Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Editorial
Point-Of-Care Ultrasound in Emergency Departments in Australia/New Zealand: An Emergency Physician's Perspective
- Pages: 3-7
- First Published: 05 March 2025
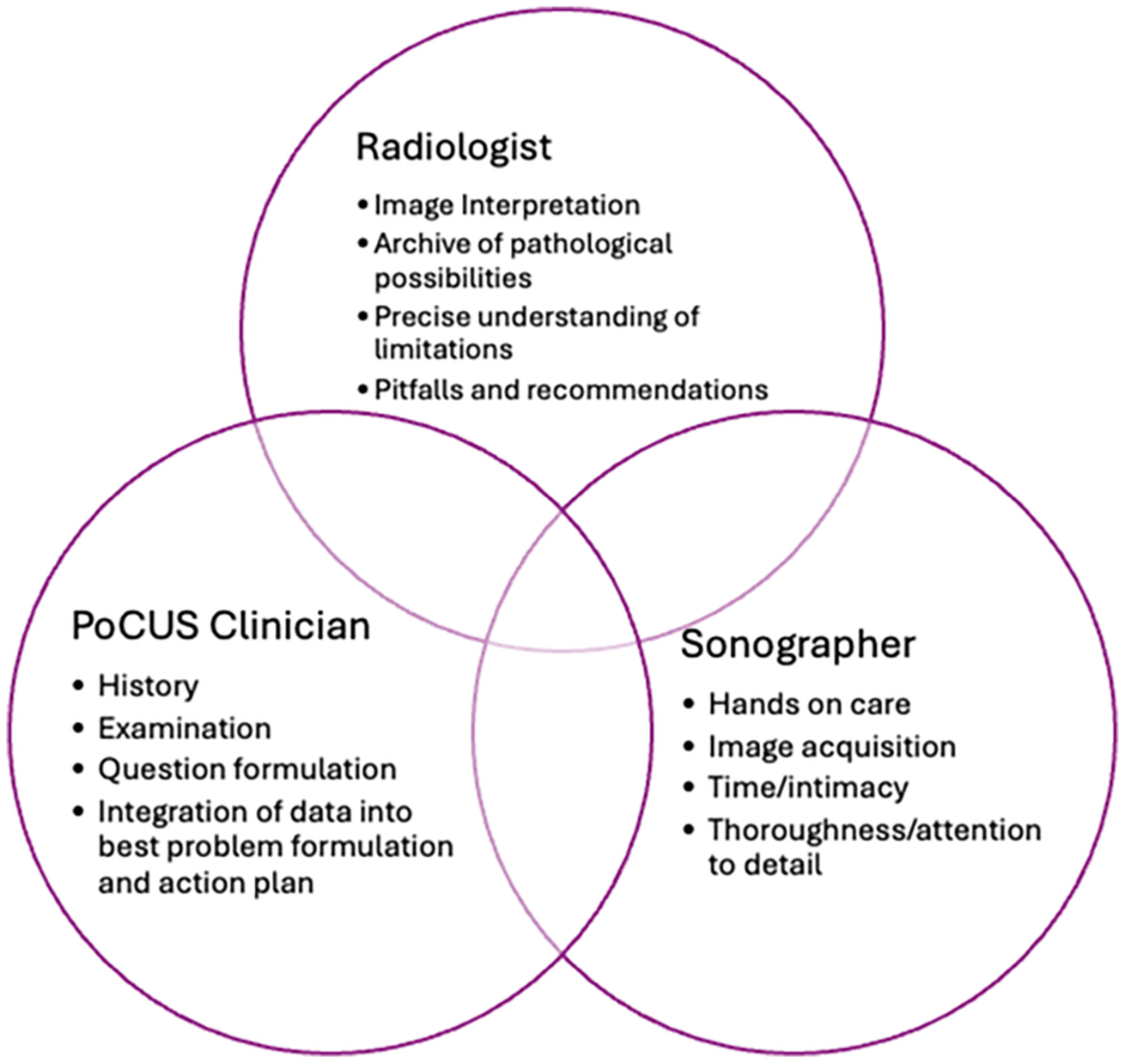
This brief overview of the current state of clinician performed focused ultrasound (Emergency PoCUS) by emergency practitioners in Australia/New Zealand (ANZ) has touched on its history, scope of practice both mandated and context-dependent, complex embedding in clinical diagnostic reasoning and range of governance issues. It is the author's hope that an ongoing understanding and interplay between the three professional groups most closely involved in the use of ultrasound to improve patient care and health-care flow can continue to work closely together for the ultimate benefit of patients in multiple contexts in ANZ and beyond.
