Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The comparison of clinical, laboratory, and radiological findings in immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients with COVID-19: A case-control study
- First Published: 12 April 2023
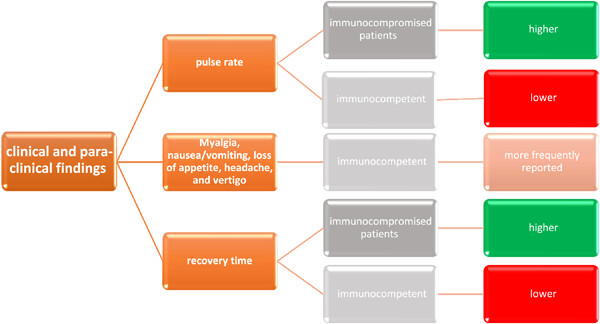
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with significant morbidity and mortality. We reported and compared the clinical and para-clinical findings of immunocompromised and immunocompetent COVID-19 patients in a case-control study at the Imam Khomeini hospital in Tehran, Iran. A total of 107 immunocompromised COVID patients as the case group and 107 immunocompetent COVID patients as the control group was recruited in the study. The participants were matched based on age and sex. The patients' information was retrieved from the hospital records in an information sheet. Associations between clinical and para-clinical findings with the immune status were assessed using bivariate and multivariate analyses. The clinical trial registration number is not applicable. The initial pulse rate and recovery time were significantly higher in immunocompromised patients (p < .05). Myalgia, nausea/vomiting, loss of appetite, headache, and vertigo were more frequently reported by the control group (p < .05). In terms of the duration of prescribed medications, Sofosbovir time was longer in the case group; while Ribavirin time was longer in the control groups (p < .05). The most common complication in the case group was acute respiratory distress syndrome although no major complications were observed in the control group. In the multivariate analysis, recovery time and Kaletra prescription were significantly higher in immunocompromised compared to the immunocompetent group. Recovery time was significantly higher in the immunocompromised compared to the immunocompetent group. This informs the current practice of dominant COVID-19 clinical course in immunocompromised patients and communicates the related implications.
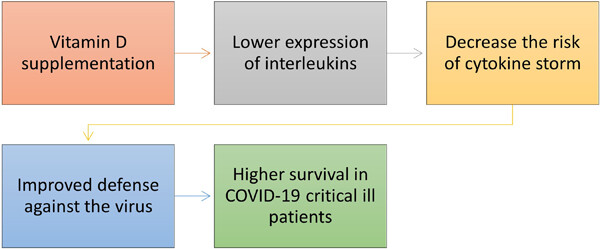
The association between vitamin D intake with inflammatory and biochemical indices and mortality in critically ill patients with COVID-19: A case-control study
- First Published: 26 April 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
The potential role of scavenger receptor B type I (SR-BI) in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- First Published: 14 April 2023
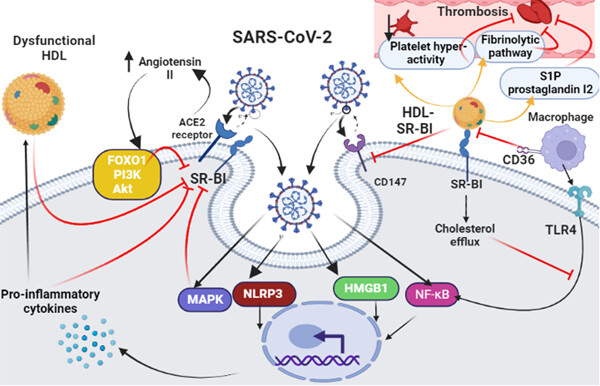
We illustrate that Scavenger receptor type B I (SR-BI), the major receptor for high-density lipoprotein (HDL) mediates delivery of cholesterol ester and cholesterol from HDL to the cell membrane. SR-BI is implicated as a receptor for entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Downregulation of SR-BI in COVID-19 could be due to direct invasion by SARS-CoV-2 or through upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, inflammatory signaling pathways and high circulating AngII.
