Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Interactions among variants in P53 apoptotic pathway genes are associated with neurologic deterioration and functional outcome after acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 07 January 2020
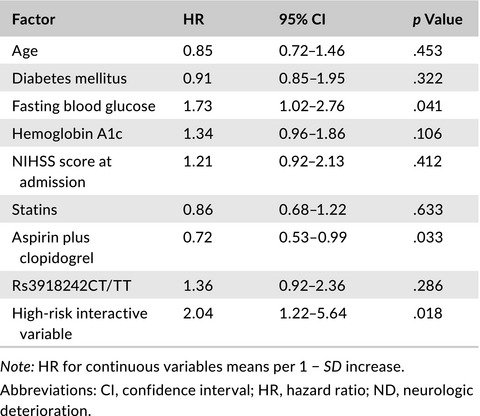
(a) The neurologic deterioration (ND) and functional outcome after ischemic stroke (IS) are not accurately predicted by clinical pictures on admission. (b) There was a gene–gene interaction among P53 rs1042522, MDM-2 rs2279744, and MMP-9 rs3918242 using GMDR analysis. (c) The interactions among P53 rs1042522, MDM-2 rs2279744, and MMP-9 rs3918242 may increase the risk of ND and poor functional outcome and may be considered as a genetic marker predicting ND and poor functional outcome after stroke.
Selegiline reduces daytime sleepiness in patients with Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 23 March 2021
Psychometric properties of Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders-Clinician Version (SCID-5-CV)
- First Published: 17 March 2021
How biopsychosocial depressive risk shapes behavioral and neural responses to social evaluation in adolescence
- First Published: 04 March 2021
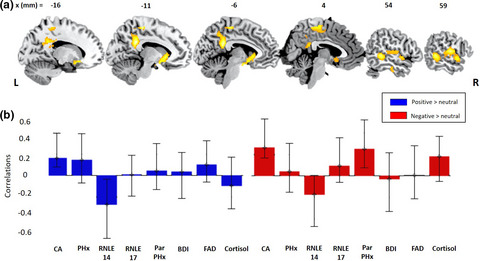
To understand the emotional responsivity style and neurocognitive profiles of depression-related processes in at-risk youth may be helpful in predicting those most likely to develop affective disorders. We explored the relationships between multivariate biopsychosocial risks for later depression, emotional response style and fMRI activity, to rejecting and inclusive social feedback. Data indicate risk for depression in adolescence is associated with a pervasive emotional insensitivity in the face of positive and negative social feedback.
Relation of retinal and hippocampal thickness in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and healthy controls
- First Published: 15 January 2021
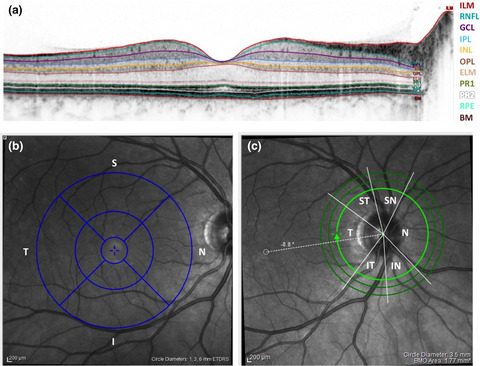
We investigated in patients with mild cognitive impairment, if and how retinal thinning aligns with neurodegeneration elsewhere in the brain. We detected a correlation of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and hippocampal thickness in healthy control participants but not in the cognitively impaired individuals. Different temporal trajectories of neurodegeneration may disrupt transregional brain structure associations in early neurodegeneration.
Hungarian validation of the Buss–Perry Aggression Questionnaire—Is the short form more adequate?
- First Published: 24 January 2021

Both the BPAQ, the BPAQ-SF and BAQ provide acceptable model fitting on a Hungarian sample of university students. While most of BPAQ items provided adequate loadings on their hypothesized factors, two items (21 and 27) did not. We argue this is the result of conceptual inaccuracy of the original items.
Separating scale-free and oscillatory components of neural activity in schizophrenia
- First Published: 03 February 2021
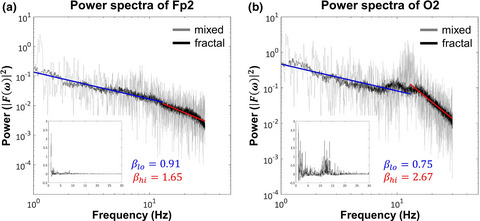
In this study, we separated the scale-free (fractal) and oscillatory components of the power spectral density (PSD) of electroencephalography recordings acquired from healthy controls (HC) and patients with schizophrenia (SZ). We found increased delta band-limited power in SZ when compared to HC in the raw PSD; however, this difference was only present in its fractal but not its oscillatory component. Our results imply strong functional significance of scale-free neural activity in SZ and suggest that abnormalities in PSD may emerge from alterations of the fractal and not only the oscillatory components of neural activity.
