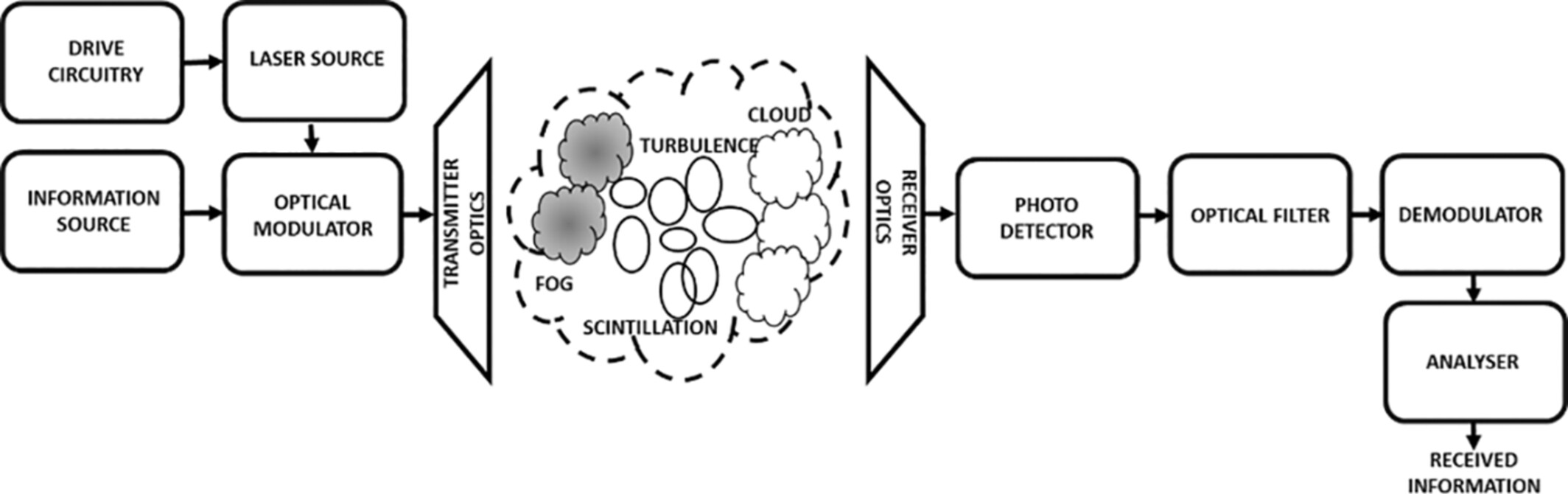
Fog-Evoked Signal Degradation (FESD) is computed for 4 consecutive months (November to February) for 6 sequential years from 2018 to 2023 for the urban coastal city of Chennai. Mathematical analysis has been carried out from the real-time measured visibility data and wind speed values. Also, the altitude of the location has been considered for computing the scattering and Turbulence-Induced Attenuation (TIA). The Link Margin (LM) is derived uniquely for summer and winter seasons to determine the feasibility for the establishment of the FSO link.
An Enhanced Encryption Scheme for IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Network Using DNA Enclosed Fully Homomorphic Approach
- First Published: 06 March 2025
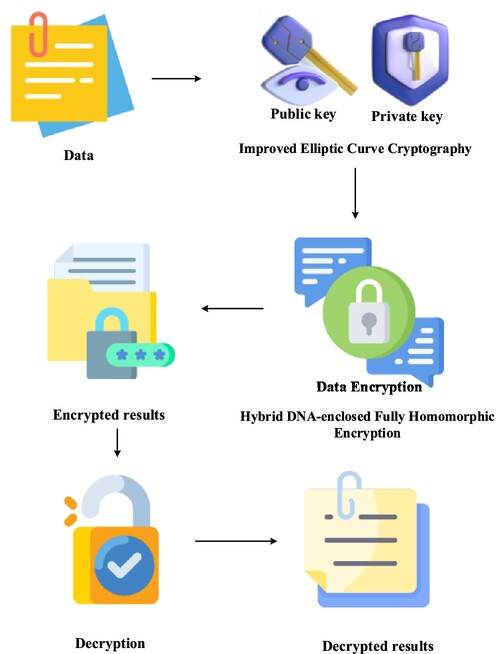
To enhance security and efficiency, an improved elliptic curve cryptography (IECC) is modeled for public and private key generation. To address challenges such as time consumption, memory overhead, and security issues, a hybrid DNA-enclosed Fully Homomorphic Encryption (HD-FHE) approach is implemented for data encryption. To ensure secure data processing, the HD-FHE method combines DNA computing with homomorphic encryption, which yields accurate decryption results.