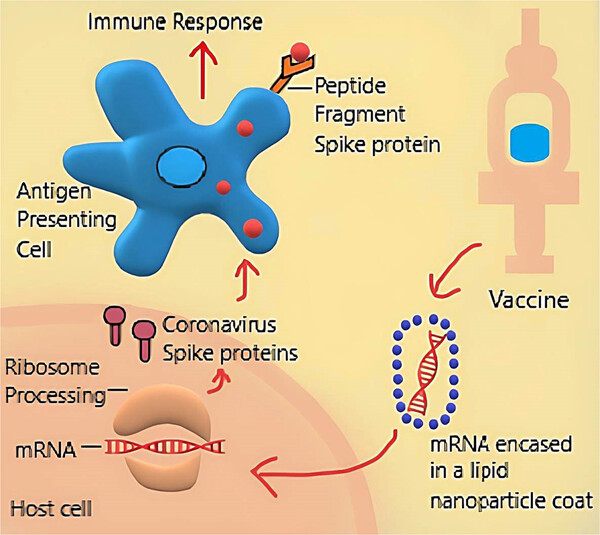
Manifestation of pityriasis rosea and pityriasis rosea-like eruptions after Covid-19 vaccine: A systematic review
- First Published: 12 April 2023
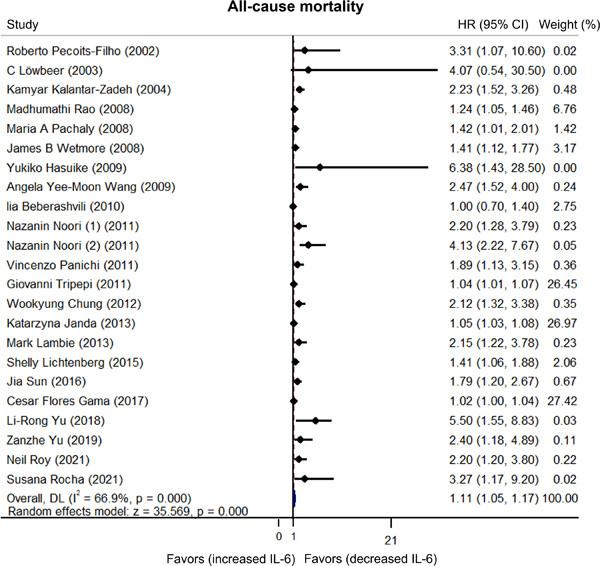
Interleukin-6 levels can be used to estimate cardiovascular and all-cause mortality risk in dialysis patients: A meta-analysis and a systematic review
- First Published: 26 April 2023
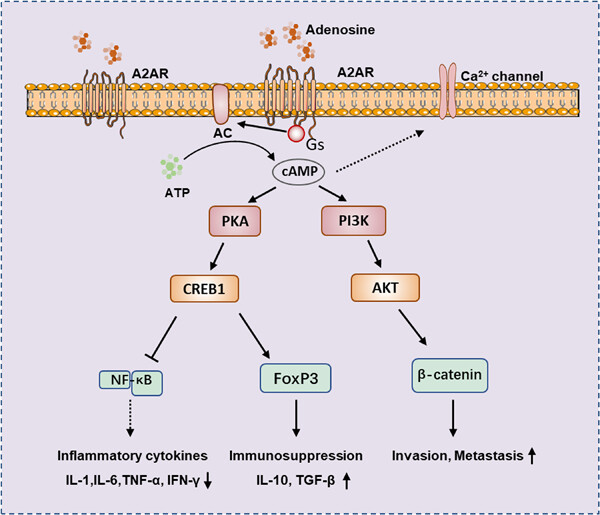
Role of adenosine A2a receptor in cancers and autoimmune diseases
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Organ-based clues for diagnosis of inborn errors of immunity: A practical guide for clinicians
- First Published: 12 April 2023
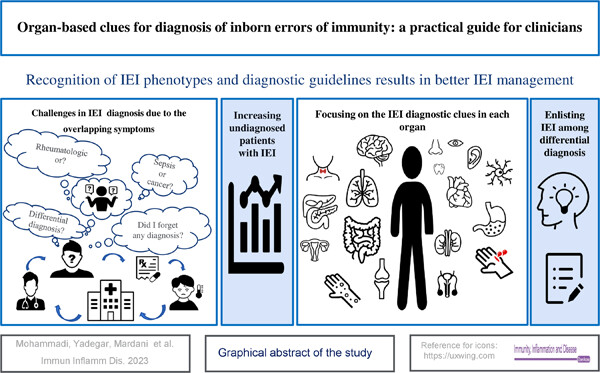
Several manifestations of inborn errors of immunity (IEI) can be misinterpreted as separate diseases and cause mismanagement. This poses physicians considerable challenges, not only regarding diagnosing but also in formulating a treatment plan. As a result of the failure to consider IEI diagnosis and the variety of diagnostic capabilities and laboratory facilities, undiagnosed patients are increasing. Stratifying these disorders through their involved organs and considering all aspects of the disease in each organ can lead to greater comprehension of IEI.