Inhibition of emotions in healthy aging: age-related differences in brain network connectivity
- First Published: 04 February 2021
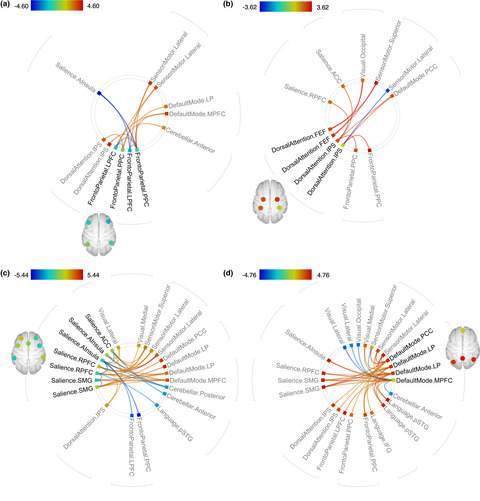
First fMRI study of face–word emotional Stroop interference in healthy aging. The interference effect did not change, and the basic pattern of brain activation was preserved with advancing adult age. The older adults had stronger between-network connectivity and weaker within-network connectivity of the major attention/control networks during the emotional interference task compared to younger adults.
REVERSE phenotyping—Can the phenotype following constitutive Tph2 gene inactivation in mice be transferred to children and adolescents with and without adhd?
- First Published: 01 February 2021
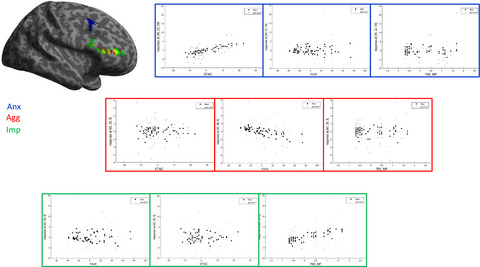
The Tph2-/- mouse has been proposed as an experimental model for ADHD. Translation of an animal phenotype into humans to examine its face validity (reverse phenotyping). Phenotyping included impulsivity, aggression, and anxiety, reflecting comorbid conditions of ADHD. Use of the RDoC approach to address phenotype dimensions in an isolated manner.
The stimulus control of local enclosures and barriers over head direction and place cell spatial firing
- First Published: 19 February 2021
Brain imaging features of children with Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome
- First Published: 18 March 2021
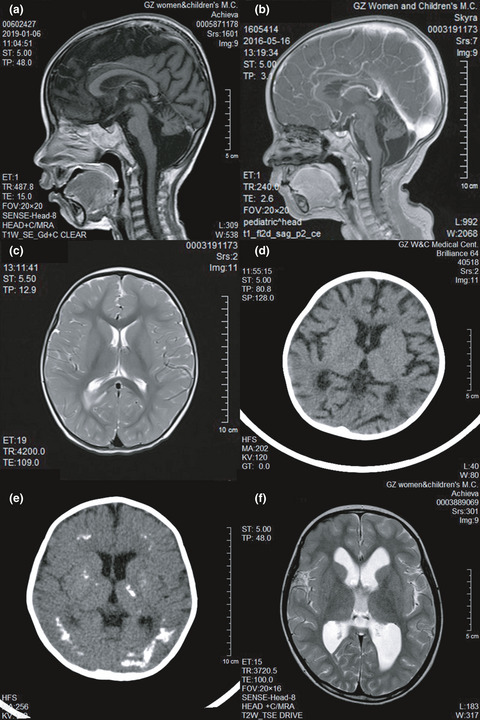
This study aimed to summarize the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) features of the central nervous system (CNS) in children with Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome. Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome is a severe variant of dyskeratosis congenita. Both DKC1 and TINF2 mutations can lead to the phenotypes of Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome. In our study, CNS imaging revealed that cerebellar hypoplasia has an important diagnostic value for Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome while delayed myelination, calcification of the parenchyma, brain atrophy, and hydrocephalus are also important findings on CNS imaging. Combining imaging features with clinical and laboratory indicators can assist the diagnosis of Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome.
TSH adenoma and syndrome of resistance to thyroid hormones—Two cases report of syndrome of inappropriate secretion of thyrotropin
- First Published: 10 March 2021
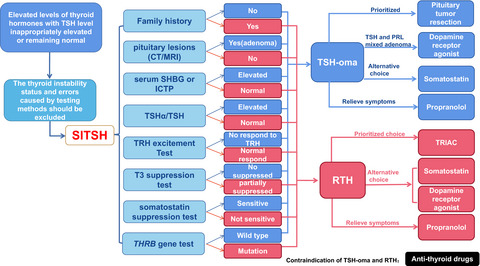
Due to the complicated manifestation of TSH-oma and RTH, the diagnosis and treatment often delayed. The clinical experiences of the TSH-oma and RTH suggest that more information should be identified. In this article, by comparing TSH-oma and RTH, we summarized the identification points, diagnosis process and treatment strategies of these two rare diseases.