Original Article
Renal screening sonography—A comparative study in a Portuguese basic emergency service
- Pages: 8-16
- First Published: 18 June 2024
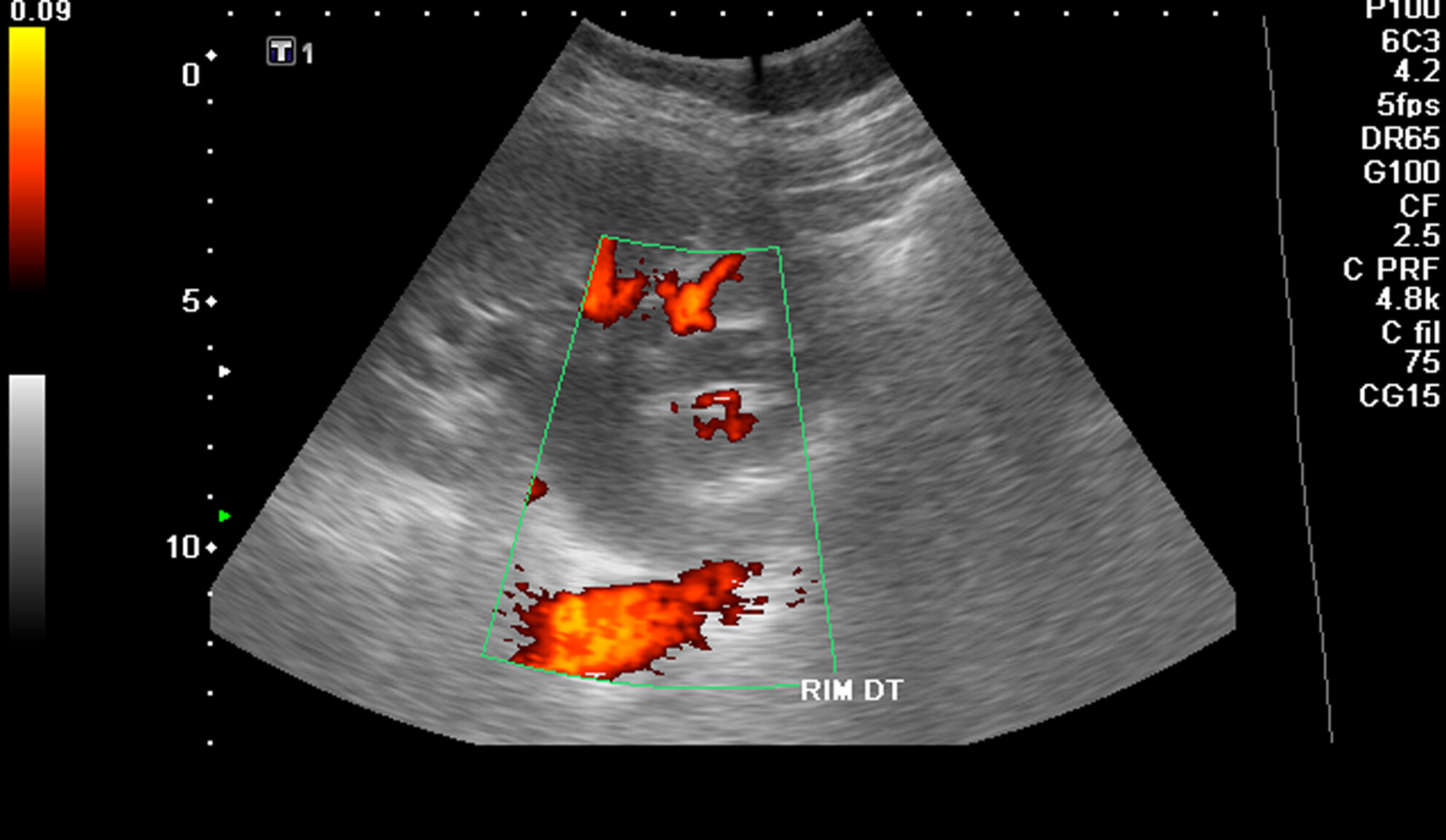
Renal sonography screening aids in clinical decision-making for patients with suspected renal colic. This study intends to compare the accuracy and pertinence of sonographic findings obtained by a sonographer in a Basic Emergency Service (BES) with that of radiologists at Referral Hospital (RH) in Portugal. Renal sonography screening was able to detect abnormalities in urinary system in patients with suspected renal colic. Sonographic findings evidenced correlation between sonographer at the BES and radiologists at the RH in Portugal. These results suggest that renal sonography screening can be a valuable tool for clinicians to scrutinise renal colic suspicion and to identify appropriate treatment and referral options.
Intrafraction motion and impact of margin reduction for MR-Linac online adaptive radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer treatments
- Pages: 17-24
- First Published: 13 October 2024
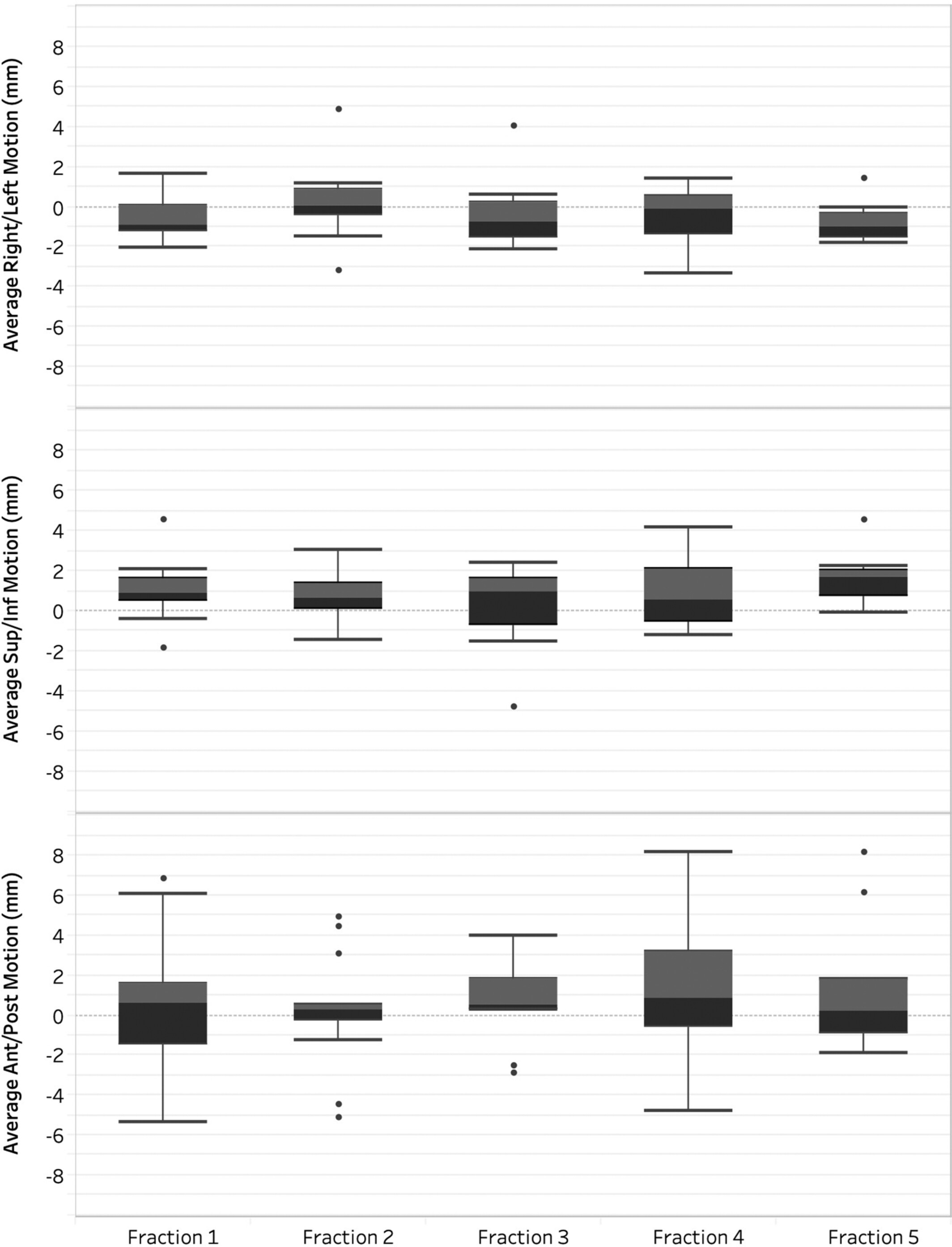
This analysis included quantification of intrafraction motion in pancreas stereotactic ablative radiotherapy treated on the MR-Linac, leading to the development of adjusted (PTV) margins. Intrafraction motion indicated an average target displacement of 1–3 mm, resulting in an adjusted PTV margin of 2 mm in the right–left and superior–inferior directions, and 3 mm in the anterior–posterior direction.
