Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Case Reports
Anemia in a neonate with placental mesenchymal dysplasia
- Pages: 463-465
- First Published: 22 March 2016
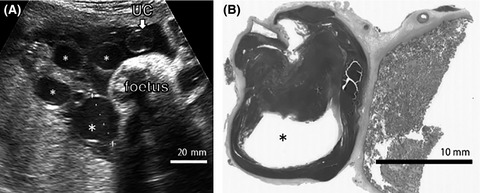
Causes of intrauterine fetal death (IUFD) are uncertain in most placental mesenchymal dysplasia (PMD) cases. Our case showed high α-fetoprotein levels in the maternal circulation, markedly dilated subchorionic vessels, and neonatal hemoglobin concentration of 8.4 g/dL, suggesting that fetal anemia may explain some adverse outcomes in PMD pregnancies.
Cardiac arrest during spinal anesthesia for cervical conization: a case report
- Pages: 466-468
- First Published: 29 March 2016
Spinal anesthesia is regularly performed worldwide and is an integral part of the modern day anesthesia practice. Although unexpected cardiac arrests during this procedure are very rare, medical professionals should be aware of the potential for this complication. In making the decision to use spinal anesthesia, judicious patient selection, adequate preventive measures, and strict monitoring are important.
Intrahepatic and extrahepatic aminotransferase elevation associated with clinical-therapeutic events in a schizophrenic patient
- Pages: 469-472
- First Published: 29 March 2016
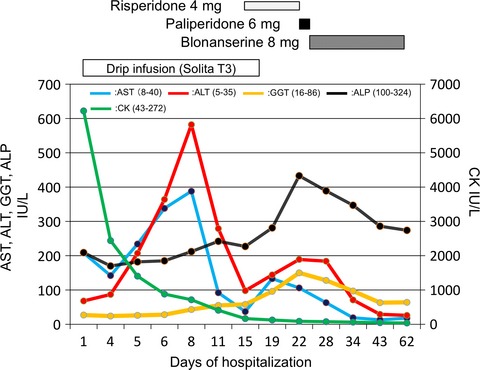
A schizophrenic patient showed rhabdomyolysis with idiopathic transaminitis. The intermixed pattern of intrahepatic and extrahepatic alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation is associated with respective clinical-therapeutic events. Aminotransferases play a role as surrogate biomarkers of “liver metabolic functioning” beyond the obsolete classical concept associating ALT elevation only with liver cellular damage.
Bone formation in subcutaneous pocket after bone flap preservation
- Pages: 473-476
- First Published: 29 March 2016
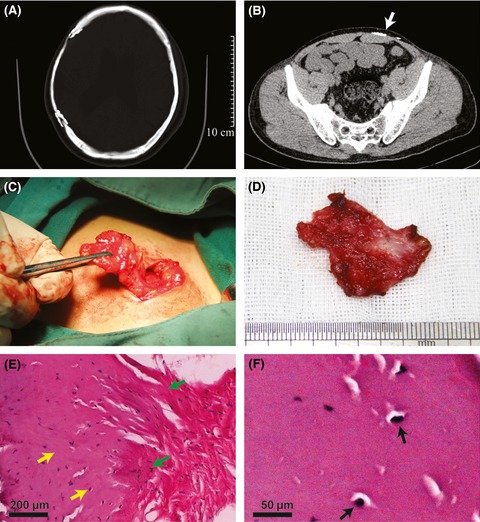
Residual periosteum developed periosteal bone formation in the pocket 10 years after cranioplasty, lumpectomy was conducted on the left lower abdomen under local anesthesia. Pathological sections revealed abundant osteocytes and mature bone matrix, and confirmed the bone formation on the residual periosteum.
Successful salvage surgery for failed transforaminal lumbosacral interbody fusion using the anterior transperitoneal approach
- Pages: 477-480
- First Published: 29 March 2016
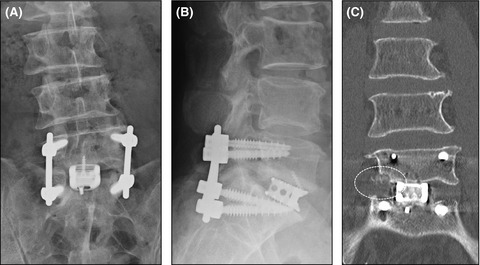
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a popular posterior spinal fusion technique, but sometimes require salvage surgery when implant failure occurs, which involves possible neural damage due to postoperative adhesion. The current report deals with successful anterior transperitoneal salvage surgery for failed L5-S TLIF with less neural invasiveness.