Optic neuritis after ocular trauma in anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
- First Published: 16 February 2021
Serum neurofilament light chain in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
- First Published: 22 February 2021
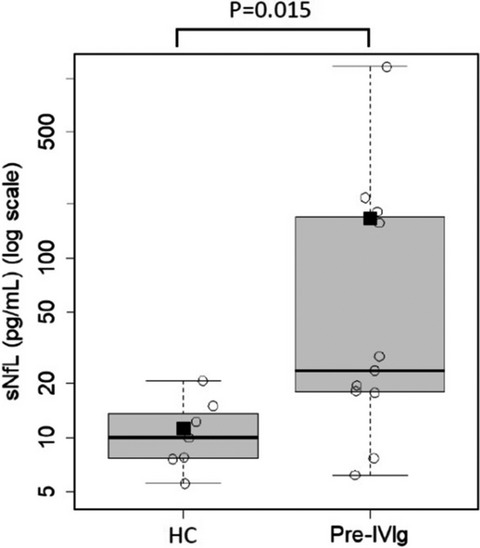
Serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) levels were assayed in patients with newly diagnosed chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). We found that the levels in CIDP patients were significantly higher than those in healthy controls, and that the levels significantly decreased over time after treatment and in remission period. sNfL may be a potential biomarker reflecting the disease activity in patients with CIDP.
Prognostic prediction of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage using CT radiomics and machine learning
- First Published: 24 February 2021
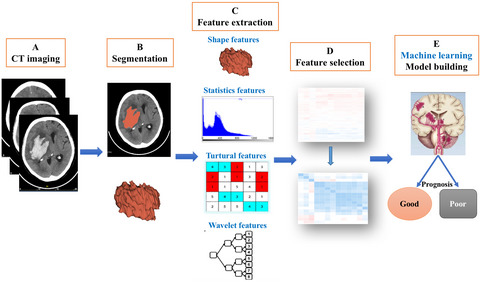
We tried to establish accurate long-term outcome predictions models for hypertensive ICH using CT radiomics and machine learning. Six machine learning algorithms were used at the same time, and the accuracies of different models were compared and selected. Finally, the random forest algorithm model demonstrated a sensitivity of 93.3%, a specificity of 92.5% and the area under the curve was 0.92, which were the best among all 6 models.
Nonmotor symptom burden grading as predictor of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease
- First Published: 01 March 2021
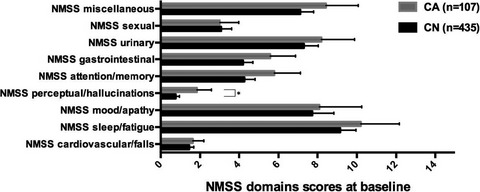
A comprehensive baseline measure of NMS and in particular hallucinations and perceptual problems assessed with a validated single instrument can be used to predict incident cognitive impairment in PD. This approach provides a simple, holistic strategy to predict future cognitive impairment in this population.
Longitudinal mental health outcomes of combat-injured service members
- First Published: 04 March 2021

In this retrospective cohort study of 7,787 combat-injured United States service members matched 1:1 to combat-deployed, uninjured service members, combat-injured service members had higher incidence rates per 100 person-years for PTSD (17.1 vs. 5.8), depression (10.4 vs. 5.7), and anxiety (9.1 vs. 4.9) when compared to uninjured service members. After adjustment, combat-injured patients were at increased risk of development of PTSD (HR 2.92, 95%CI 2.68–3.17), depression (HR 1.47, 95%CI 1.36–1.58), and anxiety (HR 1.34, 95%CI 1.24–1.45). These findings highlight the importance of increased screening, prevention, and intervention in patients with exposure to physical trauma.
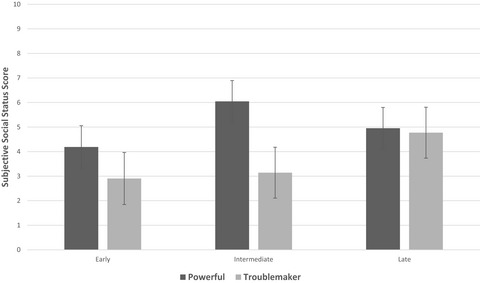
The role of chronotype and reward processing in understanding social hierarchies in adolescence
- First Published: 01 March 2021
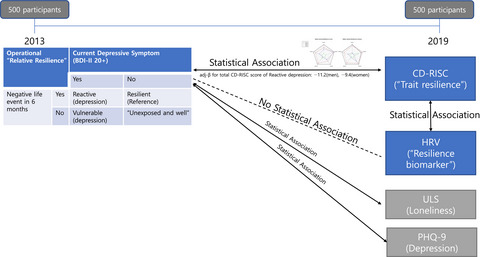
Correlates of psychological resilience and risk: Prospective associations of self-reported and relative resilience with Connor-Davidson resilience scale, heart rate variability, and mental health indices
- First Published: 27 February 2021
Influence of mobility restrictions on post-stroke pain
- First Published: 02 March 2021
The objective of this study was to investigate the role of mobility, limitations, and vitality, as well as additional factors such as comorbidities, to predict post-stroke pain. The results suggest that restrictions in mobility and low vitality are important factors for the occurrence of post-stroke pain.