Occupational burnout in nuclear medicine technologists working in Australia and New Zealand – results of a multi-national survey
- Pages: 25-33
- First Published: 27 October 2024
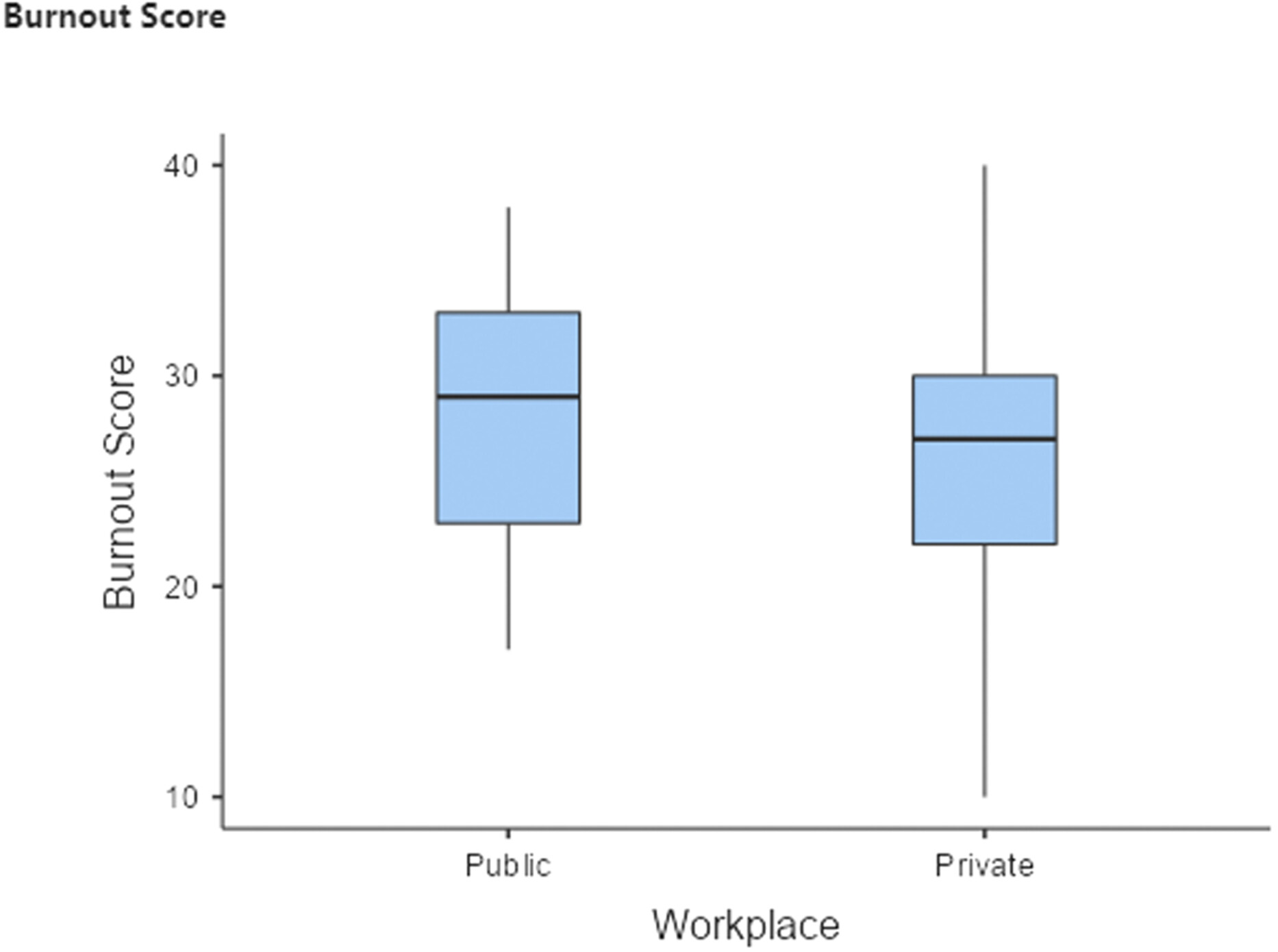
Occupational burnout is associated with negative feelings about the workplace and is often caused by a high workload and a non-supportive workplace. It is associated with absenteeism, high turnover of staff and decreased patient care. More than half of the New Zealand participants and three quarters of the Australian participants had moderate levels of burnout.
Impact of pre-examination video education in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MRI: A comparative study
- Pages: 34-41
- First Published: 11 November 2024
This study evaluates the effects of pre-examination video education on patient anxiety, satisfaction and image quality in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MRI. We found that video education significantly reduced anxiety, increased patient satisfaction and improved image quality compared to standard pre-MRI guidance, highlighting the potential of video interventions to optimise the MRI experience.