An Effective Approach for Spectral Efficiency Improvement in Massive MIMO Network Using Hybridized Optimization Assisted Optimal Pilot-Based Vector Perturbation Precoding
- First Published: 05 March 2025
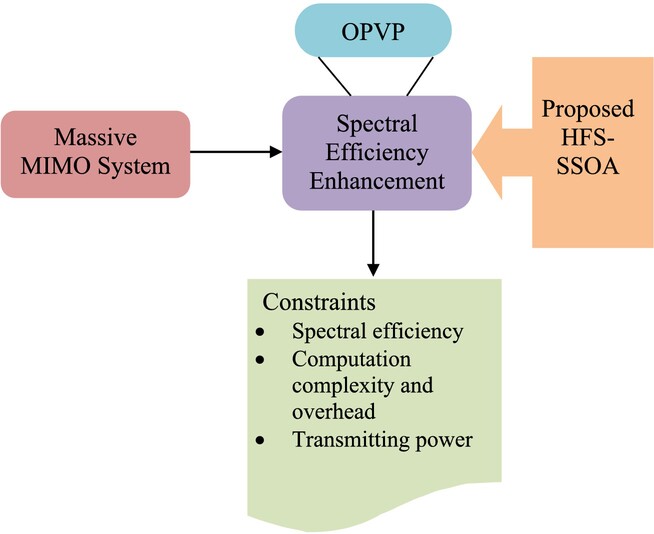
An Optimal Pilot-Based Vector Perturbation Precoding (OPVP) is introduced to improve SE in massive MIMO system. The Hybrid Flamingo Search-based Sparrow Search Optimization Algorithm (HFS-SSOA) is used to optimally select the perturbing vector for efficient reception and transmission. Further, the compressive sensing is used by OPVP for effectively selecting the low-dimensional CSI. The suggested approach effectively detects the low dimensional CSI by considering the objective functions like computational complexity, transmitting power, and computational overhead, used to develop the perturbing signal within the constellation bound. Finally, the simulation process is carried out on the developed model to prove its effectiveness.
Secure 5G Coordinating Spectrum Sharing System With Cooperation Transmitter and Receiver Pairs
- First Published: 06 March 2025
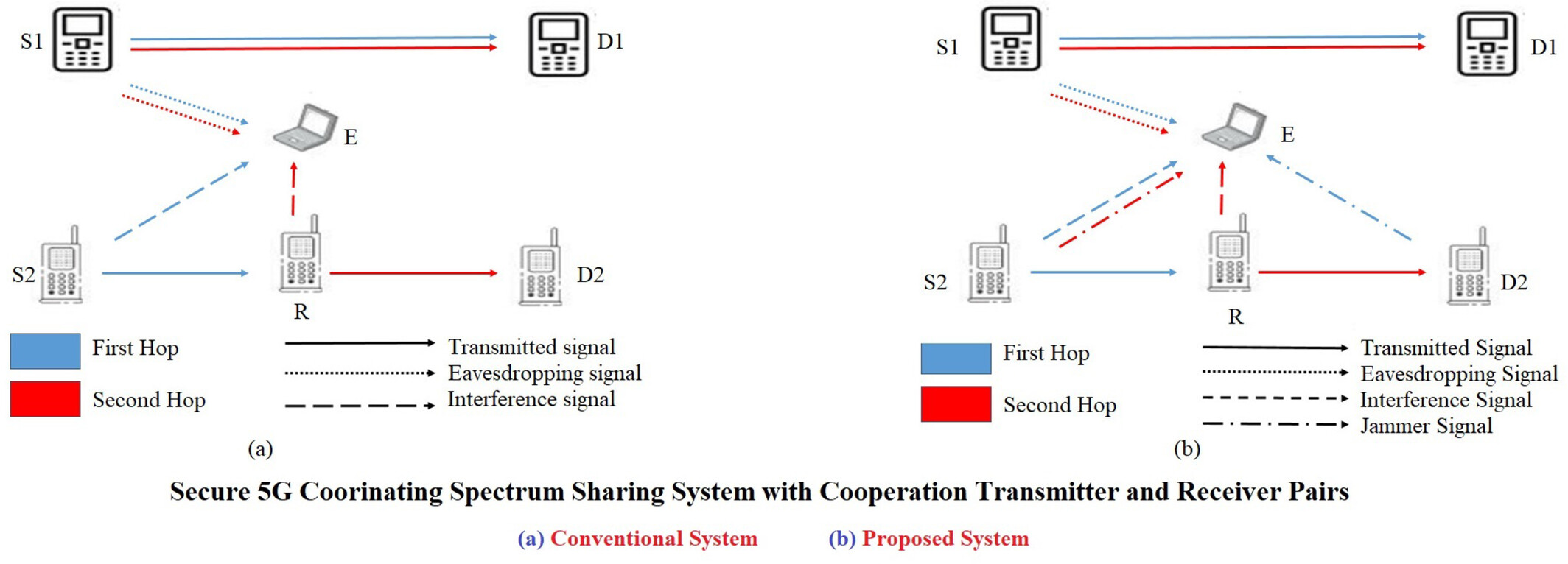
A secure 5G Coordinating Spectrum Sharing with Cooperation Transmitter and Receiver Pairs is proposed. Closed-form expressions for the intercept and outage probabilities are derived. Theoretical and simulation results proved that the proposed system can provide better security for the primary link and acceptable secondary outage probability.