Interactions between methodological and interindividual variability: How Monetary Incentive Delay (MID) task contrast maps vary and impact associations with behavior
- First Published: 22 March 2021
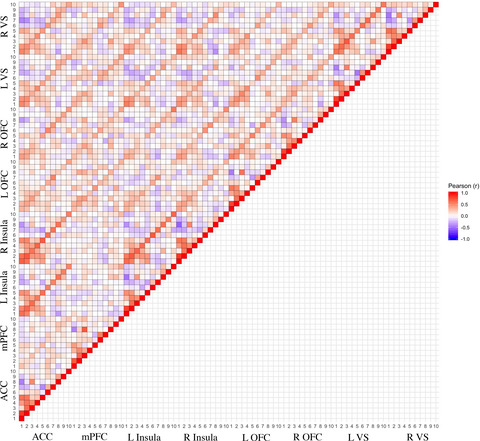
This manuscript systematically evaluates common task contrasts of the Monetary Incentive Delay task and considers within-study differences of mean-level (or group level) activation maps, their regional associations, and effectiveness in predicting substance use and socioemotional behaviors in young adults. Our findings demonstrate more similarities than differences between positive and negative cues during the anticipation contrasts, dissimilarity between some positive anticipation contrasts, a robust deactivation effect in the outcome phase , and ROI-behavior associations that are less robust than previously thought.
Characteristics associated with the risk of psychosis among immigrants and their descendants in France
- First Published: 09 April 2021
The aim of the present study is to explore the characteristics that might explain this increase: geographic origin, generation (immigrants or their descendants), social environment, and living conditions. We observed that living in deprived areas increased the incidence of psychosis, particularly among immigrants. Geographic origin was associated with the risk of psychosis although generation has little impact and Sub-Saharan African immigrants and their descendants showed the highest risk.
Electroencephalography resting-state networks in people with Stroke
- First Published: 23 March 2021
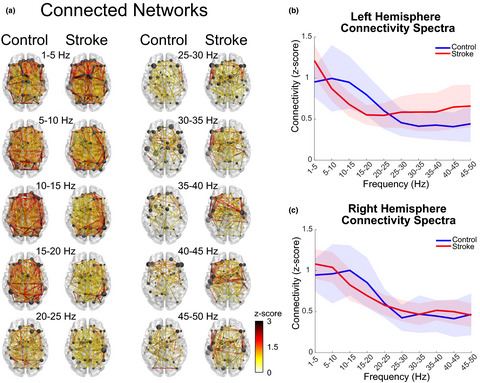
The purpose of this study was to characterize the reorganization of resting-state cortical networks after stroke using electroencephalography (EEG). We found reduced cortical activity and connectivity in the alpha and beta bands after stroke while connectivity in the gamma band increased. These findings suggest that stroke lesions cause a network reorganization to more local (higher frequency), asymmetric networks.
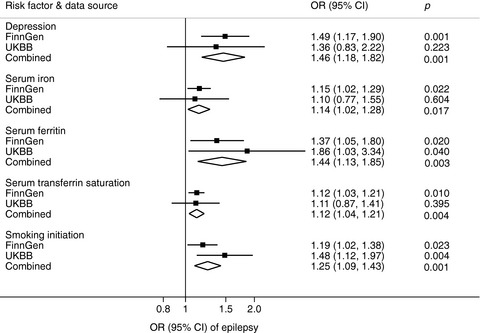
Modifiable risk factors for epilepsy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 02 March 2021
Nono-titanium dioxide exposure during the adolescent period induces neurotoxicities in rats: Ameliorative potential of bergamot essential oil
- First Published: 10 March 2021
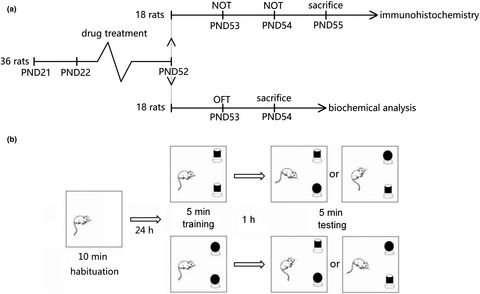
There are negative effects of TiO2 NPs exposure during adolescence on emotional control and cognitive functions, and these negative effects are associated with oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in hippocampus induced by TiO2 NPs. BEO is effective in neuroprotection and could ameliorate the negative effects induced by TiO2 NPs.
Characterizing resting-state networks in Parkinson’s disease: A multi-aspect functional connectivity study
- First Published: 30 March 2021
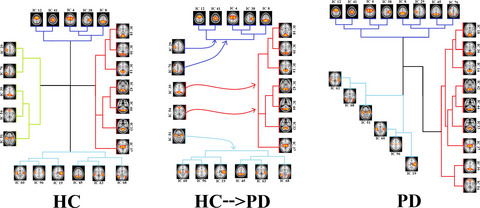
Deriving resting-state networks using group independent component analysis. Applying an RSN score based on dual regression approach and statistical analysis. Identification of the significantly different regions of the cerebellum and occipital pole. The disintegration of the default mode network cluster into the other RSN clusters in PD.