Mixed storm in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A narrative review and new term in the Covid-19 era
- First Published: 26 April 2023
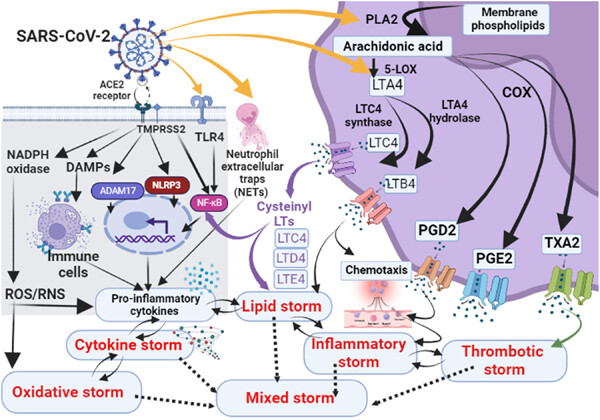
SARS-CoV-2 infection induces various storm types including cytokine storm (CS), inflammatory storm, lipid storm, thrombotic storm (TS), and oxidative storm. These storms are not developing alone since there is a close relationship between them. Therefore, the mixed storm seems to be more appropriate to be related to severe Covid-19 than CS, since it develops in Covid-19 due to the intricate interface between reactive oxygen species, proinflammatory cytokines, complement activation, coagulation disorders, and activated inflammatory signaling pathway
Toll-like receptors in pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases and their therapeutic potential
- First Published: 19 April 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Role of lncRNA MAGI2-AS3 in lipopolysaccharide-induced nucleus pulposus cells injury by regulating miR-374b-5p/interleukin-10 axis
- First Published: 17 April 2023
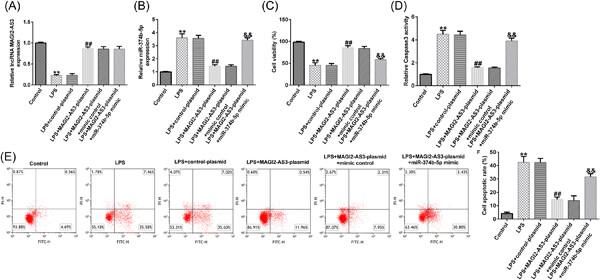
The present study aimed to expound the role of lncRNA MAGI2-AS3 in the pathogenic mechanism of IDD. Our findings revealed that LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 increased IL-10 level by sponging miR-374b-5p, which in turn alleviated LPS-triggered decrease in NP cell proliferation, increase in apoptosis, inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation. Therefore, lncRNA MAGI2-AS3 may be a potential therapeutic target for IDD.