Channel Estimation for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Assisted Cell-Free Communications
- First Published: 06 March 2025
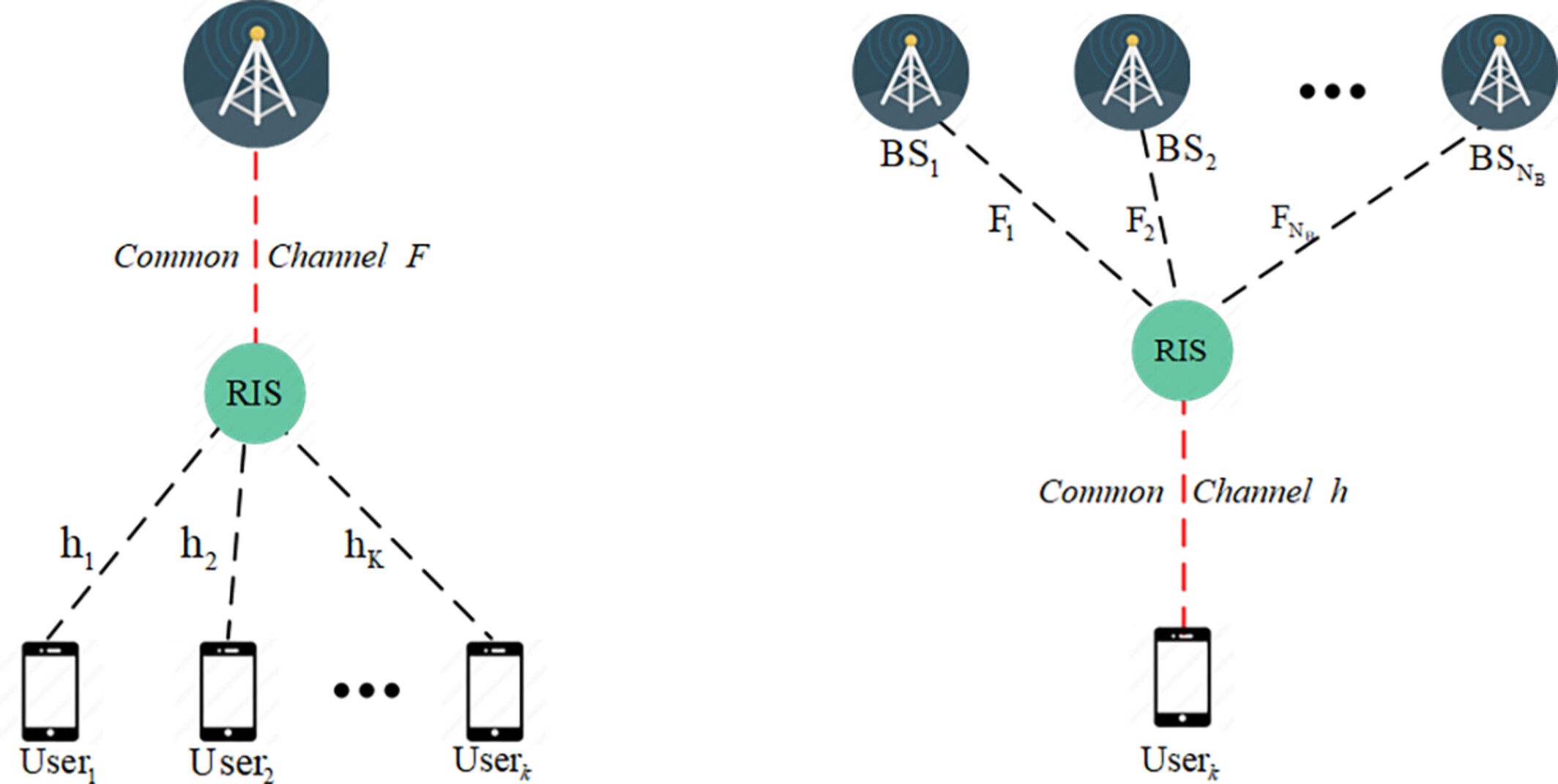
In this article, we present a three-dimensional multiple measurement vector (3D-MMV)-based CS framework for cascaded channel estimation, followed by the development of a 3D-MMV look ahead orthogonal match pursuit (3D-MLAOMP) algorithm based on tensor contraction. Besides, we propose a pilot-reduced two-timescale channel estimation strategy via multi-BS cooperation.