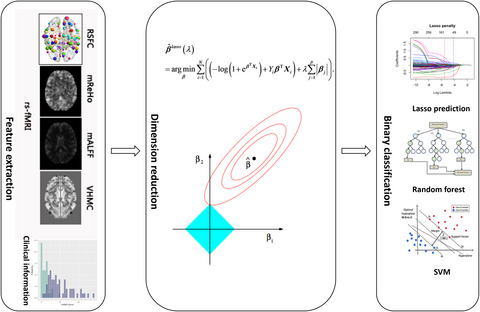
Aberrant functional connectivity and activity in Parkinson’s disease and comorbidity with depression based on radiomic analysis
- First Published: 10 March 2021
Christmas, acute ischemic stroke and stroke-related mortality in Hungary
- First Published: 09 March 2021
Individual markers of cerebral small vessel disease and domain-specific quality of life deficits
- First Published: 10 March 2021
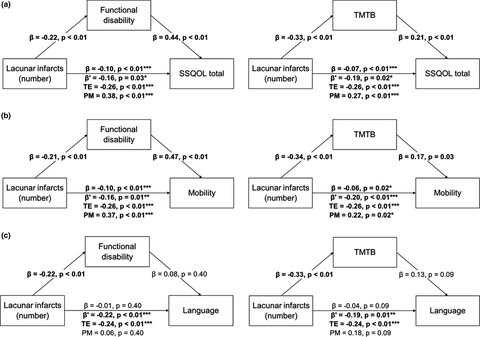
Fernando et al. investigate associations between radiological markers of cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) and subdomains of quality of life (QOL). In a pooled sample of SVD patients, they find that lacunes lead to reductions in total QOL, as well as mobility and language-related QOL, and explore potential mediating variables. These results suggest the possibility of targeted interventions to improve QOL in SVD patients.
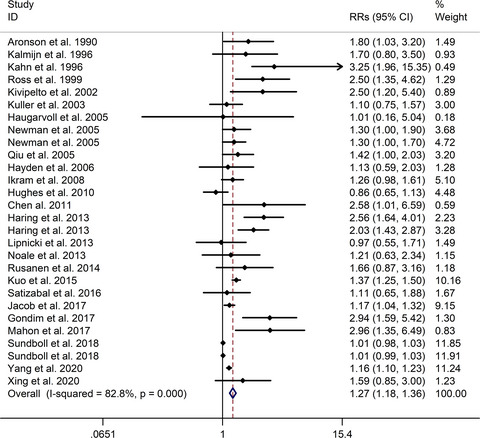
Associations between coronary heart disease and risk of cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 20 March 2021
Continuation rate for asenapine and brexpiprazole treatment in patients with schizophrenia
- First Published: 13 March 2021
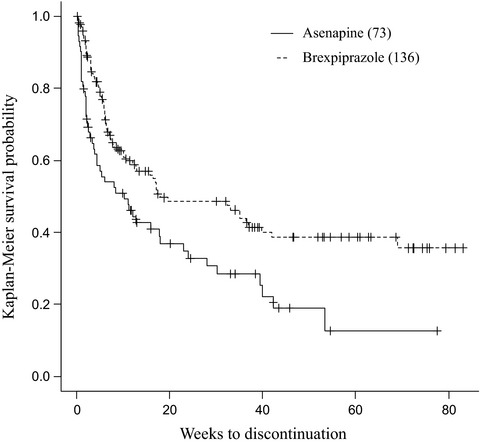
This retrospective study sought to compare the treatment continuation rates of asenapine and brexpiprazole while examining the specific factors that affect both the continuation rates and clinical efficacy of brexpiprazole in patients with schizophrenia. Results show that brexpiprazole had a significantly higher treatment continuation rate compared to asenapine. Moreover, patients who were older, had a lower CGI-severity of illness score, and those for whom the drug was initiated as an outpatient, had a higher continuation rate. Meanwhile, disease duration, CGI-S scale, and continuation duration all significantly affected the clinical efficacy of brexpiprazole.
Patients' physical activity in stroke units in Latvia and Sweden
- First Published: 23 March 2021
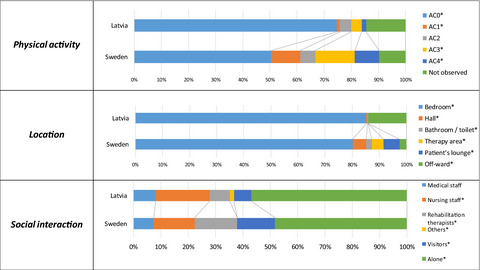
This behavioral mapping study describe levels of physical activity in patients with stroke in a comprehensive stroke unit in Sweden and Latvia. Patients are inactive and alone for a majority of the time during hospitalization in both countries. There are differences in environment in the stroke units between countries.
