Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
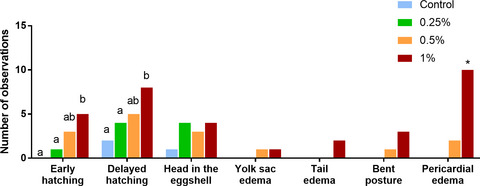
Embryonic ethanol exposure on zebrafish early development
- First Published: 03 May 2021
Cognitive deficit is correlated with sleep stability in insomnia: A cardiopulmonary coupling study
- First Published: 07 May 2021
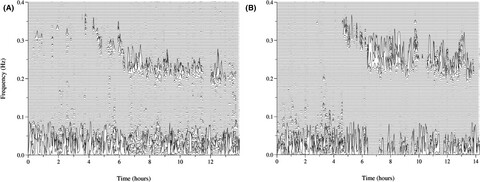
Sleep stability and mood are valuable therapy targets to potentially improve cognitive outcomes in the insomnia patients. The cardiopulmonary coupling (CPC) analysis is a practical measure for objective sleep evaluation, which is helpful to identify the insomnia patients with high risk of cognitive impairment.
Validation of the Finnish version of the Brief International Cognitive Assessment for Multiple Sclerosis (BICAMS) and evaluation of the applicability of the Multiple Sclerosis Neuropsychological Questionnaire (MSNQ) and the Fatigue Scale for Motor and Cognitive Functions (FSMC)
- First Published: 07 May 2021
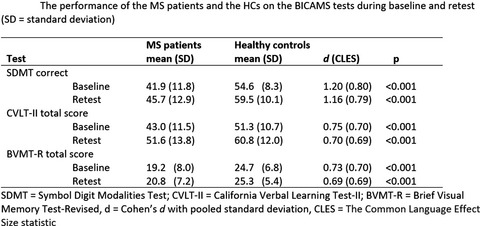
A total of 65 MS patients and 45 healthy controls (HC) were assessed with the BICAMS, the Multiple Sclerosis Neuropsychological Questionnaire (MSNQ), and the Fatigue Scale for Motor and Cognitive Functions (FSMC) twice, approximately within nine days. The BICAMS validation was performed according to published recommendations. The results supported the validity of the Finnish version of the BICAMS. The Finnish versions of the MSNQ and the FSMC proved useful tools in approaching concerns related to cognition and fatigue.
Close relationships in Parkinson´s disease patients with device-aided therapy
- First Published: 05 May 2021
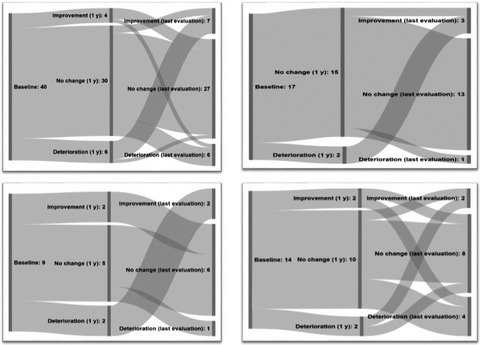
The close relationship wherein one part has PD and receives Device-Aided Therapy has a high risk of being unequal. Partners more often report changes in relationship satisfaction and report significantly higher avoidance score on the ECR-RS in contrast to patients who reports significantly higher anxiety scores.