Echocardiographic assessment of left cardiac structure and function in antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naïve people living with HIV/AIDS
- First Published: 12 April 2023
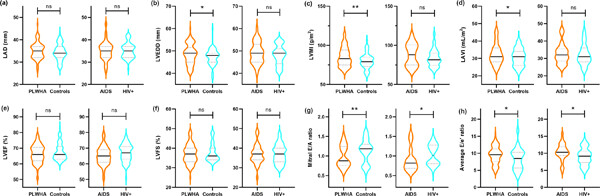
Left ventricular systolic function did not differ between patients living with HIV/AIDS (PLWHA) and controls, and left ventricular diastolic function was lower in PLWHA than in controls. Age, body mass index, and CD4+ count were independent factors affecting left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in antiretroviral therapy-naive PLWHA.
Downregulation of ROR2 attenuates LPS-induced A549 cell injury through JNK and ERK signaling pathways
- First Published: 26 April 2023

The present data indicate that downregulation of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2 may decrease lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and cell apoptosis through inhibiting of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway, which attenuates acute lung injury.
Differences in allergen-specific basophil activation and T cell proliferation in atopic dermatitis patients with comorbid allergic rhinoconjunctivitis treated with a monoclonal anti-IL-4Rα antibody or allergen-specific immunotherapy
- First Published: 12 April 2023
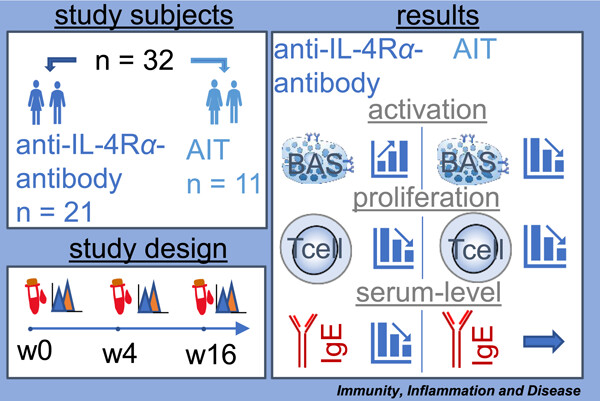
The purpose of our study was to investigate the effect of a monoclonal anti-IL-4Rα antibody on the in vitro allergic response of basophils and T cells deriving from AD patients with comorbid ARC. We conclude, that an IL-4Rα blockade induced by a monoclonal anti-IL-4Rα-antibody leads to an increased activity/sensitivity of early effector cells (such as basophils), in contrast to a decreasing reactivity observed under an AIT. The late-phase T cell reaction to allergens did not differ between the herein assessed treatments.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
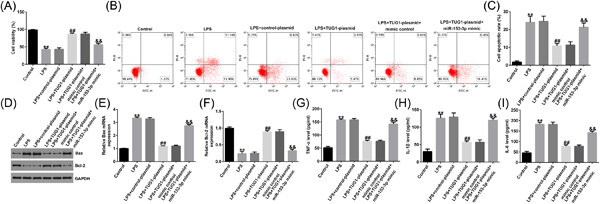
RETRACTED: LncRNA TUG1 relieves renal mesangial cell injury by modulating the miR-153-3p/Bcl-2 axis in lupus nephritis
- First Published: 12 April 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Clinical characteristics and pathogen analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia
- First Published: 27 April 2023
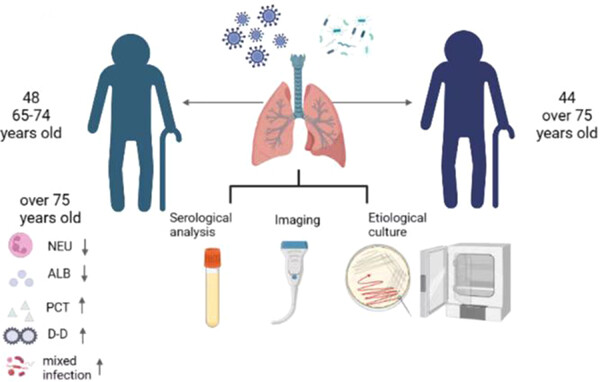
The clinical signs of elderly community-acquired pneumonia patients are not so typical. Attention should be paid to elderly patients. Compared with patients 65 to 74-year-old, patients over the age of 75 were more likely to have infections with mixed infection. They have higher PCT、D-D and lower ALB, which indicated severe infection.