A Multi-cluster Security Framework for Healthcare IoT: The Synergy of Redundant Byzantine Fault Tolerance with Extensions and Coati-Based Network
- First Published: 06 March 2025

The article details a system for healthcare IoT management using designated cluster heads for configuration, resource allocation, security, and compliance. It employs RB-BFT X for Byzantine fault tolerance and secure communication. CoatiNet's routing algorithms optimize data flow, minimize latency, and ensure dynamic threat detection and response.
Ensemble Feature Engineering and Deep Learning for Botnet Attacks Detection in the Internet of Things
- First Published: 06 March 2025
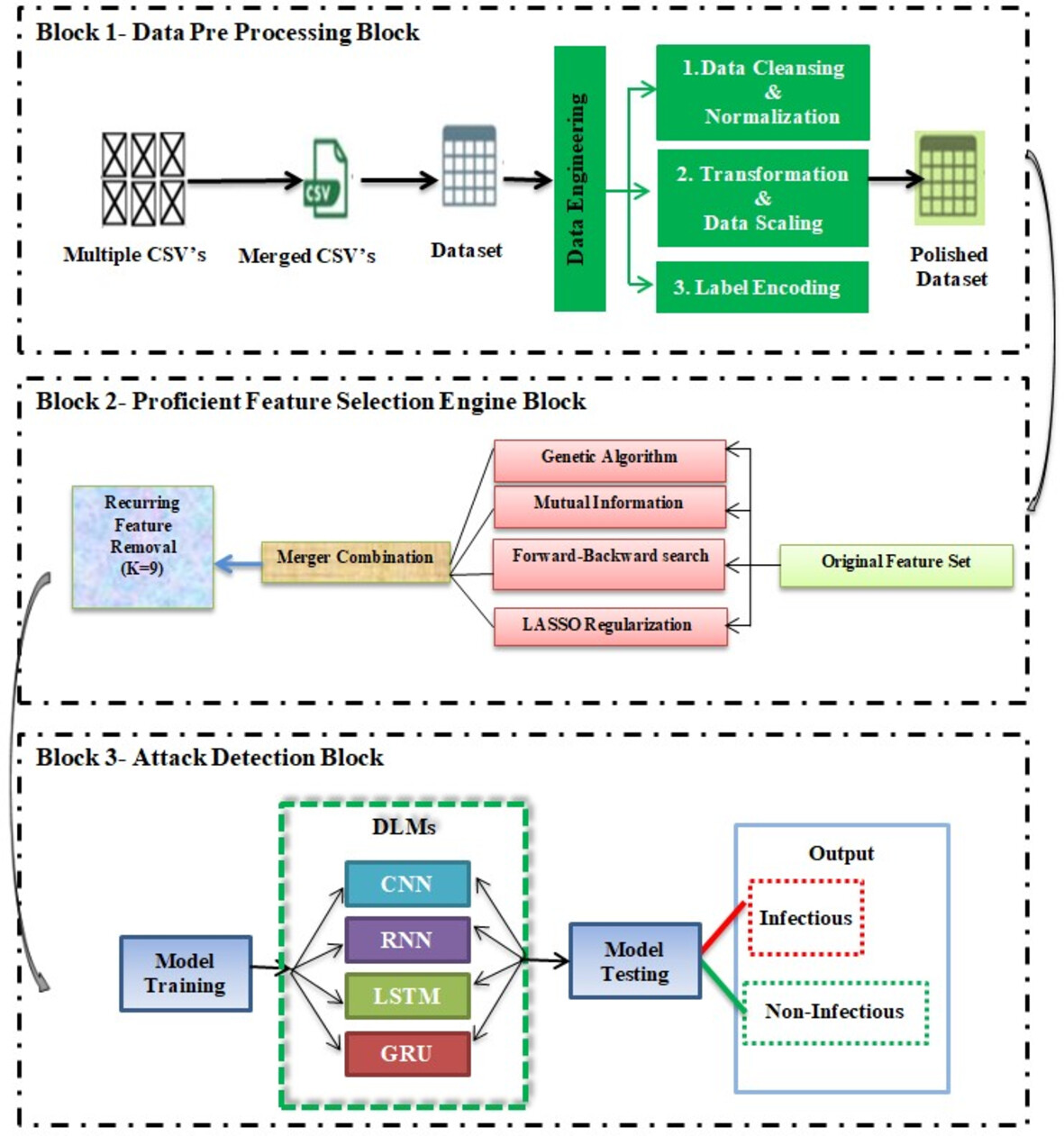
We propose an ensemble feature engineering framework combined with deep learning models, achieving detection accuracy of up to 99.21%, recall of up to 99.95%, precision of up to 98.99%, an F1-Score of up to 99.82%, an AUC-ROC of 82.37%, and specificity of 98.38% for detecting IoT botnet attacks. Our method integrates multiple feature selection techniques to enhance detection precision and minimize redundancy, demonstrating high performance in distinguishing malicious IoT traffic.