Spontaneous pneumothorax due to bronchopleural fistula following reirradiation for locoregionally recurrent squamous cell lung cancer
- Pages: 481-485
- First Published: 01 April 2016
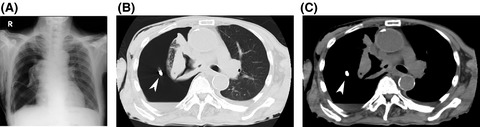
Spontaneous pneumothorax following radiotherapy for pulmonary malignancy is an unusual clinical condition. Here, we report a case of a 78-year-old male suffering from dyspnea during radiotherapy for squamous cell lung cancer of the right main bronchus. Imaging studies and fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed that pneumothorax was due to a bronchopleural fistula.
Imatinib for bleomycin induced pulmonary toxicity: a case report and evidence-base review
- Pages: 486-490
- First Published: 01 April 2016
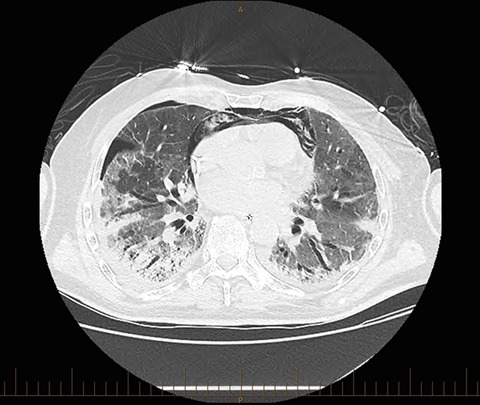
The evidence supporting therapy with imatinib for bleomycin-induced pneumonitis (BIP) is equivocal. Further experience is needed to establish its role in BIP management. While it may be considered in the management of BIP, it is important to be mindful of the adverse effects including thrombocytopenia and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Diabetes insipidus uncovered during conservative management of complicated acute appendicitis
- Pages: 491-493
- First Published: 05 April 2016
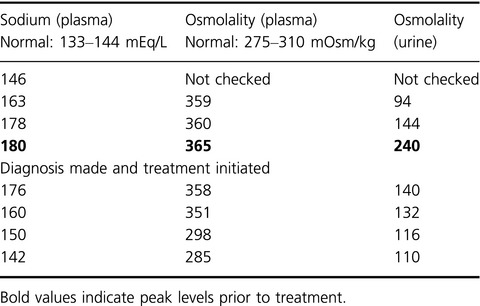
Diabetes insipidus (DI) arises from impaired function of antidiuretic hormone, characterized by hypovolemia, hypernatremia, polyuria, and polydipsia. This case is a reminder of the rare but challenging obstacle that undiagnosed DI poses in fasting surgical patients, requiring prompt recognition and vigilant management of marked homeostatic imbalances.
Teratodermoid mimicking cholecystitis
- Pages: 494-498
- First Published: 06 April 2016
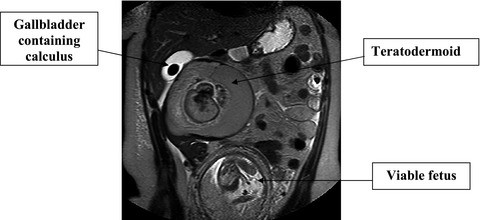
An acute abdomen assessment in pregnancy is complicated. Pain can have obstetric and nonobstetric causes. Cholecystitis is a common cause of pain in pregnancy with significant morbidity if not managed promptly. We report a case of a ruptured, torted, right ovarian teratodermoid erroneously diagnosed as cholecystitis in pregnancy.
Asenapine augmentation in bipolar disorders: a case series
- Pages: 499-504
- First Published: 07 April 2016

Asenapine, a novel second-generation antipsychotic is effective in acute treatment of bipolar I disorder patients in combination with mood stabilizers even in resistant cases. Although there is no evidence for asenapine's efficacy to be superior to currently available agents, asenapine's favorable weight and metabolic profile are of clinical interest.
Case report: false positive elevated serum-galactomannan levels after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation caused by oral nutritional supplements
- Pages: 505-508
- First Published: 12 April 2016
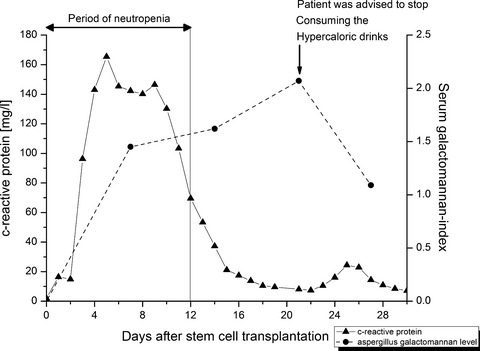
Positive galactomannan tests in patients who underwent chemotherapy without any clinical signs of a fungal infection should lead the clinician to consideration of a false-positive test result. Oral nutritional supplements may be a cause, especially in the case of concomitant disturbance of the gastrointestinal mucosal barrier because of mucositis.