Human liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 elevation in the cerebrospinal fluid in bacterial meningitis
- First Published: 03 April 2021
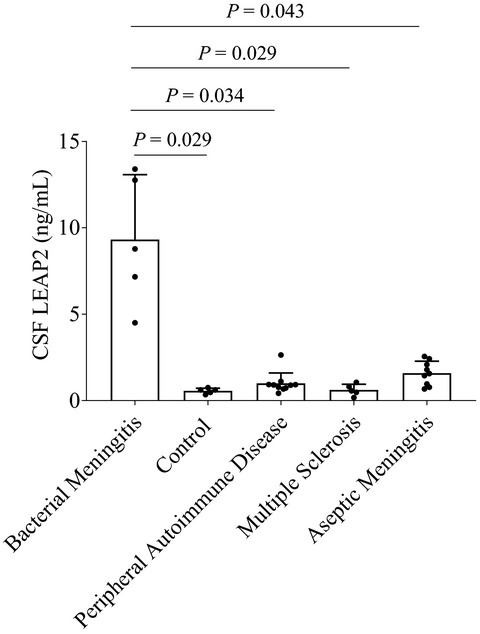
This original study describes the identification of liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP2), an antimicrobial peptide, in human CSF, and is the first to measure CSF LEAP2 in neurological disorders. CSF LEAP2 is increased in patients with bacterial meningitis, suggesting its biological significance in the pathology of CNS infections.
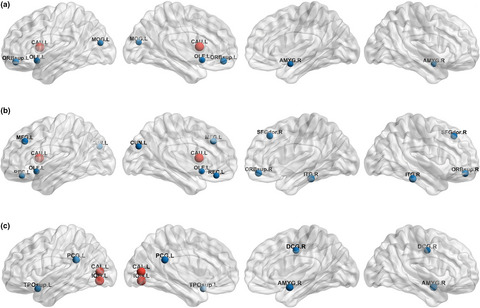
Structural connectivity networks in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disease
- First Published: 01 April 2021
Exploration of the cortical pathophysiology underlying visual disturbances in schizophrenia comorbid with depressive disorder—An evidence from mouse model
- First Published: 17 March 2021
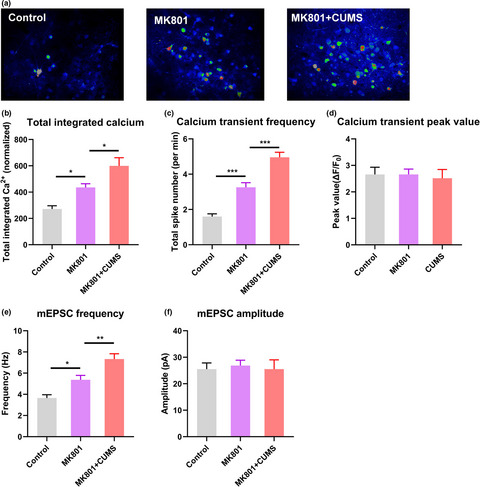
In our mouse model of schizophrenia, the hyperactivation of cortical neurons occurred without exposure to sensory stimuli, as supported by in vivo and ex vivo recordings. This elevated spontaneous activity was attributable mainly to a greater frequency, but not amplitude, of calcium activity spikes, indicating the potentiation of presynaptic transmission. Notably, comorbidity with depression further aggravated the cortical synapse pathology. These pathophysiological alterations in the visual cortex provide a possible explanation for the occurrence of visual hallucination in patients with schizophrenia.
Entorhinal cortex and parahippocampus volume reductions impact olfactory decline in aged subjects
- First Published: 26 March 2021

Left: Visualization of brain segmentation in a single subject with FreeSurfer. The entorhinal cortex (ENT) is indicated in red, and the parahippocampus (para-HI) is indicated in green. Right: Visualization of hippocampal subfield segmentation in a single subject with each subfield represented by a different color.
Hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in large cerebral infarction
- First Published: 25 March 2021
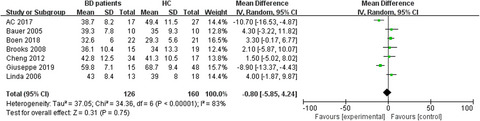
Cerebral glucose metabolism in bipolar disorder: A voxel-based meta-analysis of positron emission tomography studies
- First Published: 26 March 2021
Association of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor rs6265 G>A polymorphism and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder susceptibility: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 09 April 2021
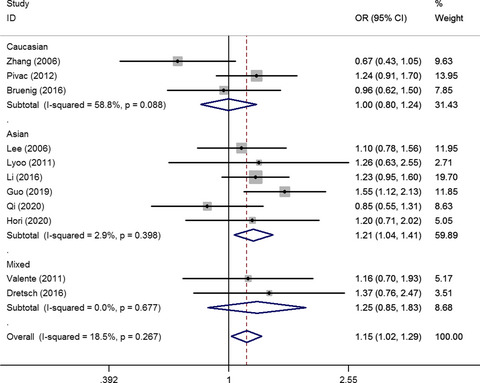
A meta-analysis focused on the association between BDNF rs6265 G > A polymorphism and PTSD risk was conducted. 16 publications involving 5,369 subjects were included in this system review and 11 case-controls were analyses in meta-analysis. Current meta-analysis suggests indicated that the BDNF rs6265 G > A polymorphism might be involved in PTSD susceptibility.