Radiography students' knowledge, attitude and practice relating to infection prevention and control in the use of contrast media injectors in computed tomography
- Pages: 42-53
- First Published: 01 September 2024
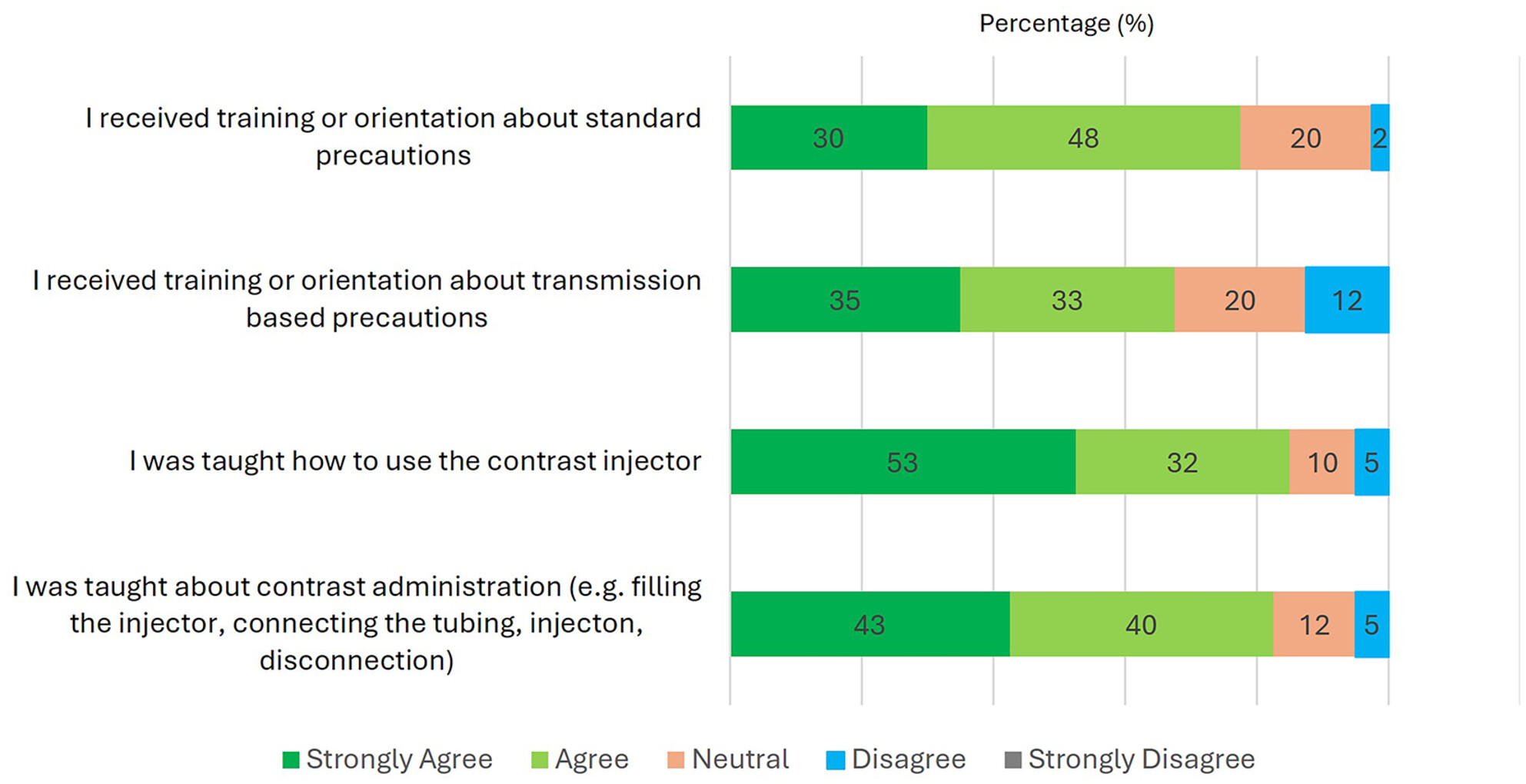
The aim of this study was to explore radiography students' knowledge, attitudes, and practice (KAP) relating to infection prevention and control (IPC) in the use of contrast media injectors in the computed tomography (CT) setting. Radiography students demonstrate varied comprehension of IPC regarding contrast media equipment within CT environment, and there is notable divergence between knowledge and actual practice. Collaborative efforts between academic institutions and clinical training sites are needed to integrate IPC protocols into the curriculum and on-site training.
Radiation therapists' perceptions of participating in Professional Supervision – a pilot study
- Pages: 54-62
- First Published: 08 September 2024
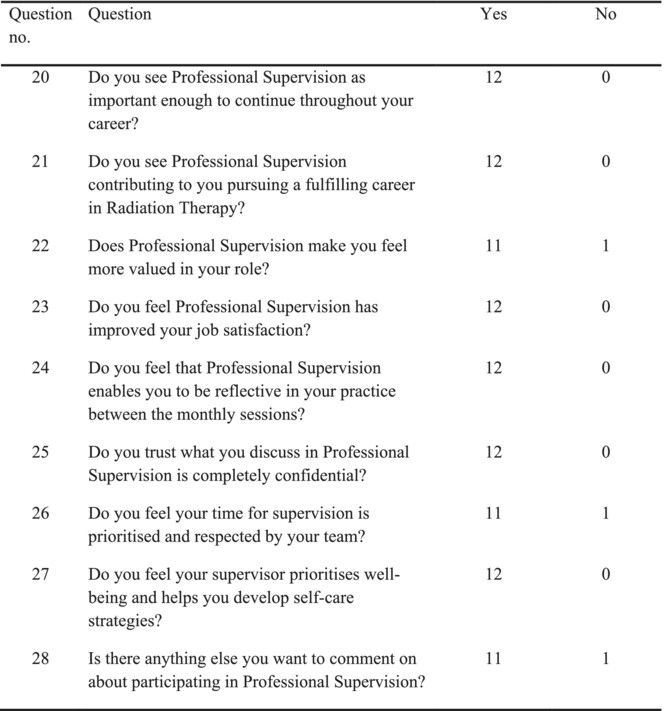
The study explores the efficacy of Professional Supervision (PS) as an intervention for mitigating burnout among radiation therapists (RTs). Twelve participants engaged in monthly face-to-face sessions. Conducted at the Christchurch Radiation Oncology Centre, the pilot study utilised a QUALTRICS questionnaire assessing the Supervisor Working Alliance Inventory (SWAI) and qualitative data analysis. Findings indicate a positive alliance between supervisor and supervisee, with RTs expressing appreciation for the reflective space and support provided by PS, suggesting its potential to address workplace stressors and promote professional growth.