Workload Prediction in Cloud Data Centers Using Complex-Valued Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Neural Network Optimized With Gazelle Optimization Algorithm
- First Published: 11 March 2025
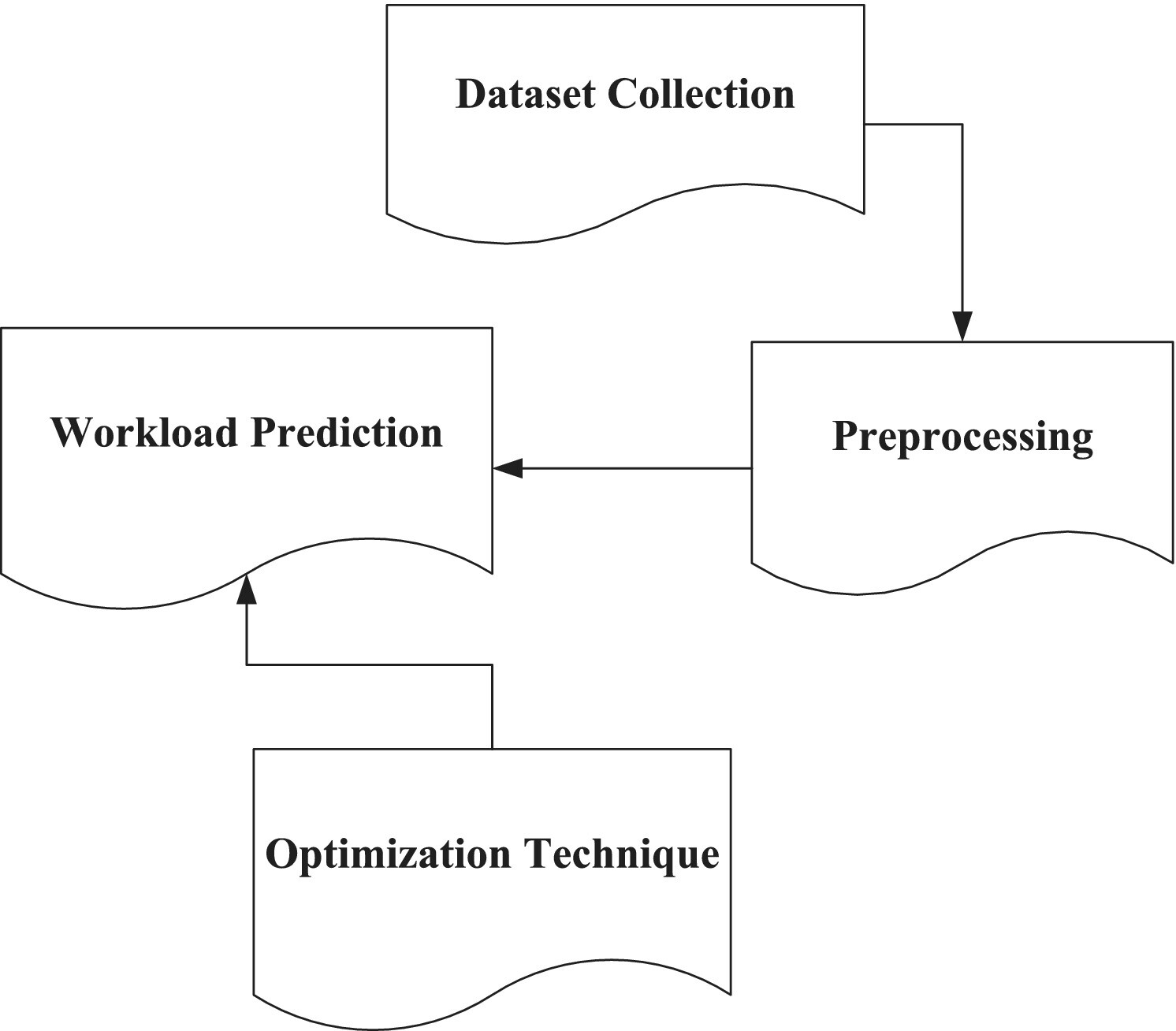
The proposed CVSTGCN-WLP-CDC method predicts cloud data center workloads by first collecting data from NASA and Saskatchewan HTTP traces. The data is preprocessed using the Multi-Window Savitzky–Golay Filter (MWSGF) to remove noise. A Complex-Valued Spatio-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network (CVSTGCN) performs the prediction, optimized by the Gazelle Optimization Algorithm (GOA). The method outperforms existing approaches, achieving 23.32%, 28.53%, and 24.65% higher accuracy and 22.34%, 25.62%, and 22.84% lower energy consumption compared to TCNN-CDC-WLP, PA-BPNN-CWPC and ARNN-EU-CDC.