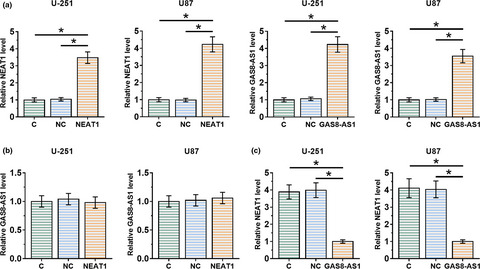
LncRNA GAS8-AS1 downregulates lncRNA NEAT1 to inhibit glioblastoma cell proliferation
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Psychiatric risk and resilience: Plasticity genes and positive mental health
- First Published: 01 May 2021
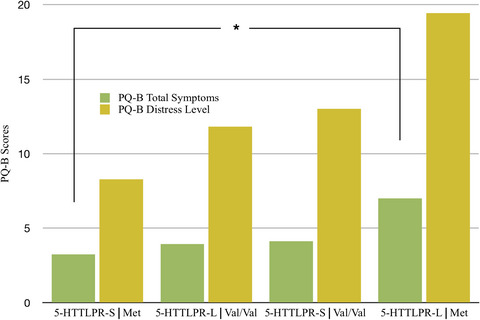
We examined the psychotic risk in relation to positive mental health and plasticity genes in a healthy college student sample. Lower psychotic risk correlated with higher positive mental health and a particular set of plasticity genes. Results point to important contributions of positive mental health and genes that support neural plasticity in mitigating general psychiatric risk and enhancing well-being.
Temporal lobe epilepsy alters neural responses to human and avatar facial expressions in the face perception network
- First Published: 05 May 2021
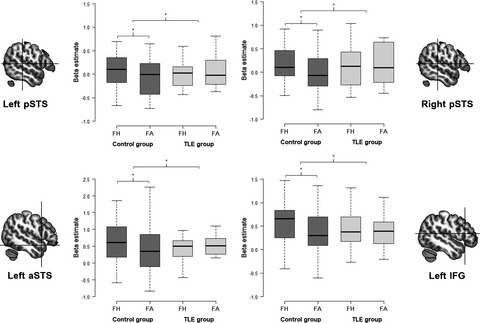
The aim of our event-related fMRI study was to compare brain activation differences in people with epilepsy and controls during the processing of fearful and neutral dynamic expressions displayed by human or avatar faces. Our fMRI results show that people with TLE exhibited reduced response differences between human and avatar fearful expressions in the dorsal pathway of the face perception network (STS and inferior frontal gyrus) as well as in the medial prefrontal cortex. Taken together, these findings suggest that brain responses to dynamic facial expressions are altered in people with TLE compared to neurologically healthy individuals—regardless of whether the face is human or computer-generated.
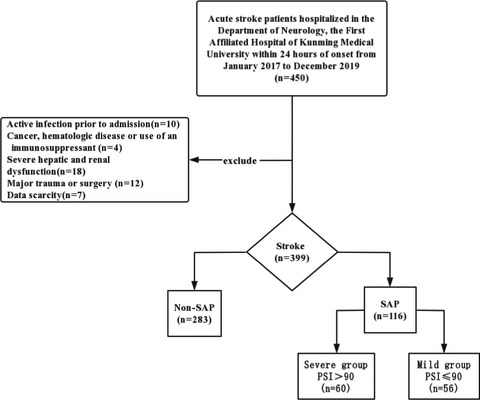
Monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of stroke-associated pneumonia: A retrospective study-based investigation
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Risk factors for early–onset seizures after stroke: A systematicreview and meta-analysis of 18 observational studies
- First Published: 04 May 2021
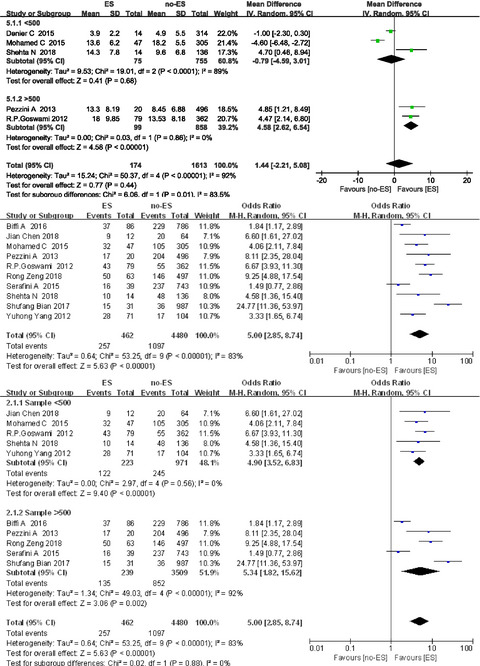
These findings suggest that cortical involvement, intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral infarction with hemorrhagic transformation are important predictors and risk factors for early seizures after stroke, while the patient's gender, age, NHISS score, alcoholism, smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, dyslipidemia , receiving surgical treatment and reperfusion therapy showed no association with the occurrence of early-onset seizures after stroke.