Learning in radiation oncology: 12-month experience with a new incident learning system
- Pages: 63-73
- First Published: 15 September 2024
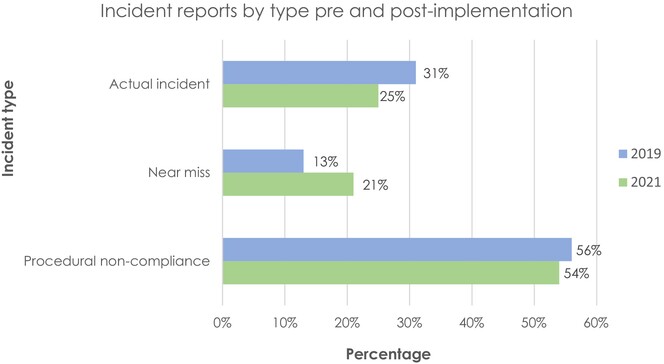
Introduction of an incident learning incident (ILS) was shown to have had a positive impact on reporting and safety culture within a local health district (LHD). Survey findings correlate with existing literature that ILSs are effective tools for improving patient safety and departmental safety facilitating quality improvement.
Open or closed: Experience of head and neck radiotherapy masks – A mixed-methods study
- Pages: 74-84
- First Published: 27 September 2024
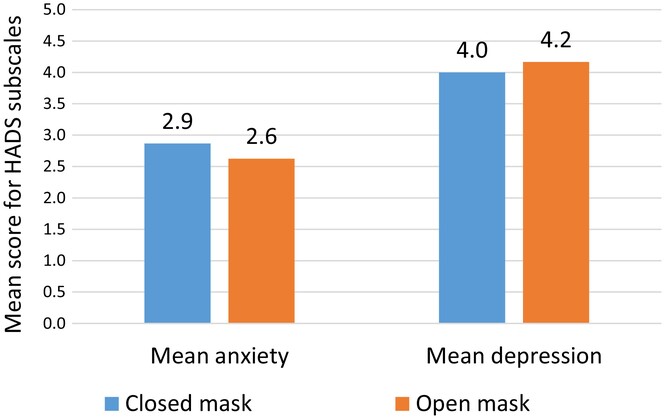
Patients with head and neck cancer received radiotherapy alternately with an open and a closed mask. The closed mask was perceived as more confining and restrictive, but it was also considered to make it easier to quickly achieve the correct position, while the open mask was perceived as less stable, although it reduced the feeling of claustrophobia for some participants. Most participants did not have a strong preference, and no difference between the masks could be detected using the HADS.
Size-specific dose estimates calculated using patient size measurements from scanned projection radiograph in high-resolution chest computed tomography
- Pages: 85-92
- First Published: 24 October 2024
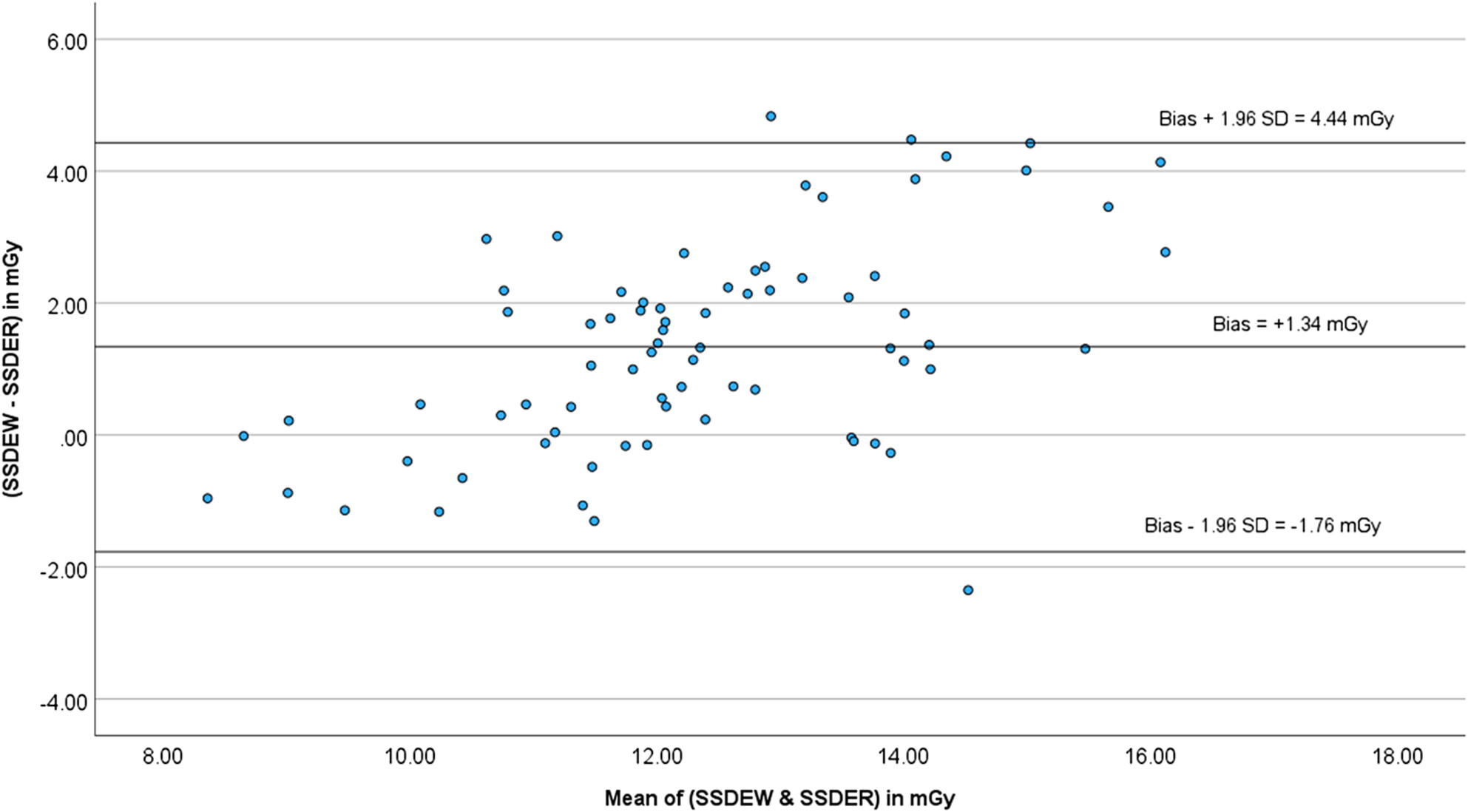
This study established that patient's lateral width measurements made from scanned projection radiograph (SPR) is an overestimate compared to those measured from tomographic slices by about 10%. Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) calculated using lateral width measured from SPR correlates well with SSDE calculated using water equivalent diameter of the patient measured from tomographic slice. The 75th percentile of the volume CT Dose index, dose-length product and SSDE have been established as 12.9 mGy, 453 mGy.cm and 14.4 mGy, respectively, for high-resolution CT scan of the adult chest.