The first genetically confirmed Japanese patient with mucolipidosis type IV
- Pages: 509-512
- First Published: 13 April 2016
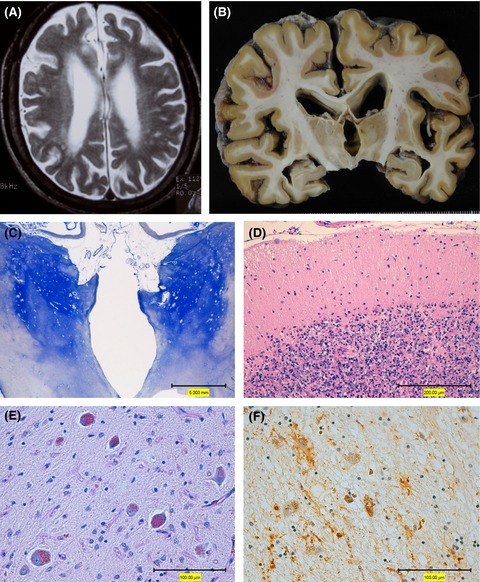
Mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder characterized by severe psychomotor delay and visual impairment. We report the brain pathology in the first Japanese patient of MLIV with a novel homozygous missense mutation in MCOLN1. We detected the localized increase in p62-reactive astrocytes in the basal ganglia.
A review of the role of anticoagulation for patients with infective endocarditis and embolic stroke
- Pages: 513-516
- First Published: 13 April 2016
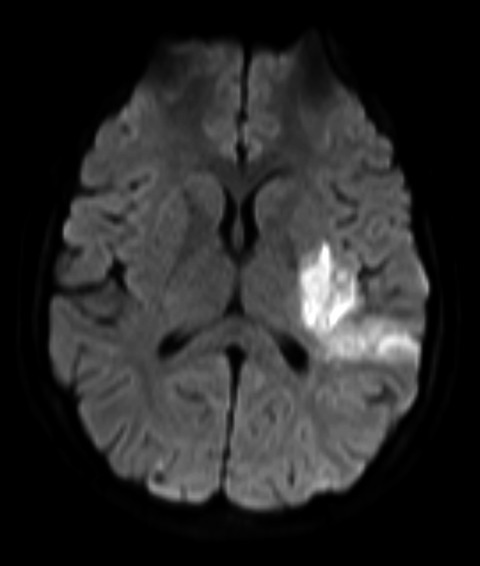
Stroke is a common embolic complication of infective endocarditis. The most important treatment to prevent stroke in endocarditis is the initiation of antibiotic therapy. It is unclear whether the initiation of de novo anticoagulation (i.e., warfarin) in patients with infective endocarditis is beneficial, since there are no large or randomized controlled trials in this area. However, this case report suggests, despite the limited evidence, that anticoagulation in this patient caused no harm and could suggest a hint of possible benefit.
A child with mastocytosis and lymphomatoid papulosis
- Pages: 517-519
- First Published: 14 April 2016
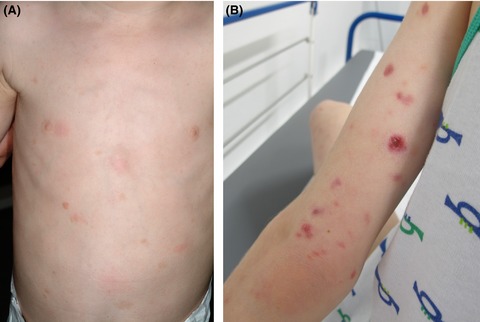
A change in clinical behavior of a disease should prompt search for differential diagnoses. Here, the appearance of ulcerated skin nodules in a preexisting cutaneous mastocytosis revealed a concurrent lymphomatoid papulosis – a CD30+ lymphoproliferative skin disease with histological features of a malignant lymphoma, but with a benign self-healing course.