Personality profile of individual sports champions
- First Published: 05 May 2021
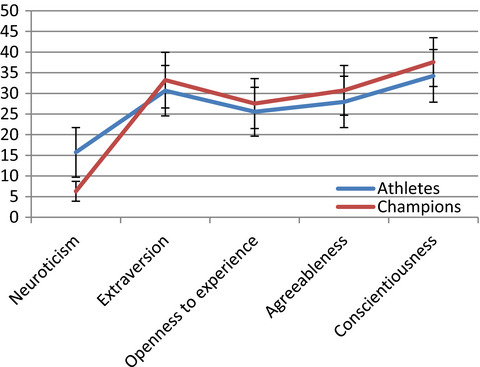
The purpose of this paper is to determine which personality traits characterize individual sports champions. Sports activity shapes the personality, and the shaped personality traits have an impact on taking solutions in the starting situation. The level of intensity of neuroticism, extraversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness may determine the result in competition in individual sports.
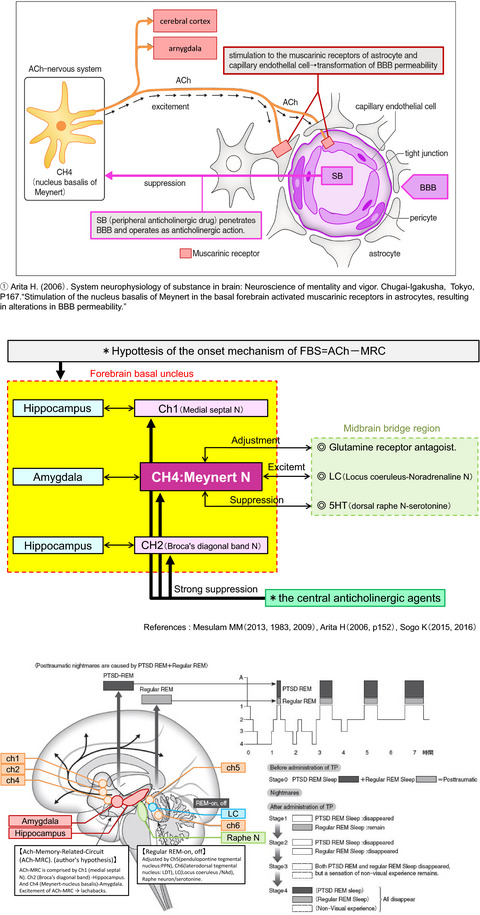
Centrally acting anticholinergic drug trihexyphenidyl is highly effective in reducing nightmares associated with post-traumatic stress disorder
- First Published: 14 May 2021
HiCommunication as a novel speech and communication treatment for Parkinson's disease: A feasibility study
- First Published: 04 May 2021

The aim of this study was to develop and study feasibility aspects of a new intervention program for group training of speech and communication in people with Parkinson's disease called HiCommunication. Results indicate that HiCommunication is feasible for people with mild-moderate PD, well-tolerated and positive outcomes following intervention were shown.
Safety and efficacy of intravenous thrombolytic treatment in wake-up stroke: Experiences from a single center
- First Published: 03 May 2021
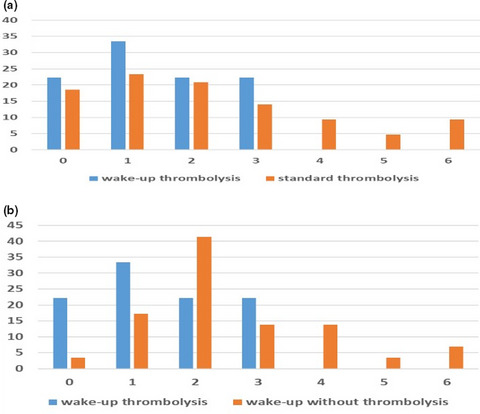
The aim of the study was to establish the safety and efficacy of intravenous thrombolytic treatment in wake-up stroke comparing to the standard thrombolysis treatment in stroke with clear onset. Wake-up stroke subjects were characterized by significantly more favorable functional outcome on discharge in contrast to the standard thrombolysis procedure subjects (p = .0289). Our study showed that intravenous thrombolytic treatment is a safe procedure and may lead to a favorable outcome in subjects who are awaken with stroke symptoms.