A two-stage model for precise identification and Gleason grading of clinically significant prostate cancer: a hybrid approach
- Pages: 93-105
- First Published: 19 December 2024
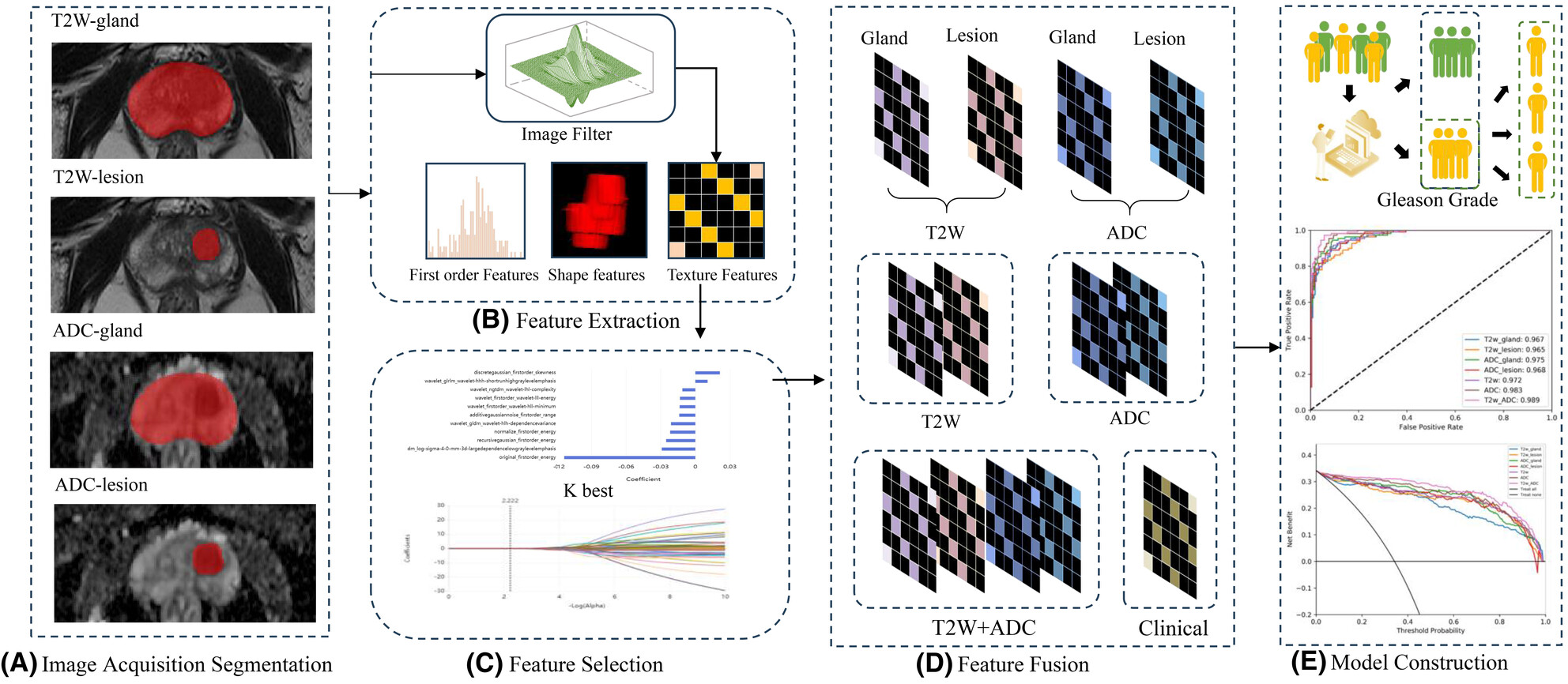
This study developed a two-stage model using radiomics-based multiparametric MRI and clinical indicators to help identify and grade clinically significant prostate cancer. The model showed promising levels of diagnostic accuracy and predictive performance. Importantly, the results were cautiously confirmed through both internal and external validation processes.