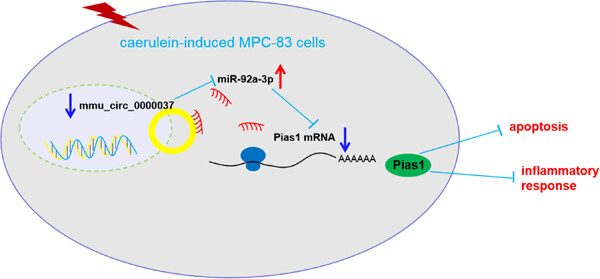
Mmu_circ_0000037 inhibits the progression of acute pancreatitis by miR-92a-3p/Pias1 axis
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Luteolin suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease through inhibition of the NOX4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway
- First Published: 27 April 2023
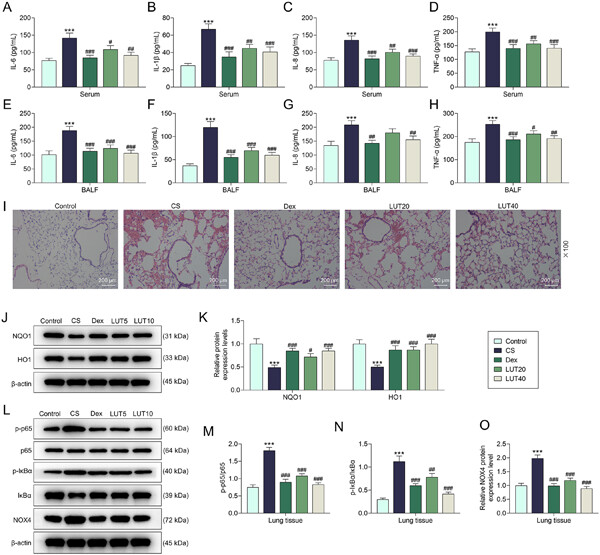
Luteolin inhibited the inflammation and oxidative stress in cigarette smoke (CS)-treated mice. Luteolin alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress in CS-treated cells. Luteolin targeted and downregulated the NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) in CS-treated mice and cells. Luteolin alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via NOX4-mediated nuclear factor-kappa B signaling.
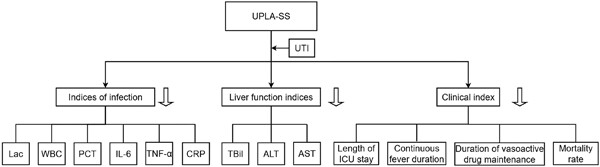
Clinical efficacy of ulinastatin in the treatment of unliquefied pyogenic liver abscess complicated by septic shock: A randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 17 April 2023
Long noncoding RNA antisense noncoding RNA in the INK4 locus inhibition alleviates airway remodeling in asthma through the regulation of the microRNA-7-5p/early growth response factor 3 axis
- First Published: 12 April 2023
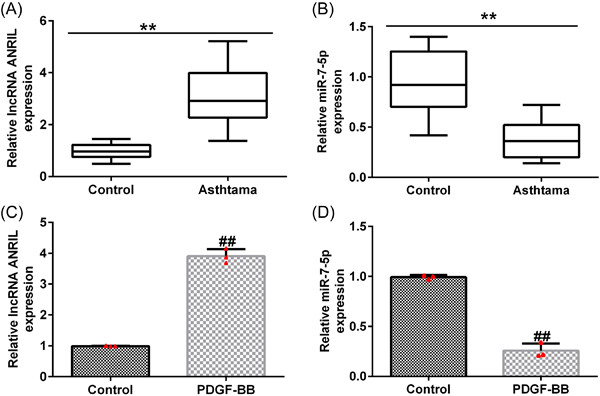
In this study, we investigated the function of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) ANRIL in proliferation and migration of airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs), and to explore the role and potential mechanisms in asthma. The data indicated that The downregulation of lncRNA ANRIL inhibits airway remodeling through regulating miR-7-5p/EGR3 signaling to inhibit proliferation and migration of platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced ASMCs.