Program development using intervention mapping in primary healthcare settings to address elder abuse: A randomized controlled pilot study
- First Published: 04 May 2021
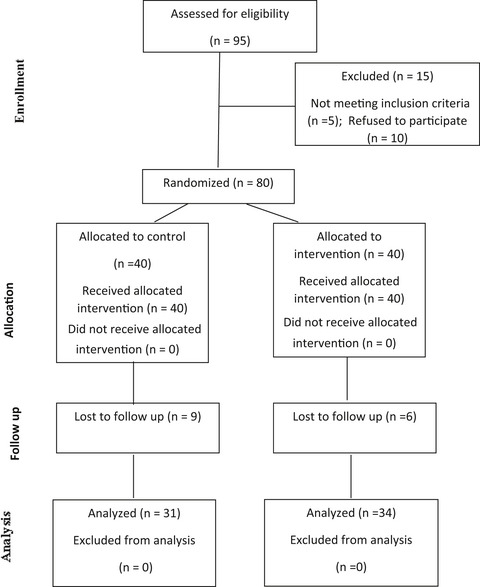
A culturally informed treatment, based on Intervention Mapping (IM), for primary healthcare settings was developed. The intervention targets family members of elderly women and seeks to reduce elder abuse. The intervention reduced psychological abuse and neglect. Physical abuse occurred at very low rates. Implementation and further testing in healthcare facilities are recommended.
Impairment of eye emotion discrimination in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes: A neuropsychological study
- First Published: 04 May 2021

To explore the characteristics and related factors of emotional recognition impairment in BECT patients, we conducted eye emotion discrimination studies on the newly diagnosed BECT and the postremission BECT, respectively, and found that the discrimination of sadness, fear, and disgust in newly diagnosed BECT patients has been impaired, and it is negatively correlated with the age of onset. More younger the age of onset, more severe the damage. However, there is no obvious damage to the discrimination of sadness, fear, and disgust in patients with BECT after remission. This result indicates that although BECT patients have impairment of eye emotion discrimination at the early stage of the disease, it can be returned to normal as the disease is relieved.
BPV associated with imaging features of SSI on MRI
- First Published: 07 May 2021
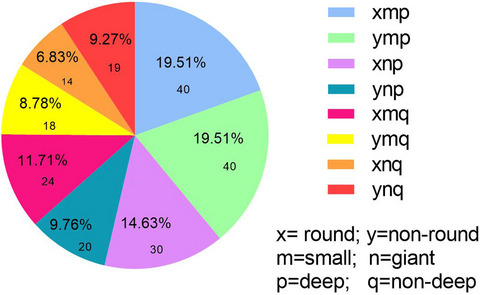
A retrospective study was performed to investigate the relationship between blood pressure variability (BPV) and imaging features of single small infarction (SSI) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Increased BPV parameters such as day-to-day and visit-to-visit (SBPMax, SBPSD, and DBPMax) were related to the SSI characterized by small in deep brain region.
When reintegration fails: Stigmatization drives the ongoing violence of ex-combatants in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo
- First Published: 04 May 2021
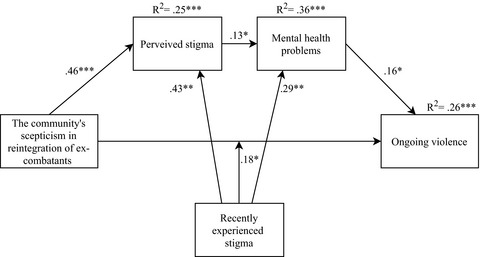
This article showed that stigmatization presents as additional burden for ex-combatants in Eastern DRC beyond posttraumatic experiences. Rejective attitudes toward ex-combatants form the basis of stigmatization and by predicting both mental health problems and aggression present as social drivers of the cycles of violence. Our study demonstrates the importance for intervention programming that combines individual treatment with interventions including ex-combatants' social environment.