SURVEY ARTICLE
Enabling Safe Co-Existence of Connected/Autonomous Cars and Road Users Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms
- First Published: 11 March 2025
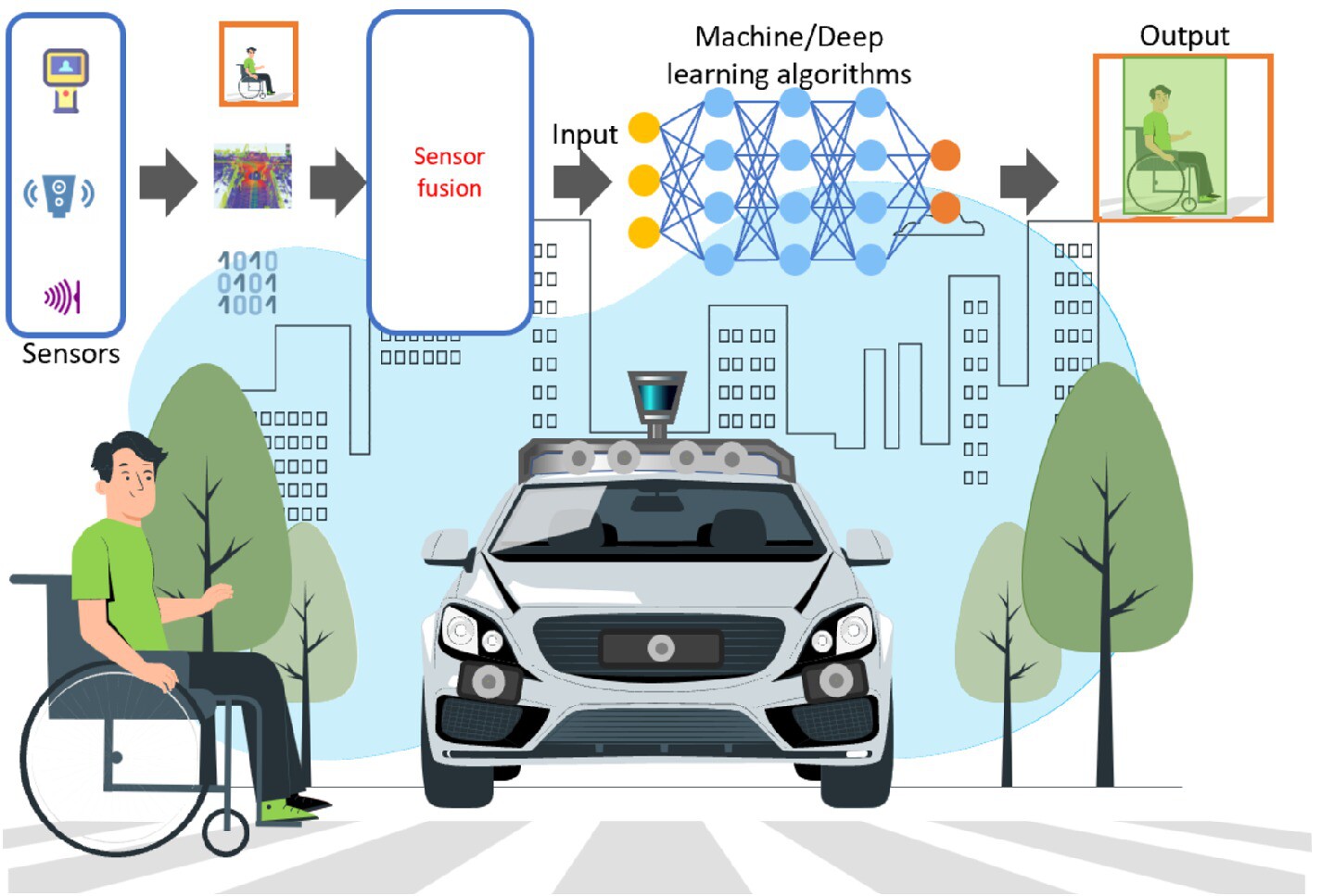
Connected and Automated Cars main objective is to be safer than non-intelligent vehicles and reduce up to 90% of vehicular accidents caused by human drivers. The market demands that Connected and Automated Cars interact safely with other cars and Vulnerable Road Users to create a safer road ecosystem.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
A New Energy-Aware Technique for Designing Resource Management System in the 5G-Enabled Internet of Things Based on Kohonen's Self-Organizing Neural Network
- First Published: 12 March 2025