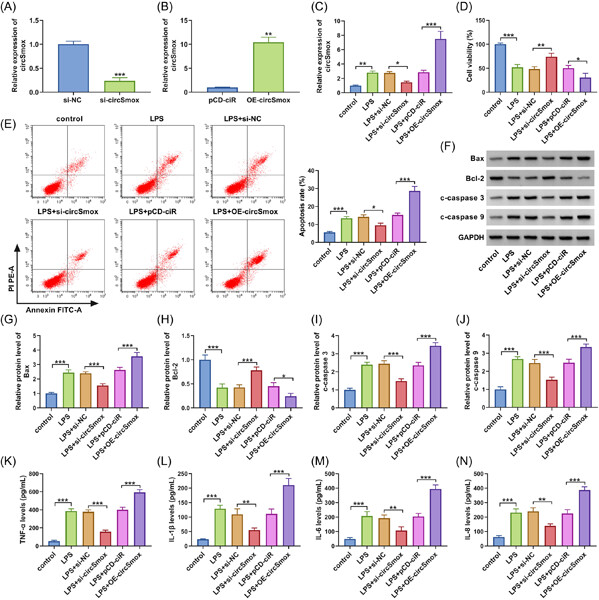
CircSmox knockdown alleviates PC12 cell apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury by miR-340-5p/Smurf1 axis
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Characterization of the lung microbiome and inflammatory cytokine levels in women exposed to environmental risk factors: A pilot study
- First Published: 17 April 2023
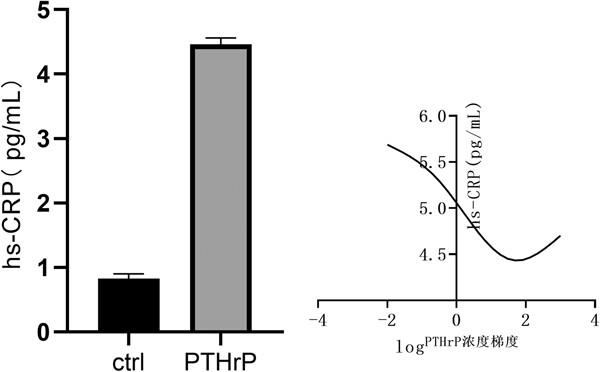
Study on the correlation between mineral bone metabolism and CRP in patients with SHPT during perioperative period
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Acinetobacter baumannii outer membrane protein A induces autophagy in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells involving the PI3K/mTOR pathway
- First Published: 12 April 2023
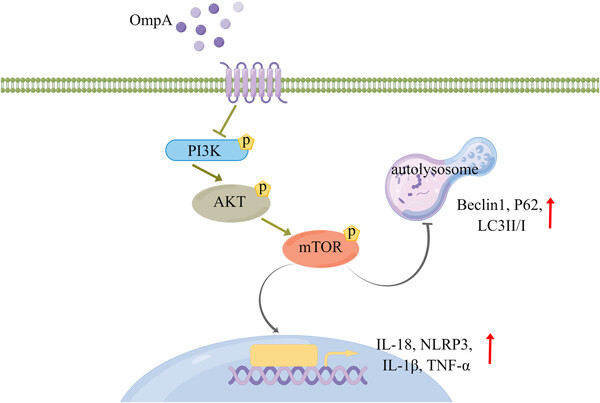
Dendritic cells are the most effective antigen-presenting cells and play a key role in regulating the immune response of multiple antigens and immune sentries. We aimed to study the role and molecular mechanisms of OmpA-induced mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells autophagy in the immune response of Acinetobacter baumannii.