Task-induced brain functional connectivity as a representation of schema for mediating unsupervised and supervised learning dynamics in language acquisition
- First Published: 05 May 2021
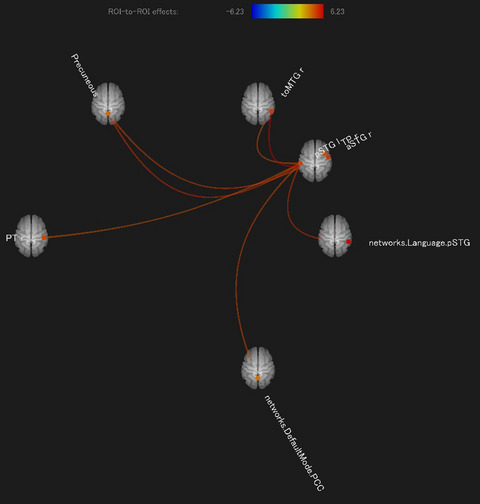
Based on the schema theory advanced by Rumelhart and Norman, we shed light on the individual variability in brain dynamics induced by hybridization of learning methodologies, particularly alternating unsupervised learning and supervised learning in language acquisition. Functional magnetic resonance imaging was performed to identify the functional network connections for schema updating by alternately using unsupervised and supervised artificial grammar learning tasks to segment potential words. The default mode network represented the first stage of spontaneous unsupervised learning, and the wrap-up accomplishment for successful subjects of the whole hybrid learning in concurrence with the task-related auditory language networks.
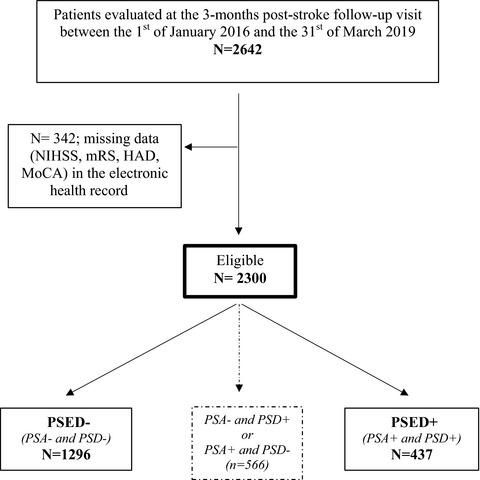
Association between neurological outcome and poststroke comorbid mood and anxiety disorders: A real-life experience
- First Published: 05 May 2021
REVIEW
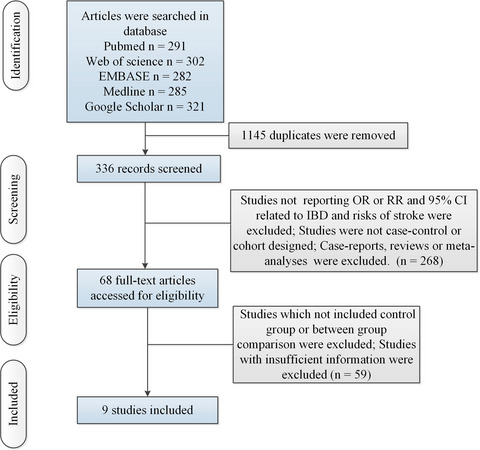
Increased risk of stroke among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis
- First Published: 07 May 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Atrial cardiopathy in embolic stroke of undetermined source
- First Published: 04 May 2021

The incidence of severe left atrial enlargement is higher in ESUS patients than in patients with noncardioembolic stroke, while there was no difference in the proportion of elevated serum NT-proBNP between them. ESUS with atrial cardiopathy was a milder form when compared to stroke caused by atrial fibrillation-induced cardioembolism.