Review Article
Optimising hypoxia PET imaging and its applications in guiding targeted radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a scoping review
- Pages: 106-118
- First Published: 18 October 2024
Sonographic localisation of lymph nodes suspicious of metastatic breast cancer to surgical axillary levels
- Pages: 119-138
- First Published: 17 November 2024
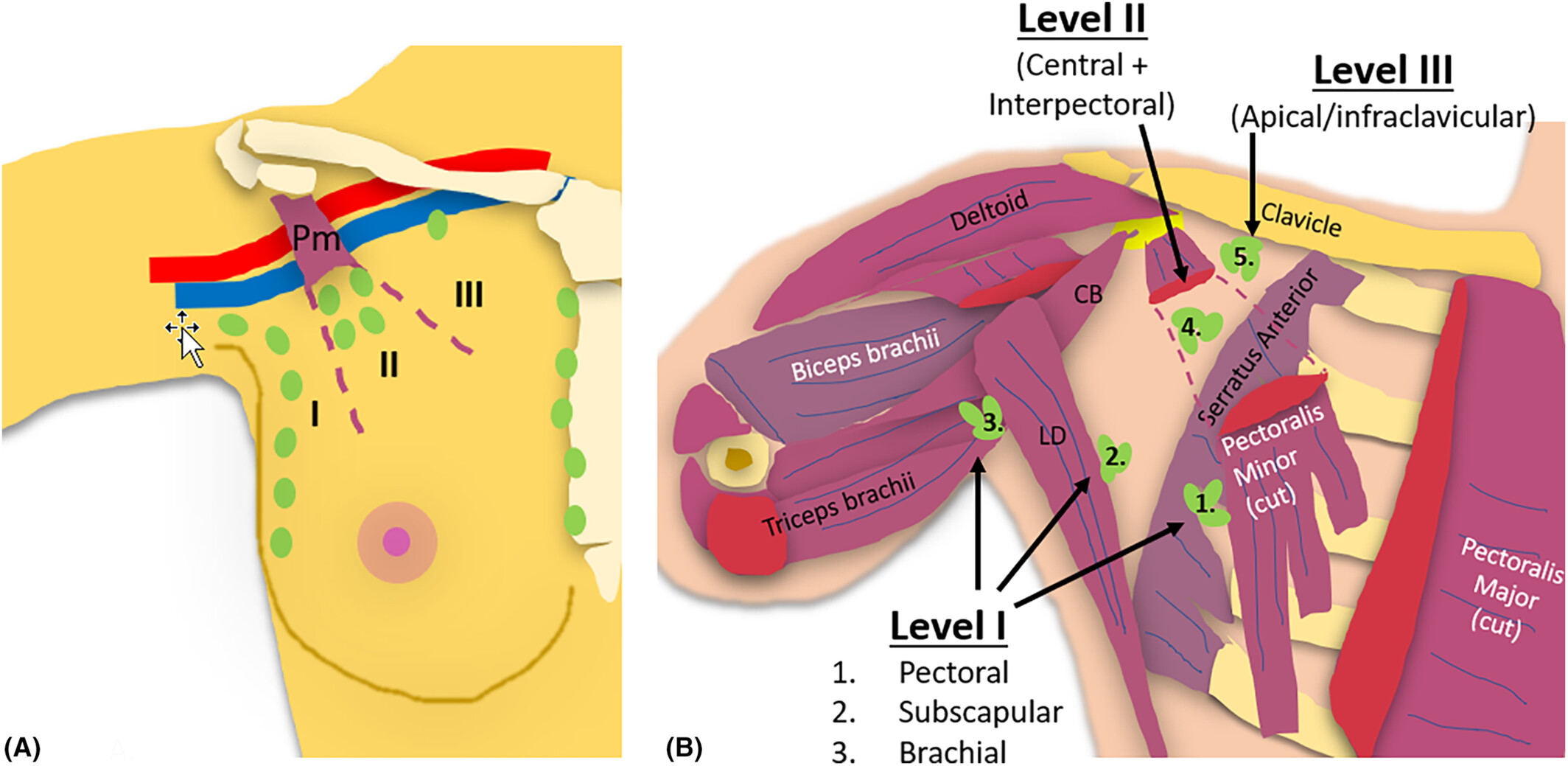
Sonographic imaging is used to identify the presence, number and location of malignant lymph nodes. Axillary lymph nodes suspicious of harbouring breast cancer metastasis can be localised to three surgical axillary levels. This paper will unpack the axillary anatomy, muscular sonographic landmarks, surgical axillary lymph node levels and the sonographic technique to image and distinguish between benign and suspicious lymph nodes.
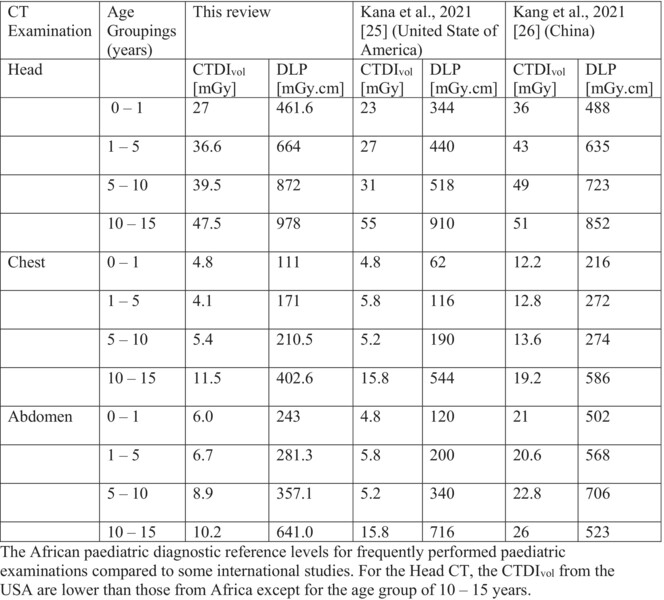
Paediatric computed tomography diagnostic reference levels in Africa: A systematic review
- Pages: 139-147
- First Published: 12 September 2024
Commentary
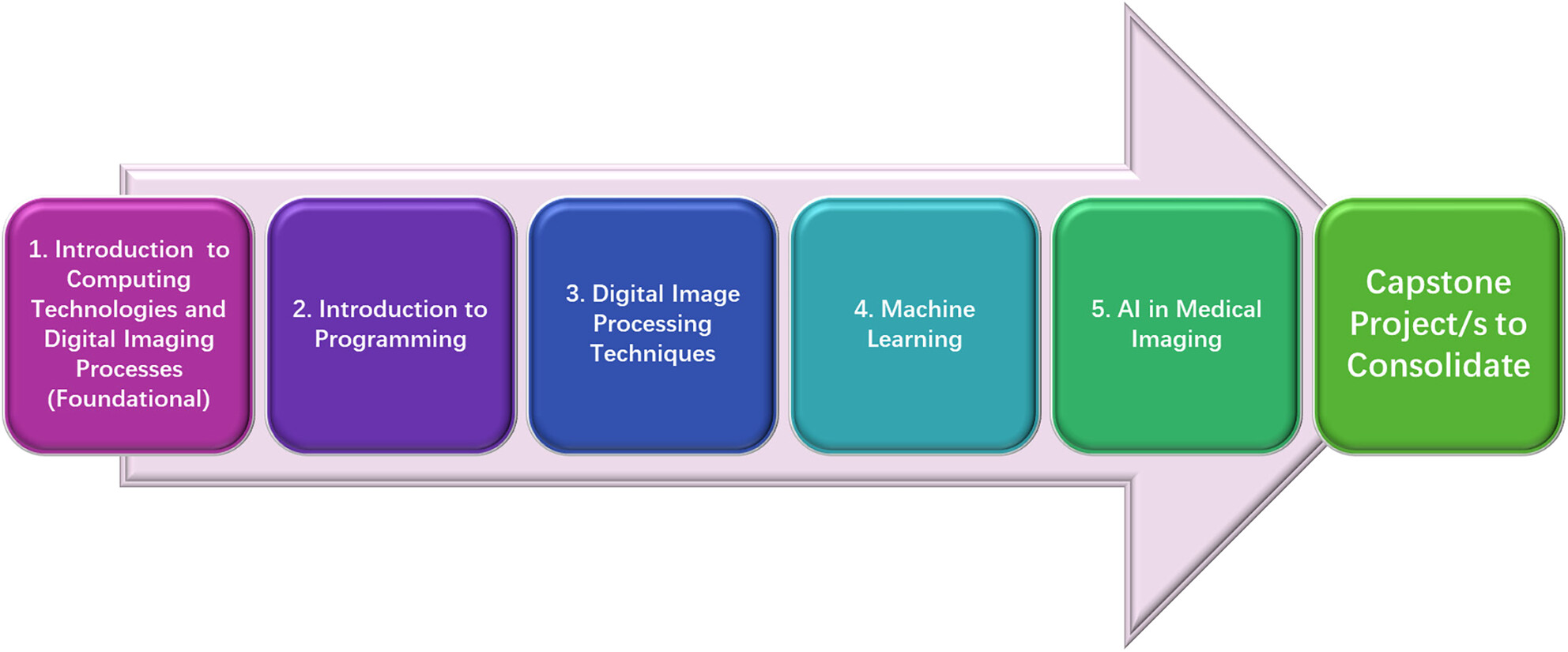
Enhancing medical imaging education: integrating computing technologies, digital image processing and artificial intelligence