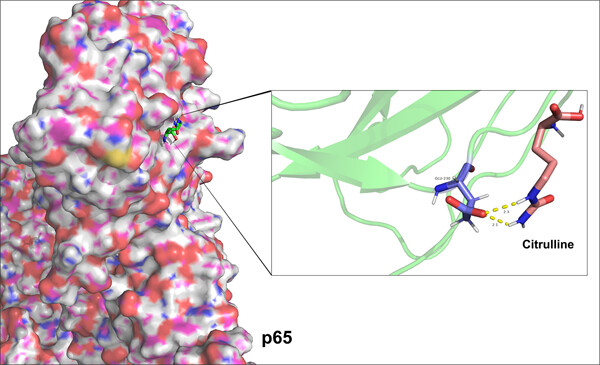
Citrulline inhibits LPS-induced pyroptosis of RAW264.7 macrophages through NF-κB signaling pathway
- First Published: 19 April 2023
The validation of artificial anti-monkeypox antibodies by in silico and experimental approaches
- First Published: 12 April 2023
Behçet syndrome: The disturbed balance between anti- (CLEC12A, CLC) and proinflammatory (IFI27) gene expressions
- First Published: 12 April 2023
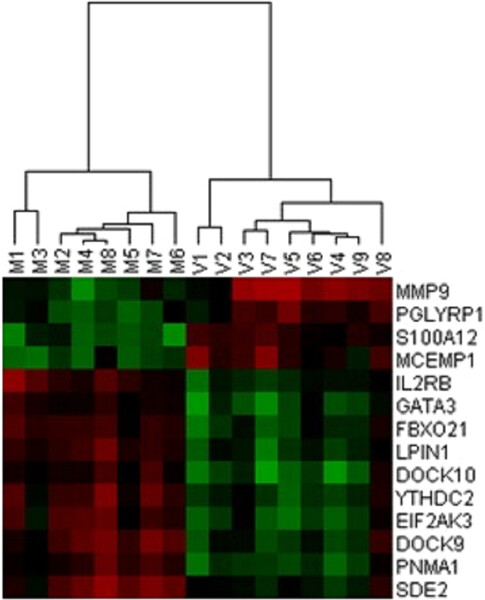
Behçet syndrome (BS), a chronic, multisystemic inflammatory condition seems to harbor an impaired balance between anti- and proinflammatory gene expressions. CLEC12A, CLC, and IFI27 may be among these differentially expressed genes in Turkish BS patients. Another significant characteristic of BS is the observation of distinct expression profiles and molecular disease mechanisms in its clinical subgroups/phenotypes.
Profiling of innate and adaptive immune cells during influenza virus infection reveals sex bias in invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells
- First Published: 12 April 2023
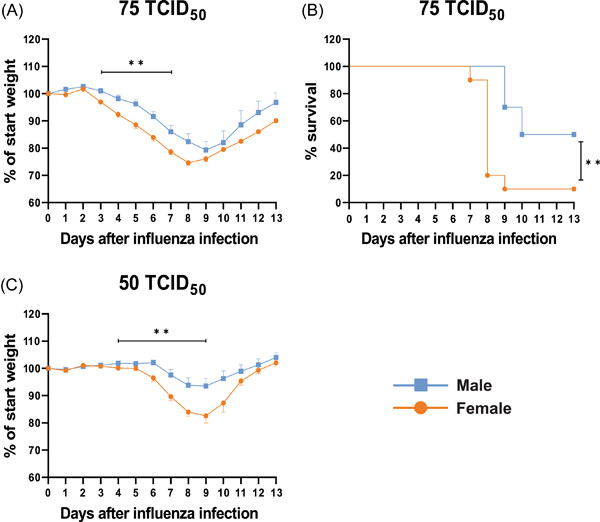
In this study, comprehensive profiling of innate and adaptive immune cells following influenza A virus infection over time in adult female and male mice was performed. The data reveals higher numbers of lung leukocytes and increased cytokine production in female mice at the onset of symptom progression. Additionally, female mice show a sex-dependent expansion of invariant natural killer T cell populations in lung at the start of disease recovery.