REVIEW
Conscious sedation compared to general anesthesia for intracranial mechanical thrombectomy: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 07 May 2021
What's already known about this topic?Endovascular therapy is the standard of care for severe acute ischemic stroke caused by large-vessel occlusion in the anterior circulation, but there is a debate on the optimal anesthetic approach during this therapy. Meta-analyses of observational studies suggest that general anesthesia increases disability and death compared with conscious sedation However, their results are conflicting. This meta-analysis study was performed to assess the relationship between the effects of general anesthesia compared to conscious sedation during endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke.What does this article add?General anesthesia has no independent relationship compared to conscious sedation during the endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with a relative relationship favoring general anesthesia only in decreasing the symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage.This relationship encouraged us to recommend either anesthetic strategy during the endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke with no possible fear of higher complication.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
On the processing of optimal performances: Studying arousal evoked by being correct and fast
- First Published: 07 May 2021
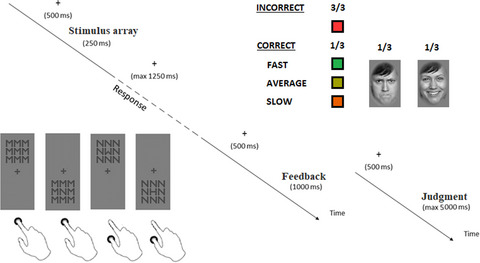
Optimal performance, like being correct and fast, leads to enhanced response-related brain activity, increased physiological arousal, and modulations in processing subsequently presented emotional faces. Since these properties are similar to those of error processing, the monitoring system is sensitive to both better-than-expected and worse-than-expected performance. This sensitivity might lead to learning from the negative reinforcement of errors and the positive reinforcement of optimal responses.
Depression and anxiety symptoms are related to pain and frailty but not cognition or delirium in older surgical patients
- First Published: 05 May 2021

Preoperative mood symptoms were related to physical pain and frailty. Taken together, these suggest that in patients without a formal psychiatric diagnosis, preoperative mood symptoms are related to physical state rather than a harbinger of early cognitive decline. Future studies are needed to understand the nature of the relationship between mood symptoms and physical state in surgical patients.
The Delta Study – Prevalence and characteristics of mood disorders in 924 individuals with low mood: Results of the of the World Health Organization Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI)
- First Published: 07 May 2021
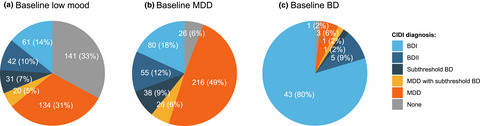
The Delta Study was undertaken to improve the diagnosis of mood disorders in individuals presenting with low mood. The current study aimed to estimate the prevalence and explore the characteristics of mood disorders in participants of the Delta Study, and discuss their implications for clinical practice. This study confirms high under- and misdiagnosis rates of mood disorders in individuals presenting with low mood, potentially leading to worsening of symptoms and decreased wellbeing, and indicate the need for improved mental health triage in primary care.
Persistence with medical treatment for Wilson disease in China based on a single center’s survey research
- First Published: 05 May 2021
Altered ripple density inside seizure onset zone in patients with focal cortical dysplasia-associated epilepsy
- First Published: 07 May 2021
Red cell index: A novel biomarker for 3-month mortality in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis
- First Published: 04 May 2021
Is obsessive–compulsive personality disorder related to stress-related exhaustion?
- First Published: 10 May 2021

Recovery from stress-related diagnoses can, in some cases, be long-lasting and several different factors could be related to such a lengthy recovery. The aim of this study was to investigate whether recovery from exhaustion disorder (ED) is associated with OCPD in 147 former patients with ED. The main result is that patients with residual clinical ED report OCPD to a greater extent compared with patients who do not longer fulfill the clinical criteria for ED, 7-10 years after seeking care. Patients with OCPD that have not recovered report “excessive devotion to work” to a higher degree than patients with OCPD that have recovered.