Optical coherence tomography angiography helps distinguish multiple sclerosis from AQP4-IgG-seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder
- First Published: 30 March 2021
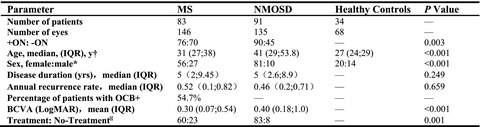
In summary, our study compared the structure and flow between patients with MS and those with AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD, indicating pathophysiological differences between them and suggesting that OCTA may have an additive effect as a biomarker in conjunction with routine OCT measurements. Combining OCTA and OCT may yield promising diagnostic properties in distinguishing both diseases.
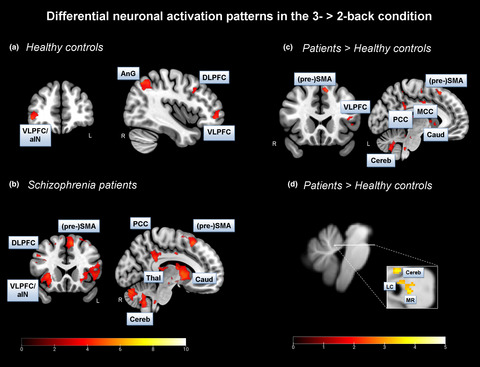
Working memory in schizophrenia: The role of the locus coeruleus and its relation to functional brain networks
- First Published: 30 March 2021
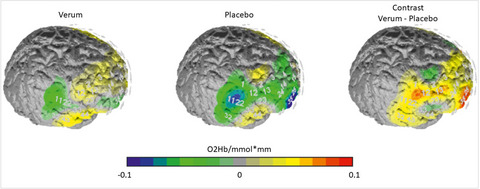
The impact of TMS-enhanced cognitive control on forgiveness processes
- First Published: 30 March 2021
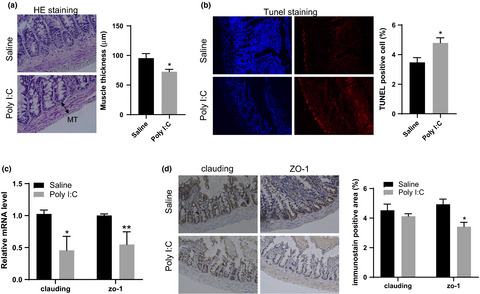
Maternal immune activation alters adult behavior, intestinal integrity, gut microbiota and the gut inflammation
- First Published: 01 April 2021
A mediating role for mental health in associations between COVID-19-related self-stigma, PTSD, quality of life, and insomnia among patients recovered from COVID-19
- First Published: 03 April 2021
Estrogen attenuates physical and psychological stress-induced cognitive impairments in ovariectomized rats
- First Published: 03 April 2021
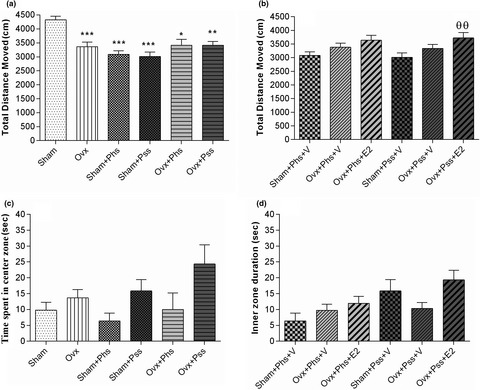
Findings from the current study delineated that exposure to both physical stress and psychological stress can cause cognitive disorders and increase anxiety-like behaviors. These findings suggest that female rats are vulnerable to both stressor types, and effects impact motor and cognitive behaviors of the animals.