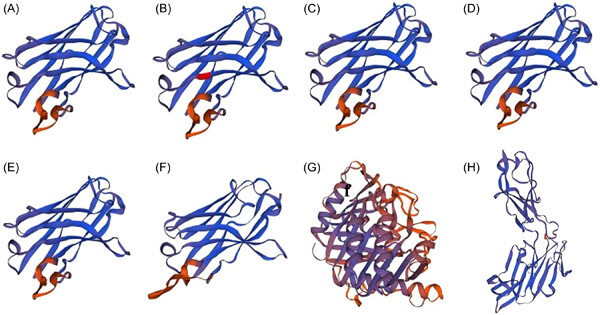
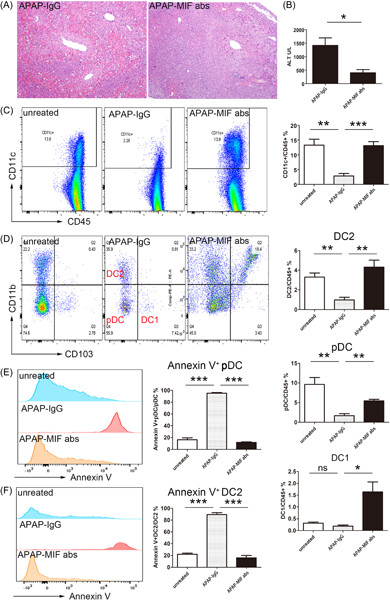
Migration inhibitory factor and cluster of differentiation 74-mediated dendritic cell apoptosis exacerbates acute acetaminophen-induced liver injury
- First Published: 17 April 2023
Elevated levels of interleukin-33 are associated with asthma: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 19 April 2023
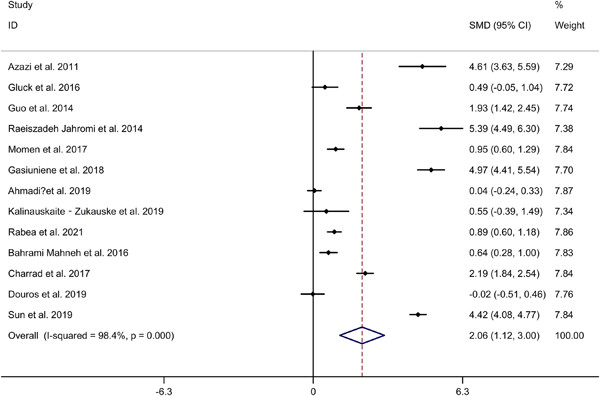
In conclusion, the main findings of present meta-analysis suggested that there was significant correlation between interleukin (IL)-33 levels and the severity of asthma. Therefore, the IL-33 levels of either serum or plasma may be regarded as a useful biomarker of asthma or the degree of disease. However, we can not ignore the influences of ethnic and age factors on the IL-33 levels. It is encouraged that data from multi-center, well-designed and large sample size studies should be conducted for validating the clinical value of IL-33 on asthma.
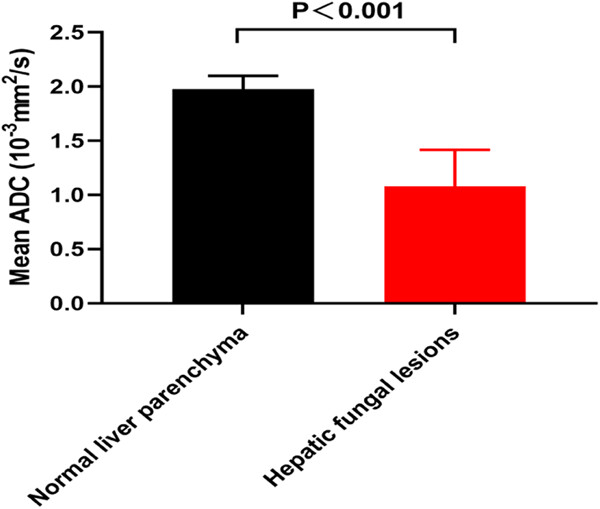
Value of diffusion-weighted imaging in diagnosis and therapy response assessment of hepatic fungal infection in patients with acute leukemia
- First Published: 26 April 2023