REVIEW
Schizophrenia outcomes in the 21st century: A systematic review
- First Published: 15 May 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Co-activation pattern alterations in autism spectrum disorder–A volume-wise hierarchical clustering fMRI study
- First Published: 16 May 2021
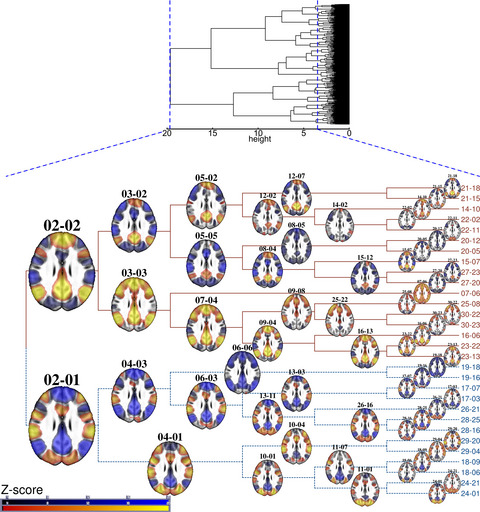
Co-activation patterns (CAPs) of resting state brain activity varyingly contain both default mode network (DMN)-positive and default mode network-negative brain state properties. With hierarchical clustering, they can be divided into shorter substates. When applied in autism spectrum disorder, this method showed simultaneous visual network and either dorsal attention or DMN overactivation during DMN-negative CAPs. Nonsequential volume gathering into CAPs provides an alternative to sliding window analysis.
REVIEWS
Cerebral blood flow impairment and cognitive decline in heart failure
- First Published: 14 May 2021
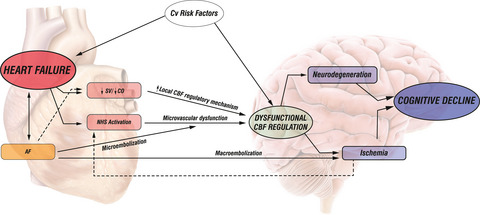
One of the postulated mechanisms underlying cognitive decline in chronic heart failure is chronic regional hypoperfusion of critical brain areas. Cognitive function may be further compromised by microvascular damage due to cardiovascular risk factors in chronic heart failure patients. Cerebral blood flow assessment is proposed for early recognition of patients at risk of cognitive decline and could guide further therapeutic strategy.
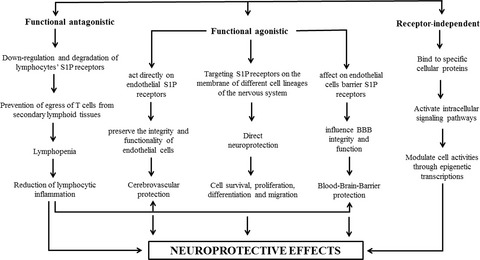
The emerging role of FTY720 as a sphingosine 1-phosphate analog for the treatment of ischemic stroke: The cellular and molecular mechanisms
- First Published: 10 May 2021
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
The relationship between body image and emotional and cognitive impairment after brain damage: A preliminary study
- First Published: 18 May 2021
Body image is a person's perception of the aesthetics or sexual attractiveness of their own body. After brain damage, the person is subjected to several physical changes with heavy consequences on both physical and emotional domains. It can lead to a dysfunction of the body image and to the risk to compromise cognitive recovery. Notably, this study confirms the relationship between body image and cognitive deficits in ABI patients, especially noticeable in vascular patients.