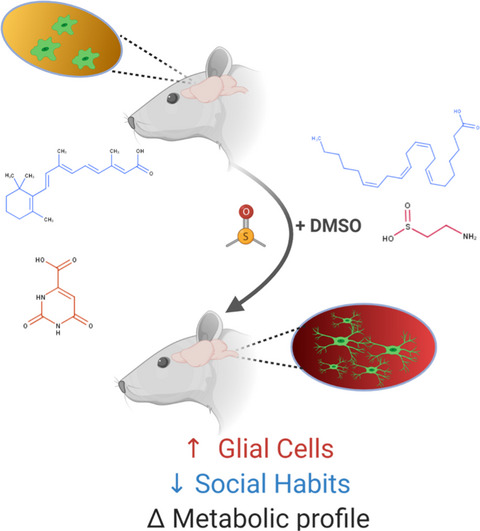
Exposure to DMSO during infancy alters neurochemistry, social interactions, and brain morphology in long-evans rats
- First Published: 10 April 2021
REVIEWS
Can seizure therapies and noninvasive brain stimulations prevent suicidality? A systematic review
- First Published: 10 April 2021
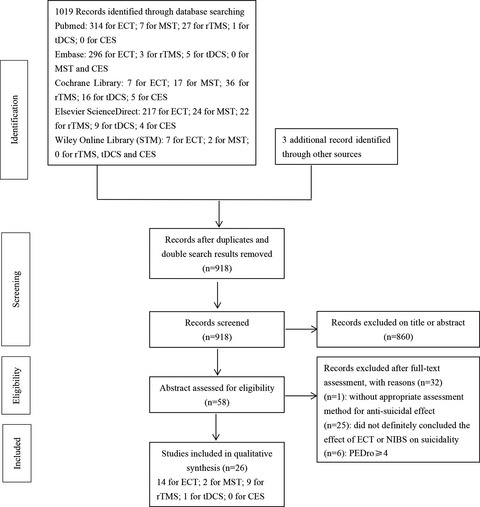
We provided an update of current evidence on the effects of seizure therapies (electroconvulsive therapy and magnetic seizure therapy) and noninvasive brain stimulations (repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation, and transcranial electrostimulation) on suicidality. The antisuicidal effect of ECT could be supported, but magnetic seizure therapy, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, transcranial direct current stimulation, and transcranial electrostimulation were not consistently recommended for treating suicidality. Long-term antisuicidal effect of seizure therapies and noninvasive brain stimulations should be further investigated both alone and in combination with pharmacotherapy or psychotherapy.
Central nervous system manifestations in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 09 January 2021
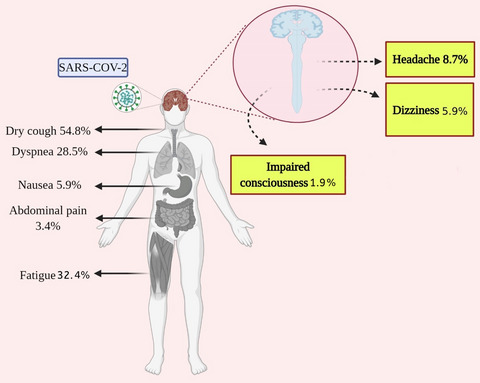
The most common CNS symptom of COVID-19 was headache (8.69%, 95%CI: 6.76%–10.82%), dizziness (5.94%, 95%CI: 3.66%–8.22%), and impaired consciousness (1.90%, 95%CI: 1.0%–2.79%). The growing number of studies has reported COVID-19, CNS presentations as remarkable manifestations that happen. Hence, understanding the CNS characteristics of COVID-19 can help us for better diagnosis and ultimately prevention of worse outcomes.
fMRI as an outcome measure in clinical trials: A systematic review in clinicaltrials.gov
- First Published: 04 March 2021
Study on the neuroprotective effects of Genistein on Alzheimer’s disease
- First Published: 11 March 2021

Recent studies have shown that genistein, one of the selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), can improve brain function through the blood–brain barrier (BBB), antagonize the toxicity of amyloid β-protein (Aβ), and have neuroprotective effects. In addition, the use of Gen can avoid the risk of endometrial cancer and breast cancer caused by estrogen therapy while exerting an estrogen-like effect, which has some potential for the delay and treatment of AD.
COMMENTARY
Cognitive decline among older adults: A hidden preexisting condition and its role in ‘brain-at-risk’ surgical patients
- First Published: 04 March 2021

Preexisting cognitive impairment is an important, but underrecognized, predictor of postoperative neurocognitive dysfunction, a common and important sequela of surgery. We have applied computerized neuropsychological testing as an efficient and reliable means of detecting preexisting cognitive impairment in two studies of cardiac and noncardiac surgical populations and propose that this tool has great potential in routine clinical diagnosis.
CORRIGENDUM
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Complications following REM sleep behavior disorder
- First Published: 30 March 2021
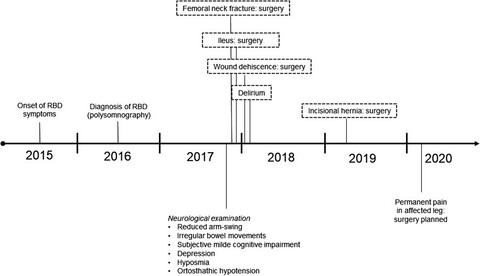
REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD) is gaining increasing attention as important prodromal marker for the development of neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's Disease. However, the clinical relevance of this disorder and its association with other prodromal markers is often underestimated in clinical routine. We here report a case of severe clinical complications following extensive nocturnal movements due to RBD, aggravated by occurrence of additional prodromal nonmotor symptoms.