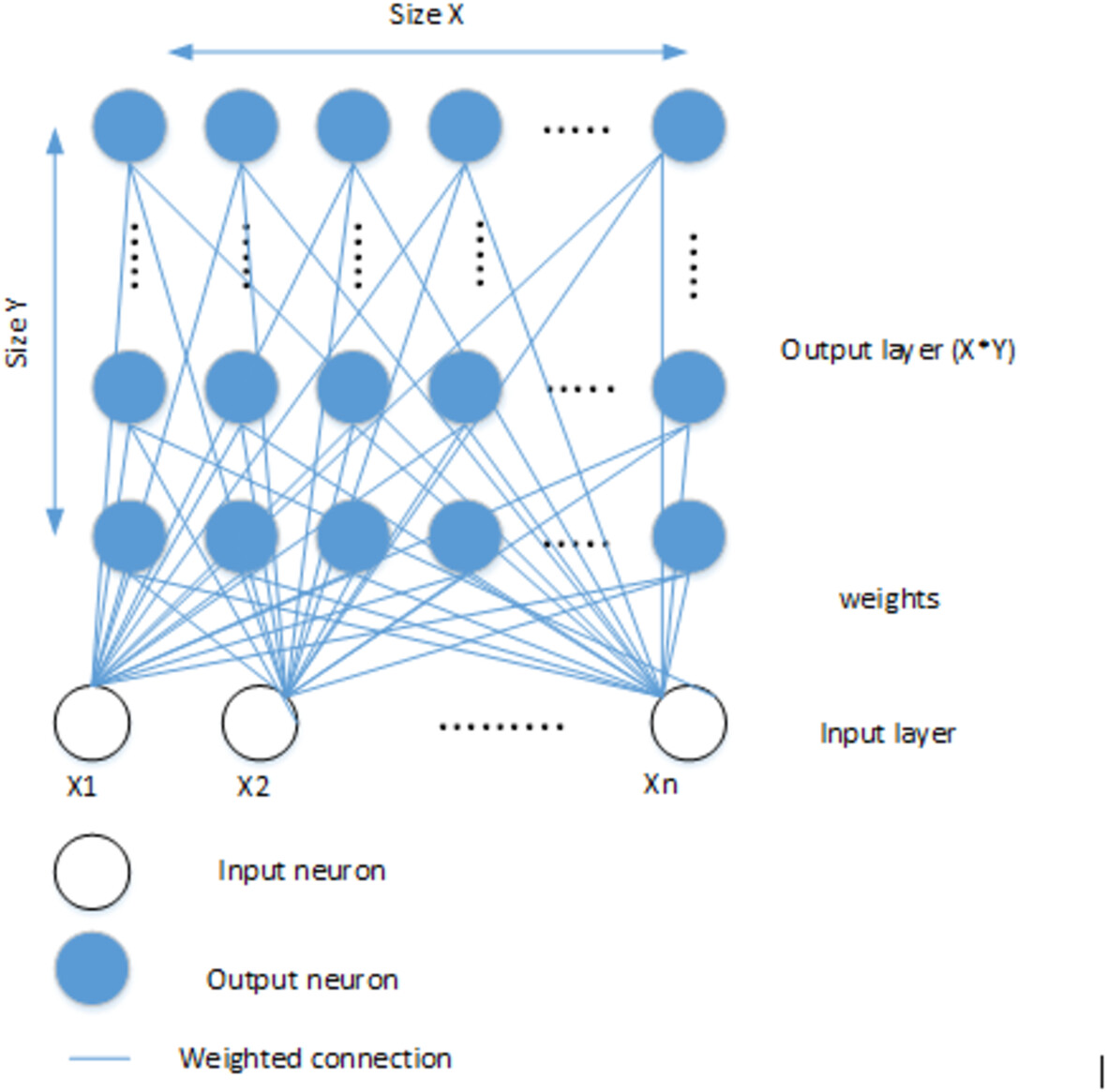
This paper proposes a novel approach to address these challenges using a Kohonen self-organizing neural network, which offers energy-aware resource management capabilities. Implementing the energy-aware technique based on Kohonen's self-organizing neural network requires a systematic approach. First, data from IoT devices must be collected and preprocessed to extract relevant features. Next, the algorithm should be employed to create a resource map that represents the distribution of resources. Finally, the resource map should be updated based on data input in real-time, ensuring efficient resource allocation. The findings show the network's substantial energy usage, cost, and delay changes using the proposed method.