Mendelian randomization suggests that head circumference, but not birth weight and length, associates with intelligence
- First Published: 10 May 2021
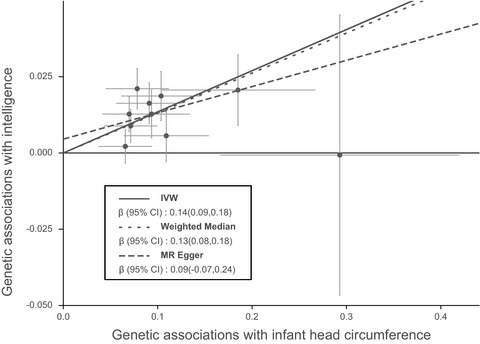
We performed a Mendelian randomization study to investigate the causal effects of infant head circumference, birth length, and birth weight on human intelligence by extracting genetic association datasets from large-scale genome-wide association studies of birth parameters and human intelligence. Our findings suggest that that head circumference, but not birth weight and length, is associated with intelligence, which might indicate that that brain development rather than general fetal growth was responsible for the development of intelligence.
Changes of coagulation function and risk of stroke in patients with COVID-19
- First Published: 16 May 2021
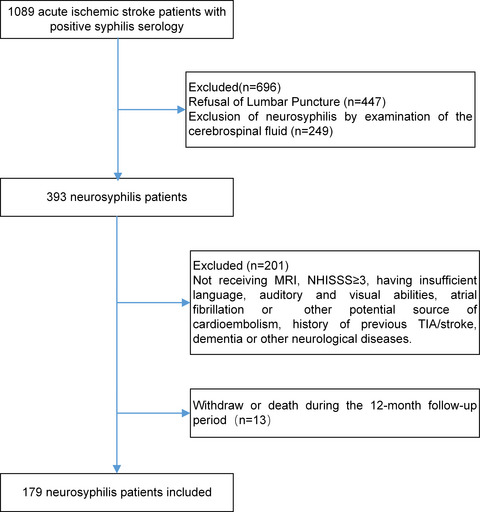
The associations of increased cerebral small vessel disease with cognitive impairment in neurosyphilis presenting with ischemic stroke
- First Published: 16 May 2021
Analysis of the neuroprotective effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist peptide on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by Quantitative Proteomics Mass Spectrometry
- First Published: 21 May 2021
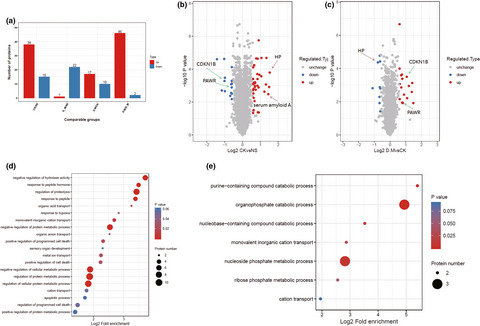
Liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, effectively reduced the infarct volume in the brain in MCAO mice. The physiological effects of liraglutide in ischemia-reperfusion injury were dependent on the suppression of oxidative stress, on the inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and a reduction in the inflammatory response.
Allophonic perception of VOT contrasts in Spanish children with dyslexia
- First Published: 21 May 2021
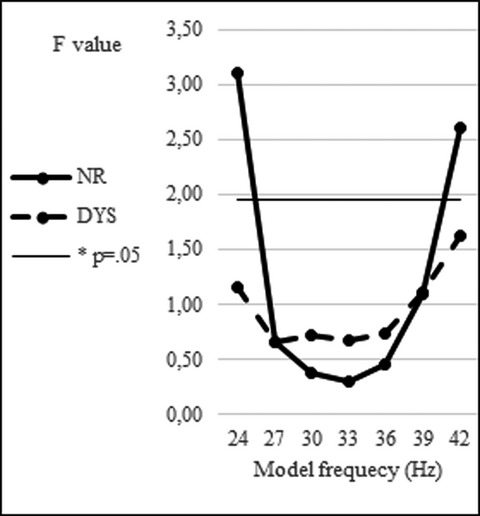
Spanish children with dyslexia exhibit a general deficit in the perception of the voicing feature on three different VOT continua (ba/pa, de/te, and di/ti). These children also exhibit a higher sensitivity in the discrimination of allophonic features, but only for the stimulus continuum that was based on a nonlexical contrast (ba/pa). Fitting a neural network model to the data suggests that allophonic perception is due to a deficit in “subharmonic coupling” between high-frequency networks.