Diagnosis of desmoplastic small-round-cell tumor by cytogenetic analysis: a case report
- Pages: 520-523
- First Published: 15 April 2016
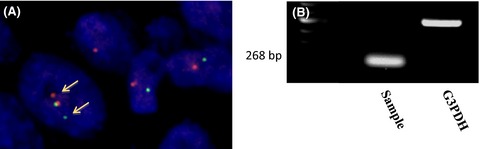
We herein present atypical histologic and immunohistochemical features of DSRCT. The various differential diagnoses of DSRCT may occasionally generate confusion. Cytogenetic analysis may solve diagnostic dilemmas such as that in our case. Further studies are required to establish a standard treatment for DSRCT.
Clinical Images
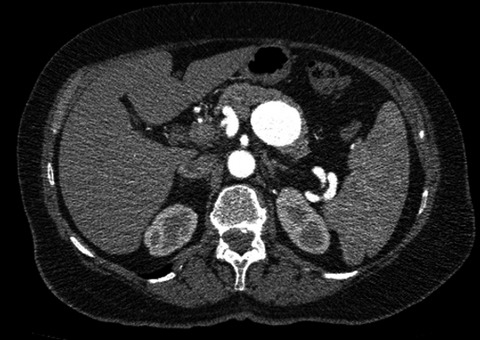
Surgical management of a splenic artery aneurysm
- Pages: 524-525
- First Published: 29 March 2016
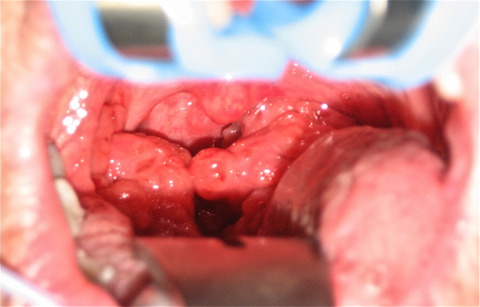
An unusual case of lingual tonsillar hypertrophy
- Pages: 526-527
- First Published: 29 March 2016
Multiple nodular lesions following Pneumocystis pneumonia in a non-HIV immunocompromised patient
- Pages: 528-530
- First Published: 01 April 2016
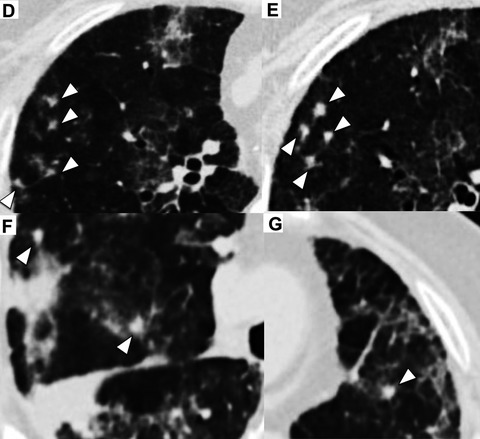
Cytomegalovirus superinfection is associated with a poor prognosis in non-HIVPneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) and can cause deterioration of PCP not only simultaneously but also after initiating PCP treatment. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia should be considered in cases with deterioration after initiating PCP treatment; multiple nodular lesions are useful findings for the diagnosis.
Giant diverticulum- A rare complication of a common surgical condition
- Pages: 531-532
- First Published: 13 April 2016
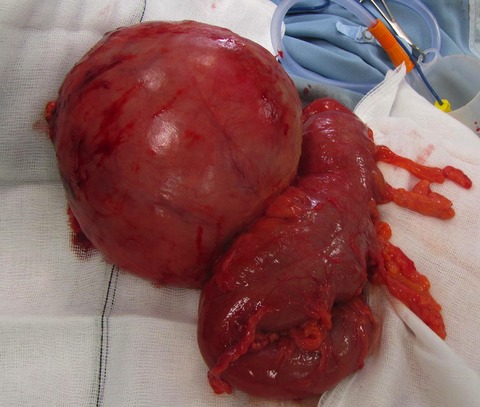
A gentleman presented with abdominal distension and pain. CT confirmed a 20 cm sigmoid diverticulum. A giant diverticulum, typified by diverticula greater than 4 cm, often requires colonic resection. Fewer than 200 cases have been reported, most measuring 7–15 cm. I present a rare complication of a common surgical condition with images.
Doctor, I am sweating on just one side of my body: unilateral hyperhidrosis associated with mesothelioma
- Pages: 533-534
- First Published: 13 April 2016
A dangerous loop
- Pages: 535-536
- First Published: 15 April 2016
A 76-year-old man developed a hemoperitoneum after ERCP for choledocholithiasis. He underwent a laparotomy and splenectomy for a capsular tear at the splenic hilum, a rare complication of ERCP. “Bowing” of the endoscope with torsion on the greater curvature of the stomach may lead to shear forces causing splenic injury.