- Pages: 148-155
- First Published: 07 November 2024
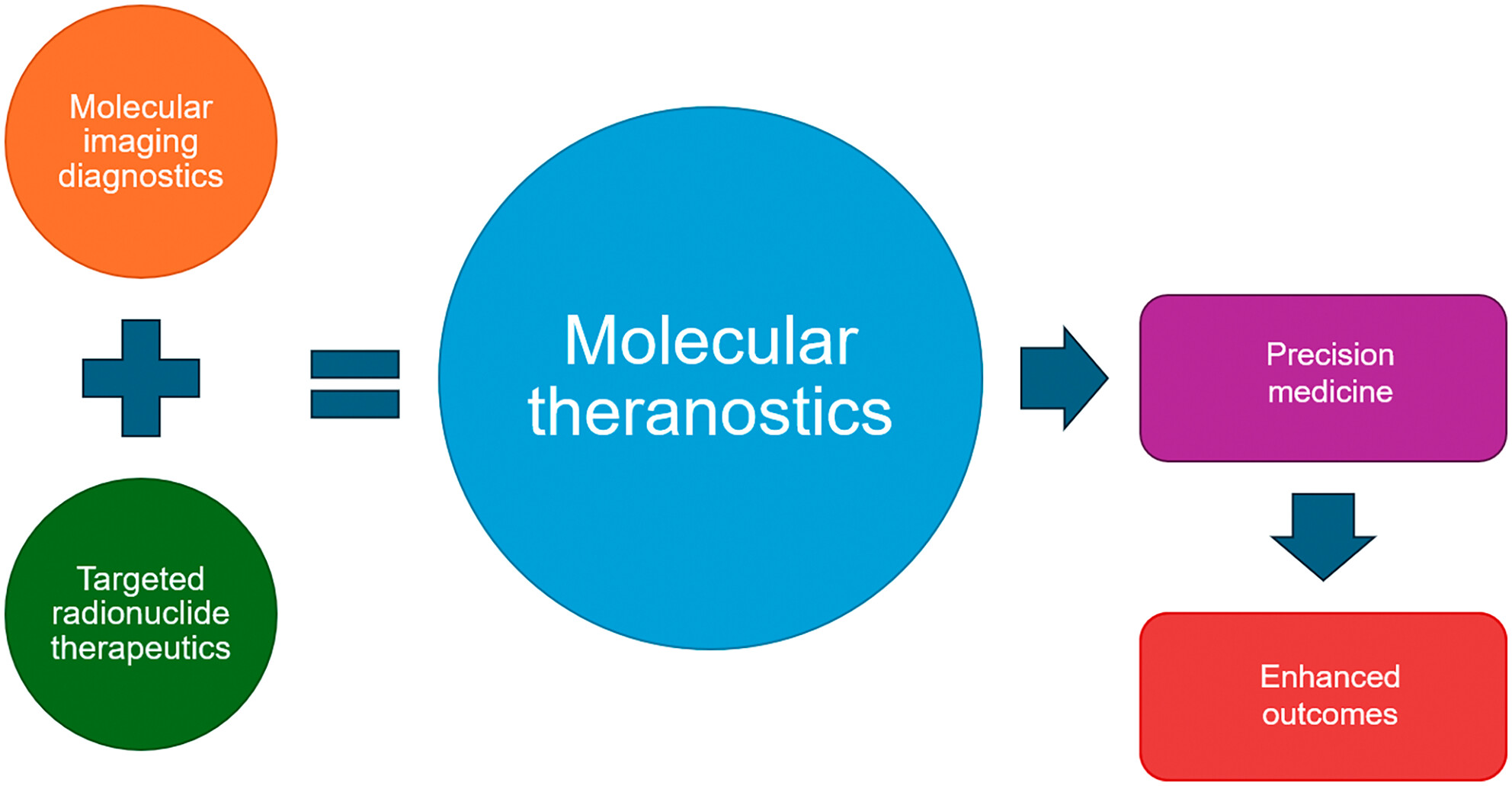
Molecular theranostics: principles, challenges and controversies
- Pages: 156-164
- First Published: 01 November 2024
How I do it
Technique considerations for implementing volumetric-modulated arc therapy for total body irradiation within an Australian tertiary institution
- Pages: 165-172
- First Published: 13 December 2024
In 2020, our institution transitioned to the Eclipse™ treatment planning system and to Truebeam® linear accelerators with 6 MV and 10 MV energies. The linear accelerators were installed in smaller bunkers that could not accommodate 400 cm FAD. A multidisciplinary team within the institution was created to evaluate existing total body irradiation literature and ultimately decide on a modern technique for implementation given our departmental considerations.
Continuing Professional Development
Continuing Professional Development–Medical Imaging
- Page: 173
- First Published: 26 February 2025
Continuing Professional Development—Radiation Therapy
- Page: 174
- First Published: 10 February 2025











-1693813706.png)