Reducing Latency in SDN: An Innovative Closed-Loop Migration Collaboration Architecture
- First Published: 13 March 2025
TwoFish-Integrated Blockchain for Secure and Optimized Healthcare Data Processing in IoT-Edge-Cloud System
- First Published: 18 March 2025
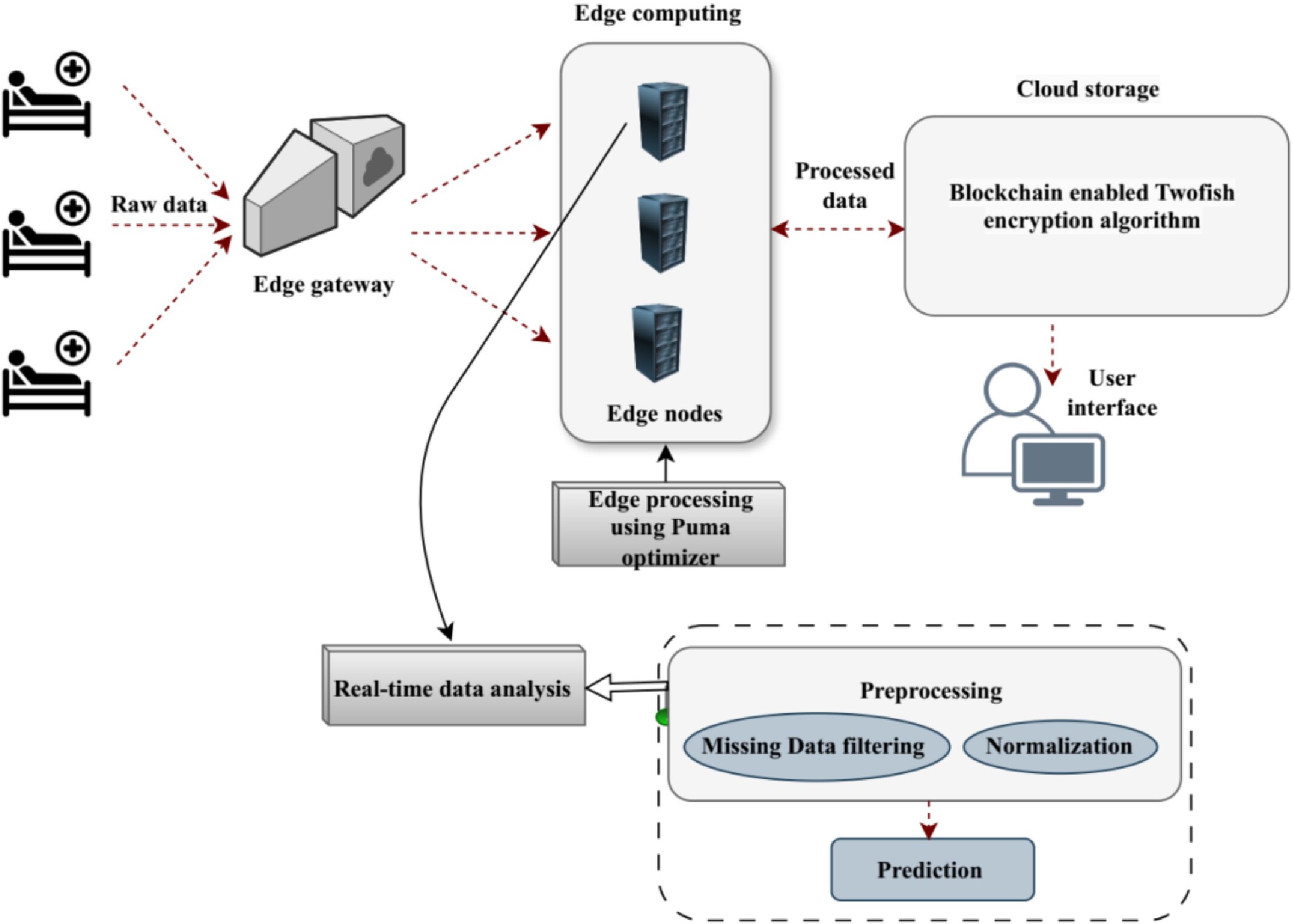
- Develop a Secure and Efficient Model for Healthcare Data Management: A novel Blockchain-Assisted Improved Puma Edge Computing Network (BA-IPEN)model that combines IoT, edge computing, and blockchain technologies is developed to ensure secure, effective, and real-time healthcare data collection, processing, and storage.
- Optimize Resource Utilization and Energy Consumption at the Edge Layer: The Modified POA is applied to improve task distribution, enhance resource utilization, and decrease energy consumption in edge computing.
- Improve Data Quality Through Preprocessing Approaches: The filtering and Z-score standardization approaches are implemented to ensure the gathered data is accurate, clean, and uniform.
- Ensure Scalability and Flexibility in Data Processing: The model capable of managing dynamic workloads and combining heterogeneous IoT devices is developed to ensure adaptability in different and scalable healthcare environments.
- Enhance Privacy and Data Security: The Blockchain-assisted Two Fish Algorithm is employed for encrypting confidential healthcare data, which ensures privacy and avoids unauthorized access through Ethereum-based smart contracts.
- Reduce Latency for Real-Time Healthcare Decision Making: Edge computing is implemented to process data locally, decreasing dependency on cloud resources and enabling real-time analysis for critical healthcare applications.